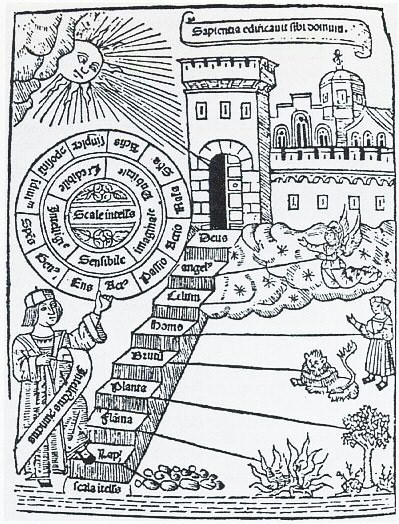
A hierarchy (from
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important concept in a wide variety of fields, such as
architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
,
philosophy
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
,
design
A design is the concept or proposal for an object, process, or system. The word ''design'' refers to something that is or has been intentionally created by a thinking agent, and is sometimes used to refer to the inherent nature of something ...
,
mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
,
computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
,
organizational theory
Organizational theory refers to a series of interrelated concepts that involve the sociological study of the structures and operations of formal social organizations. Organizational theory also seeks to explain how interrelated units of organiza ...
,
systems theory
Systems theory is the Transdisciplinarity, transdisciplinary study of systems, i.e. cohesive groups of interrelated, interdependent components that can be natural or artificial. Every system has causal boundaries, is influenced by its context, de ...
,
systematic biology
Systematics is the study of the diversification of living forms, both past and present, and the relationships among living things through time. Relationships are visualized as evolutionary trees (synonyms: phylogenetic trees, phylogenies). Phyl ...
, and the
social sciences
Social science (often rendered in the plural as the social sciences) is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of society, societies and the Social relation, relationships among members within those societies. The term was former ...
(especially
political science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and Power (social and political), power, and the analysis of political activities, political philosophy, political thought, polit ...
).
A hierarchy can link entities either directly or indirectly, and either vertically or diagonally. The only direct links in a hierarchy, insofar as they are hierarchical, are to one's immediate superior or to one of one's
subordinate
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an importan ...
s, although a system that is largely hierarchical can also incorporate alternative hierarchies. Hierarchical links can extend "vertically" upwards or downwards via multiple links in the same direction, following a
path
A path is a route for physical travel – see Trail.
Path or PATH may also refer to:
Physical paths of different types
* Bicycle path
* Bridle path, used by people on horseback
* Course (navigation), the intended path of a vehicle
* Desir ...
. All parts of the hierarchy that are not linked vertically to one another nevertheless can be "horizontally" linked through a path by traveling up the hierarchy to find a common direct or indirect superior, and then down again. This is akin to two
co-workers or
colleague
Collegiality is the relationship between colleagues, especially among peers, for example a fellow member of the same profession.
Colleagues are those explicitly united in a common purpose and, at least in theory, respect each other's abilities t ...
s; each reports to a common superior, but they have the same relative amount of authority. Organizational forms exist that are both alternative and complementary to hierarchy.
Heterarchy
A heterarchy is a system of organization where the elements of the organization are unranked (non- hierarchical) or where they possess the potential to be ranked a number of different ways. Definitions of the term vary among the disciplines: in soc ...
is one such form.
Nomenclature
Hierarchies have their own special vocabulary. These terms are easiest to understand when a hierarchy is diagrammed (see
below
Below may refer to:
*Earth
*Ground (disambiguation)
*Soil
*Floor
* Bottom (disambiguation)
*Less than
*Temperatures below freezing
*Hell or underworld
People with the surname
* Ernst von Below (1863–1955), German World War I general
* Fred Belo ...
).
In an organizational context, the following terms are often used related to hierarchies:
*
Object
Object may refer to:
General meanings
* Object (philosophy), a thing, being, or concept
** Object (abstract), an object which does not exist at any particular time or place
** Physical object, an identifiable collection of matter
* Goal, an a ...
: one entity (e.g., a person, department or
concept
A concept is an abstract idea that serves as a foundation for more concrete principles, thoughts, and beliefs.
Concepts play an important role in all aspects of cognition. As such, concepts are studied within such disciplines as linguistics, ...
or element of arrangement or member of a set)
*
System
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, str ...
: the entire set of objects that are being arranged hierarchically (e.g., an administration)
*
Dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus, a line has a dimension of one (1D) because only one coo ...
: another word for "system" from on-line analytical processing (e.g. cubes)
*
Member
Member may refer to:
* Military jury, referred to as "Members" in military jargon
* Element (mathematics), an object that belongs to a mathematical set
* In object-oriented programming, a member of a class
** Field (computer science), entries in ...
: an (element or object) at any (level or rank) in a (class-system, taxonomy or dimension)
*Terms about Positioning
**
Rank: the relative
value, worth,
complexity
Complexity characterizes the behavior of a system or model whose components interact in multiple ways and follow local rules, leading to non-linearity, randomness, collective dynamics, hierarchy, and emergence.
The term is generally used to c ...
,
power, importance,
authority
Authority is commonly understood as the legitimate power of a person or group of other people.
In a civil state, ''authority'' may be practiced by legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government,''The New Fontana Dictionary of M ...
, level etc. of an object
**
Level
Level or levels may refer to:
Engineering
*Level (optical instrument), a device used to measure true horizontal or relative heights
* Spirit level or bubble level, an instrument designed to indicate whether a surface is horizontal or vertical
*C ...
or Tier: a set of objects with the same rank OR importance
**
Ordering: the arrangement of the (ranks or levels)
**Hierarchy: the arrangement of a particular set of members into (ranks or levels). Multiple hierarchies are possible per (dimension taxonomy or Classification-system), in which selected levels of the dimension are omitted to flatten the structure
*Terms about Placement
**
Hierarch
An ordinary (from Latin ''ordinarius'') is an officer of a church or civic authority who by reason of office has ordinary power to execute laws.
Such officers are found in hierarchically organised churches of Western Christianity which have an ...
, the apex of the hierarchy, consisting of one single orphan (object or member) in the top level of a dimension. The root of an
inverted-tree structure
**
Member
Member may refer to:
* Military jury, referred to as "Members" in military jargon
* Element (mathematics), an object that belongs to a mathematical set
* In object-oriented programming, a member of a class
** Field (computer science), entries in ...
, a (member or node) in any level of a hierarchy in a dimension to which (superior and subordinate) members are attached
**
Orphan
An orphan is a child whose parents have died, are unknown, or have permanently abandoned them. It can also refer to a child who has lost only one parent, as the Hebrew language, Hebrew translation, for example, is "fatherless". In some languages ...
, a member in any level of a dimension without a parent member. Often the apex of a disconnected branch. Orphans can be grafted back into the hierarchy by creating a relationship (interaction) with a parent in the immediately superior level
**
Leaf
A leaf (: leaves) is a principal appendage of the plant stem, stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leav ...
, a member in any level of a dimension without subordinates in the hierarchy
**
Neighbour: a member adjacent to another member in the same (level or rank). Always a peer.
**
Superior: a higher level or an object ranked at a higher level (A parent or an ancestor)
**
Subordinate
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an importan ...
