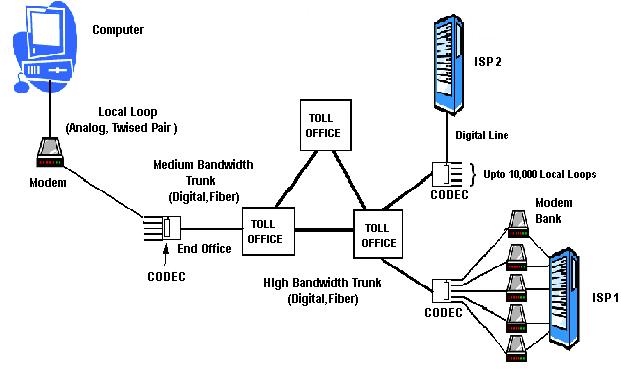
 In
In telephony
Telephony ( ) is the field of technology involving the development, application, and deployment of telecommunications services for the purpose of electronic transmission of voice, fax, or data, between distant parties. The history of telephony is ...
, the local loop (also referred to as the local tail, subscriber line, or in the aggregate as the last mile) is the physical link or circuit that connects from the demarcation point
In telephony, the demarcation point is the point at which the public switched telephone network ends and connects with the customer's on-premises wiring. It is the dividing line which determines who is responsible for installation and mainte ...
of the customer premises to the edge of the common carrier
A common carrier in common law countries (corresponding to a public carrier in some civil law (legal system), civil law systems,Encyclopædia Britannica CD 2000 "Civil-law public carrier" from "carriage of goods" usually called simply a ''carrier ...
or telecommunications service provider
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of ...
's network.
At the edge of the carrier access network
An access network is a type of telecommunications telecommunications network, network which connects subscribers to their immediate telecommunications service provider, service provider. It is contrasted with the core network, which connects l ...
in a traditional public telephone network, the local loop terminates in a circuit switch housed in an incumbent local exchange carrier
Local exchange carrier (LEC) is a regulatory term in telecommunications for the local telephone company.
In the United States, wireline telephone companies are divided into two large categories: long-distance ( interexchange carrier, or IXCs) ...
or telephone exchange
A telephone exchange, telephone switch, or central office is a central component of a telecommunications system in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or in large enterprises. It facilitates the establishment of communication circuits ...
.
Infrastructure
Traditionally, the local loop was anelectrical circuit
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., battery (electricity), batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e. ...
in the form of a single pair of conductors from the telephone on the customer's premises to the local telephone exchange
A telephone exchange, telephone switch, or central office is a central component of a telecommunications system in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or in large enterprises. It facilitates the establishment of communication circuits ...
. Single-wire earth return
Single-wire earth return (SWER) or single-wire ground return is a single-wire transmission line which supplies single-phase electric power from an electrical grid to remote areas at lowest cost. The earth (or sometimes a body of water) is used ...
lines had been used in some countries until the introduction of electric tramways from the 1900s made them unusable.
Historically the first section was often an aerial open-wire line, with several conductors attached to porcelain insulators on cross-arms on "telegraph" poles. Hence party line service was often given to residential customers to minimise the number of local loops required. Usually all these circuits went into aerial or buried cables with a twisted pair
Twisted pair cabling is a type of communications cable in which two conductors of a single circuit are twisted together for the purposes of improving electromagnetic compatibility. Compared to a single conductor or an untwisted balanced ...
for each local loop nearer the exchange, see outside plant
In telecommunications, the term outside plant has the following meanings:
*In civilian telecommunications, outside plant refers to all of the physical cabling and supporting infrastructure (such as conduit, cabinets, tower or poles), and any asso ...
.
