Suffield, Connecticut on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Suffield is a town in Hartford County,
 According to the
According to the
 As of the
As of the
 Main Street, a designated historic district with the Green, three churches, Suffield Academy and vintage colonial and Victorian homes, typifies a New England town. Named for the Kent family of Suffield, the Kent Memorial Library is an important research center for source materials, records, and documents from north-central Connecticut. A walk along Main Street reveals many examples of 18th and 19th century architecture. The Dr. Alexander King House, on the corner of Kent Avenue, and the Phelps-Hatheway House, a little farther north on Main Street, are museums open to the public from May to October.
Main Street, a designated historic district with the Green, three churches, Suffield Academy and vintage colonial and Victorian homes, typifies a New England town. Named for the Kent family of Suffield, the Kent Memorial Library is an important research center for source materials, records, and documents from north-central Connecticut. A walk along Main Street reveals many examples of 18th and 19th century architecture. The Dr. Alexander King House, on the corner of Kent Avenue, and the Phelps-Hatheway House, a little farther north on Main Street, are museums open to the public from May to October.
Town of Suffield official websiteSuffield Historical Society
{{authority control Towns in Hartford County, Connecticut Connecticut populated places on the Connecticut River Towns in Connecticut Springfield metropolitan area, Massachusetts Greater Hartford
Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its cap ...
, United States. It was once within the boundaries of Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
. The town is located in the Connecticut River Valley
The Connecticut River is the longest river in the New England region of the United States, flowing roughly southward for through four states. It rises 300 yards (270 m) south of the U.S. border with Quebec, Canada, and discharges at Long Islan ...
with the town of Enfield neighboring to the east. As of the 2020 census, the population was 15,752. The town center is a census-designated place
A census-designated place (CDP) is a concentration of population defined by the United States Census Bureau for statistical purposes only.
CDPs have been used in each decennial census since 1980 as the counterparts of incorporated places, su ...
listed as Suffield Depot in U.S. Census records.
Bordering Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
, Suffield is part of the Springfield, Massachusetts NECTA. Suffield is only from Springfield, and is more oriented toward it than toward Connecticut's capital of Hartford
Hartford is the capital city of the U.S. state of Connecticut. It was the seat of Hartford County until Connecticut disbanded county government in 1960. It is the core city in the Greater Hartford metropolitan area. Census estimates since ...
, which lies to the south.
History
Originally known as Southfield—pronounced "Suffield," on May 20, 1674, the committee for the settling of the town petitioned: The petition was granted by the Massachusetts Bay court on June 8, 1674. Suffield was incorporated as a town in March 1682. Also, on early 17th and 18th century maps, Suffield was alternatively spelled as Suthfield. Suffield and the surrounding area were part of theEquivalent Lands
The Equivalent Lands were several large tracts of land that the Province of Massachusetts Bay made available to settlers from the Connecticut Colony after April 1716. This was done as compensation for an equivalent area of territory that was under ...
compromise with Massachusetts in 1715–1716.
Suffield's native and adopted sons include The Rev. Ebenezer Gay, a renowned Congregational
Congregational churches (also Congregationalist churches or Congregationalism) are Protestant churches in the Calvinist tradition practising congregationalist church governance, in which each congregation independently and autonomously runs it ...
minister; U.S. Postmaster General Gideon Granger
Gideon Granger (July 19, 1767 – December 31, 1822) was an early American politician and lawyer. He was the father of fellow Postmaster General and U.S. Representative Francis Granger.
Early life
Granger was born in Suffield, Connecticut ...
; real estate speculator Oliver Phelps
Oliver Phelps (October 21, 1749February 21, 1809) was early in life a tavern keeper in Granville, Massachusetts. During the Revolution he was Deputy Commissary of the Continental Army and served until the end of the war. After the war ended, ...
, once the largest landowner in America; composer Timothy Swan
Timothy Swan (1758–1842) was a Yankee tunesmith and hatmaker born in Worcester, Massachusetts, USA. The son of goldsmith William Swan, Swan lived in small towns along the Connecticut River in Connecticut and Massachusetts for most of his l ...
; architect Henry A. Sykes
Henry may refer to:
People
*Henry (given name)
*Henry (surname)
* Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry
Royalty
* Portuguese royalty
** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal
** Henry, Count of Portugal, ...
; sculptor Olin Levi Warner
Olin Levi Warner (April 9, 1844August 14, 1896) was an American sculptor and artist noted for the striking bas relief portrait medallions and busts he created in the late 19th century.
