Standard Italian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Italian (, , or , ) is a
Data for EU27
, published in 2012. There are also Italian speakers in non-EU European countries (such as Switzerland,
 The Italian language has developed through a long and slow process, which began after the Western Roman Empire's fall and the onset of the
The Italian language has developed through a long and slow process, which began after the Western Roman Empire's fall and the onset of the  The language that came to be thought of as Italian developed in central Tuscany and was first formalized in the early 14th century through the works of Tuscan writer
The language that came to be thought of as Italian developed in central Tuscany and was first formalized in the early 14th century through the works of Tuscan writer
 Italian is the official language of Italy and
Italian is the official language of Italy and
Romance language
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
of the Indo-European language family
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
. It evolved from the colloquial Latin of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
. Italian is the least divergent language from Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
, together with Sardinian. It is spoken by about 68 million people, including 64 million native speakers as of 2024.
Italian is an official language
An official language is defined by the Cambridge English Dictionary as, "the language or one of the languages that is accepted by a country's government, is taught in schools, used in the courts of law, etc." Depending on the decree, establishmen ...
in Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, San Marino
San Marino, officially the Republic of San Marino, is a landlocked country in Southern Europe, completely surrounded by Italy. Located on the northeastern slopes of the Apennine Mountains, it is the larger of two European microstates, microsta ...
, Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
(Ticino
Ticino ( ), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino, is one of the Canton of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eight districts ...
and the Grisons
The Grisons (; ) or Graubünden (),Names include:
* ;
*Romansh language, Romansh:
**
**
**
**
**
**;
* ;
* ;
* .
See also list of European regions with alternative names#G, other names. more formally the Canton of the Grisons or the Canton ...
), and Vatican City
Vatican City, officially the Vatican City State (; ), is a Landlocked country, landlocked sovereign state and city-state; it is enclaved within Rome, the capital city of Italy and Bishop of Rome, seat of the Catholic Church. It became inde ...
; it has official minority status in Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
, Slovene Istria
Slovene Istria is a region in southwest Slovenia. It comprises the northern part of the Istrian peninsula and is part of the wider geographical-historical region known as the Slovene Littoral. Its largest urban center is Koper. Other large settlem ...
, Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
, and the municipalities of Santa Tereza, Encantado, and Venda Nova do Imigrante in Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
. Italian is also spoken by large immigrant and expatriate communities in the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
. Some speakers of Italian are native bilinguals of both Italian (either in its standard form or regional varieties) and a local language of Italy, most frequently the language spoken at home in their place of origin.
Italian is a major language
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed language, signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing syste ...
in Europe, being one of the official languages of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is a regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization comprising member states in Europe, North America, and Asia. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, the p ...
and one of the working languages of the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; , CdE) is an international organisation with the goal of upholding human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it is Europe's oldest intergovernmental organisation, represe ...
. It is the third-most-widely spoken native language in the European Union (13% of the EU population) and it is spoken as a second language by 13 million EU citizens (3%).Europeans and their LanguagesData for EU27
, published in 2012. There are also Italian speakers in non-EU European countries (such as Switzerland,
Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
, Monaco
Monaco, officially the Principality of Monaco, is a Sovereign state, sovereign city-state and European microstates, microstate on the French Riviera a few kilometres west of the Regions of Italy, Italian region of Liguria, in Western Europe, ...
, and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
) and on other continents. Italian is the main working language of the Holy See
The Holy See (, ; ), also called the See of Rome, the Petrine See or the Apostolic See, is the central governing body of the Catholic Church and Vatican City. It encompasses the office of the pope as the Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishop ...
, serving as the lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
in the Roman Catholic hierarchy and the official language of the Sovereign Military Order of Malta
The Sovereign Military Order of Malta (SMOM), officially the Sovereign Military Hospitaller Order of Saint John of Jerusalem, of Rhodes and of Malta, and commonly known as the Order of Malta or the Knights of Malta, is a Catholic lay religious ...
. Italian has a significant use in musical terminology
A variety of musical terms is encountered in Sheet music, printed scores, music reviews, and program notes. Most of the terms Italian musical terms used in English, are Italian, in accordance with the Italian origins of many European musical conv ...
and opera
Opera is a form of History of theatre#European theatre, Western theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by Singing, singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically ...
with numerous Italian words referring to music that have become international terms taken into various languages worldwide. Almost all native Italian words end with vowel
A vowel is a speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract, forming the nucleus of a syllable. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness a ...
s, and the language has a 7-vowel sound system ('e' and 'o' have mid-low and mid-high sounds). Italian has contrast between short and long consonants and gemination
In phonetics and phonology, gemination (; from Latin 'doubling', itself from '' gemini'' 'twins'), or consonant lengthening, is an articulation of a consonant for a longer period of time than that of a singleton consonant. It is distinct from ...