: a lower level or an object ranked at a lower level (A child or a descendant)
**
Collection: all of the objects at one level (i.e. Peers)
**
Peer: an object with the same rank (and therefore at the same level)
**
Interaction: the relationship between an object and its direct superior or subordinate (i.e. a superior/inferior pair)
*** a direct interaction occurs when one object is on a level exactly one higher or one lower than the other (i.e., on a
tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only ...
, the two objects have a line between them)
**
Distance
Distance is a numerical or occasionally qualitative measurement of how far apart objects, points, people, or ideas are. In physics or everyday usage, distance may refer to a physical length or an estimation based on other criteria (e.g. "two co ...
: the minimum number of connections between two objects, i.e., one less than the number of objects that need to be "crossed" to trace a
path
A path is a route for physical travel – see Trail.
Path or PATH may also refer to:
Physical paths of different types
* Bicycle path
* Bridle path, used by people on horseback
* Course (navigation), the intended path of a vehicle
* Desir ...
from one object to another
**
Span: a
qualitative description of the width of a level when diagrammed, i.e., the number of subordinates an object has
*Terms about Nature
**
Attribute: a heritable characteristic of (members and their subordinates) in a level (e.g. ''hair-colour'')
**
Attribute-value: the specific value of a heritable characteristic (e.g. ''Auburn'')
In a mathematical context (in
graph theory
In mathematics and computer science, graph theory is the study of ''graph (discrete mathematics), graphs'', which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. A graph in this context is made up of ''Vertex (graph ...
), the
general terminology used is different.
Most hierarchies use a more specific vocabulary pertaining to their subject, but the idea behind them is the same. For example, with
data structure
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization and storage format that is usually chosen for Efficiency, efficient Data access, access to data. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships amo ...
s, objects are known as
nodes, superiors are called
parents
A parent is either the progenitor of a child or, in humans, it can refer to a caregiver or legal guardian, generally called an adoptive parent or step-parent. Parents who are progenitors are first-degree relatives and have 50% genetic meet. ...
and subordinates are called
children
A child () is a human being between the stages of childbirth, birth and puberty, or between the Development of the human body, developmental period of infancy and puberty. The term may also refer to an unborn human being. In English-speaking ...
. In a business setting, a superior is a
supervisor/boss and a peer is a
colleague
Collegiality is the relationship between colleagues, especially among peers, for example a fellow member of the same profession.
Colleagues are those explicitly united in a common purpose and, at least in theory, respect each other's abilities t ...
.
Degree of branching
Degree of
branching refers to the number of direct
subordinates or children an object has (in graph theory, equivalent to the number of other
vertices connected to via outgoing arcs, in a directed graph) a node has. Hierarchies can be categorized based on the "maximum degree", the highest degree present in the system as a whole. Categorization in this way yields two broad classes: ''linear'' and ''branching''.
In a linear hierarchy, the maximum degree is 1.
In other words, all of the objects can be visualized in a line-up, and each object (excluding the top and bottom ones) has exactly one direct subordinate and one direct superior. This is referring to the ''objects'' and not the ''levels''; every hierarchy has this property with respect to levels, but normally each level can have an infinite number of objects.
In a branching hierarchy, one or more objects has a degree of 2 or more (and therefore the minimum degree is 2 or higher).
For many people, the word "hierarchy" automatically evokes an image of a branching hierarchy.
Branching hierarchies are present within numerous systems, including
organization
An organization or organisation (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), see spelling differences) is an legal entity, entity—such as ...
s and
classification scheme
In information science and ontology, a classification scheme is an arrangement of classes or groups of classes. The activity of developing the schemes bears similarity to taxonomy, but with perhaps a more theoretical bent, as a single classifica ...
s. The broad category of branching hierarchies can be further subdivided based on the degree.
A flat hierarchy (also known for companies as
flat organization
A flat organization (or horizontal organization) is an organizational structure with few levels of management between staff and executives. An organizational structure refers to the nature of the distribution of the units and positions within it, ...
) is a branching hierarchy in which the maximum degree approaches infinity, i.e., that has a wide span.
Most often, systems intuitively regarded as hierarchical have at most a moderate span. Therefore, a flat hierarchy is often not viewed as a hierarchy at all. For example,
diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of e ...
s and
graphite
Graphite () is a Crystallinity, crystalline allotrope (form) of the element carbon. It consists of many stacked Layered materials, layers of graphene, typically in excess of hundreds of layers. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable ...
are flat hierarchies of numerous
carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
atoms that can be further decomposed into subatomic particles.
An overlapping hierarchy is a branching hierarchy in which at least one object has two parent objects.
For example, a
graduate student
Postgraduate education, graduate education, or graduate school consists of Academic degree, academic or professional degrees, certificates, diplomas, or other qualifications usually pursued by higher education, post-secondary students who have ...
can have two
co-supervisors to whom the student reports directly and equally, and who have the same level of authority within the
university
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
hierarchy (i.e., they have the same
position
Position often refers to:
* Position (geometry), the spatial location (rather than orientation) of an entity
* Position, a job or occupation
Position may also refer to:
Games and recreation
* Position (poker), location relative to the dealer
* ...
or
tenure
Tenure is a type of academic appointment that protects its holder from being fired or laid off except for cause, or under extraordinary circumstances such as financial exigency or program discontinuation. Academic tenure originated in the United ...
status).
Etymology
Possibly the first use of the English word ''hierarchy'' cited by the ''
Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the principal historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP), a University of Oxford publishing house. The dictionary, which published its first editio ...
'' was in 1881, when it was used in reference to the three orders of three angels as depicted by
Pseudo-Dionysius the Areopagite
Pseudo-Dionysius the Areopagite (or Dionysius the Pseudo-Areopagite) was a Greek author, Christian theologian and Neoplatonic philosopher of the late 5th to early 6th century, who wrote a set of works known as the ''Corpus Areopagiticum'' ...
(5th–6th centuries). Pseudo-Dionysius used the related
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
word (ἱεραρχία, ) both in reference to the
celestial hierarchy and the
ecclesiastical hierarchy. The Greek term ''hierarchia'' means 'rule of a high priest', from (ἱεράρχης, 'president of sacred rites, high-priest') and that from ''hiereus'' (ἱερεύς, 'priest') and ''arche'' (ἀρχή, 'first place or power, rule'). Dionysius is credited with first use of it as an abstract noun.
Since hierarchical churches, such as the
Roman Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
(see
Catholic Church hierarchy
The hierarchy of the Catholic Church consists of its bishops, priests, and deacons. In the ecclesiological sense of the term, "hierarchy" strictly means the "holy ordering" of the church, the Body of Christ, so to respect the diversity of gif ...
) and
Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
churches, had tables of organization that were "hierarchical" in the modern sense of the word (traditionally with
God
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is "a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the un ...
as the pinnacle or head of the hierarchy), the term came to refer to similar organizational methods in
secular
Secularity, also the secular or secularness (from Latin , or or ), is the state of being unrelated or neutral in regards to religion. The origins of secularity can be traced to the Bible itself. The concept was fleshed out through Christian hi ...
settings.
