sun tanning on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Sun tanning or tanning is the process whereby skin color is darkened or tanned. It is most often a result of exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight or from artificial sources, such as a tanning lamp found in indoor tanning beds. People who deliberately tan their skin by exposure to the sun engage in a passive recreational activity of sun bathing. Some people use chemical products that can produce a tanning effect without exposure to ultraviolet radiation, known as sunless tanning.
Sun tanning or tanning is the process whereby skin color is darkened or tanned. It is most often a result of exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight or from artificial sources, such as a tanning lamp found in indoor tanning beds. People who deliberately tan their skin by exposure to the sun engage in a passive recreational activity of sun bathing. Some people use chemical products that can produce a tanning effect without exposure to ultraviolet radiation, known as sunless tanning.


 Melanin is a natural pigment produced by cells called melanocytes in a process called melanogenesis. Melanocytes produce two types of melanin: pheomelanin (red) and eumelanin (very dark brown). Melanin protects the body by absorbing ultraviolet radiation. Excessive UV radiation causes sunburn along with other direct and indirect DNA damage to the skin, and the body naturally combats and seeks to repair the damage and protect the skin by creating and releasing further melanin into the skin's cells. With the production of the melanin, the skin color darkens. The tanning process can be triggered by natural sunlight or by artificial UV radiation, which can be delivered in frequencies of UVA, UVB, or a combination of both. The intensity is commonly measured by the UV Index.
There are two different mechanisms involved in the production of a tan by UV exposure: Firstly, UVA radiation creates oxidative stress, which in turn oxidizes existing melanin and leads to rapid darkening of the melanin. UVA may also cause melanin to be redistributed (released from melanocytes where it is already stored), but its total quantity is unchanged. Skin darkening from UVA exposure does not lead to significantly increased production of melanin or protection against sunburn. In the second process, triggered primarily by UVB, there is an increase in production of melanin (melanogenesis), which is the body's reaction to direct DNA photodamage (formation of pyrimidine dimers) from UV radiation. Melanogenesis leads to delayed tanning, and typically becomes visible two or three days after exposure. The tan that is created by increased melanogenesis typically lasts for a few weeks or months, much longer than the tan that is caused by oxidation of existing melanin, and is also actually protective against UV skin damage and sunburn, rather than simply cosmetic. Typically, it can provide a modest Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of 3, meaning that tanned skin would tolerate up to 3 times the UV exposure as pale skin. However, in order to cause true melanogenesis-tanning by means of UV exposure, some direct DNA photodamage must first be produced, and this requires UVB exposure (as present in natural sunlight, or sunlamps that produce UVB). The ultraviolet frequencies responsible for tanning are often divided into the UVA and UVB ranges.
Melanin is a natural pigment produced by cells called melanocytes in a process called melanogenesis. Melanocytes produce two types of melanin: pheomelanin (red) and eumelanin (very dark brown). Melanin protects the body by absorbing ultraviolet radiation. Excessive UV radiation causes sunburn along with other direct and indirect DNA damage to the skin, and the body naturally combats and seeks to repair the damage and protect the skin by creating and releasing further melanin into the skin's cells. With the production of the melanin, the skin color darkens. The tanning process can be triggered by natural sunlight or by artificial UV radiation, which can be delivered in frequencies of UVA, UVB, or a combination of both. The intensity is commonly measured by the UV Index.