(doubling) of consonants.
History
Origins
 The Italian language has developed through a long and slow process, which began after the Western Roman Empire's fall and the onset of the
The Italian language has developed through a long and slow process, which began after the Western Roman Empire's fall and the onset of the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
in the 5th century.
Latin, the predominant language of the western Roman Empire, remained the established written language in Europe during the Middle Ages, although most people were illiterate. Over centuries, the Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Colloquial, Popular, Spoken or Vernacular Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. ''Vulgar Latin'' a ...
popularly spoken in various areas of Europe—including the Italian peninsula—evolved into local varieties, or dialects, unaffected by formal standards and teachings. These varieties are not in any sense "dialects" of standard Italian, which itself started off as one of these local tongues, but sister languages of Italian.
The linguistic and historical demarcations between late Vulgar Latin and early Romance varieties in Italy are imprecise. The earliest surviving texts that can definitely be called vernacular (as distinct from its predecessor Vulgar Latin) are legal formulae known as the Placiti Cassinesi from the province of Benevento
The province of Benevento () is a Provinces of Italy, province in the Campania region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Benevento.
Geography
The province has an area of 2,071 km2, and, as of 2017, a population of 279,127. There are 78 '' ...
that date from 960 to 963, although the Veronese Riddle, probably from the 8th or early 9th century, contains a late form of Vulgar Latin that can be seen as a very early sample of a vernacular dialect of Italy. The Commodilla catacomb inscription likewise probably dates to the early 9th century and appears to reflect a language somewhere between late Vulgar Latin and early vernacular.
 The language that came to be thought of as Italian developed in central Tuscany and was first formalized in the early 14th century through the works of Tuscan writer
The language that came to be thought of as Italian developed in central Tuscany and was first formalized in the early 14th century through the works of Tuscan writer Dante Alighieri
Dante Alighieri (; most likely baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri; – September 14, 1321), widely known mononymously as Dante, was an Italian Italian poetry, poet, writer, and philosopher. His ''Divine Comedy'', originally called ...
, written in his native Florentine. Dante's epic poems, known collectively as the '' Commedia'', to which another Tuscan poet Giovanni Boccaccio
Giovanni Boccaccio ( , ; ; 16 June 1313 – 21 December 1375) was an Italian people, Italian writer, poet, correspondent of Petrarch, and an important Renaissance humanism, Renaissance humanist. Born in the town of Certaldo, he became so ...
later affixed the title ''Divina'', were read throughout the Italian peninsula. His written vernacular became the touchstone for elaborating a "canonical standard" that all educated Italians could understand. The poetry of Petrarch
Francis Petrarch (; 20 July 1304 – 19 July 1374; ; modern ), born Francesco di Petracco, was a scholar from Arezzo and poet of the early Italian Renaissance, as well as one of the earliest Renaissance humanism, humanists.
Petrarch's redis ...
was also widely admired and influential in the development of the literary language, and would be identified as a model for vernacular writing by Pietro Bembo in the 16th century.
In addition to the widespread exposure gained through literature, Florentine also gained prestige due to the political and cultural significance of Florence at the time and the fact that it was linguistically a middle way between the northern and the southern Italian dialects.
Italian was progressively made an official language of most of the Italian states predating unification, slowly replacing Latin, even when ruled by foreign powers (such as Spain in the Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples (; ; ), officially the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was established by the War of the Sicilian Vespers (1282–1302). Until ...
, or Austria in the Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia), although the masses kept speaking primarily their local vernaculars. Italian was also one of the many recognised languages in the Austro-Hungarian Empire.
Italy has always had a distinctive dialect for each city because the cities, until recently, were thought of as city-states. Those dialects now have considerable variety. As Tuscan-derived Italian came to be used throughout Italy, features of local speech were naturally adopted, producing various versions of Regional Italian
Regional Italian (, ) is any regional"Regional" in the broad sense of the word; not to be confused with the Italian endonym , for Italy's administrative units. variety of the Italian language.