Representing hierarchies
A hierarchy is typically depicted as a
pyramid
A pyramid () is a structure whose visible surfaces are triangular in broad outline and converge toward the top, making the appearance roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be of any polygon shape, such as trian ...
, where the height of a level represents that level's status and width of a level represents the quantity of items at that level relative to the whole. For example, the few
Directors of a company could be at the
apex
The apex is the highest point of something. The word may also refer to:
Arts and media Fictional entities
* Apex (comics)
A-Bomb
Abomination
Absorbing Man
Abraxas
Abyss
Abyss is the name of two characters appearing in Ameri ...
, and the
base could be thousands of people who have no subordinates.
These pyramids are often
diagrammed with a
triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three corners and three sides, one of the basic shapes in geometry. The corners, also called ''vertices'', are zero-dimensional points while the sides connecting them, also called ''edges'', are one-dimension ...
diagram which serves to emphasize the size differences between the levels (but not all triangle/pyramid diagrams are hierarchical; for example, the 1992
USDA food guide pyramid). An example of a triangle diagram appears to the right.
Another common representation of a hierarchical scheme is as a
tree diagram.
Phylogenetic trees
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA. In o ...
,
charts
A chart (sometimes known as a graph) is a graphical representation for data visualization, in which "the data is represented by symbols, such as bars in a bar chart, lines in a line chart, or slices in a pie chart". A chart can represent t ...
showing the structure of , and
playoff brackets in sports are often illustrated this way.
More recently, as computers have allowed the storage and navigation of ever larger data sets, various methods have been developed to represent hierarchies in a manner that makes more efficient use of the available space on a computer's screen. Examples include
fractal
In mathematics, a fractal is a Shape, geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scale ...
maps,
TreeMaps and
Radial Trees.
Visual hierarchy
In the design field, mainly graphic design, successful layouts and formatting of the content on documents are heavily dependent on the rules of
visual hierarchy
Visual hierarchy, according to Gestalt psychology, is a pattern in the visual field wherein some elements tend to "stand out," or attract attention, more strongly than other elements, suggesting a hierarchy of importance. While it may occur natura ...
. Visual hierarchy is also important for proper organization of files on computers.
An example of visually representing hierarchy is through nested clusters. Nested clusters represent hierarchical relationships using layers of information. The child element is within the parent element, such as in a
Venn diagram
A Venn diagram is a widely used diagram style that shows the logical relation between set (mathematics), sets, popularized by John Venn (1834–1923) in the 1880s. The diagrams are used to teach elementary set theory, and to illustrate simple ...
. This structure is most effective in representing simple hierarchical relationships. For example, when directing someone to open a file on a computer desktop, one may first direct them towards the main folder, then the subfolders within the main folder. They will keep opening files within the folders until the designated file is located.
For more complicated hierarchies, the stair structure represents hierarchical relationships through the use of visual stacking. Visually imagine the top of a downward staircase beginning at the left and descending on the right. Child elements are towards the bottom of the stairs and parent elements are at the top. This structure represents hierarchical relationships through the use of visual stacking.
Informal representation
In plain English, a hierarchy can be thought of as a
set
Set, The Set, SET or SETS may refer to:
Science, technology, and mathematics Mathematics
*Set (mathematics), a collection of elements
*Category of sets, the category whose objects and morphisms are sets and total functions, respectively
Electro ...
in which:
# No element is superior to itself, and
# One element, the (''apex'' or ''hierarch''), is superior to all of the other elements in the set.
The first requirement is also interpreted to mean that a hierarchy can have no
circular relationships; the association between two objects is always
transitive.
The second requirement asserts that a hierarchy must have a leader or
root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
that is common to all of the objects.
Mathematical representation
Mathematically, in its most general form, a hierarchy is a
partially ordered set
In mathematics, especially order theory, a partial order on a Set (mathematics), set is an arrangement such that, for certain pairs of elements, one precedes the other. The word ''partial'' is used to indicate that not every pair of elements need ...
or ''poset''.
The
system
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, str ...
in this case is the entire poset, which is constituted of elements. Within this system, each element shares a particular unambiguous property. Objects with the same property value are grouped together, and each of those resulting
levels is referred to as a
class
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used d ...
.
"Hierarchy" is particularly used to refer to a poset in which the classes are organized in terms of increasing complexity.
Operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division are often performed in a certain sequence or order. Usually, addition and subtraction are performed after multiplication and division has already been applied to a problem. The use of parentheses is also a representation of hierarchy, for they show which operation is to be done prior to the following ones. For example:
(2 + 5) × (7 - 4).
In this problem, typically one would multiply 5 by 7 first, based on the rules of mathematical hierarchy. But when the parentheses are placed, one will know to do the operations within the parentheses first before continuing on with the problem. These rules are largely dominant in algebraic problems, ones that include several steps to solve. The use of hierarchy in mathematics is beneficial to quickly and efficiently solve a problem without having to go through the process of slowly dissecting the problem. Most of these rules are now known as the proper way into solving certain equations.
Subtypes
Nested hierarchy

A nested hierarchy or ''inclusion hierarchy'' is a hierarchical ordering of
nested sets.
The concept of nesting is exemplified in Russian
matryoshka dolls. Each doll is encompassed by another doll, all the way to the outer doll. The outer doll holds all of the inner dolls, the next outer doll holds all the remaining inner dolls, and so on. Matryoshkas represent a nested hierarchy where each level contains only one object, i.e., there is only one of each size of doll; a generalized nested hierarchy allows for multiple objects within levels but with each object having only one parent at each level. The general concept is both demonstrated and mathematically formulated in the following example:
:
A square can always also be referred to as a quadrilateral, polygon or shape. In this way, it is a hierarchy. However, consider the set of polygons using this classification. A square can ''only'' be a quadrilateral; it can never be a
triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three corners and three sides, one of the basic shapes in geometry. The corners, also called ''vertices'', are zero-dimensional points while the sides connecting them, also called ''edges'', are one-dimension ...
,
hexagon
In geometry, a hexagon (from Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexagon
A regular hexagon is de ...
, etc.
Nested hierarchies are the organizational schemes behind
taxonomies
image:Hierarchical clustering diagram.png, 280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy
Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme o ...
and systematic classifications. For example, using the original
Linnaean taxonomy
Linnaean taxonomy can mean either of two related concepts:
# The particular form of biological classification (taxonomy) set up by Carl Linnaeus, as set forth in his ''Systema Naturae'' (1735) and subsequent works. In the taxonomy of Linnaeus th ...
(the version he laid out in the 10th edition of ''
Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the Orthographic ligature, ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Sweden, Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the syste ...
''), a human can be formulated as:
:
Taxonomies may change frequently (as seen in
biological taxonomy), but the underlying concept of nested hierarchies is always the same.
In many programming taxonomies and syntax models (as well as fractals in mathematics), nested hierarchies, including Russian dolls, are also used to illustrate the properties of
self-similarity
In mathematics, a self-similar object is exactly or approximately similar to a part of itself (i.e., the whole has the same shape as one or more of the parts). Many objects in the real world, such as coastlines, are statistically self-similar ...
and
recursion
Recursion occurs when the definition of a concept or process depends on a simpler or previous version of itself. Recursion is used in a variety of disciplines ranging from linguistics to logic. The most common application of recursion is in m ...