Modern implementations may include a digital loop carrier
A digital loop carrier (DLC) is a system which uses digital transmission to extend the range of the local loop further than would be possible using only twisted pair copper wires. A DLC digitizes and multiplexes the individual signals carried by ...
system segment or fiber optic
An optical fiber, or optical fibre, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light from one end to the other. Such fibers find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at ...
transmission system. The local loop may terminate at a circuit switch owned by a competitive local exchange carrier
A competitive local exchange carrier (CLEC) is a North American telecommunications provider classification that emerged based on the competition model of the Telecommunications Act of 1996 in the United States. The act required the previously esta ...
and housed in a point of presence
A point of presence (PoP) is an artificial demarcation point or network interface point between communicating entities. A common example is an ISP point of presence, the local access point that allows users to connect to the Internet with their ...
(POP), which typically is an incumbent local exchange carrier telephone exchange. A local loop supports voice and/or data communications applications in the following ways:
* analog voice and signaling used in traditional POTS
* Integrated Services Digital Network
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is a set of communication standards for simultaneous digital transmission of voice, video, data, and other network services over the digitalised circuits of the public switched telephone network. ...
(ISDN)
* variants of digital subscriber line
Digital subscriber line (DSL; originally digital subscriber loop) is a family of technologies that are used to transmit digital data over telephone lines. In telecommunications marketing, the term DSL is widely understood to mean asymmetric dig ...
(DSL).
The term "local loop" is sometimes used for any " last mile" connection to the customer, regardless of technology or intended purpose. Local loop interrelations in this sense include:
*Electric power lines.
*Cable connections used with television, internet and telephone.
*Wireless signals or local loop (WLL): LMDS, WiMAX
Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX) is a family of wireless broadband communication standards based on the IEEE 802.16 set of standards, which provide physical layer (PHY) and media access control (MAC) options.
The WiMA ...
, GPRS
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), also called 2.5G, is a mobile data standard on the 2G cellular communication network's Global System for Mobile Communications, global system for mobile communications (GSM). Networks and mobile devices wit ...
, HSDPA
High Speed Packet Access (HSPA) is an amalgamation of two mobile protocols—High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) and High Speed Uplink Packet Access (HSUPA)—that extends and improves the performance of existing 3G mobile telecommunic ...
, DECT
Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT) is a cordless telephony standard maintained by ETSI. It originated in Europe, where it is the common standard, replacing earlier standards, such as CT1 and CT2. Since the DECT-2020 standard ...
*Satellite connections for beamed signal.
*Optical or fiber optics services.
See also
*Access network
An access network is a type of telecommunications telecommunications network, network which connects subscribers to their immediate telecommunications service provider, service provider. It is contrasted with the core network, which connects l ...
* ISDN
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is a set of communication standards for simultaneous digital transmission of voice, video, data, and other network services over the digitalised circuits of the public switched telephone network. ...
(Integrated Services Digital Network)
* Local-loop unbundling
Local loop unbundling (LLU or LLUB) is the regulatory process of allowing multiple telecommunications operators to use connections from a telephone exchange to the customer's location. The physical wire connection between the local exchange and th ...
* Metallic path facilities Metallic path facility (MPF) are the unshielded twisted pair of copper wires that run from a main distribution frame (MDF) at a local telephone exchange to the customer. In this variant, both broadband and voice (''baseband'') services, together p ...
* Outside plant
In telecommunications, the term outside plant has the following meanings:
*In civilian telecommunications, outside plant refers to all of the physical cabling and supporting infrastructure (such as conduit, cabinets, tower or poles), and any asso ...
(as an instance of a local loop)
* Serving area interface
The serving area interface or service area interface (SAI) is an outdoor enclosure or metal box that allows access to telecommunications wiring.
Alternate names
*Access point (AP)
*Cabinet (cab)
*B-box (breakout box)
*Cross box
*Cross-connect b ...
* Telephone line
A telephone line or telephone circuit (or just line or circuit industrywide) is a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system. It is designed to reproduce speech of a quality that is understandable. It is the physical wire or oth ...
References
{{Authority control Telecommunications infrastructure