Stingray Nebula on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Stingray Nebula (Hen 3-1357) is the youngest-known
 In 1995 the central planetary nebula nucleus was observed as a DA
In 1995 the central planetary nebula nucleus was observed as a DA 
The Scale of the Universe
(
Stingray Nebula at Constellation Guide
{{DEFAULTSORT:Stingray Nebula Planetary nebulae Ara (constellation) ? ? Arae, V839
planetary nebula
A planetary nebula is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.
The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelated to planets. The ...
, having appeared in the 1980s. The nebula is located in the direction of the southern constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
Ara
Ara may refer to:
Biology
* ''Ara'' (bird), a genus of parrots
* Ara (fish) (''Niphon spinosus''), a species of fish
* L-arabinose operon, also known as ara
Places
* Ara (mountain), a mountain in Armenia
* Ara, Armenia, a village in Armenia
...
(the Altar), and is located away. Although it is some 130 times the size of the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
, the Stingray Nebula is only about one tenth the size of most other known planetary nebulae. The central star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
of the nebula is the fast-evolving star SAO 244567. Until the early 1970s, it was observed on Earth as a preplanetary nebula in which the gas had not yet become hot and ionized.
The image of the nebula shows how the older outer shells of gas are acting as a collimator
A collimator is a device which narrows a beam of particles or waves. To narrow can mean either to cause the directions of motion to become more aligned in a specific direction (i.e., make collimated light or parallel rays), or to cause the spat ...
for the more recent gas outflow from the central star—an important observation, as this process has not been well understood.
History
Prior to the discovery of the nebula, its central star was known as He 3-1357, whichKarl Gordon Henize
Karl Gordon Henize (;JPL-80 "NASA Creates Portrait of Life and ...
classified as an A- or B-type Hα emission-line
A spectral line is a weaker or stronger region in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum. It may result from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to ...
star in 1976. It was observed in 1971 to be post-asymptotic giant branch B1 or B2 supergiant
Supergiants are among the most massive and most luminous stars. Supergiant stars occupy the top region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram, with absolute visual magnitudes between about −3 and −8. The temperatures of supergiant stars range ...
. Planetary nebula emission lines were identified in this star in 1989 by the International Ultraviolet Explorer
International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE or Explorer 57, formerly SAS-D) was the first Space telescope, space observatory primarily designed to take ultraviolet (UV) electromagnetic spectrum. The satellite was a collaborative project between NA ...
