stinkhorns on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Phallaceae is a
Phallaceae is a
 The gelatinous layer of the stinkhorn ''(
The gelatinous layer of the stinkhorn ''(
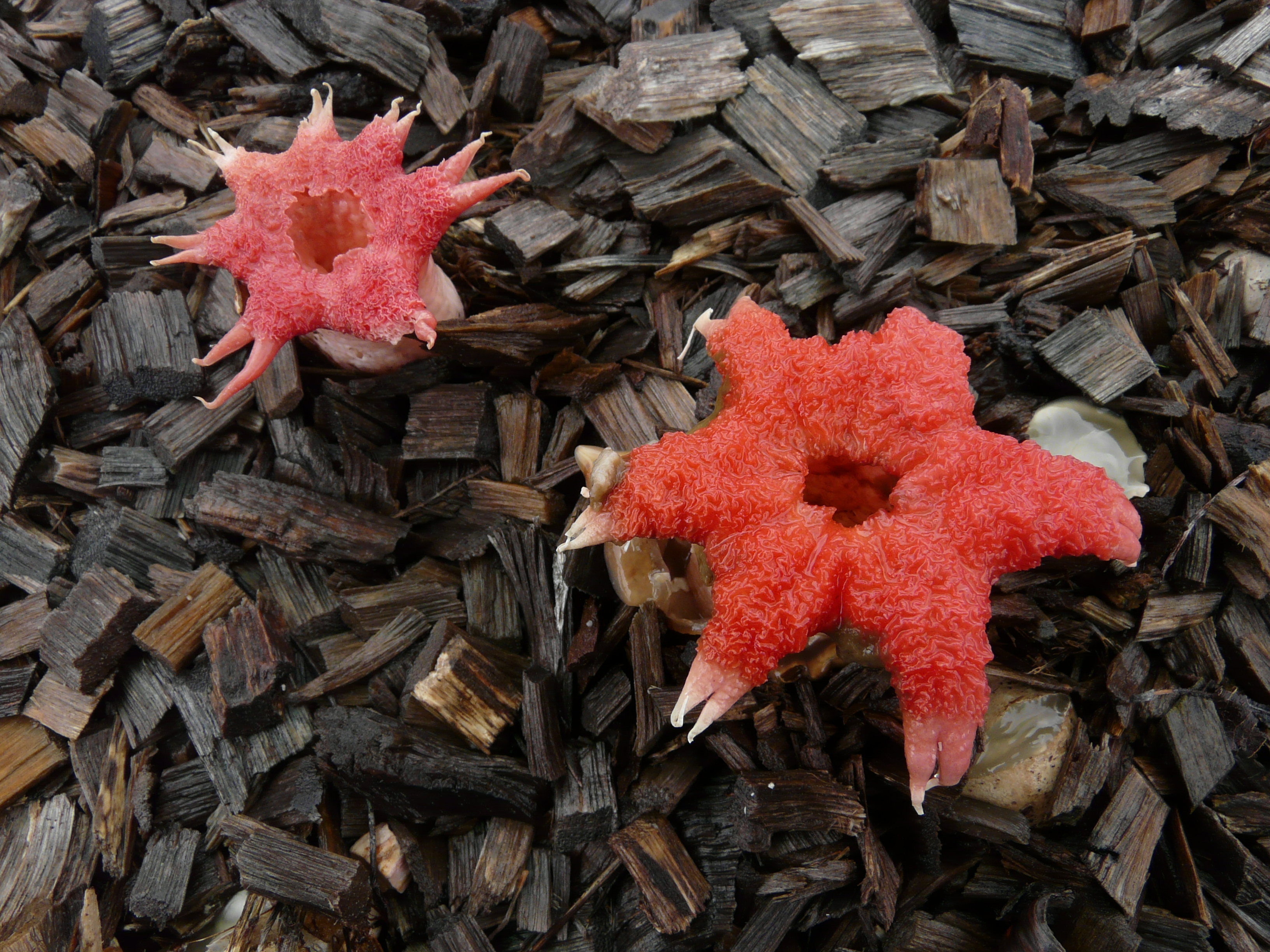 Mature fruiting bodies contain a roughly cylindrical white or pinkish stalk approximately 6 × 2 cm, with a volva at the base. At the top is a bright red disc with a variable number of arms, typically 3–7 cm long. The gleba found on the disc and inner side of the arms is slimy, foetid, and green colored. Spores are
Mature fruiting bodies contain a roughly cylindrical white or pinkish stalk approximately 6 × 2 cm, with a volva at the base. At the top is a bright red disc with a variable number of arms, typically 3–7 cm long. The gleba found on the disc and inner side of the arms is slimy, foetid, and green colored. Spores are  Fruiting bodies are latticed (clathrate), and made of hollow tubular arms that originate from the basal tissue within the volva. Spores are elliptical, smooth, hyaline, with dimensions of 4–6 ×1.5–2.5 μm.Miller and Miller, p. 80. Examples include ''
Fruiting bodies are latticed (clathrate), and made of hollow tubular arms that originate from the basal tissue within the volva. Spores are elliptical, smooth, hyaline, with dimensions of 4–6 ×1.5–2.5 μm.Miller and Miller, p. 80. Examples include '' ; '' Ligiella'' J.A. Sáenz (1980):Fruiting bodies are 4.5–6.5 cm long, 2.2–5 cm in diameter, and have four or five thick white chambered arms that are joined at the top, but free at the base. This
; '' Ligiella'' J.A. Sáenz (1980):Fruiting bodies are 4.5–6.5 cm long, 2.2–5 cm in diameter, and have four or five thick white chambered arms that are joined at the top, but free at the base. This  Fruiting bodies consist of a long stalk with 3 or 4 short, thick arms. These arms, initially joined together, but usually separate at maturity, are covered with the brownish-olivaceous gleba. Spores are ellipsoidal, with dimensions of 4–5 × 1.5–2 μm.
; '' Mutinus'' (Huds.) Fr. (1849):The mature fruiting body has a spongy, cylindrical hollow stalk which ends in a slender, tapered, sometimes curved head covered with the dark olivaceous, slimy gleba. In older specimens, the gleba may be washed or worn off to show the orange or red color of the head itself. Notable species include the dog stinkhorn ''
Fruiting bodies consist of a long stalk with 3 or 4 short, thick arms. These arms, initially joined together, but usually separate at maturity, are covered with the brownish-olivaceous gleba. Spores are ellipsoidal, with dimensions of 4–5 × 1.5–2 μm.