. Recursion itself is included as a subset of hierarchical programming, and recursive thinking can be synonymous with a form of hierarchical thinking and logic.
Containment hierarchy
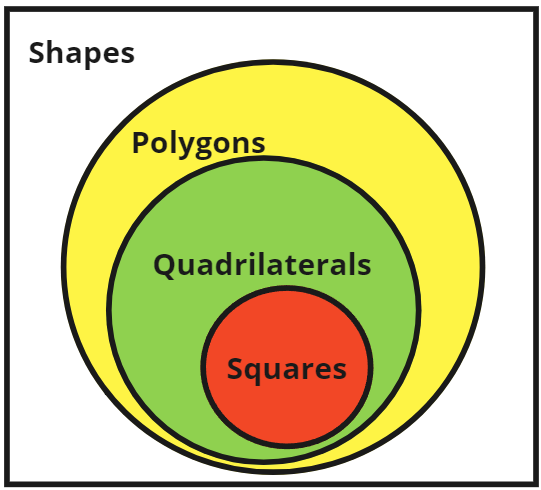
A containment hierarchy is a direct extrapolation of the
nested hierarchy
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important ...
concept. All of the ordered sets are still nested, but every set must be "
strict
In mathematical writing, the term strict refers to the property of excluding equality and equivalence and often occurs in the context of inequality and monotonic functions. It is often attached to a technical term to indicate that the exclusiv ...
"—no two sets can be identical. The shapes example above can be modified to demonstrate this:
:
The notation
means ''x'' is a subset of ''y'' but is not equal to ''y''.
A general example of a containment hierarchy is demonstrated in
class inheritance in
object-oriented programming
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of '' objects''. Objects can contain data (called fields, attributes or properties) and have actions they can perform (called procedures or methods and impl ...
.
Two types of containment hierarchies are the ''subsumptive'' containment hierarchy and the ''compositional'' containment hierarchy. A subsumptive hierarchy "
subsumes" its children, and a compositional hierarchy is "
composed" of its children. A hierarchy can also be both subsumptive ''and'' compositional.
Subsumptive containment hierarchy
A ''
subsumptive'' containment hierarchy is a classification of object classes from the general to the specific. Other names for this type of hierarchy are "taxonomic hierarchy" and "
IS-A
In knowledge representation, ontology components and ontology engineering, including for object-oriented programming and design, is-a (also written as is_a or is a) is a subsumptive relationship between abstractions (e.g., types, classes), wh ...
hierarchy".
The last term describes the relationship between each level—a lower-level object "is a" member of the higher class. The taxonomical structure outlined above is a subsumptive containment hierarchy. Using again the example of Linnaean taxonomy, it can be seen that an object that is a member of the level ''Mammalia'' "is a" member of the level ''Animalia''; more specifically, a human "is a" primate, a primate "is a" mammal, and so on. A subsumptive hierarchy can also be defined abstractly as a hierarchy of "
concept
A concept is an abstract idea that serves as a foundation for more concrete principles, thoughts, and beliefs.
Concepts play an important role in all aspects of cognition. As such, concepts are studied within such disciplines as linguistics, ...
s".
For example, with the Linnaean hierarchy outlined above, an entity name like ''Animalia'' is a way to group all the species that fit the
conceptualization
A concept is an abstract idea that serves as a foundation for more concrete principles, thoughts, and beliefs.
Concepts play an important role in all aspects of cognition. As such, concepts are studied within such disciplines as linguistics, psy ...
of an animal.
Compositional containment hierarchy
A ''compositional'' containment hierarchy is an ordering of the parts that make up a system—the system is "composed" of these parts.
Most engineered structures, whether natural or artificial, can be broken down in this manner.
The compositional hierarchy that every person encounters at every moment is the
hierarchy of life. Every person can be reduced to
organ system
An organ system is a biological system consisting of a group of organ (biology), organs that work together to perform one or more bodily functions. Each organ has a specialized role in an organism body, and is made up of distinct Tissue (biolog ...
s, which are composed of
organs, which are composed of
tissues, which are composed of
cells, which are composed of
molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
s, which are composed of
atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s. In fact, the last two levels apply to all
matter
In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms, which are made up of interacting subatomic pa ...
, at least at the
macroscopic scale
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or phenomena are large enough to be visible with the naked eye, without magnifying optical instruments. It is the opposite of microscopic.
Overview
When applied to physical phenom ...
. Moreover, each of these levels inherit all the properties of their
children
A child () is a human being between the stages of childbirth, birth and puberty, or between the Development of the human body, developmental period of infancy and puberty. The term may also refer to an unborn human being. In English-speaking ...
.
In this particular example, there are also ''
emergent properties
In philosophy, systems theory, science, and art, emergence occurs when a complex entity has properties or behaviors that its parts do not have on their own, and emerge only when they interact in a wider whole.
Emergence plays a central role ...
''—functions that are not seen at the lower level (e.g.,
cognition
Cognition is the "mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, ...
is not a property of
neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
s but is of the
brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
)—and a scalar quality (molecules are bigger than atoms, cells are bigger than molecules, etc.). Both of these concepts commonly exist in compositional hierarchies, but they are not a required general property. These ''level hierarchies'' are characterized by bi-directional
causation.
''Upward causation'' involves lower-level entities causing some property of a higher level entity; children entities may interact to yield parent entities, and parents are composed at least partly by their children. ''
Downward causation In philosophy, downward causation is a causal relationship from higher levels of a system to lower-level parts of that system: for example, mental events acting to cause physical events. The term was originally coined in 1974 by the philosopher and ...
'' refers to the effect that the incorporation of entity ''x'' into a higher-level entity can have on ''xs properties and interactions. Furthermore, the entities found at each level are ''
autonomous''.
Contexts and applications
Kulish (2002) suggests that almost every system of organization which humans apply to the world is arranged hierarchically.
Some conventional definitions of the terms "nation" and "government" suggest that every
nation
A nation is a type of social organization where a collective Identity (social science), identity, a national identity, has emerged from a combination of shared features across a given population, such as language, history, ethnicity, culture, t ...
has a government and that every government is hierarchical. Sociologists can analyse socioeconomic systems in terms of stratification into a social hierarchy (the
social stratification
Social stratification refers to a society's categorization of its people into groups based on socioeconomic factors like wealth, income, race, education, ethnicity, gender, occupation, social status, or derived power (social and political ...
of societies), and all
systematic classification schemes (
taxonomies
image:Hierarchical clustering diagram.png, 280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy
Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme o ...
