Standard Widget Toolkit on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Standard Widget Toolkit (SWT) is a graphical
 SWT is a wrapper around native code objects, such as
SWT is a wrapper around native code objects, such as
 SWT widgets have the same ''
SWT widgets have the same ''
 The following is a basic
The following is a basic
import org.eclipse.swt.*;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.*;
public class HelloWorld
Contrary to Swing, a ''Display'' class is necessary to access the underlying
 SWT must be ported to every new GUI library that needs supporting. Unlike Swing and AWT, SWT is not available on every Java-supported platform since SWT is not part of the Java release. There is also some evidence that the performance of SWT on platforms other than Windows is noticeably less efficient. Since SWT uses a different native library for each platform, SWT programs may be exposed to platform-specific bugs.
SWT exposes programs to more low-level details than Swing. This is because SWT is technically just a layer over native library provided GUI functionality, exposing the programmer to native GUI code is part of the design intent of SWT: "Its goal is not to provide a rich user-interface design framework but rather the thinnest possible user-interface API that can be implemented uniformly on the largest possible set of platforms while still providing sufficient functionality to build rich graphical user interface (GUI) applications."
Since the SWT implementation is different for each platform, a platform-specific SWT library (JAR file) must be distributed with each application.
, SWT supports these platforms and/or GUI libraries:
*
SWT must be ported to every new GUI library that needs supporting. Unlike Swing and AWT, SWT is not available on every Java-supported platform since SWT is not part of the Java release. There is also some evidence that the performance of SWT on platforms other than Windows is noticeably less efficient. Since SWT uses a different native library for each platform, SWT programs may be exposed to platform-specific bugs.
SWT exposes programs to more low-level details than Swing. This is because SWT is technically just a layer over native library provided GUI functionality, exposing the programmer to native GUI code is part of the design intent of SWT: "Its goal is not to provide a rich user-interface design framework but rather the thinnest possible user-interface API that can be implemented uniformly on the largest possible set of platforms while still providing sufficient functionality to build rich graphical user interface (GUI) applications."
Since the SWT implementation is different for each platform, a platform-specific SWT library (JAR file) must be distributed with each application.
, SWT supports these platforms and/or GUI libraries:
* 
widget toolkit
A widget toolkit, widget library, GUI toolkit, or UX library is a library (computing), library or a collection of libraries containing a set of graphical control elements (called ''widgets'') used to construct the graphical user interface (GUI) of ...
for use with the Java platform
Java is a set of computer software and specifications that provides a software platform for developing application software and deploying it in a cross-platform computing environment. Java is used in a wide variety of computing platforms fr ...
. It was originally developed by Stephen Northover at IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
and is now maintained by the Eclipse Foundation
The Eclipse Foundation AISBL is an independent, Europe-based not-for-profit organization that acts as a steward of the Eclipse open source software development community, with legal jurisdiction in the European Union. It is an organization supp ...
in tandem with the Eclipse IDE. It is an alternative to the Abstract Window Toolkit (AWT) and Swing Java graphical user interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such ...
(GUI) toolkits provided by Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc., often known as Sun for short, was an American technology company that existed from 1982 to 2010 which developed and sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services. Sun contributed sig ...
as part of the Java Platform, Standard Edition
Java Platform, Standard Edition (Java SE) is a computing platform for development and deployment of porting, portable code for desktop computer, desktop and server (computing), server environments. Java SE was formerly known as Java 2 Platform, S ...
(J2SE).
To display GUI elements, the SWT implementation accesses the native GUI libraries of the operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
using Java Native Interface (JNI) in a manner that is similar to those programs written using operating system-specific application programming interface
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software Interface (computing), interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that des ...
s (APIs). Programs that call SWT are portable, but the implementation of the toolkit, despite part of it being written in Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
, is unique for each platform.
The toolkit is free and open-source software
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is software available under a license that grants users the right to use, modify, and distribute the software modified or not to everyone free of charge. FOSS is an inclusive umbrella term encompassing free ...
distributed under the Eclipse Public License, which is approved by the Open Source Initiative
The Open Source Initiative (OSI) is a California public benefit corporation "actively involved in Open Source community-building, education, and public advocacy to promote awareness and the importance of non-proprietary software".