; '' Mutinus'' (Huds.) Fr. (1849):The mature fruiting body has a spongy, cylindrical hollow stalk which ends in a slender, tapered, sometimes curved head covered with the dark olivaceous, slimy gleba. In older specimens, the gleba may be washed or worn off to show the orange or red color of the head itself. Notable species include the dog stinkhorn ''
Index Fungorum
* ttp://www.mushroomexpert.com/phallaceae.html Stinkhorns: The Phallaceae and Clathraceae {{Authority control Mushroom types Phallales Basidiomycota families Taxa named by August Carl Joseph Corda Taxa described in 1842
 Phallaceae is a
Phallaceae is a family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
of fungi, commonly known as stinkhorns, within the order Phallales. Stinkhorns have a worldwide distribution, but are especially prevalent in tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
regions. They are known for their foul-smelling, sticky spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual reproduction, sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for biological dispersal, dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores fo ...
masses, or gleba
Gleba (, from Latin ''glaeba, glēba'', "lump") is the fleshy spore-bearing inner mass of certain fungi such as the puffball or stinkhorn.
The gleba is a solid mass of spores, generated within an enclosed area within the sporocarp. The conti ...
, borne on the end of a stalk called the receptaculum. The characteristic fruiting-body structure, a single, unbranched receptaculum with an externally attached gleba on the upper part, distinguishes the Phallaceae from other families in the Phallales. The spore mass typically smells of carrion
Carrion (), also known as a carcass, is the decaying flesh of dead animals.
Overview
Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures ...
or dung, and attracts flies
Flies are insects of the Order (biology), order Diptera, the name being derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwin ...
, beetles
Beetles are insects that form the Taxonomic rank, order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Holometabola. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 40 ...
and other insects to help disperse the spores. Although there is great diversity in body structure shape among the various genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ...
, all species in the Phallaceae begin their development as oval or round structures known as "eggs". The appearance of Phallaceae is often sudden, as gleba can erupt from the underground egg and burst open within an hour. According to a 2008 estimate, the family contains 21 genera and 77 species.
