Sunuwar Script on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Sunuwar alphabet (previously the Jenticha script, occasionally Kõits script) is an
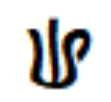 The ''laissi symbol'' /:/ (or /ː/ when using the IPA symbol instead of the generic colon punctuation) is used to extend vowel length. It is a non-original character. A colon may also be used as punctuation; if it occurs after a word ending with a vowel letter it will typically be preceded by a space in order to remove ambiguity.
The symbol ''pvo'' is used to mark the
The ''laissi symbol'' /:/ (or /ː/ when using the IPA symbol instead of the generic colon punctuation) is used to extend vowel length. It is a non-original character. A colon may also be used as punctuation; if it occurs after a word ending with a vowel letter it will typically be preceded by a space in order to remove ambiguity.
The symbol ''pvo'' is used to mark the
alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letter (alphabet), letters written to represent particular sounds in a spoken language. Specifically, letters largely correspond to phonemes as the smallest sound segments that can distinguish one word from a ...
developed by Krishna Bahadur Jentich in 1942, to write the Sunwar language
Sunuwar, or Koinch (; ; other spellings are Koinch and Koincha), is a Kiranti language of the Sino-Tibetan language family spoken in Nepal and India by the Sunuwar people. It was first comprehensively attested by the Himalayan Languages Pro ...
, a member of the Kiranti language family spoken in Eastern Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
, as in Sikkim
Sikkim ( ; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Koshi Province of Nepal in the west, and West Bengal in the ...
. It is recognised in Sikkim and used as an official writing system. The alphabet has 33 letters, 10 numerals and 1 'auspicious sign'.
It is a grammatological isolate, though some symbols bear recognition to the Limbu
Limbu may refer to:
* Limbu people, an indigenous tribe living in Nepal, Sikkim (India) and Bhutan
** Limbu language, their Sino-Tibetan language
*** Limbu script
**** Limbu (Unicode block)
* Rambahadur Limbu
Rambahadur Limbu, (; 8 July 1939 � ...
and Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
scripts. The script is written left to right. The writing system currently has no official standard.
When first created, the script was a pure alphabet, and has come to include a default non written /a/, giving it a feature of an abugida
An abugida (; from Geʽez: , )sometimes also called alphasyllabary, neosyllabary, or pseudo-alphabetis a segmental Writing systems#Segmental writing system, writing system in which consonant–vowel sequences are written as units; each unit ...
.
History
When Jentich first created the alphabet, it was limited to 22 letters, in addition to the 10 digits. Vowel length was not written, letters could also represent theirretroflex consonant
A retroflex () or cacuminal () consonant is a coronal consonant where the tongue has a flat, concave, or even curled shape, and is articulated between the alveolar ridge and the hard palate. They are sometimes referred to as cerebral consona ...
equivalent, and aspirated consonants were written as digraphs, using the letter ''hamso.'' The letter ''na'' was used to represent both nasal consonants
In phonetics, a nasal, also called a nasal occlusive or nasal stop in contrast with an oral stop or nasalized consonant, is an occlusive consonant produced with a lowered velum, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. The vast major ...
and vowel nasalisation, also through the use of digraphs. The velar nasal �was shown with a digraph of the consonants ''na'' and ''gil'', as in English /ng/. Tones were also not shown in the orthography
An orthography is a set of convention (norm), conventions for writing a language, including norms of spelling, punctuation, Word#Word boundaries, word boundaries, capitalization, hyphenation, and Emphasis (typography), emphasis.
Most national ...
, despite Sunwar being a tonal language
Tone is the use of pitch in language to distinguish lexical or grammatical meaning—that is, to distinguish or to inflect words. All oral languages use pitch to express emotional and other para-linguistic information and to convey emphasi ...
. The letter ''secha'' was used to show both the voiceless postalveolar fricative
A voiceless postalveolar fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some Speech, spoken languages. The International Phonetic Association uses the term ''voiceless postalveolar fricative'' only for the sound #Voiceless palato-alveolar frica ...