Governance
The ...
.
History
The first Java GUI toolkit was the Abstract Window Toolkit (AWT), introduced withJava Development Kit
The Java Development Kit (JDK) is a distribution of Java technology by Oracle Corporation. It implements the Java Language Specification (JLS) and the Java Virtual Machine Specification (JVMS) and provides the Standard Edition (SE) of the Java ...
(JDK) 1.0 as one component of Sun Microsystems' Java platform. The original AWT was a simple Java wrapper library around native (operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
-supplied) widgets such as menus, windows, and buttons.
Swing was the next generation GUI toolkit introduced by Sun in Java Platform, Standard Edition
Java Platform, Standard Edition (Java SE) is a computing platform for development and deployment of porting, portable code for desktop computer, desktop and server (computing), server environments. Java SE was formerly known as Java 2 Platform, S ...
(J2SE) 1.2. Swing was developed to provide a richer set of GUI software component
A software component is a modular unit of software that encapsulates specific functionality. The desired characteristics of a component are reusability and maintainability.
Value
Components allow software development to assemble software ...
s than AWT. Swing GUI elements are all-Java with no native code: instead of wrapping native GUI components, Swing draws its own components by using Java 2D to call low-level operating system drawing routines.
The roots of SWT go back to work that Object Technology International (OTI), did in the 1990s when creating multiplatform, portable, native widget interfaces for Smalltalk
Smalltalk is a purely object oriented programming language (OOP) that was originally created in the 1970s for educational use, specifically for constructionist learning, but later found use in business. It was created at Xerox PARC by Learni ...
, originally for OTI Smalltalk, which became IBM Smalltalk in 1993. IBM Smalltalk's Common Widget layer provided fast, native access to multiple platform widget sets while still providing a common API without suffering the ''lowest common denominator'' problem typical of other portable graphical user interface (GUI) toolkits. IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
was developing VisualAge, an integrated development environment
An integrated development environment (IDE) is a Application software, software application that provides comprehensive facilities for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source-code editor, build automation tools, an ...
(IDE) written in Smalltalk. They decided to open-source the project, which led to the development of Eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event which occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three ...
, intended to compete against other IDEs such as Microsoft Visual Studio
Visual Studio is an integrated development environment (IDE) developed by Microsoft. It is used to develop computer programs including websites, web apps, web services and mobile apps. Visual Studio uses Microsoft software development platforms ...
. Eclipse is written in Java, and IBM developers, deciding that they needed a toolkit that had "native look and feel
In software design, the look and feel of a graphical user interface comprises aspects of its design, including elements such as colors, shapes, layout, and typefaces (the "look"), as well as the behavior of dynamic elements such as buttons, boxes ...
" and "native performance
A performance is an act or process of staging or presenting a play, concert, or other form of entertainment. It is also defined as the action or process of carrying out or accomplishing an action, task, or function.
Performance has evolved glo ...
", created SWT as a Swing replacement.
Design
 SWT is a wrapper around native code objects, such as
SWT is a wrapper around native code objects, such as GTK
GTK (formerly GIMP ToolKit and GTK+) is a free software cross-platform widget toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces (GUIs). It is licensed under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License, allowing both Free software, free and ...
objects, Motif objects etc. Because of this, SWT widgets are often referred to as "heavyweight", evoking images of a light Java wrapper around a "heavy" native object. In cases where native platform GUI libraries do not support the functionality required for SWT, SWT implements its own GUI code in Java, similar to Swing. In essence, SWT is a compromise between the low-level performance and look and feel of AWT and the high-level ease of use of Swing.
According to the Eclipse Foundation, "SWT and Swing are different tools that were built with different goals in mind. The purpose of SWT is to provide a common API for accessing native widgets across a spectrum of platforms. The primary design goals are high performance, native look and feel, and deep platform integration. Swing, on the other hand, is designed to allow for a highly customizable look and feel that is common across all platforms."
It has been argued that SWT features a clean design, in part inspired by Erich Gamma of Design Patterns fame.
SWT is a simpler toolkit than Swing, with less (possibly) extraneous functionality for the average developer. This has led some people to argue that SWT lacks functionality when compared to Swing.