Life
Warner was born in Suffield, Connecticut. Warner's gr ...
; Seth Pease, surveyor of the Western Reserve
The Connecticut Western Reserve was a portion of land claimed by the Colony of Connecticut and later by the state of Connecticut in what is now mostly the northeastern region of Ohio. The Reserve had been granted to the Colony under the terms o ...
lands in Ohio, most of which were controlled by Suffield financiers and speculators; and Thaddeus Leavitt, inventor of an early cotton gin
A cotton gin—meaning "cotton engine"—is a machine that quickly and easily separates cotton fibers from their seeds, enabling much greater productivity than manual cotton separation.. Reprinted by McGraw-Hill, New York and London, 1926 (); a ...
, merchant and patentee of the Western Reserve
The Connecticut Western Reserve was a portion of land claimed by the Colony of Connecticut and later by the state of Connecticut in what is now mostly the northeastern region of Ohio. The Reserve had been granted to the Colony under the terms o ...
lands. Thanks to the town's early prominence and wealth, it boasts an astonishing collection of early New England architecture. The Kent family, for whom the town's library is named, originated in Gloucester, Massachusetts
Gloucester () is a city in Essex County, Massachusetts, in the United States. It sits on Cape Ann and is a part of Massachusetts's North Shore. The population was 29,729 at the 2020 U.S. Census. An important center of the fishing industry and ...
, and boasted relations to many prominent early New England families, including the Dwight family of Northampton, Massachusetts
The city of Northampton is the county seat of Hampshire County, Massachusetts, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population of Northampton (including its outer villages, Florence and Leeds) was 29,571.
Northampton is known as an a ...
, the Hooker
Hooker may refer to:
People
* Hooker (surname)
Places Antarctica
* Mount Hooker (Antarctica)
* Cape Hooker (Antarctica)
* Cape Hooker (South Shetland Islands)
New Zealand
* Hooker River
* Mount Hooker (New Zealand) in the Southern Alps
* Hoo ...
family of Hartford, the Dudleys of Guilford, Connecticut
Guilford is a town in New Haven County, Connecticut, United States, that borders Madison, Branford, North Branford and Durham, and is situated on I-95 and the Connecticut seacoast. The population was 22,073 at the 2020 census.
History
Guil ...
, and the Leavitts of Suffield. Descendants of Robert Olds, who arrived from Sherborne
Sherborne is a market town and civil parish in north west Dorset, in South West England. It is sited on the River Yeo, on the edge of the Blackmore Vale, east of Yeovil. The parish includes the hamlets of Nether Coombe and Lower Clatcombe. T ...
, Dorset
Dorset ( ; archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the unitary authority areas of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole and Dorset. Covering an area of ...
, in 1667, include automotive pioneer Ransom Eli Olds
Ransom Eli Olds (June 3, 1864 – August 26, 1950) was a pioneer of the American automotive industry, after whom the Oldsmobile and REO brands were named. He claimed to have built his first steam car as early as 1887 and his first gasoline-power ...
, Copperhead Ohio politician Edson Baldwin Olds
Edson Baldwin Olds (June 3, 1802 – January 24, 1869) was a three-term U.S. Representative from Ohio. During the American Civil War, he was a leading member of the Peace Democrats. He was the great-grandfather of United States Army Air Forces M ...
, his great-grandson USAAF
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
General Robert Olds
Robert Olds (June 15, 1896 – April 28, 1943) was a general officer in the United States Army Air Forces, theorist of strategic air power, and proponent of an independent United States Air Force. Olds is best known today as the father of Brig. ...
, and his son, iconic USAF
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Aerial warfare, air military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part ...
fighter pilot Robin Olds
Robin Olds (July 14, 1922 – June 14, 2007) was an American fighter pilot and general officer in the United States Air Force (USAF). He was a " triple ace", with a combined total of 17 victories in World War II and the Vietnam War. Q ...
.
Slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
was common throughout the Connecticut River Valley
The Connecticut River is the longest river in the New England region of the United States, flowing roughly southward for through four states. It rises 300 yards (270 m) south of the U.S. border with Quebec, Canada, and discharges at Long Islan ...