Description
Species of stinkhorns havegasteroid
The gasteroid fungi are a group of fungi in the Basidiomycota. Species were formerly placed in the obsolete class Gasteromycetes Fr. (literally "stomach fungi"), or the equally obsolete order Gasteromycetales Rea, because they produce spores insi ...
, or internally produced, spores. Fruiting bodies originate as a gelatinous, spherical, or egg-shaped structure that may be completely or partially buried underground. The peridium, the outer layer of the egg, is white, or purple/red, with two or three layers. The outer layer is thin, membranous, and elastic, while the inner layer is thicker, gelatinous, and continuous. At maturity, the peridium opens up and remains as a volva at the base of the receptaculum.
This porous mushroom is among the fastest growing in the world, extending by 5 mm per minute, so fast that a crackling sound can be heard. Technically it is not really growing, as it uses a form of cellular origami to increase its size by absorbing water.
The fertile portion of the fruiting body is often borne on the end of a wide, fleshy or spongy stalk (as in the Phallales), which may be cylindrical, star-shaped, or reticulate (forming a network). They may be brightly colored, sometimes with a lattice- or veil-like membrane enclosing and protecting the spores. The spore-containing substance, the gleba
Gleba (, from Latin ''glaeba, glēba'', "lump") is the fleshy spore-bearing inner mass of certain fungi such as the puffball or stinkhorn.
The gleba is a solid mass of spores, generated within an enclosed area within the sporocarp. The conti ...
, is typically gelatin
Gelatin or gelatine () is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from collagen taken from animal body parts. It is brittle when dry and rubbery when moist. It may also be referred to as hydrolyzed collagen, coll ...
ous, often foul-smelling, and deliquescent (becoming liquid from the absorption of water). The gleba is formed on the exterior face of the cap or the upper part of the receptacle.
The basidia
A basidium (: basidia) is a microscopic spore-producing structure found on the hymenophore of reproductive bodies of basidiomycete fungi. The presence of basidia is one of the main characteristic features of the group. These bodies are also ...
are small and narrowly club-shaped or fusiform
Fusiform (from Latin ''fusus'' ‘spindle’) means having a spindle (textiles), spindle-like shape that is wide in the middle and tapers at both ends. It is similar to the lemon (geometry), lemon-shape, but often implies a focal broadening of a ...
, short-lived (evanescent), with four to eight sterigmata
In biology, a sterigma (: sterigmata) is a small supporting structure.
It commonly refers to an extension of the basidium (the spore-bearing cells) consisting of a basal filamentous part and a slender projection which carries a spore at the tip ...
. The spores are usually ellipsoid or cylindrical in shape, hyaline
A hyaline substance is one with a glassy appearance. The word is derived from , and .
Histopathology
Hyaline cartilage is named after its glassy appearance on fresh gross pathology. On light microscopy of H&E stained slides, the extracellula ...
or pale brown, smooth, more or less smooth-walled, and truncated at the base.
 The gelatinous layer of the stinkhorn ''(
The gelatinous layer of the stinkhorn ''(Clathrus ruber
''Clathrus ruber'' is a species of fungus in the family Phallaceae, and the type species of the genus ''Clathrus''. It is commonly known as the latticed stinkhorn, the basket stinkhorn, or the red cage, alluding to the striking Sporocarp (fungus), ...
)'' contains high concentrations of potassium, calcium, manganese, and iron. A moderate amount of calcium is found in the receptacle and gleba
Gleba (, from Latin ''glaeba, glēba'', "lump") is the fleshy spore-bearing inner mass of certain fungi such as the puffball or stinkhorn.
The gleba is a solid mass of spores, generated within an enclosed area within the sporocarp. The conti ...
as well as a high amount of manganese is also found in the gleba. Retaining a high potassium concentration is important for the growth of the stem of the fruiting body called the carpophore, where potassium plays a key component in regulating osmotic pressure. This osmotic pressure helps maintain the shape of the carpophore. The calcium found in the gelatinous layer contributes to the slimy characteristics of the gel and protects the carpophore during growth. The strong adhesive gelatinous layer consists of polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long-chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wat ...
s that are formed by the sequestration of calcium ions. The high manganese and iron concentrations in the gelatinous layer and gleba are theorized to produce enzymes that produce sugars and odorous compounds that play a role in attracting insects.