Such vernacular varieties and standard Italian exi ...
. The most characteristic differences, for instance, between Roman Italian and Milan
Milan ( , , ; ) is a city in northern Italy, regional capital of Lombardy, the largest city in Italy by urban area and the List of cities in Italy, second-most-populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of nea ...
ese Italian are syntactic gemination of initial consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract, except for the h sound, which is pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Examples are and pronou ...
s in some contexts and the pronunciation of stressed "e", and of "s" between vowels in many words: e.g. ''va bene'' 'all right' is pronounced by a Roman (and by any standard Italian speaker), by a Milanese (and by any speaker whose native dialect lies to the north of the La Spezia–Rimini Line); ''a casa'' 'at home' is for Roman, or for standard, for Milanese and generally northern.
In contrast to the Gallo-Italic linguistic panorama of northern Italy, the Italo-Dalmatian
The Italo-Dalmatian languages, or Central Romance languages, are a group of Romance languages spoken in Italy, Corsica (France), and formerly in Dalmatia (Croatia).
Italo-Dalmatian can be split into:Hammarström, Harald & Forkel, Robert & Haspe ...
, Neapolitan and its related dialects were largely unaffected by the Franco- Occitan influences introduced to Italy mainly by bard
In Celtic cultures, a bard is an oral repository and professional story teller, verse-maker, music composer, oral historian and genealogist, employed by a patron (such as a monarch or chieftain) to commemorate one or more of the patron's a ...
s from France during the Middle Ages, but after the Norman conquest of southern Italy, Sicily became the first Italian land to adopt Occitan lyric moods (and words) in poetry. Even in the case of northern Italian languages, however, scholars are careful not to overstate the effects of outsiders on the natural indigenous developments of the languages.
The economic might and relatively advanced development of Tuscany at the time (Late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the Periodization, period of History of Europe, European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period ( ...
) gave its language weight, although Venetian remained widespread in medieval Italian commercial life, and Ligurian (or Genoese) remained in use in maritime trade alongside the Mediterranean. The increasing political and cultural relevance of Florence during the periods of the rise of the Medici Bank, humanism
Humanism is a philosophy, philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential, and Agency (philosophy), agency of human beings, whom it considers the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The me ...
, and the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
made its dialect, or rather a refined version of it, a standard in the arts.
Renaissance
TheRenaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
era, known as in Italian, was seen as a time of rebirth, which is the literal meaning of both (from French) and (Italian). Among its many manifestations, the Renaissance saw a reinvigorated interest in both classical antiquity and vernacular literature.
Advancements in technology played a crucial role in the diffusion of the Italian language. The printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a printing, print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in whi ...
was invented in the 15th century, and spread rapidly. By the year 1500, there were 56 printing presses in Italy, more than anywhere else in Europe. The printing press enabled the production of literature and documents in higher volumes and at lower cost, further accelerating the spread of Italian.
Italian became the language used in the courts of every state in the Italian peninsula, and the prestige variety
Prestige in sociolinguistics is the level of regard normally accorded a specific language or dialect within a speech community, relative to other languages or dialects. Prestige varieties are language or dialect families which are generally co ...
used on the island of Corsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
(but not in the neighbouring Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; ; ) is the Mediterranean islands#By area, second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia an ...
, which on the contrary underwent Italianization well into the late 18th century, under Savoyard sway: the island's linguistic composition, roofed by the prestige of Spanish among the Sardinians, would therein make for a rather slow process of assimilation to the Italian cultural sphere). The rediscovery of Dante's , and a renewed interest in linguistics in the 16th century, sparked a debate that raged throughout Italy concerning the criteria that should govern the establishment of a modern Italian literary and spoken language. This discussion, known as questione della lingua (i.e., the ''problem of the language''), ran through the Italian culture until the end of the 19th century, often linked to the political debate on achieving a united Italian state. Renaissance scholars divided into three main factions:
* The purists, headed by Venetian Pietro Bembo
Pietro Bembo, (; 20 May 1470 – 18 January 1547) was a Venetian scholar, poet, and literary theory, literary theorist who also was a member of the Knights Hospitaller and a cardinal of the Catholic Church. As an intellectual of the Italian Re ...
(who, in his , claimed the language might be based only on the great literary classics, such as Petrarch
Francis Petrarch (; 20 July 1304 – 19 July 1374; ; modern ), born Francesco di Petracco, was a scholar from Arezzo and poet of the early Italian Renaissance, as well as one of the earliest Renaissance humanism, humanists.