) are hierarchical. Most
organized religion
Organized religion, also known as institutional religion, is religion in which belief systems and rituals are systematically arranged and formally established, typically by an official doctrine (or dogma), a hierarchical or bureaucratic leadership ...
s, regardless of their internal governance structures, operate as a hierarchy under
deities
A deity or god is a supernatural being considered to be sacred and worthy of worship due to having authority over some aspect of the universe and/or life. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines ''deity'' as a God (male deity), god or god ...
and
priesthoods. Many
Christian denomination
A Christian denomination is a distinct Religion, religious body within Christianity that comprises all Church (congregation), church congregations of the same kind, identifiable by traits such as a name, particular history, organization, leadersh ...
s have an
autocephalous
Autocephaly (; ) is the status of a hierarchical Christian church whose head bishop does not report to any higher-ranking bishop. The term is primarily used in Eastern Orthodox and Oriental Orthodox churches. The status has been compared with t ...
ecclesiastical hierarchy of
leadership
Leadership, is defined as the ability of an individual, group, or organization to "", influence, or guide other individuals, teams, or organizations.
"Leadership" is a contested term. Specialist literature debates various viewpoints on the co ...
. Families can be viewed as hierarchical structures in terms of
cousinship (e.g., first cousin once removed, second cousin, etc.),
ancestry
An ancestor, also known as a forefather, fore-elder, or a forebear, is a parent or ( recursively) the parent of an antecedent (i.e., a grandparent, great-grandparent, great-great-grandparent and so forth). ''Ancestor'' is "any person from ...
(as depicted in a
family tree
A family tree, also called a genealogy or a pedigree chart, is a chart representing family relationships in a conventional tree structure. More detailed family trees, used in medicine and social work, are known as genograms.
Representations of ...
) and
inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Offi ...
(
succession
Succession is the act or process of following in order or sequence.
Governance and politics
*Order of succession, in politics, the ascension to power by one ruler, official, or monarch after the death, resignation, or removal from office of ...
and
heir
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Offi ...
ship). All the requisites of a well-rounded life and
lifestyle can be organized using
Maslow's hierarchy of human needs - according to Maslow's hierarchy of human needs.
Learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, value (personal and cultural), values, Attitude (psychology), attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, non-human animals, and ...
steps often follow a hierarchical scheme—to master
differential equations one must first learn
calculus
Calculus is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations.
Originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the ...
; to learn calculus one must first learn
elementary algebra
Elementary algebra, also known as high school algebra or college algebra, encompasses the basic concepts of algebra. It is often contrasted with arithmetic: arithmetic deals with specified numbers, whilst algebra introduces variable (mathematics ...
; and so on.
Nature
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physic ...
offers hierarchical structures, as numerous schemes such as
Linnaean taxonomy
Linnaean taxonomy can mean either of two related concepts:
# The particular form of biological classification (taxonomy) set up by Carl Linnaeus, as set forth in his ''Systema Naturae'' (1735) and subsequent works. In the taxonomy of Linnaeus th ...
, the
organization of life, and
biomass pyramids attempt to document.
While the above examples are often clearly depicted in a hierarchical form and are classic examples, hierarchies exist in numerous systems where this branching structure is not immediately apparent. For example, most
postal-code systems are hierarchical. Using the
Canadian postal code system as an example, the top level's binding concept, the
"postal district", consists of 18 objects (letters). The next level down is the "zone", where the objects are the digits 0–9. This is an example of an
overlapping hierarchy, because each of these 10 objects has 18 parents. The hierarchy continues downward to generate, in theory, 7,200,000 unique codes of the format ''A0A 0A0'' (the second and third letter positions allow 20 objects each). Most
library classification
A library classification is a system used within a library to organize materials, including books, sound and video recordings, electronic materials, etc., both on shelves and in catalogs and indexes. Each item is typically assigned a call number ...
systems are also hierarchical. The
Dewey Decimal System is infinitely hierarchical because there is no finite bound on the number of digits can be used after the decimal point.

Organizations
Organization
An organization or organisation (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), see spelling differences) is an legal entity, entity—such as ...
s can be structured as a
dominance hierarchy
In the zoological field of ethology, a dominance hierarchy (formerly and colloquially called a pecking order) is a type of social hierarchy that arises when members of animal social animal, social groups interact, creating a ranking system. Dif ...
. In an organizational hierarchy, there is a single person or group with the most
power or
authority
Authority is commonly understood as the legitimate power of a person or group of other people.
In a civil state, ''authority'' may be practiced by legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government,''The New Fontana Dictionary of M ...
, and each subsequent level represents a lesser authority. Most organizations are structured in this manner, including
governments
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a m ...
,
companies
A company, abbreviated as co., is a legal entity representing an association of legal people, whether natural, juridical or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members share a common purpose and unite to achieve specifi ...
,
armed forces
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a ...
,
militia
A militia ( ) is a military or paramilitary force that comprises civilian members, as opposed to a professional standing army of regular, full-time military personnel. Militias may be raised in times of need to support regular troops or se ...
and
organized religion
Organized religion, also known as institutional religion, is religion in which belief systems and rituals are systematically arranged and formally established, typically by an official doctrine (or dogma), a hierarchical or bureaucratic leadership ...
s. The units or persons within an organization may be depicted hierarchically in an
organizational chart
An organizational chart, also called organigram, organogram, or organizational breakdown structure (OBS), is a diagram that shows the structure of an organization and the relationships and relative ranks of its parts and positions/jobs. The ter ...
.
In a
reverse hierarchy, the conceptual
pyramid
A pyramid () is a structure whose visible surfaces are triangular in broad outline and converge toward the top, making the appearance roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be of any polygon shape, such as trian ...
of authority is turned upside-down, so that the apex is at the bottom and the base is at the top. This mode represents the idea that members of the higher rankings are responsible for the members of the lower rankings.
Biology
Empirically, when we observe in nature a large proportion of the (complex) biological systems, they exhibit hierarchic structure. On theoretical grounds we could expect complex systems to be hierarchies in a world in which complexity had to evolve from simplicity.
System
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, str ...
hierarchies analysis performed in the 1950s, laid the empirical foundations for a
field that would become, from the 1980s, hierarchical ecology.
The theoretical foundations are summarized by
thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, Work (thermodynamics), work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed b ...
.
When
biological systems
A biological system is a complex Biological network inference, network which connects several biologically relevant entities. Biological organization spans several scales and are determined based different structures depending on what the system is ...
are modeled as
physical system
A physical system is a collection of physical objects under study. The collection differs from a set: all the objects must coexist and have some physical relationship.
In other words, it is a portion of the physical universe chosen for analys ...
s, in the most general abstraction, they are
thermodynamic open systems that exhibit
self-organised behavior, and the
set/subset relations between
dissipative structures
A dissipative system is a thermodynamically open system which is operating out of, and often far from, thermodynamic equilibrium in an environment with which it exchanges energy and matter. A tornado may be thought of as a dissipative system. Dis ...
can be characterized in a hierarchy.
Other hierarchical representations related to biology include
ecological pyramids which illustrate energy flow or
trophic levels in
ecosystems
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
, and
taxonomic hierarchies, including the
Linnean classification scheme and
phylogenetic trees
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA. In o ...
that reflect inferred patterns of evolutionary relationship among living and extinct species.
Computer-graphic imaging
CGI and
computer-animation programs mostly use hierarchies for models. On a
3D model of a
human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
for example, the
chest
The thorax (: thoraces or thoraxes) or chest is a part of the anatomy of mammals and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen.
