Stye02 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A stye, also known as a hordeolum, is a bacterial infection of an oil gland in the

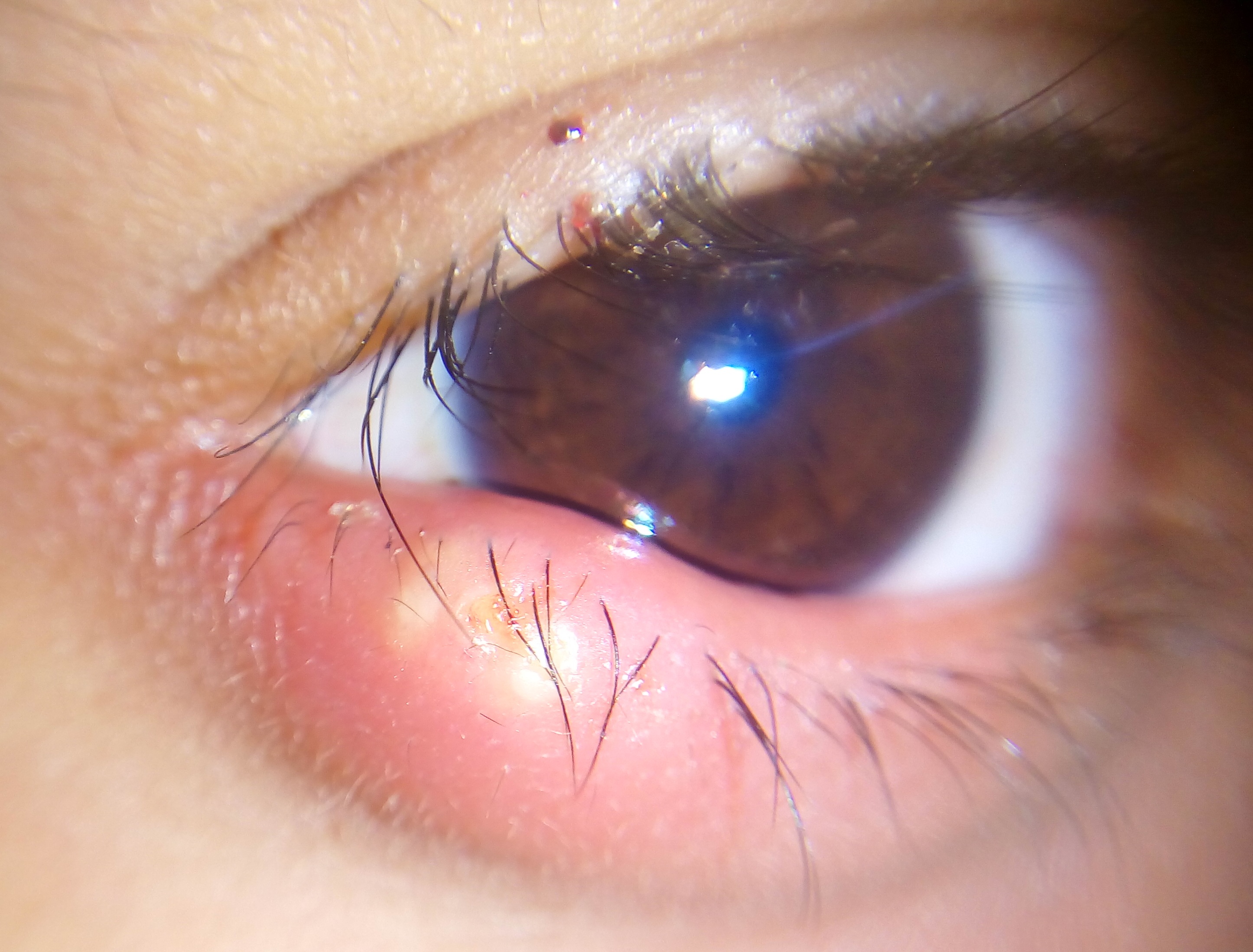 The first sign of a stye is a small, yellowish spot at the center of the bump that develops as
The first sign of a stye is a small, yellowish spot at the center of the bump that develops as
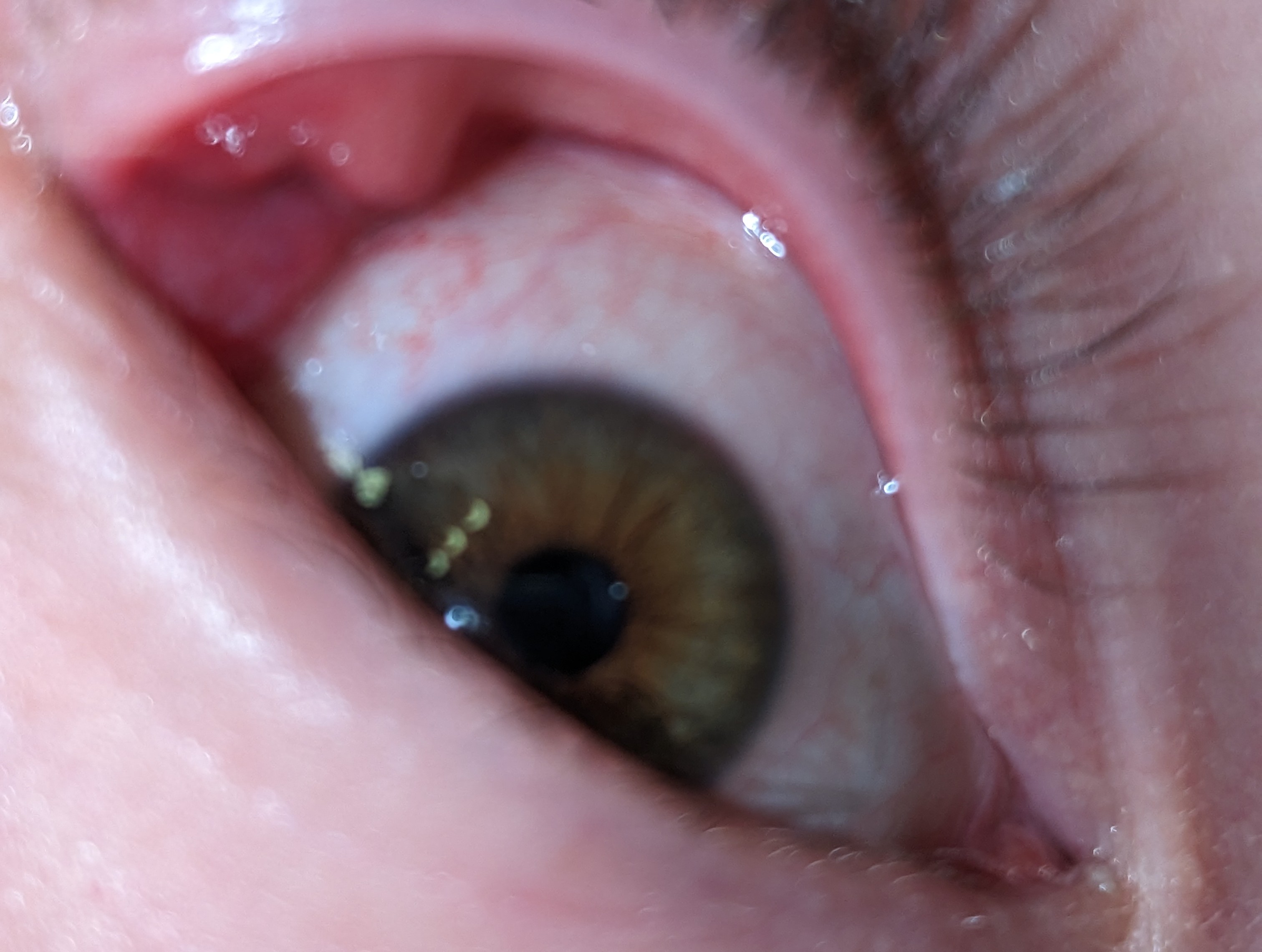 Stye complications occur in very rare cases. However, the most frequent complication of styes is progression to a
Stye complications occur in very rare cases. However, the most frequent complication of styes is progression to a
Merck Manual
* {{Eye pathology Disorders of eyelid, lacrimal system and orbit Eye Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate
eyelid
An eyelid ( ) is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid, exposing the cornea to the outside, giving vision. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. "Palpebral ...
. This results in a red tender bump at the edge of the eyelid. The outside or the inside of the eyelid can be affected.
The cause of a stye is usually a bacterial infection
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and many are beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of t ...
by ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
''. Internal styes are due to infection of the meibomian gland
Meibomian glands (also called tarsal glands, palpebral glands, and tarsoconjunctival glands) are sebaceous glands along the rims of the eyelid inside the tarsal plate. They produce meibum, an oily substance that prevents evaporation of the eye, ...
while external styes are due to an infection of the gland of Zeis. A chalazion
A chalazion (; plural chalazia or chalazions) or meibomian cyst is not a cyst but a granuloma in the eyelid that results from a blocked meibomian gland. It typically occurs in the middle of the eyelid, red, and not painful. They tend to come ...
on the other hand is a blocked meibomian gland without infection. A chalazion is typically in the middle of the eyelid and not painful.