There are two different mechanisms involved in the production of a tan by UV exposure: Firstly, UVA radiation creates oxidative stress, which in turn oxidizes existing melanin and leads to rapid darkening of the melanin. UVA may also cause melanin to be redistributed (released from melanocytes where it is already stored), but its total quantity is unchanged. Skin darkening from UVA exposure does not lead to significantly increased production of melanin or protection against sunburn. In the second process, triggered primarily by UVB, there is an increase in production of melanin (melanogenesis), which is the body's reaction to direct DNA photodamage (formation of pyrimidine dimers) from UV radiation. Melanogenesis leads to delayed tanning, and typically becomes visible two or three days after exposure. The tan that is created by increased melanogenesis typically lasts for a few weeks or months, much longer than the tan that is caused by oxidation of existing melanin, and is also actually protective against UV skin damage and sunburn, rather than simply cosmetic. Typically, it can provide a modest Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of 3, meaning that tanned skin would tolerate up to 3 times the UV exposure as pale skin. However, in order to cause true melanogenesis-tanning by means of UV exposure, some direct DNA photodamage must first be produced, and this requires UVB exposure (as present in natural sunlight, or sunlamps that produce UVB). The ultraviolet frequencies responsible for tanning are often divided into the UVA and UVB ranges.
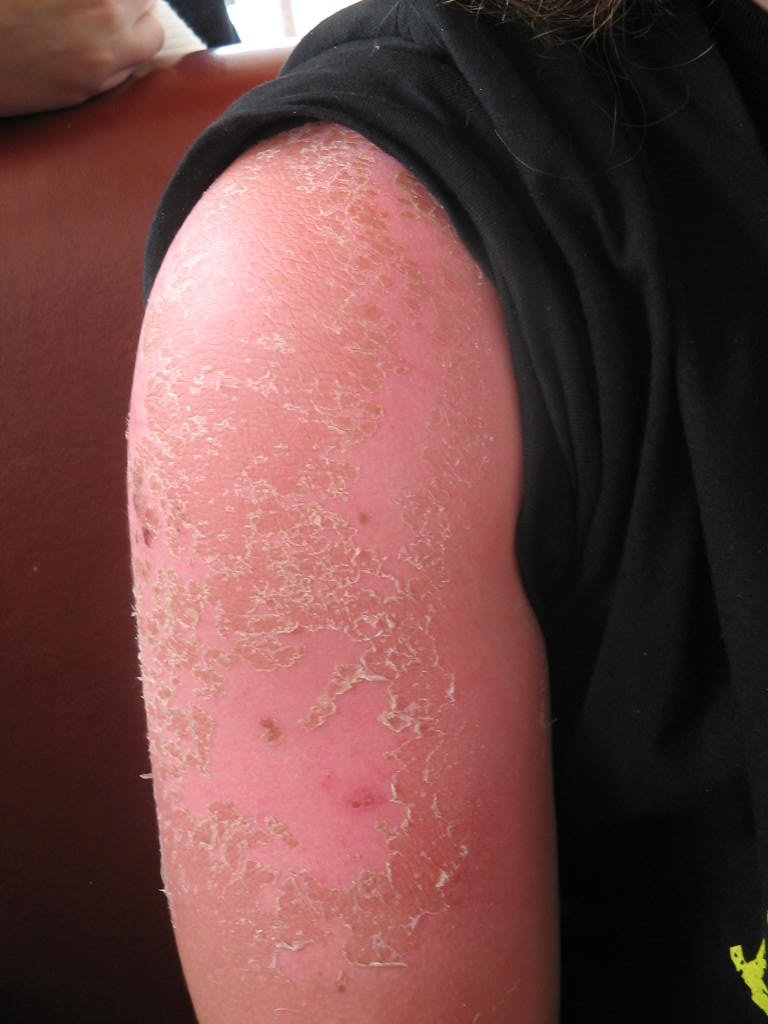
 The most common risk of exposure to ultraviolet radiation is sunburn, the speed and severity of which vary among individuals. This can be alleviated at least to some extent by the prior application of a suitable-strength sunscreen, which also hinders the tanning process due to the blocking of UV light. Overexposure to ultraviolet radiation is known to cause skin cancer, make skin age and wrinkle faster, mutate DNA, and impair the immune system. Frequent tanning bed use triples the risk of developing melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, according to a 2010 study. The study suggests that the melanoma risk is linked more closely to total exposure than it is to the age at which an individual first uses a tanning bed.Peeples, Lynne
The most common risk of exposure to ultraviolet radiation is sunburn, the speed and severity of which vary among individuals. This can be alleviated at least to some extent by the prior application of a suitable-strength sunscreen, which also hinders the tanning process due to the blocking of UV light. Overexposure to ultraviolet radiation is known to cause skin cancer, make skin age and wrinkle faster, mutate DNA, and impair the immune system. Frequent tanning bed use triples the risk of developing melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, according to a 2010 study. The study suggests that the melanoma risk is linked more closely to total exposure than it is to the age at which an individual first uses a tanning bed.Peeples, Lynne
Study: Frequent tanning-bed use triples melanoma risk.