In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main di ...
is a
parent
A parent is either the progenitor of a child or, in humans, it can refer to a caregiver or legal guardian, generally called an adoptive parent or step-parent. Parents who are progenitors are First-degree relative, first-degree relatives and have ...
of the upper left arm, which is a parent of the lower left arm, which is a parent of the
hand
A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the Koala#Characteristics, koala (which has two thumb#O ...
. This pattern is used in
modeling and
animation
Animation is a filmmaking technique whereby still images are manipulated to create moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on transparent celluloid sheets to be photographed and exhibited on film. Animati ...
for almost everything built as a 3D
digital
Digital usually refers to something using discrete digits, often binary digits.
Businesses
*Digital bank, a form of financial institution
*Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) or Digital, a computer company
*Digital Research (DR or DRI), a software ...
model.
Linguistics
Many grammatical theories, such as
phrase-structure grammar
The term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammar studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue ( Post canonical systems). Some authors, however, reserve the term for more restricted grammars in th ...
, involve hierarchy.
Direct–inverse languages such as
Cree
The Cree, or nehinaw (, ), are a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American Indigenous people, numbering more than 350,000 in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations in Canada, First Nations. They live prim ...
and
Mapudungun
Mapuche ( , ; from 'land' and 'people', meaning 'the people of the land') or Mapudungun (from 'land' and 'speak, speech', meaning 'the speech of the land'; also spelled Mapuzugun and Mapudungu) is either a language isolate or member of the s ...
distinguish subject and object on
verb
A verb is a word that generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual description of English, the basic f ...
s not by different subject and object markers, but via a hierarchy of persons.
In this system, the three (or four with
Algonquian languages
The Algonquian languages ( ; also Algonkian) are a family of Indigenous languages of the Americas and most of the languages in the Algic language family are included in the group. The name of the Algonquian language family is distinguished from ...
) persons occur in a hierarchy of
salience. To distinguish which is subject and which object, ''inverse markers'' are used if the object outranks the subject.
On the other hand, languages include a variety of phenomena that are not hierarchical. For example, the relationship between a pronoun and a prior noun-phrase to which it refers commonly crosses grammatical boundaries in non-hierarchical ways.
Music
The structure of a musical composition is often understood hierarchically (for example by
Heinrich Schenker
Heinrich Schenker (19 June 1868 – 14 January 1935) was an Austrian music theory, music theorist #Theoretical writings, whose writings have had a profound influence on subsequent musical analysis. His approach, now termed Schenkerian analysis ...
(1768–1835, see
Schenkerian analysis
Schenkerian analysis is a method of musical analysis, analyzing tonal music based on the theories of Heinrich Schenker (1868–1935). The goal is to demonstrate the organic coherence of the work by showing how the "foreground" (all notes in the sco ...
), and in the (1985)
Generative Theory of Tonal Music, by composer
Fred Lerdahl
Alfred Whitford (Fred) Lerdahl (born March 10, 1943) is an American music theorist and composer. Best known for his work on musical grammar, Music cognition, cognition, Rhythm, rhythmic theory, and pitch space, he and the linguist Ray Jackendoff d ...
and linguist Ray
Jackendoff). The sum of all notes in a piece is understood to be an all-inclusive surface, which can be reduced to successively more sparse and more fundamental types of motion. The levels of structure that operate in Schenker's theory are the foreground, which is seen in all the details of the musical score; the middle ground, which is roughly a summary of an essential contrapuntal progression and voice-leading; and the background or
Ursatz, which is one of only a few basic "long-range counterpoint" structures that are shared in the gamut of tonal music literature.
The
pitches and
form of
tonal music are organized hierarchically, all pitches deriving their importance from their relationship to a
tonic key, and secondary themes in other
keys are brought back to the tonic in a recapitulation of the primary theme.
Examples of other applications
Information-based
*
Library classification
A library classification is a system used within a library to organize materials, including books, sound and video recordings, electronic materials, etc., both on shelves and in catalogs and indexes. Each item is typically assigned a call number ...
**
Dewey Decimal Classification
The Dewey Decimal Classification (DDC) (pronounced ) colloquially known as the Dewey Decimal System, is a proprietary library classification system which allows new books to be added to a library in their appropriate location based on subject. ...
City planning-based
*
Green transport hierarchy
*
Roads
A road is a thoroughfare used primarily for movement of traffic. Roads differ from streets, whose primary use is local access. They also differ from stroads, which combine the features of streets and roads. Most modern roads are paved.
The ...
**
Streets
Streets is the plural of street, a type of road.
Streets or The Streets may also refer to: Music
* Streets (band), a rock band fronted by Kansas vocalist Steve Walsh
* ''Streets'' (punk album), a 1977 compilation album of various early UK punk ba ...
*
Settlement hierarchy
**
As of 2010
**
As of 2100 (estimate according to Doxiadis, 1968)
Linguistics-oriented
*
Language family tree
*
Levels of adequacy for evaluating grammars
*
Direct–inverse languages
*
Structural linguistics
Structural linguistics, or structuralism, in linguistics, denotes schools or theories in which language is conceived as a self-contained, self-regulating semiotic system whose elements are defined by their relationship to other elements within th ...
**
Parse tree
A parse tree or parsing tree (also known as a derivation tree or concrete syntax tree) is an ordered, rooted tree that represents the syntactic structure of a string according to some context-free grammar. The term ''parse tree'' itself is use ...
**
Formal grammar
A formal grammar is a set of Terminal and nonterminal symbols, symbols and the Production (computer science), production rules for rewriting some of them into every possible string of a formal language over an Alphabet (formal languages), alphabe ...
s
**
Abstract syntax tree
An abstract syntax tree (AST) is a data structure used in computer science to represent the structure of a program or code snippet. It is a tree representation of the abstract syntactic structure of text (often source code) written in a formal ...
*
Evolution of basic color terminology in languages
Power- or authority-based
*
Aristocratic hierarchies
** In
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
** In
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
*
Ecclesiastical hierarchies
**
Catholic Church hierarchy
The hierarchy of the Catholic Church consists of its bishops, priests, and deacons. In the ecclesiological sense of the term, "hierarchy" strictly means the "holy ordering" of the church, the Body of Christ, so to respect the diversity of gif ...
**
LDS Church hierarchy
**
Kimbanguist Church hierarchy
**
Raëlism Church hierarchy
** see also
autocephaly
Autocephaly (; ) is the status of a hierarchical Christian church whose head bishop does not report to any higher-ranking bishop. The term is primarily used in Eastern Orthodox and Oriental Orthodox churches. The status has been compared with t ...
*
Prussian three-class franchise
* Political party hierarchies
**
Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party ( or NSDAP), was a far-right politics, far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported the ideology of Nazism. Its precursor ...
(''pace'' overlapping fields
[
Compare:
])
***
SS
***
Hierarchy of subdivisions within the Gau
**
Communist Party of the Soviet Union
The Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU),. Abbreviated in Russian as КПСС, ''KPSS''. at some points known as the Russian Communist Party (RCP), All-Union Communist Party and Bolshevik Party, and sometimes referred to as the Soviet ...