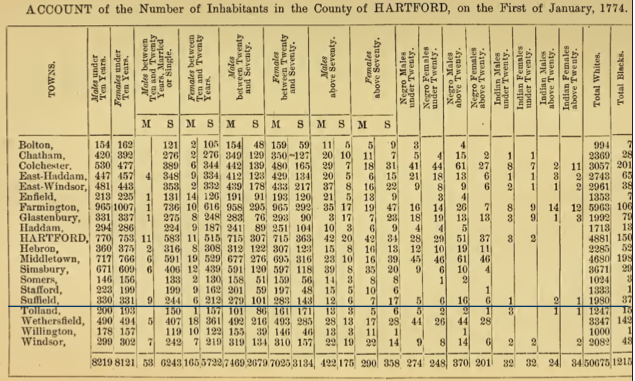
during the 18th century, and the 1774 Census for the Colony of Connecticut
The ''Connecticut Colony'' or ''Colony of Connecticut'', originally known as the Connecticut River Colony or simply the River Colony, was an English colony in New England which later became Connecticut. It was organized on March 3, 1636 as a settl ...
listed 37 slaves in Suffield. Throughout the Connecticut valley, wealthy merchants, tavern owners and town ministers owned slaves. When Major John Pynchon originally purchased from the Pequonnocks and Agawam tribes a six-mile tract of land, which he called Stoney Brooke Plantation, he first ordered the construction of a sawmill, and used two of his slaves, Harry and Roco, for the construction. Suffield's third minister, Reverend Ebenezer Devotion, became minister in 1710, and "sixteen years later the town voted to give him £20 to purchase a slave. Reverend Ebenezer Gay, Devotion's successor, owned six slaves throughout his long term, 1742–1796. Reverend Ebenezer Gay Jr. manumitted his family's three remaining slaves in 1812. They were Titus, Ginny and Dinah. "Princess," a slave belonging to early Suffield settler, Lieut. Joshua Leavitt, died November 5, 1732. Some of Leavitt's descendants became ardent abolitionists
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
, including Joshua Leavitt
Rev. Joshua Leavitt (September 8, 1794, Heath, Massachusetts – January 16, 1873, Brooklyn, New York) was an American Congregationalist minister and former lawyer who became a prominent writer, editor and publisher of abolitionist literature ...
and his cousin Roger Hooker Leavitt, who operated an Underground Railroad
The Underground Railroad was a network of clandestine routes and safe houses established in the United States during the early- to mid-19th century. It was used by enslaved African Americans primarily to escape into free states and Canada. ...
station in Charlemont, Massachusetts
Charlemont is a town in Franklin County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 1,185 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Springfield, Massachusetts Metropolitan Statistical Area.
History
Charlemont was first colonized by Moses R ...
.
One of the earliest graduates of the Yale Medical School
The Yale School of Medicine is the graduate medical school at Yale University, a private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. It was founded in 1810 as the Medical Institution of Yale College and formally opened in 1813.
The primary t ...
was one of Suffield's earliest physicians. Dr. Asaph Leavitt Bissell, born in 1791 at Hanover, New Hampshire
Hanover is a town located along the Connecticut River in Grafton County, New Hampshire, United States. As of the 2020 census, its population was 11,870. The town is home to the Ivy League university Dartmouth College, the U.S. Army Corps of ...
, to parents originally from Suffield, attended Dartmouth College
Dartmouth College (; ) is a private research university in Hanover, New Hampshire. Established in 1769 by Eleazar Wheelock, it is one of the nine colonial colleges chartered before the American Revolution. Although founded to educate Native ...
, and later graduated in the second class of the Yale Medical School. Bissell moved to Suffield, where he rode horseback to make house calls on his patients. Bissell's saddlebags are today in the collection of the Yale Medical School's Historical Society.
Geography
 According to the
According to the United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy
An economy is an area of th ...
, the town has a total area of , of which is land and , or 1.58%, is water. The town center ( Suffield Depot CDP) has a total area of , all of it land.
Suffield is on the west bank of the Connecticut River, south of the river's largest city, Springfield, Massachusetts, and north of Connecticut's capital, Hartford
Hartford is the capital city of the U.S. state of Connecticut. It was the seat of Hartford County until Connecticut disbanded county government in 1960. It is the core city in the Greater Hartford metropolitan area. Census estimates since ...