CNN, 27 May 2010. Frequent tanning also has behavioural reinforcing effects, following UVA radiation epidermal keratinocytes synthesize POMC inducing the production of β-Endorphins, which are opioid agonists. An opioid blockade also then causes withdrawal signs after habitual UV exposure leading to many tanners meeting the DSM-IV criteria for addiction. Several organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO), the American Cancer Society and the US Surgeon General have issued guidelines warning about sun tanning and UV radiation exposure, either from the sun or from indoor tanning. Production of vitamin D is essential for human health. Moderate exposure (avoiding sunburn) to UV radiation provides benefits such as increased vitamin D, as well as other possible benefits that are still being studied. Several tanning activators have used different forms of psoralen, which are known to be photocarcinogenic. Health authorities have banned psoralen since July 1996.
 In the United States and Western Europe before the 1920s, tanned skin was associated with the lower classes because they worked outdoors and were exposed to the sunlight. Parasols and long sleeves were typically worn, even at beaches. By the 1920s, however, a cultural transformation took place, and tan skin became the ideal.
By the early 20th century, therapeutic benefits of sunlight were advertised to the public. In 1903, Niels Finsen was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his "Finsen Light Therapy". The therapy was a cure for diseases such as lupus vulgaris and rickets. Vitamin D deficiency was found to be a cause of rickets, and exposure to sunlight would allow vitamin D to be produced in a person. Therefore, sunlight exposure was a remedy to curing several diseases, especially rickets.
In 1910 a scientific expedition went to the island of Tenerife to test the wider health benefits of "heliotherapy", and by 1913 "sunbathing" was referred to as a desirable activity for the leisured class. Shortly thereafter, in the 1920s, fashion-designer Coco Chanel accidentally got sunburnt while visiting the French Riviera. When she arrived home, she arrived with a sun tan and her fans apparently liked the look and started to adopt darker skin tones themselves. Tanned skin became a trend partly because of Coco's status and the longing for her lifestyle by other members of society. In addition, Parisians fell in love with Josephine Baker, a "caramel-skinned" singer in Paris, and idolized her darker skin. These two women were leading figures of the transformation that tan skin underwent, in which it became perceived as fashionable, healthy, and luxurious. Jean Patou capitalized on the new tanning fad, launching the first sun tan oil "Huile de Chaldee" in 1927. Just before the 1930s, sunlight therapy became a popularly subscribed cure for almost every ailment from simple fatigue to tuberculosis. In the 1940s, advertisements encouraging sunbathing began to appear in women's magazines. At the same time, swimsuits' skin coverage began decreasing, with the bikini radically changing swimsuit style after it made its appearance in 1946. In the 1950s, baby oil was commonly used to increase tanning.
Coppertone, in 1953, marketed its sunscreen with a drawing of a young girl and her cocker spaniel tugging on her bathing suit bottom, revealing her bare bottom and tan line; this advertisement was modified around the turn of the 21st century and now shows a little girl wearing a one-piece bathing suit or shorts. In the latter part of the 1950s, silver metallic reflectors were common to enhance one's tan. In 1962, sunscreen commenced to be SPF rated, although SPF labeling in the US was not standardized by the FDA until 1978. In the 1970s, Mattel introduced Malibu Barbie, which had tanned skin and further popularized sun tanning among women.