Stinkhorns are edible, but only at the egg stage when the smell is less strong. The inner layer can be cut out with a knife and eaten raw – it is crisp and crunchy with a radish-like taste.
The mushrooms also contain several pharmaceutical compounds with potential for cancer treatment.
Genera
; '' Anthurus'' Kalchbr. & MacOwan (1880):Fruiting bodies have a short stalk from which arises a spore-bearing structure (the receptaculum) of 5–8 arched arms. These arms, initially joined at the top, disconnect and curve irregularly to expose the inner surface of each arm, which is covered with green spore-containing gleba. Spores are 3–4 × 1–1.5 μm.Ellis and Ellis, p. 219. ; '' Aporophallus'' Möller (1895) ; '' Aseroë'' Labill. (1800): Mature fruiting bodies contain a roughly cylindrical white or pinkish stalk approximately 6 × 2 cm, with a volva at the base. At the top is a bright red disc with a variable number of arms, typically 3–7 cm long. The gleba found on the disc and inner side of the arms is slimy, foetid, and green colored. Spores are
Mature fruiting bodies contain a roughly cylindrical white or pinkish stalk approximately 6 × 2 cm, with a volva at the base. At the top is a bright red disc with a variable number of arms, typically 3–7 cm long. The gleba found on the disc and inner side of the arms is slimy, foetid, and green colored. Spores are hyaline
A hyaline substance is one with a glassy appearance. The word is derived from , and .
Histopathology
Hyaline cartilage is named after its glassy appearance on fresh gross pathology. On light microscopy of H&E stained slides, the extracellula ...
, with dimensions of 4–6 1.5–2 μm. '' Aseroë rubra'', an Australian and Pacific species which has spread to Europe and North America.
;'' Blumenavia'' Möller (1895)
; '' Clathrus'' P. Micheli ex L. (1753): Fruiting bodies are latticed (clathrate), and made of hollow tubular arms that originate from the basal tissue within the volva. Spores are elliptical, smooth, hyaline, with dimensions of 4–6 ×1.5–2.5 μm.Miller and Miller, p. 80. Examples include ''
Fruiting bodies are latticed (clathrate), and made of hollow tubular arms that originate from the basal tissue within the volva. Spores are elliptical, smooth, hyaline, with dimensions of 4–6 ×1.5–2.5 μm.Miller and Miller, p. 80. Examples include ''Clathrus ruber
''Clathrus ruber'' is a species of fungus in the family Phallaceae, and the type species of the genus ''Clathrus''. It is commonly known as the latticed stinkhorn, the basket stinkhorn, or the red cage, alluding to the striking Sporocarp (fungus), ...
'', the lattice stinkhorn, '' Clathrus archeri'', the octopus stinkhorn, and '' Clathrus columnatus'', the columned stinkhorn.
;'' Colus'' Cavalier & Séchier (1835) : A genus of four species with fruit bodies that are a short stalk from which six columns arise, joining at the top to form a red, arching, clathrate receptaculum. The gleba is smeared on the inside surface of the receptaculum.Miller and Miller, p. 91.
; '' Echinophallus'' Henn. (1898)
; '' Endophallus'' Zang & Petersen (1989): Contains a single species, ''E. yunnanensis'' found in China, that resembles ''Phallus'' except for a peridium that is separated from the base of the stem and which does not persist as a volva.
; ''Ileodictyon
''Ileodictyon'' is a genus of fungi in the family (biology), family Phallaceae. Basidiocarps (fruit bodies) are clathroid (resembling those in the genus ''Clathrus''), emerging from egg-like peridium, peridia and forming spongy "arms" which conne ...
'' Tul. ex M. Raoul (1844):Fruiting bodies are latticed (clathrate), and have gelatinous arms that lie sessile within the volva. Spores are elliptical, and have dimensions of 4–6 1.5–2.5 μm. The New Zealand native, ''Ileodictyon cibarium
''Ileodictyon cibarium'' is a saprotrophic species of fungus in the family (biology), family Phallaceae. It is native to Australia and New Zealand, where it is commonly known as the basket fungus or the white basket fungus, alluding to its basid ...