**
Chinese Communist Party
The Communist Party of China (CPC), also translated into English as Chinese Communist Party (CCP), is the founding and One-party state, sole ruling party of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Founded in 1921, the CCP emerged victorious in the ...
*
Chain of command
**
Military ranks
Military ranks is a system of hierarchy, hierarchical relationships within armed forces, police, Intelligence agency, intelligence agencies, paramilitary groups, and other institutions organized along military organisation , military lines, such ...
**
Military units
**
U.S. Military Combatant Commands
*
Intraspecial dominance
**
Pecking order
*
Social classes
A social class or social stratum is a grouping of people into a set of hierarchical social categories, the most common being the working class and the capitalist class. Membership of a social class can for example be dependent on education, ...
**
Caste system in India
The caste system in India is the paradigmatic ethnographic instance of social classification based on castes. It has its origins in ancient India, and was transformed by various ruling elites in medieval, early-modern, and modern India, espe ...
**
Hierarchical structure of Feudal Japan
**
White racist hierarchy
**
Hierarchy of Exclusion (Ender's Game)
Value-related
*
Hierarchy of genres in art
*
Evidence
Evidence for a proposition is what supports the proposition. It is usually understood as an indication that the proposition is truth, true. The exact definition and role of evidence vary across different fields. In epistemology, evidence is what J ...
*
Human needs
A need is a deficiency at a point of time and in a given context. Needs are distinguished from wants. In the case of a need, a deficiency causes a clear adverse outcome: a dysfunction or death. In other words, a need is something required for a ...
*
Precious substances
*
Judicial hierarchy of social values
Perception-based
*
Color wheel
A color wheel or color circle is an abstract illustrative organization of color hues around a circle, which shows the relationships between primary colors, secondary colors, tertiary colors etc.
Some sources use the terms ''color wheel'' an ...
**
Primary colors
Primary colors are colorants or colored lights that can be mixed in varying amounts to produce a gamut of colors. This is the essential method used to create the perception of a broad range of colors in, e.g., electronic displays, color printin ...
***
Secondary colors
****
Tertiary colors
History-oriented
*
Three-age system
The three-age system is the periodization of human prehistory (with some overlap into the history, historical periods in a few regions) into three time-periods: the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, although the concept may also re ...
*
Cyclic theory of civilization
**
Oswald Spengler
Oswald Arnold Gottfried Spengler (29 May 1880 – 8 May 1936) was a German polymath whose areas of interest included history, philosophy, mathematics, science, and art, as well as their relation to his organic theory of history. He is best know ...
**
Arnold J. Toynbee
*
Spiral dynamics
Spiral Dynamics is a model of developmental psychology
Developmental psychology is the scientific study of how and why humans grow, change, and adapt across the course of their lives. Originally concerned with infants and children, the fiel ...
Science-focussed
*
Hierarchy of organization within the Universe
*
Star systems
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. It may sometimes be used to refer to a single star. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a ''st ...
*
Biological classification
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon), and these groups are give ...
*
Biological organization
*
Phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA. In ...
*
Evolutionary development
*
Hierarchy of ecological georegions
Technology-based
*
Memory hierarchy
In computer architecture, the memory hierarchy separates computer storage into a hierarchy based on response time. Since response time, complexity, and capacity are related, the levels may also be distinguished by their performance and contr ...
**
Cache hierarchy
Cache hierarchy, or multi-level cache, is a memory architecture that uses a hierarchy of memory stores based on varying access speeds to cache data. Highly requested data is cached in high-speed access memory stores, allowing swifter access by cent ...
*
Clusters
*
Class constructs
*
Data organization
**
Hierarchical query
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important ...
*
Data storage
Data storage is the recording (storing) of information (data) in a storage medium. Handwriting, phonographic recording, magnetic tape, and optical discs are all examples of storage media. Biological molecules such as RNA and DNA are con ...
**
Computer files
A computer file is a resource for recording data on a computer storage device, primarily identified by its filename. Just as words can be written on paper, so too can data be written to a computer file. Files can be shared with and transferred b ...
*
Devices
*
IP addresses
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label such as that is assigned to a device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. IP addresses serve two main functions: network interface id ...
*
Memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembe ...
**
Virtual memory allocation
*
Networks
Network, networking and networked may refer to:
Science and technology
* Network theory, the study of graphs as a representation of relations between discrete objects
* Network science, an academic field that studies complex networks
Mathematics
...
*
Radio cells
*
States (configurations)
*
Web addresses
*
Structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
**
Data Structure
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization and storage format that is usually chosen for Efficiency, efficient Data access, access to data. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships amo ...
*
Inheritance (object-oriented programming)
In object-oriented programming, inheritance is the mechanism of basing an Object (computer science), object or Class (computer programming), class upon another object (Prototype-based programming, prototype-based inheritance) or class (Class-base ...
Religion-related
* Levels of consciousness
**
Chakras
**
Great chain of being
The great chain of being is a hierarchical structure of all matter and life, thought by medieval Christianity to have been decreed by God. The chain begins with God and descends through angels, Human, humans, Animal, animals and Plant, plants to ...
**
G.I. Gurdjieff
**
Timothy Leary
Timothy Francis Leary (October 22, 1920 – May 31, 1996) was an American psychologist and author known for his strong advocacy of psychedelic drugs. Evaluations of Leary are polarized, ranging from "bold oracle" to "publicity hound". Accordin ...
* Levels of spiritual development
** In
Theravada Buddhism
''Theravāda'' (; 'School of the Elders'; ) is Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school's adherents, termed ''Theravādins'' ( anglicized from Pali ''theravādī''), have preserved their version of the Buddha's teaching or '' Dhamma'' in ...
** In
Mahayana Buddhism
Mahāyāna ( ; , , ; ) is a term for a broad group of Buddhist traditions, texts, philosophies, and practices developed in ancient India ( onwards). It is considered one of the three main existing branches of Buddhism, the others being Thera ...
* Ages in the evolution of society
** In
Astrology
Astrology is a range of Divination, divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that propose that information about human affairs and terrestrial events may be discerned by studying the apparent positions ...
** In
Hellenism (the Ancient Greek Religion)
**
Dispensations in Protestantism
**
Dispensations in Mormonism
*
Degrees of communion between various Christian churches
*
UFO religion
A UFO religion, also called a UFO cult or flying saucer cult, is any religion in which the existence of extraterrestrial (ET) entities and communication with them is a core belief. Typically, adherents of such religions believe the ETs to be i ...
s
**
Command hierarchy of the ''Ashtar Galactic Command'' flying saucer fleet
* Deities
** In
Japanese Buddhism
Buddhism was first established in Japan in the 6th century CE. Most of the Japanese Buddhists belong to new schools of Buddhism which were established in the Kamakura period (1185-1333). During the Edo period (1603–1868), Buddhism was cont ...
** In
Theosophy
Theosophy is a religious movement established in the United States in the late 19th century. Founded primarily by the Russian Helena Blavatsky and based largely on her writings, it draws heavily from both older European philosophies such as Neop ...