. Two bridges span the river to the town of Enfield: the Amtrak/Springfield Terminal Railroad Bridge and the Enfield–Suffield Veterans Bridge
The Enfield–Suffield Veterans Bridge, commonly known in either town as the Enfield Bridge or Suffield Bridge, is the main traffic crossing that connects the towns of Enfield and Suffield, Connecticut over the Connecticut River
The Connecti ...
.
The Metacomet Ridge
The Metacomet Ridge, Metacomet Ridge Mountains, or Metacomet Range of southern New England is a narrow and steep fault-block mountain ridge known for its extensive cliff faces, scenic vistas, microclimate ecosystems, and rare or endangered plants. ...
, a mountainous trap rock
Trap rock, also known as either trapp or trap, is any dark-colored, fine-grained, non-granitic intrusive or extrusive igneous rock. Types of trap rock include basalt, peridotite, diabase, and gabbro.Neuendorf, K.K.E., J.P. Mehl, Jr., and J.A. ...
ridgeline that stretches from Long Island Sound to nearly the Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to the ...
border, runs through the center of Suffield from south to north as West Suffield Mountain. The Metacomet Trail
The Metacomet Trail is a '' Blue-Blazed'' hiking trail that traverses the Metacomet Ridge of central Connecticut and is a part of the newly designated New England National Scenic Trail. Despite being easily accessible and close to large popul ...
traverses the ridge.
Demographics
 As of the
As of the census
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses in ...
of 2000, there were 13,552 people, 4,660 households, and 3,350 families residing in the town. The population density was . There were 4,853 housing units at an average density of . The racial makeup of the town was 88.67% White
White is the lightness, lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully diffuse reflection, reflect and scattering, scatter all the ...
, 6.95% African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American ...
, 0.24% Native American, 0.94% Asian, 0.04% Pacific Islander
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of Ocea ...
, 2.03% from other races, and 1.13% from two or more races. Hispanic
The term ''Hispanic'' ( es, hispano) refers to people, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or Hispanidad.
The term commonly applies to countries with a cultural and historical link to Spain and to viceroyalties for ...
or Latino of any race were 4.25% of the population.
There were 4,660 households, out of which 32.8% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 62.2% were married couples
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognized union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between t ...
living together, 6.9% had a female householder with no husband present, and 28.1% were non-families. 23.3% of all households were made up of individuals, and 11.6% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.55 and the average family size was 3.04.
In the town, the population was spread out, with 22.1% under the age of 18, 8.0% from 18 to 24, 31.7% from 25 to 44, 24.1% from 45 to 64, and 14.1% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 39 years. For every 100 females, there were 116.9 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 121.1 males.
The median income for a household in the town was $66,698, and the median income for a family was $79,189. Males had a median income of $52,096 versus $35,188 for females. The per capita income
Per capita income (PCI) or total income measures the average income earned per person in a given area (city, region, country, etc.) in a specified year. It is calculated by dividing the area's total income by its total population.
Per capita i ...
for the town was $28,171. About 1.8% of families and 3.6% of the population were below the poverty line
The poverty threshold, poverty limit, poverty line or breadline is the minimum level of income deemed adequate in a particular country. The poverty line is usually calculated by estimating the total cost of one year's worth of necessities for ...
, including 2.5% of those under age 18 and 6.2% of those age 65 or over.
Education
The town's public school system,Suffield Public Schools
The Suffield Public Schools system is a school district based in Suffield, Connecticut in the United States of America.
It includes A. Ward Spaulding Elementary School, McAlister Intermediate School, Suffield Middle School, and Suffield High Sch ...
, includes Spaulding Elementary School, McAlister Intermediate School, Suffield Middle School, and Suffield High School
Suffield High School is located in West Suffield, Connecticut, a town in Hartford County that abuts the Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət' ...
.
Suffield is also the home of Suffield Academy
Suffield Academy is a private preparatory school located in Suffield, Connecticut. It was founded in 1833 to train young men for ministry in the Baptist Church. The tuition fees for students are currently $65,000 for boarders and $38,700 for day s ...
, a private coeducational preparatory school.