Petrarch's redis ...
and some part of Boccaccio). The purists thought the ''Divine Comedy
The ''Divine Comedy'' (, ) is an Italian narrative poetry, narrative poem by Dante Alighieri, begun and completed around 1321, shortly before the author's death. It is widely considered the pre-eminent work in Italian literature and one of ...
'' was not dignified enough because it used elements from non-lyric registers of the language.
* Niccolò Machiavelli
Niccolò di Bernardo dei Machiavelli (3 May 1469 – 21 June 1527) was a Florentine diplomat, author, philosopher, and historian who lived during the Italian Renaissance. He is best known for his political treatise '' The Prince'' (), writte ...
and other Florentines preferred the version spoken by ordinary people in their own times.
* The courtier
A courtier () is a person who attends the royal court of a monarch or other royalty. The earliest historical examples of courtiers were part of the retinues of rulers. Historically the court was the centre of government as well as the officia ...
s, such as Baldassare Castiglione and Gian Giorgio Trissino
Gian Giorgio Trissino (8 July 1478 – 8 December 1550), also called Giovan Giorgio Trissino and self-styled as Giovan Giωrgio Trissino, was a Venetian Renaissance humanist, poet, dramatist, diplomat, grammarian, linguist, and philosopher. ...
, insisted that each local vernacular contribute to the new standard.
A fourth faction claimed that the best Italian was the one that the papal court adopted, which was a mixture of the Tuscan and Roman dialects. Eventually, Bembo's ideas prevailed, and the foundation of the in Florence (1582–1583), the official legislative body of the Italian language, led to the publication of Agnolo Monosini's Latin tome in 1604 followed by the first Italian dictionary in 1612.
Modern era
An important event that helped the diffusion of Italian was the conquest and occupation of Italy byNapoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
(himself of Italian-Corsican descent) in the early 19th century. This conquest propelled the unification of Italy
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century Political movement, political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the Proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, annexation of List of historic states of ...
some decades after and pushed the Italian language into the status of a lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
, used not only among clerks, nobility, and functionaries in the Italian courts, but also by the bourgeoisie
The bourgeoisie ( , ) are a class of business owners, merchants and wealthy people, in general, which emerged in the Late Middle Ages, originally as a "middle class" between the peasantry and aristocracy. They are traditionally contrasted wi ...
.
Contemporary times
The publication of Italian literature's first modern novel, ('' The Betrothed'') byAlessandro Manzoni
Alessandro Francesco Tommaso Antonio Manzoni (, , ; 7 March 1785 – 22 May 1873) was an Italian poet, novelist and philosopher.
He is famous for the novel ''The Betrothed (Manzoni novel), The Betrothed'' (orig. ) (1827), generally ranked among ...
, both reflected and furthered the growing trend towards Italian as a national standard language. Manzoni, a Milanesian, chose to write the book in the Florentine dialect, describing this choice, in the preface to his 1840 edition, as "rinsing" his Milanese "in the waters of the Arno" (Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
's river). The novel is commonly described as "the most widely read work in the Italian language". It became a model for subsequent Italian literary fiction, helping to galvanize national linguistic unity around the Florentine dialect.
This growth was relative; linguistic diversity continued during the unification of Italy (1848–1871). The Italian linguist Tullio De Mauro estimated that only 2.5% of Italy's population could speak the Italian standardized language properly in 1861, while Arrigo Castellani estimated the same value as 10%.
After unification, a huge number of civil servants and soldiers recruited from all over the country introduced many more words and idioms from their home languages. For example, is derived from the Venetian word ('slave', that is 'your servant'), and comes from the Lombard word .
Classification
Italian is aRomance language
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
, a descendant of Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Colloquial, Popular, Spoken or Vernacular Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. ''Vulgar Latin'' a ...
(colloquial spoken Latin). Standard Italian is based on Tuscan, especially its Florentine dialect, and is, therefore, an Italo-Dalmatian language, a classification that includes most other central and southern Italian languages and the extinct Dalmatian. As in most Romance languages, stress is distinctive in Italian.
According to ''Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It w ...
'', lexical similarity
In linguistics, lexical similarity is a measure of the degree to which the word sets of two given languages are similar. A lexical similarity of 1 (or 100%) would mean a total overlap between vocabularies, whereas 0 means there are no common words. ...
is 89% with French, 87% with Catalan, 85% with Sardinian, 82% with Spanish, 82% with Portuguese, 78% with Ladin, 77% with Romanian. Estimates may differ according to sources.