* Angels
** In
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
** In
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
** In
Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
***
Kabbalistic
** In
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism ( ), also called Mazdayasnā () or Beh-dīn (), is an Iranian religions, Iranian religion centred on the Avesta and the teachings of Zoroaster, Zarathushtra Spitama, who is more commonly referred to by the Greek translation, ...
* Devils and Demons
**
Devils
**
Demons
*
Hell
In religion and folklore, hell is a location or state in the afterlife in which souls are subjected to punishment after death. Religions with a linear divine history sometimes depict hells as eternal destinations, such as Christianity and I ...
s
** In
Catholicism (Nine Levels of Hell)
** In
Buddhism (Sixteen Levels of Hell)
*
Religions in society
* (organizational hierarchies are listed under )
Methods using hierarchy
Criticisms
In the work of diverse theorists such as
William James
William James (January 11, 1842 – August 26, 1910) was an American philosopher and psychologist. The first educator to offer a psychology course in the United States, he is considered to be one of the leading thinkers of the late 19th c ...
(1842 to 1910),
Michel Foucault
Paul-Michel Foucault ( , ; ; 15 October 192625 June 1984) was a French History of ideas, historian of ideas and Philosophy, philosopher who was also an author, Literary criticism, literary critic, Activism, political activist, and teacher. Fo ...
(1926 to 1984) and
Hayden White (1928 to 2018), important critiques of hierarchical
epistemology
Epistemology is the branch of philosophy that examines the nature, origin, and limits of knowledge. Also called "the theory of knowledge", it explores different types of knowledge, such as propositional knowledge about facts, practical knowle ...
are advanced. James famously asserts in his work
Radical Empiricism
Radical empiricism is a philosophical doctrine put forth by William James. It asserts that experience includes both particulars and relations between those particulars, and that therefore both deserve a place in our explanations. In concrete term ...
that clear distinctions of type and category are a constant but unwritten goal of scientific reasoning, so that when they are discovered, success is declared. But if aspects of the world are organized differently, involving inherent and intractable ambiguities, then scientific questions are often considered unresolved.
Feminists
Feminism is a range of socio-political movements and ideology, ideologies that aim to define and establish the political, economic, personal, and social gender equality, equality of the sexes. Feminism holds the position that modern soci ...
,
Marxists
Marxism is a political philosophy and method of socioeconomic analysis. It uses a dialectical and materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to analyse class relations, social conflict, and ...
,
anarchists
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that seeks to abolish all institutions that perpetuate authority, coercion, or hierarchy, primarily targeting the state and capitalism. Anarchism advocates for the replacement of the state w ...
,
communists
Communism () is a sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology within the socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered on common ownership of the means of production, d ...
,
critical theorists
Critical theory is a social, historical, and political school of thought and philosophical perspective which centers on analyzing and challenging systemic power relations in society, arguing that knowledge, truth, and social structures are fu ...
and others, all of whom have multiple interpretations, criticize the hierarchies commonly found within human society, especially in social relationships. Hierarchies are present in all parts of society: in businesses, schools, families, etc. These relationships are often viewed as necessary. Entities that stand in hierarchical arrangements are animals, humans, plants, etc.
Ethics, behavioral psychology, philosophies of identity
In
ethics
Ethics is the philosophy, philosophical study of Morality, moral phenomena. Also called moral philosophy, it investigates Normativity, normative questions about what people ought to do or which behavior is morally right. Its main branches inclu ...
, various
virtues
A virtue () is a trait of excellence, including traits that may be moral, social, or intellectual. The cultivation and refinement of virtue is held to be the "good of humanity" and thus is valued as an end purpose of life or a foundational pri ...
are enumerated and sometimes organized hierarchically according to certain brands of
virtue theory.
In some of these random examples, there is an asymmetry of 'compositional' significance between levels of structure, so that small parts of the whole hierarchical array depend, for their meaning, on their membership in larger parts. There is a hierarchy of activities in human life: productive activity serves or is guided by the moral life; the moral life is guided by practical reason; practical reason (used in moral and political life) serves contemplative reason (whereby we contemplate God). Practical reason sets aside time and resources for contemplative reason.
See also
Structure-related concepts
''(For example, in )''
*
Is-a
In knowledge representation, ontology components and ontology engineering, including for object-oriented programming and design, is-a (also written as is_a or is a) is a subsumptive relationship between abstractions (e.g., types, classes), wh ...
**
Hypernymy (and
supertype)
**
Hyponymy
Hypernymy and hyponymy are the wikt:Wiktionary:Semantic relations, semantic relations between a generic term (''hypernym'') and a more specific term (''hyponym''). The hypernym is also called a ''supertype'', ''umbrella term'', or ''blanket term ...
(and
subtype)
*
Has-a
In database design, object-oriented programming and Object-oriented design, design, has-a (has_a or has a) is a Object composition, composition relationship where one object (often called the constituted object, or part/constituent/member object) ...
**
Holonymy
In linguistics, meronymy () is a semantic relation between a meronym denoting a part and a holonym denoting a whole. In simpler terms, a meronym is in a ''part-of'' relationship with its holonym. For example, ''finger'' is a meronym of ''hand, ...
**
Meronymy
In linguistics, meronymy () is a semantic relation between a meronym denoting a part and a holonym denoting a whole. In simpler terms, a meronym is in a ''part-of'' relationship with its holonym. For example, ''finger'' is a meronym of ''hand, ...
Footnotes
Works cited
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
** Also includes full copies of:
**
**
External links
*
{{Authority control
Patterns
Structure
Political culture
 A hierarchy (from
A hierarchy (from  A nested hierarchy or ''inclusion hierarchy'' is a hierarchical ordering of nested sets. The concept of nesting is exemplified in Russian matryoshka dolls. Each doll is encompassed by another doll, all the way to the outer doll. The outer doll holds all of the inner dolls, the next outer doll holds all the remaining inner dolls, and so on. Matryoshkas represent a nested hierarchy where each level contains only one object, i.e., there is only one of each size of doll; a generalized nested hierarchy allows for multiple objects within levels but with each object having only one parent at each level. The general concept is both demonstrated and mathematically formulated in the following example:
:
A square can always also be referred to as a quadrilateral, polygon or shape. In this way, it is a hierarchy. However, consider the set of polygons using this classification. A square can ''only'' be a quadrilateral; it can never be a
A nested hierarchy or ''inclusion hierarchy'' is a hierarchical ordering of nested sets. The concept of nesting is exemplified in Russian matryoshka dolls. Each doll is encompassed by another doll, all the way to the outer doll. The outer doll holds all of the inner dolls, the next outer doll holds all the remaining inner dolls, and so on. Matryoshkas represent a nested hierarchy where each level contains only one object, i.e., there is only one of each size of doll; a generalized nested hierarchy allows for multiple objects within levels but with each object having only one parent at each level. The general concept is both demonstrated and mathematically formulated in the following example:
:
A square can always also be referred to as a quadrilateral, polygon or shape. In this way, it is a hierarchy. However, consider the set of polygons using this classification. A square can ''only'' be a quadrilateral; it can never be a  A containment hierarchy is a direct extrapolation of the
A containment hierarchy is a direct extrapolation of the  In
In