�and the voiceless alveolar sibilant
The voiceless alveolar fricatives are a type of fricative consonant pronounced with the tip or blade of the tongue against the alveolar ridge (gum line) just behind the teeth. This refers to a class of sounds, not a single sound. There are at leas ...
During the tail end of the 20th century, users of the language added a further 11 letters into the script:
* ''aal'' - borrowed from Limbu
Limbu may refer to:
* Limbu people, an indigenous tribe living in Nepal, Sikkim (India) and Bhutan
** Limbu language, their Sino-Tibetan language
*** Limbu script
**** Limbu (Unicode block)
* Rambahadur Limbu
Rambahadur Limbu, (; 8 July 1939 � ...
to write /a/ with long vowel length
* ''kloko'' - to write the Glottal stop
The glottal stop or glottal plosive is a type of consonantal sound used in many Speech communication, spoken languages, produced by obstructing airflow in the vocal tract or, more precisely, the glottis. The symbol in the International Phonetic ...
/ʔ/
* ''ṭentu, ṭhele, ḍonga'' - to improve clarity by having separate symbols for retroflexive consonants
* ''kha, chhelap, phar, thari'' - to improve clarity by having separate symbols for aspirated consonants
* ''sheyer'' - a letter for /ʃ/, to replace the digraph (sh)
* ''ngar -'' a letter for /ŋ/ to replace the digraph (ng)
* ''laissi'' - a character to denote Vowel length
In linguistics, vowel length is the perceived or actual length (phonetics), duration of a vowel sound when pronounced. Vowels perceived as shorter are often called short vowels and those perceived as longer called long vowels.
On one hand, many ...
Due to the lack of a set standard, the orthography can be vague, with digraphs still being used occasionally, and consonants still being used to denote retroflexives.
Soon after the creation of the script, conferences were held in villages in Dolakha District
Dolakha, often known as Dolkha or Dholkha (Nepal Bhasa:दोलखा जिल्ला)), a part of Bagmati Province, is one of the List of districts of Nepal, seventy-seven districts of Nepal. The district, with Charikot as its district headqu ...
, to promote it, and help shape its future.
Letters
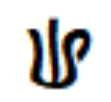 The ''laissi symbol'' /:/ (or /ː/ when using the IPA symbol instead of the generic colon punctuation) is used to extend vowel length. It is a non-original character. A colon may also be used as punctuation; if it occurs after a word ending with a vowel letter it will typically be preceded by a space in order to remove ambiguity.
The symbol ''pvo'' is used to mark the
The ''laissi symbol'' /:/ (or /ː/ when using the IPA symbol instead of the generic colon punctuation) is used to extend vowel length. It is a non-original character. A colon may also be used as punctuation; if it occurs after a word ending with a vowel letter it will typically be preceded by a space in order to remove ambiguity.
The symbol ''pvo'' is used to mark the Voiceless bilabial implosive
The voiceless bilabial implosive is a rare consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is or . A dedicated IPA letter, , was withdrawn in 1993.
Features
Featur ...
/ɓ̥/. It is referred to as an 'auspicious symbol'. In spoken Sunuwar, the consonant is often said twice, and is often found in salutations and well wishes.
Numbers
Sunuwar uses a set of ten numerals, inbase 10
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers (''decimal fractions'') of t ...
, derived from Arabic numerals
The ten Arabic numerals (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9) are the most commonly used symbols for writing numbers. The term often also implies a positional notation number with a decimal base, in particular when contrasted with Roman numera ...
. They were also created by Jentrich.
Unicode
The Sunuwar alphabet was added to theUnicode
Unicode or ''The Unicode Standard'' or TUS is a character encoding standard maintained by the Unicode Consortium designed to support the use of text in all of the world's writing systems that can be digitized. Version 16.0 defines 154,998 Char ...
Standard in September, 2024 with the release of version 16.0.
The Unicode block for Sunuwar is U+11BC0–U+11BFF:
{{Unicode chart Sunuwar
References