James Gosling
James Arthur Gosling (born 19 May 1955) is a Canadian computer scientist, best known as the founder and lead designer behind the Java (programming language), Java programming language.
Gosling was elected a member of the National Academy of E ...
, the creator of the Java language, has argued that SWT is too simple, and is a difficult toolkit to port to new platforms for the same reason that AWT once had porting problems: that it is too simple, too low level, and too tied to the Win32 GUI API, leading to problems adapting the SWT API to other GUI toolkits, such as Motif and OS X Carbon.
Although SWT does not implement the popular model–view–controller
Model–view–controller (MVC) is a software architectural pattern commonly used for developing user interfaces that divides the related program logic into three interconnected elements. These elements are:
* the model, the internal representat ...
(MVC) architecture used in Swing and multiple other high-level GUI toolkits, the JFace library, which is developed as part of the same Eclipse project, does provide a cross-platform
Within computing, cross-platform software (also called multi-platform software, platform-agnostic software, or platform-independent software) is computer software that is designed to work in several Computing platform, computing platforms. Some ...
, higher-level MVC abstraction atop SWT. Developers may choose to use JFace to provide more flexible and abstract data models for complex SWT controls such as trees, tables, and lists, or access those controls directly as needed.
Look and feel
 SWT widgets have the same ''
SWT widgets have the same ''look and feel
In software design, the look and feel of a graphical user interface comprises aspects of its design, including elements such as colors, shapes, layout, and typefaces (the "look"), as well as the behavior of dynamic elements such as buttons, boxes ...
'' as native widgets because they often are the same native widgets. This is in contrast to the Swing toolkit where all widgets are emulations of native widgets. In some cases the difference is distinguishable. For example, the macOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
tree widget features a subtle animation when a tree is expanded and default buttons have an animated pulsing glow to focus the user's attention on them. The default Swing version of these widgets does not animate.
Since SWT is simply a wrapper around native GUI code, it does not require large numbers of updates when that native code is changed, providing that operating system vendors are careful not to break clients of their API when the operating systems are updated. The same cannot be said of Swing, which supports the ability to change the look and feel of the running application with "pluggable looks and feels". These enable emulating the native platform user interface using themes, which must be updated to mirror operating system GUI changes, such as theme or other look and feel updates.
SWT aims for "deep platform integration", the Eclipse reference to SWT's use of native widgets. According to Mauro Marinillia of developer.com, "whenever one needs a tight integration with the native platform, SWT can be a plus". This deep integration can be useful in a number of ways, for example enabling SWT to wrap ActiveX
ActiveX is a deprecated software framework created by Microsoft that adapts its earlier Component Object Model (COM) and Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) technologies for content downloaded from a network, particularly from the World Wide W ...
objects on Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
.
Programming
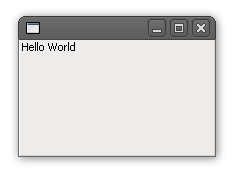
 The following is a basic
The following is a basic "Hello, World!" program
A "Hello, World!" program is usually a simple computer program that emits (or displays) to the screen (often the Console application, console) a message similar to "Hello, World!". A small piece of code in most general-purpose programming languag ...
using SWT. It shows a window (''Shell'') and a label.
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
, and its resources must be explicitly disposed of when they are no longer used.
Platform support
 SWT must be ported to every new GUI library that needs supporting. Unlike Swing and AWT, SWT is not available on every Java-supported platform since SWT is not part of the Java release. There is also some evidence that the performance of SWT on platforms other than Windows is noticeably less efficient. Since SWT uses a different native library for each platform, SWT programs may be exposed to platform-specific bugs.
SWT exposes programs to more low-level details than Swing. This is because SWT is technically just a layer over native library provided GUI functionality, exposing the programmer to native GUI code is part of the design intent of SWT: "Its goal is not to provide a rich user-interface design framework but rather the thinnest possible user-interface API that can be implemented uniformly on the largest possible set of platforms while still providing sufficient functionality to build rich graphical user interface (GUI) applications."
Since the SWT implementation is different for each platform, a platform-specific SWT library (JAR file) must be distributed with each application.