In 1978, both sunscreen with an SPF 15 rating as well as tanning beds first appeared. In 2007, there were an estimated 50,000 outlets for indoor tanning; it was a five-billion-dollar industry in the United States, and had spawned an auxiliary industry for indoor tanning lotions including bronzers, intensifiers, and accelerators. Since then, the indoor tanning industry has become more constrained by health regulations. In China, darker skin is still considered by many to be the mark of the lower classes. As recently as 2012, in some parts of China, ski masks were becoming popular items to wear at the beach in order to protect the wearer's face from the effects of sunlight. A 1969 innovation is tan-through swimwear, which uses fabric perforated with thousands of micro holes that are nearly invisible to the naked eye, but which transmit enough sunlight to approach an all-over tan, especially if the fabric is stretched taut. Tan-through swimwear typically allows more than one-third of UV rays to pass through (equivalent to SPF 3 or less), and an application of sunscreen even to the covered area is recommended.
In the United States and Western Europe before the 1920s, tanned skin was associated with the lower classes because they worked outdoors and were exposed to the sunlight. Parasols and long sleeves were typically worn, even at beaches. By the 1920s, however, a cultural transformation took place, and tan skin became the ideal.
By the early 20th century, therapeutic benefits of sunlight were advertised to the public. In 1903, Niels Finsen was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his "Finsen Light Therapy". The therapy was a cure for diseases such as lupus vulgaris and rickets. Vitamin D deficiency was found to be a cause of rickets, and exposure to sunlight would allow vitamin D to be produced in a person. Therefore, sunlight exposure was a remedy to curing several diseases, especially rickets.
In 1910 a scientific expedition went to the island of Tenerife to test the wider health benefits of "heliotherapy", and by 1913 "sunbathing" was referred to as a desirable activity for the leisured class. Shortly thereafter, in the 1920s, fashion-designer Coco Chanel accidentally got sunburnt while visiting the French Riviera. When she arrived home, she arrived with a sun tan and her fans apparently liked the look and started to adopt darker skin tones themselves. Tanned skin became a trend partly because of Coco's status and the longing for her lifestyle by other members of society. In addition, Parisians fell in love with Josephine Baker, a "caramel-skinned" singer in Paris, and idolized her darker skin. These two women were leading figures of the transformation that tan skin underwent, in which it became perceived as fashionable, healthy, and luxurious. Jean Patou capitalized on the new tanning fad, launching the first sun tan oil "Huile de Chaldee" in 1927. Just before the 1930s, sunlight therapy became a popularly subscribed cure for almost every ailment from simple fatigue to tuberculosis. In the 1940s, advertisements encouraging sunbathing began to appear in women's magazines. At the same time, swimsuits' skin coverage began decreasing, with the bikini radically changing swimsuit style after it made its appearance in 1946. In the 1950s, baby oil was commonly used to increase tanning.
Coppertone, in 1953, marketed its sunscreen with a drawing of a young girl and her cocker spaniel tugging on her bathing suit bottom, revealing her bare bottom and tan line; this advertisement was modified around the turn of the 21st century and now shows a little girl wearing a one-piece bathing suit or shorts. In the latter part of the 1950s, silver metallic reflectors were common to enhance one's tan. In 1962, sunscreen commenced to be SPF rated, although SPF labeling in the US was not standardized by the FDA until 1978. In the 1970s, Mattel introduced Malibu Barbie, which had tanned skin and further popularized sun tanning among women.
In 1978, both sunscreen with an SPF 15 rating as well as tanning beds first appeared. In 2007, there were an estimated 50,000 outlets for indoor tanning; it was a five-billion-dollar industry in the United States, and had spawned an auxiliary industry for indoor tanning lotions including bronzers, intensifiers, and accelerators. Since then, the indoor tanning industry has become more constrained by health regulations. In China, darker skin is still considered by many to be the mark of the lower classes. As recently as 2012, in some parts of China, ski masks were becoming popular items to wear at the beach in order to protect the wearer's face from the effects of sunlight. A 1969 innovation is tan-through swimwear, which uses fabric perforated with thousands of micro holes that are nearly invisible to the naked eye, but which transmit enough sunlight to approach an all-over tan, especially if the fabric is stretched taut. Tan-through swimwear typically allows more than one-third of UV rays to pass through (equivalent to SPF 3 or less), and an application of sunscreen even to the covered area is recommended.