Government and politics
List of First Selectmen
Historic homes and sites
 Main Street, a designated historic district with the Green, three churches, Suffield Academy and vintage colonial and Victorian homes, typifies a New England town. Named for the Kent family of Suffield, the Kent Memorial Library is an important research center for source materials, records, and documents from north-central Connecticut. A walk along Main Street reveals many examples of 18th and 19th century architecture. The Dr. Alexander King House, on the corner of Kent Avenue, and the Phelps-Hatheway House, a little farther north on Main Street, are museums open to the public from May to October.
Main Street, a designated historic district with the Green, three churches, Suffield Academy and vintage colonial and Victorian homes, typifies a New England town. Named for the Kent family of Suffield, the Kent Memorial Library is an important research center for source materials, records, and documents from north-central Connecticut. A walk along Main Street reveals many examples of 18th and 19th century architecture. The Dr. Alexander King House, on the corner of Kent Avenue, and the Phelps-Hatheway House, a little farther north on Main Street, are museums open to the public from May to October.
Historic sites
The town includes 11 historic sites that are listed on theNational Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artist ...
:
* Alexander King House – 232 S. Main St. (added 1976)
* Babb's Beach
Babb's Beach is a municipal public recreation area located at 435 Babbs Rd. in Suffield, Connecticut. It is the former site of what was known as Babb's Beach Amusement Park, a small amusement park that was active in the first half of the 20th cent ...
– 435 Babb's Rd. (added 2006)
* Farmington Canal-New Haven and Northampton Canal – Roughly from Suffield to New Haven (added 1985)
* Gothic Cottage – 1425 Mapleton Ave. (added 1982)
* Hastings Hill Historic District
The Hastings Hill Historic District encompasses a rural crossroads settlement of the early 19th century at the junction of Spruce Street, Hill Street, and Russell Avenue in Suffield, Connecticut. The area includes well-preserved examples of 18 ...
– 987–1308 Hill St., 1242 Spruce St. and 1085-1162 Russell Ave. (added 1979)
* Hatheway House (also known as "Phelps-Hatheway House & Garden") – 55 S. Main St., reflects two architectural styles: the original 1761 building is a typical colonial house, the 1794 north wing is one of the first examples of the Neoclassical style in the Connecticut River Valley (added September 6, 1975)
* Hilltop Farm
Hilltop Farm is a historic country estate and gentleman's farm on Mapleton Avenue in northern Suffield, Connecticut. It was established in 1913 by George M. Hendee, one of the founders of the Indian Motorcycle Manufacturing Company, one of the n ...
– 1550–1760 Mapleton Ave. (added 2005)
* John Fuller House
The John Fuller House is a historic house at 463 Halladay Avenue in Suffield, Connecticut. Built in 1824, it was the main house for Suffield's town farm, its facility for supporting the poor and needy, between 1887 and 1952. It is a well-prese ...
– 463 Halladay Ave. (added 1982)
* King's Field House
The King's Field House is a historic house at 827 North Street in Suffield, Connecticut. Built about 1723 by the son of an early settler, it is a well-preserved example of 18th-century residential architecture. It was listed on the National Reg ...
– 827 North St. (added 1982)
* Lewis-Zukowski House – 1095 S. Grand St. (added 1990)
* Suffield Historic District – Runs along North and South Main Streets (added 1979)
Notable people
*Willis Seaver Adams
Willis Seaver Adams (1844–1921) was a landscape painter who studied under James Abbott McNeill Whistler. He studied at the Royal Academy of Fine Arts in Antwerp, Belgium and was part of the Tonalism movement, which took place in the late 19 ...
(1842–1921), landscape painter and part of the Tonalism
Tonalism was an artistic style that emerged in the 1880s when American artists began to paint landscape forms with an overall tone of colored atmosphere or mist. Between 1880 and 1915, dark, neutral hues such as gray, brown or blue, often dominat ...
movement which took place in the late 19th century; born in Suffield
* Ran Blake
Ran Blake (born April 20, 1935) is an American pianist, composer, and educator. He is known for his unique style that combines blues, gospel, classical, and film noir influences into an innovative and dark jazz sound. His career spans over 40 rec ...
, pianist
* Selden M. Bronson
Selden M. Bronson was a member of the Wisconsin State Assembly in 1881. He was a Republican. Bronson was a bookkeeper by trade. He was born on September 12, 1819, in Suffield, Connecticut
Suffield is a town in Hartford County, Connecticut, Unit ...