'', known as the basket fungus, has a fruiting body shaped somewhat like a round or oval ball with interlaced or latticed branches.
; '' Itajahya'' Möller (1895):Characters in this genus include a white calyptra (tissue which covers the top of the fruiting body to which the gleba is attached), lamellate plates covered with gleba. The gleba has a white mottled surface, and the pileus appears wig-like when removed of the gleba. The thick, stout stalk has many chambered walls.
; '' Kobayasia'' (Kobayasi) S. Imai & A. Kawam. (1958): This genus circumscribes the single species ''Kobayasia nipponica'', found in Japan in 1958.
; ''Laternea
''Laternea'' is a genus of fungus in the family Phallaceae. The genus was first described by French Botany, botanist Pierre Jean François Turpin in 1822. It contains two species found in tropical regions of the Americas.
Species
Source:
Ref ...
'' Turpin (1822): ; '' Ligiella'' J.A. Sáenz (1980):Fruiting bodies are 4.5–6.5 cm long, 2.2–5 cm in diameter, and have four or five thick white chambered arms that are joined at the top, but free at the base. This
; '' Ligiella'' J.A. Sáenz (1980):Fruiting bodies are 4.5–6.5 cm long, 2.2–5 cm in diameter, and have four or five thick white chambered arms that are joined at the top, but free at the base. This monotypic
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unisp ...
genus, containing the single species ''L. rodrigueziana'', is known only from Costa Rica
Costa Rica, officially the Republic of Costa Rica, is a country in Central America. It borders Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, as well as Maritime bo ...
.
; '' Lysurus'' Fr. (1823): Fruiting bodies consist of a long stalk with 3 or 4 short, thick arms. These arms, initially joined together, but usually separate at maturity, are covered with the brownish-olivaceous gleba. Spores are ellipsoidal, with dimensions of 4–5 × 1.5–2 μm.
; '' Mutinus'' (Huds.) Fr. (1849):The mature fruiting body has a spongy, cylindrical hollow stalk which ends in a slender, tapered, sometimes curved head covered with the dark olivaceous, slimy gleba. In older specimens, the gleba may be washed or worn off to show the orange or red color of the head itself. Notable species include the dog stinkhorn ''
Fruiting bodies consist of a long stalk with 3 or 4 short, thick arms. These arms, initially joined together, but usually separate at maturity, are covered with the brownish-olivaceous gleba. Spores are ellipsoidal, with dimensions of 4–5 × 1.5–2 μm.
; '' Mutinus'' (Huds.) Fr. (1849):The mature fruiting body has a spongy, cylindrical hollow stalk which ends in a slender, tapered, sometimes curved head covered with the dark olivaceous, slimy gleba. In older specimens, the gleba may be washed or worn off to show the orange or red color of the head itself. Notable species include the dog stinkhorn ''Mutinus caninus
''Mutinus caninus'', commonly known as the dog stinkhorn, is a small thin, phallus-shaped woodland fungus, with a dark tip. It is often found growing in small groups on wood debris, or in leaf litter, during summer and autumn in Europe, Asia, ...
''.
; '' Neolysurus'' O.K. Mill., Ovrebo & Burk (1991): This genus contains the single species ''Neolysurus arcipulvinus'', described from Costa Rica
Costa Rica, officially the Republic of Costa Rica, is a country in Central America. It borders Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, as well as Maritime bo ...
. The stipe and arms have a tubular construction, similar to species from ''Lysurus''. ''Neolysurus'' is unique in having a long stipe, ending in arms or columns that branch and interconnect to support a cushion-shaped, olive green gleba. The glebal cushion is divided into polygonal compartments by a fine pinkish white, solid mesh. The hymenium
The hymenium is the tissue layer on the hymenophore of a fungal fruiting body where the cells develop into basidia or asci, which produce spores. In some species all of the cells of the hymenium develop into basidia or asci, while in oth ...
is continuous between the mesh.
; ''Phallus
A phallus (: phalli or phalluses) is a penis (especially when erect), an object that resembles a penis, or a mimetic image of an erect penis. In art history, a figure with an erect penis is described as ''ithyphallic''.
Any object that symbo ...