 To avoid exposure to UVB and UVA rays, or in seasons without strong sunshine, some people take alternative steps to appear with darkened skin. They may use sunless tanning (also known as self-tanners); stainers that are based on dihydroxyacetone (DHA); or cosmetics such as bronzers. Many sunless tanning products are available in the form of darkening creams, gels, lotions, and sprays that are self-applied on the skin. There is also a professional spray-on tanning option or " tanning booth" that is offered by spas, salons, and tanning businesses. Spray tanning does not involve a color being sprayed on the body, instead it uses a colorless chemical that reacts with proteins in the top layer of the skin, resulting in a brown color.
To avoid exposure to UVB and UVA rays, or in seasons without strong sunshine, some people take alternative steps to appear with darkened skin. They may use sunless tanning (also known as self-tanners); stainers that are based on dihydroxyacetone (DHA); or cosmetics such as bronzers. Many sunless tanning products are available in the form of darkening creams, gels, lotions, and sprays that are self-applied on the skin. There is also a professional spray-on tanning option or " tanning booth" that is offered by spas, salons, and tanning businesses. Spray tanning does not involve a color being sprayed on the body, instead it uses a colorless chemical that reacts with proteins in the top layer of the skin, resulting in a brown color.
Information on tanning from The Skin Cancer Foundation
Research on the benefits of UV exposureMelanoma Research Alliance
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sun Tanning Sun tanning
 Sun tanning or tanning is the process whereby skin color is darkened or tanned. It is most often a result of exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight or from artificial sources, such as a tanning lamp found in indoor tanning beds. People who deliberately tan their skin by exposure to the sun engage in a passive recreational activity of sun bathing. Some people use chemical products that can produce a tanning effect without exposure to ultraviolet radiation, known as sunless tanning.
Sun tanning or tanning is the process whereby skin color is darkened or tanned. It is most often a result of exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight or from artificial sources, such as a tanning lamp found in indoor tanning beds. People who deliberately tan their skin by exposure to the sun engage in a passive recreational activity of sun bathing. Some people use chemical products that can produce a tanning effect without exposure to ultraviolet radiation, known as sunless tanning.
Impact on skin health

Moderate exposure
Moderate exposure to direct sunlight contributes to the production of melanin and vitamin D by the body.Excessive exposure
Excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays has negative health effects, including sunburn. Some people tan or sunburn more easily than others. This may be the result of different skin types and natural skin color, and these may be a result of genetics. The term "tanning" has a cultural origin, arising from the color tan. Its origin lies in the Western culture of Europe when it became fashionable for young women to seek a less pale complexion (see Cultural history below).Long-term
Excessive exposure may in the long-term increase the risk of skin cancer, as well as depressed immune system function and accelerated aging of the skin.Tanning process
 Melanin is a natural pigment produced by cells called melanocytes in a process called melanogenesis. Melanocytes produce two types of melanin: pheomelanin (red) and eumelanin (very dark brown). Melanin protects the body by absorbing ultraviolet radiation. Excessive UV radiation causes sunburn along with other direct and indirect DNA damage to the skin, and the body naturally combats and seeks to repair the damage and protect the skin by creating and releasing further melanin into the skin's cells. With the production of the melanin, the skin color darkens. The tanning process can be triggered by natural sunlight or by artificial UV radiation, which can be delivered in frequencies of UVA, UVB, or a combination of both. The intensity is commonly measured by the UV Index.