Often a stye will go away without any specific treatment in a few days or weeks. Recommendations to speed improvement include warm compresses. Occasionally antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
eye ointment may be recommended. While these measures are often recommended, there is little evidence for use in internal styes. The frequency at which styes occur is unclear, though they may occur at any age.
Signs and symptoms

 The first sign of a stye is a small, yellowish spot at the center of the bump that develops as
The first sign of a stye is a small, yellowish spot at the center of the bump that develops as pus
Pus is an exudate, typically white-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammation during infections, regardless of cause. An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collect ...
and expands in the area.
Other stye symptoms may include:
* A lump on the top or bottom eyelid
An eyelid ( ) is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid, exposing the cornea to the outside, giving vision. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. "Palpebral ...
* Localized swelling of the eyelid
* Localized pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or res ...
* Redness
* Tenderness
* Crusting of the eyelid margins
* Burning in the eye
* Droopiness of the eyelid
* Scratchy sensation on the eyeball
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system.
In higher organisms, the eye ...
(itching)
* Blurred vision
Blurred vision is an ocular symptom where vision becomes less precise and there is added difficulty to resolve fine details.
Temporary blurred vision may involve dry eyes, eye infections, alcohol poisoning, hypoglycemia, or low blood pressur ...
* Mucous discharge in the eye
* Irritation of the eye
* Light sensitivity
* Tearing
* Discomfort during blinking
* Sensation of a foreign body in the eye
Complications
 Stye complications occur in very rare cases. However, the most frequent complication of styes is progression to a
Stye complications occur in very rare cases. However, the most frequent complication of styes is progression to a chalazion
A chalazion (; plural chalazia or chalazions) or meibomian cyst is not a cyst but a granuloma in the eyelid that results from a blocked meibomian gland. It typically occurs in the middle of the eyelid, red, and not painful. They tend to come ...
that causes cosmetic deformity, corneal irritation, and often requires surgical removal. Complications may also arise from the improper surgical lancing, and mainly consist of disruption of lash growth, lid deformity or lid fistula
In anatomy, a fistula (: fistulas or fistulae ; from Latin ''fistula'', "tube, pipe") is an abnormal connection (i.e. tube) joining two hollow spaces (technically, two epithelialized surfaces), such as blood vessels, intestines, or other h ...
. Large styes may interfere with one's vision.
Eyelid cellulitis
Cellulitis is usually a bacterial infection involving the inner layers of the skin. It specifically affects the dermis and subcutaneous fat. Signs and symptoms include an area of redness which increases in size over a few days. The borders of ...
is another potential complication of eye styes, which is a generalized infection of the eyelid. Progression of a stye to a systemic infection (spreading throughout the body) is extremely rare, and only a few instances of such spread have been recorded.
Cause
A stye is caused by a bacterial infection. The bacteria are ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
'' in about 95% of cases. The infection leads to the blocking of an oil gland at the base of the eyelash
An eyelash (also called lash) (Neo-Latin: ''cilium'', plural ''cilia'') is one of the hairs that grows at the edges of the top and bottom eyelids, spanning outwards and away from the eyes. The lashes grow in up to six layers on each of the upper ...
. Styes are experienced by people of all ages. Styes can be triggered by poor nutrition, sleep deprivation
Sleep deprivation, also known as sleep insufficiency or sleeplessness, is the condition of not having adequate duration and/or quality of sleep to support decent alertness, performance, and health. It can be either Chronic (medicine), chronic ...
, lack of hygiene, lack of water, and rubbing of the eyes. Styes can be secondary to blepharitis
Blepharitis, sometimes known as granulated eyelids, is one of the most common ocular conditions characterized by inflammation, scaling, reddening, and crusting of the eyelid. This condition may also cause swelling, burning, itching, or a grainy ...
or a deficiency in immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as pathogenic bacteria, bacteria and viruses, includin ...
.