'' Junius ex L. (1753):In species of ''Phallus'', the receptaculum is a tall unbranched stalk that ends in a cap
A cap is a flat headgear, usually with a visor. Caps have crowns that fit very close to the head. They made their first appearance as early as 3200 BC. The origin of the word "cap" comes from the Old French word "chapeau" which means "head co ...
-like structure that bears the gleba. Notable species include ''Phallus impudicus
''Phallus impudicus'', known colloquially as the common stinkhorn, is a widespread fungus in the Phallaceae (stinkhorn) family. It is recognizable for its foul odor and its phallic shape when mature, the latter feature giving rise to several ...
'', the common stinkhorn, '' Phallus hadriani'', '' Phallus ravenelii'', and '' Phallus indusiatus'' (syn. ''Dictyophora indusiata''), the Chinese "bamboo fungus", eaten as a food in southwestern China after the foul smelling cap is removed.
; '' Protubera'' Möller (1895):Fruiting bodies are egg-shaped, 2.2–3.5 cm in diameter by 3–4 cm high, with a dull white, soft exoperidium (roughly 1 mm thick) and a grayish exoperidium (3–4 mm thick). The gleba is contained within internal chambers that are separated by whitish, gelatinous tissue that originates from a columella-like, gelatinous central core. Spores are elliptical, smooth, nearly hyaline, and 3.5–4.5 1.5–2 μm.Miller and Miller, p. 83.
; '' Protuberella'' (S. Imai) S. Imai & Kawam. (1958):This genus resembles the ''Protubera'', except that the tissue is "gelatinous fleshy in the peridium and not so distinctly gelatinous as in ''Protubera maracuja'', they are less gelatinous in the nature of the sterile strands than those of ''P. maracuja''". Spores are clylindric, thin-walled, and 3.7–5 2–2.5 μm. This monotypic genus contains the single species ''Protuberella borealis'', known only from Asia.
;'' Pseudoclathrus'' B. Liu & Y.S. Bau (1980)
; '' Pseudocolus'' Lloyd (1907)
; '' Staheliomyces'' E. Fisch. (1921)
Volatile compounds
The number and type of volatile compounds produced by stinkhorn mushrooms changes throughout its life course. When the stinkhorn is still in its egg stage, the total amount of volatile substances is relatively low. The sulfuric odorous compounds (that attract insects) is absent. During this stage the mushroom’s veil covers up the slime covered cap that contains the spores. When the stinkhorn grows into a more mature-fruit body, there are over twenty-two volatile compounds found in the mature-fruit bodies including dimethyl oligosulfides, aroma-activephenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituent, substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of ...
s and various terpenoid
The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic compound, organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeabl ...
s that act as insect attractants. In an over-ripe stinkhorn, forty-one volatile components are present, many of which also act as insect attractants. Dimethyl oligosulfides are not as commonly found in over-ripe fruit as they were in the mature fruit bodies since many of the insects already carried the smelly slime away.
The stinkhorn contains compounds of carrion
Carrion (), also known as a carcass, is the decaying flesh of dead animals.
Overview
Carrion is an important food source for large carnivores and omnivores in most ecosystems. Examples of carrion-eaters (or scavengers) include crows, vultures ...
, such as oligosulfides, and of feces, such as phenol
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire.
The molecule consists of a phenyl group () ...
, indole
Indole is an organic compound with the formula . Indole is classified as an aromatic heterocycle. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole ring. Indoles are derivatives of indole ...
and p-cresol
''para''-Cresol, also 4-methylphenol, is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4(OH). It is a colourless solid that is widely used intermediate in the production of other chemicals. It is a derivative of phenol and is an isomer of ''o''- ...
. This provides evidence for mimicry of carrion and feces and convergence in the putrid scents of fungus. The stinkhorn’s scent is similar to that of rotten meat and dog feces. This scent profile supports the assumption that the stinkhorn mimics fly brood sites and food sources. The flies are being lured in by the exploitation of their innate attraction to smell of the decaying animal matter that the stinkhorn gives off.
References
Books cited
* *External links
* *Index Fungorum
* ttp://www.mushroomexpert.com/phallaceae.html Stinkhorns: The Phallaceae and Clathraceae {{Authority control Mushroom types Phallales Basidiomycota families Taxa named by August Carl Joseph Corda Taxa described in 1842