There are two different mechanisms involved in the production of a tan by UV exposure: Firstly, UVA radiation creates oxidative stress, which in turn oxidizes existing melanin and leads to rapid darkening of the melanin. UVA may also cause melanin to be redistributed (released from melanocytes where it is already stored), but its total quantity is unchanged. Skin darkening from UVA exposure does not lead to significantly increased production of melanin or protection against sunburn. In the second process, triggered primarily by UVB, there is an increase in production of melanin (melanogenesis), which is the body's reaction to direct DNA photodamage (formation of pyrimidine dimers) from UV radiation. Melanogenesis leads to delayed tanning, and typically becomes visible two or three days after exposure. The tan that is created by increased melanogenesis typically lasts for a few weeks or months, much longer than the tan that is caused by oxidation of existing melanin, and is also actually protective against UV skin damage and sunburn, rather than simply cosmetic. Typically, it can provide a modest Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of 3, meaning that tanned skin would tolerate up to 3 times the UV exposure as pale skin. However, in order to cause true melanogenesis-tanning by means of UV exposure, some direct DNA photodamage must first be produced, and this requires UVB exposure (as present in natural sunlight, or sunlamps that produce UVB). The ultraviolet frequencies responsible for tanning are often divided into the UVA and UVB ranges.
Melanin is a natural pigment produced by cells called melanocytes in a process called melanogenesis. Melanocytes produce two types of melanin: pheomelanin (red) and eumelanin (very dark brown). Melanin protects the body by absorbing ultraviolet radiation. Excessive UV radiation causes sunburn along with other direct and indirect DNA damage to the skin, and the body naturally combats and seeks to repair the damage and protect the skin by creating and releasing further melanin into the skin's cells. With the production of the melanin, the skin color darkens. The tanning process can be triggered by natural sunlight or by artificial UV radiation, which can be delivered in frequencies of UVA, UVB, or a combination of both. The intensity is commonly measured by the UV Index.
There are two different mechanisms involved in the production of a tan by UV exposure: Firstly, UVA radiation creates oxidative stress, which in turn oxidizes existing melanin and leads to rapid darkening of the melanin. UVA may also cause melanin to be redistributed (released from melanocytes where it is already stored), but its total quantity is unchanged. Skin darkening from UVA exposure does not lead to significantly increased production of melanin or protection against sunburn. In the second process, triggered primarily by UVB, there is an increase in production of melanin (melanogenesis), which is the body's reaction to direct DNA photodamage (formation of pyrimidine dimers) from UV radiation. Melanogenesis leads to delayed tanning, and typically becomes visible two or three days after exposure. The tan that is created by increased melanogenesis typically lasts for a few weeks or months, much longer than the tan that is caused by oxidation of existing melanin, and is also actually protective against UV skin damage and sunburn, rather than simply cosmetic. Typically, it can provide a modest Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of 3, meaning that tanned skin would tolerate up to 3 times the UV exposure as pale skin. However, in order to cause true melanogenesis-tanning by means of UV exposure, some direct DNA photodamage must first be produced, and this requires UVB exposure (as present in natural sunlight, or sunlamps that produce UVB). The ultraviolet frequencies responsible for tanning are often divided into the UVA and UVB ranges.