, SWT supports these platforms and/or GUI libraries:
*
SWT must be ported to every new GUI library that needs supporting. Unlike Swing and AWT, SWT is not available on every Java-supported platform since SWT is not part of the Java release. There is also some evidence that the performance of SWT on platforms other than Windows is noticeably less efficient. Since SWT uses a different native library for each platform, SWT programs may be exposed to platform-specific bugs.
SWT exposes programs to more low-level details than Swing. This is because SWT is technically just a layer over native library provided GUI functionality, exposing the programmer to native GUI code is part of the design intent of SWT: "Its goal is not to provide a rich user-interface design framework but rather the thinnest possible user-interface API that can be implemented uniformly on the largest possible set of platforms while still providing sufficient functionality to build rich graphical user interface (GUI) applications."
Since the SWT implementation is different for each platform, a platform-specific SWT library (JAR file) must be distributed with each application.
, SWT supports these platforms and/or GUI libraries:
* Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
:
** Win32
** Windows Presentation Foundation
Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) is a free and open-source user interface framework for Windows-based desktop applications. WPF applications are based in .NET, and are primarily developed using C# and XAML.
Originally developed by Microso ...
(WPF), under development
* Unix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X, *nix or *NIX) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Uni ...
: Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
, FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free-software Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). The first version was released in 1993 developed from 386BSD, one of the first fully functional and free Unix clones on affordable ...
:
** GTK
GTK (formerly GIMP ToolKit and GTK+) is a free software cross-platform widget toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces (GUIs). It is licensed under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License, allowing both Free software, free and ...
* macOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
:
** Cocoa
, SWT 4.7.3a (and 4.8M6) is officially compatible with the following operating systems (graphic library or similar if explicitly required / processors):
* Microsoft Windows (x86 and x86_64)
* Linux (GTK / PPC64 and PPC64LE)
* macOS (Cocoa / x86_64)

Windows XP
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct successor to Windows 2000 for high-end and business users a ...
has historically been supported as have Linux on s390, Solaris 11 (SPARCv9), Solaris 10 (x86_64), HP-UX
HP-UX (from "Hewlett Packard Unix") is a proprietary software, proprietary implementation of the Unix operating system developed by Hewlett Packard Enterprise; current versions support HPE Integrity Servers, based on Intel's Itanium architect ...
(ia64), AIX (PPC and PPC64).
Performance
SWT was designed to be a ''high performance'' GUI toolkit; faster, more responsive and lighter on system resource usage than Swing. There has been some attemptedbenchmarking
Benchmarking is the practice of comparing business processes and performance metrics to industry bests and best practices from other companies. Dimensions typically measured are Project management triangle, quality, time and cost.
Benchmarking is ...
of SWT and Swing, which concluded that SWT should be more efficient than Swing, although the applications benchmarked in this case were not complex enough to draw solid conclusions for all possible SWT or Swing uses. A fairly thorough set of benchmarks concluded that neither Swing nor SWT outperformed the other in the general case.
Extensibility and comparison to other Java code
Due to the use of native code, SWT classes do not allow for easy inheritance for all widget classes, which some users consider can hurt extensibility. This can make customizing existing widgets more difficult to achieve with SWT than if one were using Swing. Both toolkits support writing new widgets using only Java code, however in SWT extra work is needed to make the new widget work on every platform. SWT widgets, unlike almost any other Java toolkit, requires manual object deallocation, in contrast to the standard Java practice of automatic garbage collection. SWT objects must be explicitly deallocated using thedispose method, which is analogous to the C language
C (''pronounced'' '' – like the letter c'') is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities o ...
's free. If this is not done, memory leak
In computer science, a memory leak is a type of resource leak that occurs when a computer program incorrectly manages memory allocations in a way that memory which is no longer needed is not released. A memory leak may also happen when an objec ...
s or other unintended behavior may result. On this matter, some have commented that "explicitly de-allocating the resources could be a step back in development time (and costs) at least for the average Java developer" and that "this is a mixed blessing. It means more control (and more complexity) for the SWT developer instead of more automation (and slowness) when using Swing." The need for manual object deallocation when using SWT is largely due to SWT's use of native objects. These objects are not tracked by the Java JVM, so it cannot track whether or not such objects are in use, and thus cannot garbage collect them at a suitable time.
Development
There is some development activity to enable combining Swing and SWT. Two different approaches are being attempted: * ''SwingWT'' is a project to provide an alternative Swing implementation. It uses an SWT back end to display its widgets, thus providing the native look and feel and performance advantages of SWT along with the same programming model as Swing. * ''SWTSwing'' is a project to provide a Swing back end for SWT. In effect, SWT could be run using ''Swing native objects'' instead of, for example, GTK or Windows native objects. This would enable SWT to work on every platform that Swing supports. Starting in 2006, there was an SWT-3.2 port to the programming language D called DWT. Since then, the project supports Windows 32-bit, and Linux GTK 32-bit for SWT-3.4. The DWT project also has an addon package that contains a port of JFace and Eclipse Forms. With JavaFX becoming part of the Java SE platform there has been interest in developing a backend for SWT that relies on JavaFX in a similar way to SWTSwing relies on Swing. A prominent project trying to achieve that was ''SWT on JavaFX'' which became part of ''e(fx)clipse'' in 2014.Uses
Applications (alphabetically sorted) using SWT include: * Apache Directory Studio, an LDAP browser–editor *Eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event which occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three ...
and its plug-ins
* GumTree Platform, scientific workbench
* Haystack, information manager
* IBM Rational Software products: Rational Application Developer, Rational Software Architect, Rational Team Concert and others.
* IBM Lotus software
Lotus Software (called Lotus Development Corporation before its acquisition by IBM) was an American software company based in Massachusetts; it was sold to India's HCL Technologies in 2018.
Lotus is most commonly known for the Lotus 1-2-3 sprea ...
products: Notes, Sametime, Symphony
A symphony is an extended musical composition in Western classical music, most often for orchestra. Although the term has had many meanings from its origins in the ancient Greek era, by the late 18th century the word had taken on the meaning c ...
, and Expeditor
* Studio 3T, GUI client for MongoDB
MongoDB is a source-available, cross-platform, document-oriented database program. Classified as a NoSQL database product, MongoDB uses JSON-like documents with optional database schema, schemas. Released in February 2009 by 10gen (now MongoDB ...
database
* RSSOwl, feed aggregator
* SmartGit, a Git, Mercurial, and Apache Subversion
Apache Subversion (often abbreviated SVN, after its command name ''svn'') is a version control system distributed as open source under the Apache License. Software developers use Subversion to maintain current and historical versions of files su ...
(SVN) client
* TuxGuitar, an open-source tablature editor
* uDig, GIS tool
* Vuze, formerly named Azureus
Recent open-source efforts in the Eclipse community have led to a porting of SWT (and JFace) into a widget toolkit appropriate for the web. The result has been the Eclipse Remote Application Platform (RAP), which combines the qooxdoo Ajax library with the SWT API. Like other Java Ajax
Ajax may refer to:
Greek mythology and tragedy
* Ajax the Great, a Greek mythological hero, son of King Telamon and Periboea
* Ajax the Lesser, a Greek mythological hero, son of Oileus, the king of Locris
* Ajax (play), ''Ajax'' (play), by the an ...
projects (such as Echo2, Vaadin
Vaadin () is an open-source web application development platform for Java. Vaadin includes a set of Web Components, a Java web framework, and a set of tools that enable developers to implement modern web graphical user interfaces (GUI) using the ...
and Google Web Toolkit
Google Web Toolkit (GWT ), or GWT Web Toolkit, is an open-source software, open-source set of Programming tool, tools that allows web developers to create and maintain JavaScript Front and back ends, front-end applications in Java (programming ...
), the usage of the SWT API allows developing applications quickly for the web in much the same way as for the desktop.
See also
*List of widget toolkits
This article provides a list of widget toolkits (also known as GUI frameworks), used to construct the graphical user interface (GUI) of programs, organized by their relationships with various operating systems.
Low-level widget toolkits
Integrat ...
Notes
References
* * * * * *External links
* {{Java desktop Eclipse (software) Eclipse software Eclipse technology Free computer libraries Java (programming language) libraries Software using the Eclipse Public License Widget toolkits