, former Wisconsin State Assemblyman
* Sylvester Graham
Sylvester Graham (July 5, 1794 – September 11, 1851) was an American Presbyterian minister and dietary reformer known for his emphasis on vegetarianism, the temperance movement, and eating whole-grain bread. His preaching
inspired the graham ...
(1794–1851), American diet
Diet may refer to:
Food
* Diet (nutrition), the sum of the food consumed by an organism or group
* Dieting, the deliberate selection of food to control body weight or nutrient intake
** Diet food, foods that aid in creating a diet for weight loss ...
ary reformer; born in Suffield
* Amos P. Granger, former US Congressman
* Francis Granger
Francis Granger (December 1, 1792 – August 31, 1868) was an American politician who represented Ontario County, New York, in the United States House of Representatives for three non-consecutive terms. He was a leading figure in the state and ...
, former US Congressman and Postmaster General
* Gideon Granger
Gideon Granger (July 19, 1767 – December 31, 1822) was an early American politician and lawyer. He was the father of fellow Postmaster General and U.S. Representative Francis Granger.
Early life
Granger was born in Suffield, Connecticut ...
, former US Postmaster General
* Chris Kellogg, current morning host of The Kellogg Krew morning show on WMAS-FM
* W. Bruce Lincoln
William Bruce Lincoln (September 6, 1938 – April 9, 2000) was an American scholar and author who wrote a number of widely-read books on Russian history. An expert noted for his narrative skills, he explained that he began "to write for a broad ...
, scholar of Russian history
* Thaddeus J. Martin. Major General in the United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army S ...
and Connecticut Adjutant General
The Adjutant General of Connecticut is the highest-ranking military officer in the Armed Forces of the State of Connecticut which includes the Connecticut National Guard, the four units of the Governor's Guards, the Connecticut State Guard, the C ...
* David Newton Sheldon
David Newton Sheldon (June 26, 1807 – October 4, 1889) was the fifth President of Colby College, Maine, United States from 1843–1853. He was also a pastor, missionary, and educator.
Early life
Sheldon was born in Suffield, Connecticut, to ...
, 5th President of Colby College
Colby College is a Private college, private Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts college in Waterville, Maine. It was founded in 1813 as the Maine Literary and Theological Institution, then renamed Waterville College after the ...
* Israel Smith
Israel Smith (April 4, 1759 – December 2, 1810) was an American lawyer and politician. He held a wide variety of positions in the state of Vermont, including as a member of the United States House of Representatives, a member of the United Sta ...
(1759–1810), served as a member of the United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together the ...
, a member of the United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and ...
and Governor of Vermont
The governor of Vermont is the head of government of Vermont. The officeholder is elected in even-numbered years by direct voting for a term of 2 years. Vermont and bordering New Hampshire are the only states to hold gubernatorial elections every ...
; born in Suffield
* Noah Smith (1756–1812), brother of Israel Smith
Israel Smith (April 4, 1759 – December 2, 1810) was an American lawyer and politician. He held a wide variety of positions in the state of Vermont, including as a member of the United States House of Representatives, a member of the United Sta ...
, Justice of the Vermont Supreme Court
The Vermont Supreme Court is the highest judicial authority of the U.S. state of Vermont. Unlike most other states, the Vermont Supreme Court hears appeals directly from the trial courts, as Vermont has no intermediate appeals court.
The Cou ...
* Timothy Swan
Timothy Swan (1758–1842) was a Yankee tunesmith and hatmaker born in Worcester, Massachusetts, USA. The son of goldsmith William Swan, Swan lived in small towns along the Connecticut River in Connecticut and Massachusetts for most of his l ...
(1758–1842), composer and hatmaker; resident of Suffield
* Emily Sweeney, member of 2018 US Olympic luger team
* John Tod
John Tod (1779March 27, 1830) was an American judge and politician who served as a Democratic-Republican member of the U.S. House of Representatives for Pennsylvania's 8th congressional district from 1821 to 1823 and for Pennsylvania's 13th co ...
(1779–1830), United States Congressman for Pennsylvania
References
External links
Town of Suffield official website
{{authority control Towns in Hartford County, Connecticut Connecticut populated places on the Connecticut River Towns in Connecticut Springfield metropolitan area, Massachusetts Greater Hartford