. As the nebula would be newly formed and very small, ground-based observations were not able to resolve it; so Bobrowsky observed it with the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most ...
, discovering the nebula, which he named the "Stingray Nebula".
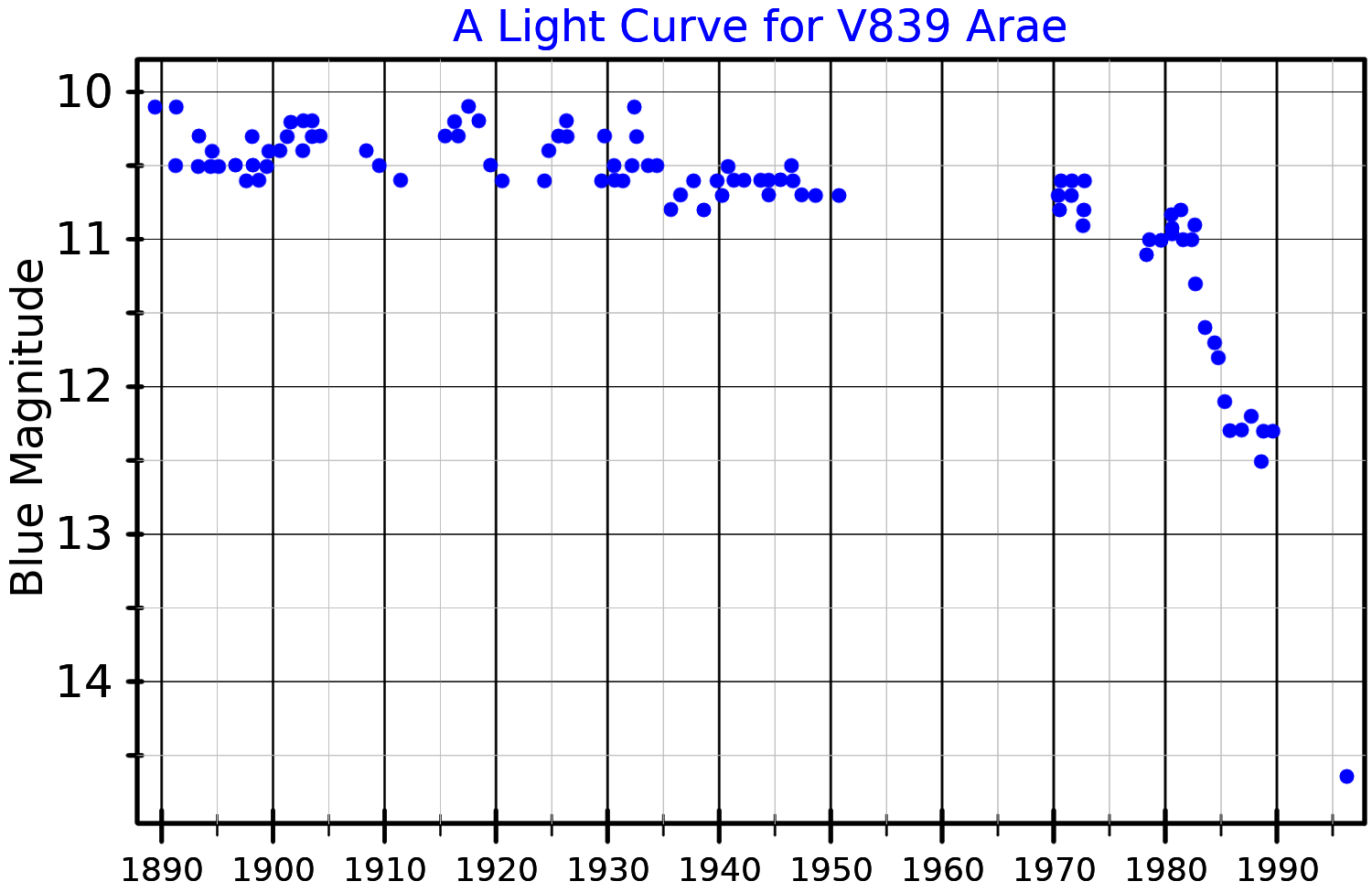
In 1993, M. Parthasarathy ''et al.'' looked at the history of measurements of the brightness of the central star, and concluded that it was fading in the optical region of the spectrum. It was given its variable star designation
In astronomy, a variable-star designation is a unique identifier given to variable stars. It extends the Bayer designation format, with an identifying label (as described below) preceding the Latin genitive of the name of the constellation in whic ...
, V839 Arae, in 1997.
 In 1995 the central planetary nebula nucleus was observed as a DA
In 1995 the central planetary nebula nucleus was observed as a DA white dwarf
A white dwarf is a Compact star, stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very density, dense: in an Earth sized volume, it packs a mass that is comparable to the Sun. No nuclear fusion takes place i ...
, having seemingly faded by a factor of three between 1987 and 1995. The white dwarf has an estimated mass of and luminosity of and has an observed companion star separated by 0.3 arcsecond
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a degree. Since one degree is of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is of a tu ...
. The mass of the nebula is estimated as .
In 1998 Bobrowsky et al. described how the Hubble Space Telescope observations revealed a 17th-magnitude companion to the Stingray's 15th-magnitude central star.
The central star is unusual in that it has brightened and faded over a period of 20 years. Its temperature went up by 40,000 °C. An explanation for this is that it has undergone a helium flash
A helium flash is a very brief thermal runaway nuclear fusion of large quantities of helium into carbon through the triple-alpha process in the core of low-mass stars (between 0.5-0.44 solar masses () and 2.0 ) during their red giant phase. The Su ...
.
In January 2021, NASA discovered that the nebula had been fading since the 1990s, when it reached its peak brightness. Previously photoionized, the positive ions of the nebula have been recombining with the electrons. In a NASA statement a team member, Martín A. Guerrero of the Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía
The Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (, IAA-CSIC) is a research institute funded by the High Council of Scientific Research of the Spanish government Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC), and is located in Granada, And ...
in Granada, Spain, said: "This is very, very dramatic, and very weird. What we're witnessing is a nebula's evolution in real time. In a span of years, we see variations in the nebula. We have not seen that before with the clarity we get with this view."

References
External links
*The Scale of the Universe
(
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include ...
2012 March 12)Stingray Nebula at Constellation Guide
{{DEFAULTSORT:Stingray Nebula Planetary nebulae Ara (constellation) ? ? Arae, V839