Prevention
Stye prevention is closely related to proper hygiene. Proper hand washing can reduce the risks of developing not only styes, but also many other types of infections. Upon awakening, application of a warm washcloth to the eyelids for one to two minutes may be beneficial in decreasing the occurrence of styes by liquefying the contents of the oil glands of the eyelid and thereby preventing blockage. To prevent styes, cosmetics and cosmetic eye tools should not be shared among people. Like with all infections, regular hand washing is essential, and the eyes should not be rubbed or touched with unclean hands. Contaminated eye makeup should be discarded and sharing of washcloths or face towels should be curtailed, to avoid spreading the infection between individuals. Breaking the stye may spread bacteria contained in the pus and should be avoided.Treatment
Most cases of styes resolve on their own within one to two weeks, without professional care. The primary treatment is application of warm compresses. As a part of self-care at home, people may cleanse the affected eyelid with tap water or with a mild, nonirritating soap or shampoo (such as baby shampoo) to help clean crusted discharge. Cleansing must be done gently and while the eyes are closed to prevent eye injuries. People with styes should avoid eye makeup (e.g., eyeliner), lotions, and wearing contact lenses, since these can aggravate and spread the infection (sometimes to the cornea). People are advised not to lance the stye themselves, as serious infection can occur. Pain relievers such as acetaminophen may be used.Antibiotics
Evidence to support the use ofantibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
eye ointment is poor. Occasionally erythromycin ophthalmic ointment is recommended. Other antibiotics, such as chloramphenicol or amoxicillin may also be used. Chloramphenicol is used successfully in many parts of the world, but contains a black box warning in the United States due to concerns about aplastic anemia, which on rare occasions can be fatal.
Antibiotics are normally given to people with multiple styes or with styes that do not seem to heal, and to people who have blepharitis
Blepharitis, sometimes known as granulated eyelids, is one of the most common ocular conditions characterized by inflammation, scaling, reddening, and crusting of the eyelid. This condition may also cause swelling, burning, itching, or a grainy ...
or rosacea.
Procedures
Incision and drainage is performed if resolution does not begin in the next 48 hours after warm compresses are started. Medical professionals will sometimes lance a particularly persistent or irritating stye with a needle to accelerate its draining. Surgery is the last resort in stye treatment. Styes that do not respond to any type of therapies are usually surgically removed. Stye surgery is performed by an ophthalmologist, and generally under local anesthesia. The procedure consists of making a small incision on the inner or outer surface of the eyelid, depending if the stye is pointing externally or not. After the incision is made, the pus is drained out of the gland, and very small Surgical suture, sutures are used to close the lesion. Sometimes the removed stye is sent for a Histopathology, histopathological examination to investigate possibility of skin cancer.Alternative medicine
A 2017 Cochrane review found low-certainty and low-quality evidence that acupuncture helps in hordeolum compared with antibiotics or warm compresses. as well as that acupuncture plus conventional treatment may yield improvement, though they could not rule out placebo or observer effect, since the studies reviewed either had no positive control, were not blinded, or both.Prognosis
Although styes are harmless in most cases and complications are very rare, styes often recur. They do not cause intraocular damage, meaning they do not affect the eye. Styes normally heal on their own by rupturing within a few days to a week causing the relief of symptoms, but if one does not improve or it worsens within two weeks, a doctor's opinion should be sought. Few people require surgery as part of stye treatment. With adequate treatment, styes tend to heal quickly and without complications. The prognosis is better if one does not attempt to squeeze or puncture the stye, as infection may spread to adjacent tissues. Also, patients are recommended to call a doctor if they encounter problems with vision, the eyelid bump becomes very painful, the stye bleeds or reoccurs, or the eyelid or eyes becomes red.Etymology
The word ''stye'' (first recorded in the 17th century) is probably a back-formation from ''styany'' (first recorded in the 15th century), which in turn comes from ''styan'' plus ''eye'', the former of which in turn comes from the old English ''stīġend'', meaning "riser", from the verb ''stīgan'', "to rise". The older form ''styan'' is still used in Ulster Scots today. The homonym ''sty'' found in the combination ''pigsty'' has a slightly different origin, namely it comes from the Old English ''stiġ-fearh''—''fearh'' (farrow) is the Old English word for "piglet"—where ''stiġ'' meant "hall" (cf. ''steward''), possibly an early Old Norse loanword, which could be cognate with the word ''stīgan'' above.sty, n.3: The synonymous late Latin expression is ''hordeolum'', a modulation of the word ''hordeolus'', which is related to ''hordeum'' ("barley"), after its resemblance to a barley, barleycorn. In Czech, a sty is called ''ječné zrno'' (from ''ječmen'' "barley" and ''zrno'' "seed or grain"); in German, it is called ''Gerstenkorn'' (barleycorn). In Hebrew it is called שעורה Seh-oh-Ráh ("barley"). In Polish it is called ''jęczmień'' ("barley"). In Hungarian it is called ''árpa'' ("barley"). In Turkish it is called ''arpacık'' (small barley, barleylet)See also
* BoilReferences
External links
Merck Manual
* {{Eye pathology Disorders of eyelid, lacrimal system and orbit Eye Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate