receptor
Receptor may refer to:
* Sensory receptor, in physiology, any neurite structure that, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and respond ...
. Some sensory modalities include: light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
, sound
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the br ...
, temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
, taste
The gustatory system or sense of taste is the sensory system that is partially responsible for the perception of taste. Taste is the perception stimulated when a substance in the mouth biochemistry, reacts chemically with taste receptor cells l ...
, pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
, and smell. The type and location of the sensory receptor
Sensory neurons, also known as afferent neurons, are neurons in the nervous system, that convert a specific type of stimulus, via their receptors, into action potentials or graded receptor potentials. This process is called sensory transduc ...
activated by the stimulus plays the primary role in coding the sensation. All sensory modalities work together to heighten stimuli sensation when necessary.
Multimodal perception
Multimodal perception is the ability of the mammalian nervous system to combine all of the different inputs of thesensory nervous system
The sensory nervous system is a part of the nervous system responsible for processing sense, sensory information. A sensory system consists of sensory neurons (including the sensory receptor cells), neural pathways, and parts of the brain invol ...
to result in an enhanced detection or identification of a particular stimulus. Combinations of all sensory modalities are done in cases where a single sensory modality results in an ambiguous and incomplete result.
 Integration of all sensory modalities occurs when multimodal neurons receive sensory information which overlaps with different modalities. Multimodal neurons are found in the superior colliculus; they respond to the versatility of various sensory inputs. The multimodal neurons lead to change of behavior and assist in analyzing behavior responses to certain stimulus. Information from two or more
Integration of all sensory modalities occurs when multimodal neurons receive sensory information which overlaps with different modalities. Multimodal neurons are found in the superior colliculus; they respond to the versatility of various sensory inputs. The multimodal neurons lead to change of behavior and assist in analyzing behavior responses to certain stimulus. Information from two or more sense
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the surroundings through the detection of Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. Although, in some cultures, five human senses were traditio ...
s is encountered. Multimodal perception is not limited to one area of the brain: many brain regions are activated when sensory information is perceived from the environment. In fact, the hypothesis of having a centralized multisensory region is receiving continually more speculation, as several regions previously uninvestigated are now considered multimodal. The reasons behind this are currently being investigated by several research groups, but it is now understood to approach these issues from a decentralized theoretical perspective. Moreover, several labs using invertebrate model organisms will provide invaluable information to the community as these are more easily studied and are considered to have decentralized nervous systems.
Lip reading
Lip reading is a multimodal process for humans. By watching movements of lips and face, humans get conditioned and practice lip reading. Silent lip reading activates the auditory cortex. When sounds are matched or mismatched with the movements of the lips, temporal sulcus of the left hemisphere becomes more active.Integration effect
Multimodalperception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous syste ...
comes into effect when a unimodal stimulus fails to produce a response. Integration effect is applied when the brain detects weak unimodal signals and combines them to create a multimodal perception for the mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
. Integration effect is plausible when different stimuli are coincidental. This integration is depressed when multisensory information is not coincidentally presented.
Polymodality
''Polymodality'' is the feature of a single receptor of responding to multiple modalities, such as free nerve endings which can respond to temperature, mechanical stimuli (touch, pressure, stretch) or pain (nociception
In physiology, nociception , also nocioception; ) is the Somatosensory system, sensory nervous system's process of encoding Noxious stimulus, noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a pai ...
).
Light modality
Description
The stimulus modality for vision is light; the human eye is able to access only a limited section of theelectromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. From low to high ...
, between 380 and 760 nanometres. Specific inhibitory responses that take place in the visual cortex help create a visual focus on a specific point rather than the entire surrounding.
Perception
To perceive a light stimulus, the eye must first refract the light so that it directly hits theretina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
. Refraction in the eye is completed through the combined efforts of the cornea
The cornea is the transparency (optics), transparent front part of the eyeball which covers the Iris (anatomy), iris, pupil, and Anterior chamber of eyeball, anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and Lens (anatomy), lens, the cornea ...
, lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements'') ...
and iris. The transduction of light into neural activity occurs via the photoreceptor cell
A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuroepithelial cell found in the retina that is capable of visual phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (visible electromagnetic radiation ...
s in the retina. When there is no light, Vitamin A
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that is an essential nutrient. The term "vitamin A" encompasses a group of chemically related organic compounds that includes retinol, retinyl esters, and several provitamin (precursor) carotenoids, most not ...
in the body attaches itself to another molecule and becomes a protein. The entire structure consisting of the two molecules becomes a photopigment
Photopigments are unstable pigments that undergo a chemical change when they absorb light. The term is generally applied to the non-protein chromophore Moiety (chemistry), moiety of photosensitive chromoproteins, such as the pigments involved in ph ...
. When a particle of light hits the photoreceptors of the eye, the two molecules come apart from each other and a chain of chemical reactions occurs. The chemical reaction begins with the photoreceptor sending a message to a neuron called the bipolar cell through the use of an action potential
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly ri ...
, or nerve impulse. Finally, a message is sent to the ganglion cell and then finally the brain.
Adaptation
The eye is able to detect a visual stimulus when the photons (light packets) cause a photopigment molecule, primarilyrhodopsin
Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is a protein encoded by the ''RHO'' gene and a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is a light-sensitive receptor protein that triggers visual phototransduction in rod cells. Rhodopsin mediates dim ...
, to come apart. Rhodopsin, which is usually pink, becomes bleached in the process. At high levels of light, photopigments are broken apart faster than can be regenerated. Because a low number of photopigments have been regenerated, the eyes are not sensitive to light. When entering a dark room after being in a well lit area, the eyes require time for a good quantity of rhodopsin to regenerate. As more time passes, there is a higher chance that the photons will split an unbleached photopigment because the rate of regeneration will have surpassed the rate of bleaching. This is called adaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the p ...
.
Colour stimuli
Humans are able to see an array of colours because light in the visible spectrum is made up of different wavelengths (from 380 to 760 nm). Our ability to see in colour is due to three different cone cells in the retina, containing three different photopigments. The three cones are each specialized to best pick up a certain wavelength (420, 530 and 560 nm or roughly the colours blue, green and red). The brain is able to distinguish the wavelength and colour in the field of vision by figuring out which cone has been stimulated. The physical dimensions of colour includewavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
, intensity and purity while the related perceptual dimensions include hue, brightness and saturation.
Primates are the only mammals with colour vision.
The Trichromatic theory was proposed in 1802 by Thomas Young. According to Young, the human visual system is able to create any colour through the collection of information from the three cones. The system will put together the information and systematize a new colour based on the amount of each hue that has been detected.
Subliminal visual stimuli
Some studies show that subliminal stimuli can affect attitude. In a 1992 study Krosnick, Betz, Jussim and Lynn conducted a study where participants were shown a series of slides in which different people were going through normal every day activities (i.e. going to the car, sitting in a restaurant). These slides were preceded by slides that caused either positive emotional arousal (i.e. bridal couple, a child with a Mickey Mouse doll) or negative emotional arousal (i.e. a bucket of snakes, a face on fire) for a period 13 milliseconds that participants consciously perceived as a sudden flash of light. None of the individuals were told of the subliminal images. The experiment found that during the questionnaire round, participants were more likely to assign positive personality traits to those in the pictures that were preceded by the positive subliminal images and negative personality traits to those in the pictures that were preceded by the negative subliminal images.Tests
Some common tests that measure visual health includevisual acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of visual perception, vision, but technically rates an animal's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity depends on optical and neural factors. Optical factors of the eye ...
tests, refraction tests, visual field tests and colour vision tests. Visual acuity tests are the most common tests and they measure the ability to bring details into focus at different distances. Usually this test is conducted by having participants read a map of letters or symbols while one eye is covered. Refraction tests measure the eye's need for glasses or corrective lenses. This test is able to detect whether a person may be nearsighted or farsighted. These conditions occur when the light rays entering the eye are unable to converge on a single spot on the retina
The retina (; or retinas) is the innermost, photosensitivity, light-sensitive layer of tissue (biology), tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some Mollusca, molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focus (optics), focused two-dimensional ...
. Both refractive errors require corrective lenses in order to cure blurriness of vision. Visual field tests detect any gaps in peripheral vision. In healthy normal vision, an individual should be able to partially perceive objects to the left or right of their field of view using both eyes at one time. The center field of vision is seen in most detail. Colour vision tests are used to measure one's ability to distinguish colours. It is used to diagnose colour blindness. This test is also used as an important step in some job screening processes as the ability to see colour in such jobs may be crucial. Examples include military work or law enforcement.
Sound modality
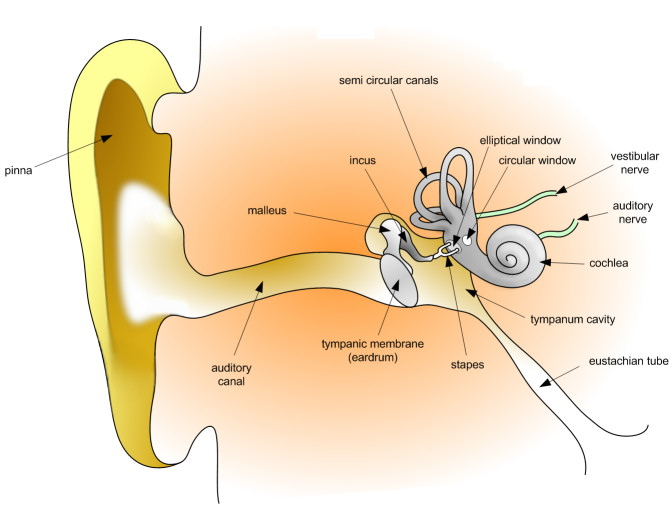
Description
The stimulus modality for hearing is sound. Sound is created through changes in the pressure of the air. As an object vibrates, it compresses the surrounding molecules of air as it moves towards a given point and expands the molecules as it moves away from the point. Periodicity in sound waves is measured inhertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or Cycle per second, cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in ter ...
. Humans, on average, are able to detect sounds as pitched when they contain periodic or quasi-periodic variations that fall between the range of 30 to 20000 hertz.
Perception
When there are vibrations in the air, theeardrum
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Its function is to transmit changes in pres ...
is stimulated. The eardrum collects these vibrations and sends them to receptor cells. The ossicles
The ossicles (also called auditory ossicles) are three irregular bones in the middle ear of humans and other mammals, and are among the smallest bones in the human body. Although the term "ossicle" literally means "tiny bone" (from Latin ''ossi ...
which are connected to the eardrum pass the vibrations to the fluid-filled cochlea
The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus (cochlea), modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the organ of Cort ...
. Once the vibrations reach the cochlea, the stirrup (part of the ossicles) puts pressure on the oval window. This opening allows the vibrations to move through the liquid in the cochlea where the receptive organ is able to sense it.
Pitch, loudness and timbre
There are many different qualities in sound stimuli including loudness, pitch andtimbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instrument ...
.
The human ear is able to detect differences in pitch through the movement of auditory hair cells found on the basilar membrane. High frequency sounds will stimulate the auditory hair cells at the base of the basilar membrane while medium frequency sounds cause vibrations of auditory hair cells located at the middle of the basilar membrane. For frequencies that are lower than 200 Hz, the tip of the basilar membrane vibrates in sync with the sound waves. In turn, neurons are fired at the same rate as the vibrations. The brain is able to measure the vibrations and is then aware of any low frequency pitches.
When a louder sound is heard, more hair cells are stimulated and the intensity of firing of axons
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis) or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences) is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action pot ...
in the cochlear nerve is increased. However, because the rate of firing also defines low pitch the brain has an alternate way of encoding for loudness of low frequency sounds. The number of hair cells that are stimulated is thought to communicate loudness in low pitch frequencies.
Aside from pitch and loudness, another quality that distinguishes sound stimuli is timbre. Timbre allows us to hear the difference between two instruments that are playing at the same frequency and loudness, for example. When two simple tones are put together they create a complex tone. The simple tones of an instrument are called harmonics or overtones. Timbre is created by putting the harmonics together with the fundamental frequency
The fundamental frequency, often referred to simply as the ''fundamental'' (abbreviated as 0 or 1 ), is defined as the lowest frequency of a Periodic signal, periodic waveform. In music, the fundamental is the musical pitch (music), pitch of a n ...
(a sound's basic pitch). When a complex sound is heard, it causes different parts in the basilar membrane to become simultaneously stimulated and flex. In this way, different timbres can be distinguished.
Sound stimuli and human fetuses
A number of studies have shown that a human fetus will respond to sound stimuli coming from the outside world. In a series of 214 tests conducted on 7 pregnant women, a reliable increase in fetal movement was detected in the minute directly following the application of a sound stimulus to the abdomen of the mother with a frequency of 120 per second.Tests
Hearing tests are administered to ensure optimal function of the ear and to observe whether or not sound stimuli is entering the ear drum and reaching the brain as should be. The most common hearing tests require the spoken response to words or tones. Some hearing tests include the whispered speech test, pure tone audiometry, the tuning fork test, speech reception and word recognition tests, otoacoustic emissions (OAE) test and auditory brainstem response (ABR) test. During a whispered speech test, the participant is asked to cover the opening of one ear with a finger. The tester will then step back 1 to 2 feet behind the participant and say a series of words in a soft whisper. The participant is then asked to repeat what is heard. If the participant is unable to distinguish the word, the tester will speak progressively louder until the participant is able to understand what is being said. The other ear is then tested. In pure tone audiometry, an audiometer is used to play a series of tones using headphones. The participants listen to the tones which will vary in pitch and loudness. The test will play with the volume controls and the participant is asked to signal when he or she can no longer hear the tone being played. The testing is completed after listening to a range of pitches. Each ear is tested individually. During the tuning fork test, the tester will have the tuning fork vibrate so that it makes a sound. The tuning fork is placed in a specific place around the participant and hearing is observed. In some instances, individuals will show trouble hearing in places such as behind the ear. Speech recognition and word recognition tests measure how well an individual can hear normal day-to-day conversation. The participant is told to repeat conversation being spoken at different volumes. The spondee threshold test is a related test that detects the loudness at which the participant is able to repeat half of a list of two syllable words or spondees. Otoacoustic emissions test (OAE) and auditory brainstem response (ABR) testing measures the brain's response to sounds. The OAE measures hearing of newborns by placing an emitting sound into the baby's ear through a probe. A microphone placed in the baby'sear canal
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the auricle to the eardrum and is about in length and in diameter.
S ...
will pick up the inner ear's response to sound stimulation and allows for observation. The ABR, also known as the brainstem auditory evoked response (BAER) test or auditory brainstem evoked potential (ABEP) test measure the brain's response to clicking sounds sent through headphones. Electrodes on the scalp and earlobes record a graph of the response.
Taste modality
Description
Taste modality in mammals
In mammals, taste stimuli are encountered by axonless receptor cells located intaste bud
Taste buds are clusters of taste receptor cells, which are also known as gustatory cells. The taste receptors are located around the small structures known as papillae found on the upper surface of the tongue, soft palate, upper esophagus, ...
s on the tongue and
pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates ...
. Receptor cells disseminate onto different neuron
A neuron (American English), neurone (British English), or nerve cell, is an membrane potential#Cell excitability, excitable cell (biology), cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network (biology), neural net ...
s and convey the message of a particular taste in a single medullar nucleus. This pheromone
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavio ...
detection system deals with taste stimuli. The pheromone detection system is distinct from the normal taste system, and is designed like the olfactory system
The olfactory system, is the sensory nervous system, sensory system used for the sense of smell (olfaction). Olfaction is one of the special senses directly associated with specific organs. Most mammals and reptiles have a main olfactory system ...
.
Taste modality in flies and mammals
In insect and mammalian taste, receptor cells changes into attractive or aversive stimulus. The number of taste receptors in a mammaliantongue
The tongue is a Muscle, muscular organ (anatomy), organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for chewing and swallowing as part of the digestive system, digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper s ...
and on the tongue of the fly ( labellum) is same in amount. Most of the receptors are dedicated to detect repulsive ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's el ...
.
Perception
Perceptions of taste is generated by the following sensory afferents: gustatory, olfactory, and somatosensory fibers. Taste perception is created by combining multiple sensory inputs. Different modalities help determine perception of taste especially when attention is drawn to particular sensory characteristics which is different from taste.Integration of taste and smell modality
Impression of both taste and smell occurs in heteromodal regions of the limbic and paralimbic brain. Taste–odor integration occurs at earlier stages of processing. By life experience, factors such as the physiological significance of a given stimulus is perceived. Learning and affective processing are the primary functions of limbic and paralimbic brain. Taste perception is a combination of oral somatosensation and retronasal olfaction.Pleasure of food
The sensation of taste come from oral somatosensory stimulation and with retronasal olfaction. The perceived pleasure encountered when eating and drinking is influenced by: # sensory features, such as taste quality # experience, such as prior exposure to taste-odor mixtures # internal state # cognitive context, such as information about brandTemperature modality
Description
Temperature modality excites or elicits a symptom through cold or hot temperature. Different mammalian species have different temperature modality.Perception
The cutaneous somatosensory system detects changes in temperature. The perception begins when thermal stimuli from a homeostatic set-point excite temperature specific sensory nerves in the skin. Then with the help of sensing range, specific thermosensory fibers respond to warmth and to cold. Then specific cutaneous cold and warm receptors conduct units that exhibit a discharge at constant skin temperature.Nerve fibers for temperature
Warm and cold sensitive nerve fibers differ in structure and function. The cold-sensitive and warm-sensitive nerve fibers are underneath the skin surface. Terminals of each temperature-sensitive fiber do not branch away to different organs in the body. They form a small sensitive point which are unique from neighboring fibers. Skin used by the single receptor ending of a temperature-sensitive nerve fiber is small. There are 20 cold points per square centimeter in the lips, 4 in the finger, and less than 1 cold point per square centimeter in trunk areas. There are 5 times as many cold sensitive points as warm sensitive points.Pressure modality
Description
The sense of touch, or tactile perception, is what allows organisms to feel the world around them. The environment acts as an external stimulus, and tactile perception is the act of passively exploring the world to simply sense it. To make sense of the stimuli, an organism will undergo active exploration, orhaptic perception
Haptic perception ( "palpable", ''haptikόs'' "suitable for touch") means literally the ability "to grasp something", and is also known as stereognosis. Perception in this case is achieved through the active exploration of surfaces and objects by a ...
, by moving their hands or other areas with environment-skin contact. This will give a sense of what is being perceived, and give information about size, shape, weight, temperature, and material. Tactile stimulation can be direct in the form of bodily contact, or indirect through the use of a tool or probe. Direct and indirect send different types messages to the brain, but both provide information regarding roughness, hardness, stickiness, and warmth. The use of a probe elicits a response based on the vibrations in the instrument rather than direct environmental information. Tactual perception gives information regarding cutaneous stimuli (pressure, vibration, and temperature), kinaesthetic stimuli (limb movement), and proprioceptive stimuli (position of the body). There are varying degrees of tactual sensitivity and thresholds, both between individuals and between different time periods in an individual's life. It has been observed that individuals have differing levels of tactile sensitivity between each hand. This may be due to callouses forming on the skin of the most used hand, creating a buffer between the stimulus and the receptor. Alternately, the difference in sensitivity may be due to a difference in the cerebral functions or ability of the left and right hemisphere. Tests have also shown that deaf children have a greater degree of tactile sensitivity than that of children with normal hearing ability, and that girls generally have a greater degree of sensitivity than that of boys.
Tactile information is often used as additional stimuli to resolve a sensory ambiguity. For example, a surface can be seen as rough, but this inference can only be proven through touching the material. When sensory information from each modality involved corresponds, the ambiguity is resolved.
Somatosensory information
Touch messages, in comparison to other sensory stimuli, have a large distance to travel to get to the brain. Tactile perception is achieved through the response of mechanoreceptors ( cutaneous receptors) in the skin that detect physical stimuli. The response from a mechanoreceptor detecting pressure can be experienced as a touch, discomfort, or pain. Mechanoreceptors are situated in highly vascularized skin, and appear in both glabrous and hairy skin. Each mechanoreceptor is tuned to a different sensitivity, and will fire its action potential only when there is enough energy. The axons of these single tactile receptors will converge into a single nerve trunk, and the signal is then sent to the spinal cord where the message makes its way to thesomatosensory system
The somatosensory system, or somatic sensory system is a subset of the sensory nervous system. The main functions of the somatosensory system are the perception of external stimuli, the perception of internal stimuli, and the regulation of bod ...
in the brain.
Mechanoreceptors
There are four types of mechanoreceptors: Meissner corpuscles and merkel cell neurite complexes, located between the epidermis and dermis, and Pacinian corpuscles and Ruffini endings, located deep within the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. Mechanoreceptors are classified in terms of their adaptation rate and the size of their receptive field. Specific mechanoreceptors and their functions include:Wolfe, J., Kluender, K., & Levi, D. (2009). Sensation and perception. (2 ed.). Sunderland: Sinauer Associates. * Thermoreceptors that detect changes in skin temperature. * Kinesthetic receptors detect movements of the body, and the position of the limbs. * Nociceptors that have bare nerve endings that detect tissue damage and give the sensation of pain.Tests
A common test used to measure the sensitivity of a person to tactile stimuli is measuring their two-point touch threshold. This is the smallest separation of two points at which two distinct points of contact can be sensed rather than one. Different parts of the body have different degrees of tactile acuity, with extremities such as the fingers, face, and toes being the most sensitive. When two distinct points are perceived, it means that your brain receives two different signals. The differences of acuity for different parts of the body are the result of differences in the concentration of receptors.Use in clinical psychology
Tactile stimulation is used in clinical psychology through the method of prompting. Prompting is the use of a set of instructions designed to guide a participant through learning a behavior. A physical prompt involves stimulation in the form of physically guided behavior in the appropriate situation and environment. The physical stimulus perceived through prompting is similar to the physical stimulus that would be experienced in a real-world situation, and is makes the target behavior more likely in a real situation.Smell modality
Sensation
The sense of smell is calledolfaction
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste.
In humans, ...
. All materials constantly shed molecules, which float into the nose or are sucked in through breathing. Inside the nasal chambers is the neuroepithelium, a lining deep within the nostrils that contains the receptors responsible for detecting molecules that are small enough to smell. These receptor neurons then synapse at the olfactory cranial nerve (CN I), which sends the information to the olfactory bulbs in the brain for initial processing. The signal is then sent to the remaining olfactory cortex for more complex processing.
Odors
An olfactory sensation is called anodor
An odor (American English) or odour ( Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is a smell or a scent caused by one or more volatilized chemical compounds generally found in low concentrations that humans and many animals can perceive ...
. For a molecule to trigger olfactory receptor neuron
An olfactory receptor neuron (ORN), also called an olfactory sensory neuron (OSN), is a sensory neuron within the olfactory system.
Structure
Humans have between 10 and 20 million olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs). In vertebrates, ORNs are Bi ...
s, it must have specific properties. The molecule must be:
# volatile (able to float through the air)
# small (less than 5.8 x 10-22 grams)
# hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the chemical property of a molecule (called a hydrophobe) that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water. In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water.
Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thu ...
(repellant to water)
However, humans do not detect or process the smell of various common molecules such as nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
or water vapor
Water vapor, water vapour, or aqueous vapor is the gaseous phase of Properties of water, water. It is one Phase (matter), state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from th ...
.
Olfactory ability can vary due to different conditions. For example, olfactory detection thresholds can change due to molecules with differing lengths of carbon chains. A molecule with a longer carbon chain is easier to detect, and has a lower detection threshold. Additionally, women generally have lower olfactory thresholds than men, and this effect is magnified during a woman's ovulatory period. People can sometimes experience a hallucination of smell, as in the case of phantosmia.
Interaction with other modalities
Olfaction interacts with other sensory modalities in significant ways. The strongest interaction is that of olfaction with taste. Studies have shown that an odor coupled with a taste increases the perceived intensity of the taste, and that an absence of a corresponding smell decreases the perceived intensity of a taste. The olfactory stimulation can occur before or during the episode of taste stimulation. The dual perception of the stimulus produces an interaction that facilitates association of the experience through an additive neural response and memorization of the stimulus. This association can also be made between olfactory and tactile stimuli during the act of swallowing. In each case, temporal synchrony is important.Tests
A common psychophysical test of olfactory ability is the triangle test. In this test, the participant is given three odors to smell. Of these three odors, two are the same and one is different, and the participant must choose which odor is the unique one. To test the sensitivity of olfaction, the staircase method is often used. In this method, the odor's concentration is increased until the participant is able to sense it, and subsequently decreased until the participant reports no sensation.See also
* Autonomous sensory meridian response * Crossmodal Attention *Synesthesia
Synesthesia (American English) or synaesthesia (British English) is a perceptual phenomenon in which stimulation of one sensory or cognitive pathway leads to involuntary experiences in a second sensory or cognitive pathway. People with sy ...
( Ideasthesia)
*Modality (semiotics)
In semiotics, a modality is a particular way in which information is to be encoded for presentation to humans, i.e. to the type of sign and to the status of reality ascribed to or claimed by a sign, text, or genre. It is more closely associated ...
* Pallesthesia
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Stimulus Modality Sensory systems Perception