UVA
Ultraviolet A (UVA) radiation is in the wavelength range 320 to 400 nm.UVB
Ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation is in the wavelength range 280 to 320 nm. Much of this band is blocked by the Earth's ozone layer, but some penetrates. UVB: * triggers the formation of CPD-DNA damage ( direct DNA damage), which in turn induces an increased melanin production. * is more likely to cause a sunburn than UVA as a result of overexposure. The mechanism for sunburn and increased melanogenesis is identical. Both are caused by the direct DNA damage (formation of CPDs). * produces Vitamin D in human skin. * is reduced by virtually all sunscreens in accordance with their SPF. * is thought, but not proven, to cause the formation of moles and some types of skin cancer. * stimulates the production of new melanin, which leads to an increase in the dark-colored pigment within a few days.Tanning behavior of different skin colors
A person's natural skin color affects their reaction to exposure to sunlight. An individual's natural skin color can vary from a dark brown to a nearly colorless pigmentation, which may appear white. In 1975, Harvard dermatologist Thomas B. Fitzpatrick devised the Fitzpatrick scale to describe the common tanning behavior of various skin types, as follows: Dark skin does provide some protection against the sun’s ultraviolet rays, but people with dark skin are still subject to photoaging and melanoma.Health aspects
 The most common risk of exposure to ultraviolet radiation is sunburn, the speed and severity of which vary among individuals. This can be alleviated at least to some extent by the prior application of a suitable-strength sunscreen, which also hinders the tanning process due to the blocking of UV light. Overexposure to ultraviolet radiation is known to cause skin cancer, make skin age and wrinkle faster, mutate DNA, and impair the immune system. Frequent tanning bed use triples the risk of developing melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, according to a 2010 study. The study suggests that the melanoma risk is linked more closely to total exposure than it is to the age at which an individual first uses a tanning bed.Peeples, Lynne
The most common risk of exposure to ultraviolet radiation is sunburn, the speed and severity of which vary among individuals. This can be alleviated at least to some extent by the prior application of a suitable-strength sunscreen, which also hinders the tanning process due to the blocking of UV light. Overexposure to ultraviolet radiation is known to cause skin cancer, make skin age and wrinkle faster, mutate DNA, and impair the immune system. Frequent tanning bed use triples the risk of developing melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer, according to a 2010 study. The study suggests that the melanoma risk is linked more closely to total exposure than it is to the age at which an individual first uses a tanning bed.Peeples, LynneStudy: Frequent tanning-bed use triples melanoma risk.
CNN, 27 May 2010. Frequent tanning also has behavioural reinforcing effects, following UVA radiation epidermal keratinocytes synthesize POMC inducing the production of β-Endorphins, which are opioid agonists. An opioid blockade also then causes withdrawal signs after habitual UV exposure leading to many tanners meeting the DSM-IV criteria for addiction. Several organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO), the American Cancer Society and the US Surgeon General have issued guidelines warning about sun tanning and UV radiation exposure, either from the sun or from indoor tanning. Production of vitamin D is essential for human health. Moderate exposure (avoiding sunburn) to UV radiation provides benefits such as increased vitamin D, as well as other possible benefits that are still being studied. Several tanning activators have used different forms of psoralen, which are known to be photocarcinogenic. Health authorities have banned psoralen since July 1996.
Cultural history
Sunless tanning
 To avoid exposure to UVB and UVA rays, or in seasons without strong sunshine, some people take alternative steps to appear with darkened skin. They may use sunless tanning (also known as self-tanners); stainers that are based on dihydroxyacetone (DHA); or cosmetics such as bronzers. Many sunless tanning products are available in the form of darkening creams, gels, lotions, and sprays that are self-applied on the skin. There is also a professional spray-on tanning option or " tanning booth" that is offered by spas, salons, and tanning businesses. Spray tanning does not involve a color being sprayed on the body, instead it uses a colorless chemical that reacts with proteins in the top layer of the skin, resulting in a brown color.
To avoid exposure to UVB and UVA rays, or in seasons without strong sunshine, some people take alternative steps to appear with darkened skin. They may use sunless tanning (also known as self-tanners); stainers that are based on dihydroxyacetone (DHA); or cosmetics such as bronzers. Many sunless tanning products are available in the form of darkening creams, gels, lotions, and sprays that are self-applied on the skin. There is also a professional spray-on tanning option or " tanning booth" that is offered by spas, salons, and tanning businesses. Spray tanning does not involve a color being sprayed on the body, instead it uses a colorless chemical that reacts with proteins in the top layer of the skin, resulting in a brown color.
See also
* Sunburn * Sunning * Indoor tanning * Perineum sunning * Skin whiteningReferences
External links
Information on tanning from The Skin Cancer Foundation
Research on the benefits of UV exposure
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sun Tanning Sun tanning