A 1949 study by the linguist Mario Pei concluded that out of seven Romance languages, Italian's stressed vowel phonology was the second-closest to that of Vulgar Latin (after Sardinian). The study emphasized, however, that it represented only "a very elementary, incomplete and tentative demonstration" of how statistical methods could measure linguistic change, assigned "frankly arbitrary" point values to various types of change, and did not compare languages in the sample with respect to any characteristics or forms of divergence other than stressed vowels, among other caveats.
Geographic distribution
 Italian is the official language of Italy and
Italian is the official language of Italy and San Marino
San Marino, officially the Republic of San Marino, is a landlocked country in Southern Europe, completely surrounded by Italy. Located on the northeastern slopes of the Apennine Mountains, it is the larger of two European microstates, microsta ...
and is spoken fluently by the majority of the countries' populations. Italian is the third most spoken language in Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
(after German and French; see Swiss Italian
The Italian language in Italian Switzerland or Swiss Italian (, ) is the variety of the Italian language taught in the Italian-speaking area of Switzerland. While this variety is mainly spoken in the canton of Ticino and in the southern part ...
), although its use there has moderately declined since the 1970s. It is official both on the national level and on regional level in two cantons: Ticino
Ticino ( ), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino, is one of the Canton of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eight districts ...
and Grisons
The Grisons (; ) or Graubünden (),Names include:
* ;
*Romansh language, Romansh:
**
**
**
**
**
**;
* ;
* ;
* .
See also list of European regions with alternative names#G, other names. more formally the Canton of the Grisons or the Canton ...
. In the latter canton, however, it is only spoken by a small minority, in the Italian Grisons. Ticino, which includes Lugano
Lugano ( , , ; ) is a city and municipality within the Lugano District in the canton of Ticino, Switzerland. It is the largest city in both Ticino and the Italian-speaking region of southern Switzerland. Lugano has a population () of , and an u ...
, the largest Italian-speaking city outside Italy, is the only canton where Italian is predominant. Italian is also used in administration and official documents in Vatican City
Vatican City, officially the Vatican City State (; ), is a Landlocked country, landlocked sovereign state and city-state; it is enclaved within Rome, the capital city of Italy and Bishop of Rome, seat of the Catholic Church. It became inde ...
.
Italian is also spoken by a minority in Monaco
Monaco, officially the Principality of Monaco, is a Sovereign state, sovereign city-state and European microstates, microstate on the French Riviera a few kilometres west of the Regions of Italy, Italian region of Liguria, in Western Europe, ...
and France, especially in the southeastern part of the country. Italian was the official language in Savoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
and in Nice
Nice ( ; ) is a city in and the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative city limits, with a population of nearly one millionTreaty of Turin, a development that triggered the " Niçard exodus", or the emigration of a quarter of the  It formerly had official status in
It formerly had official status in  It formerly had official status in
It formerly had official status in  Italian is also spoken by large immigrant and expatriate communities in the Americas and Australia. Although over 17 million Americans are of Italian descent, only a little over one million people in the United States speak Italian at home. Nevertheless, an Italian language media market does exist in the country. In Canada, Italian is the second most spoken non-official language when
Italian is also spoken by large immigrant and expatriate communities in the Americas and Australia. Although over 17 million Americans are of Italian descent, only a little over one million people in the United States speak Italian at home. Nevertheless, an Italian language media market does exist in the country. In Canada, Italian is the second most spoken non-official language when
 Italian is widely taught in many schools around the world, but rarely as the first foreign language. In the 21st century, technology also allows for the continual spread of the Italian language, as people have new ways to learn how to speak, read, and write languages at their own pace and at any given time. For example, the free website and application
Italian is widely taught in many schools around the world, but rarely as the first foreign language. In the 21st century, technology also allows for the continual spread of the Italian language, as people have new ways to learn how to speak, read, and write languages at their own pace and at any given time. For example, the free website and application
 From the late 19th to the mid-20th century, millions of Italians settled in Argentina, Uruguay, southern Brazil, and Venezuela, and in Canada and the United States, where they formed a physical and cultural presence.
In some cases, colonies were established where variants of regional
From the late 19th to the mid-20th century, millions of Italians settled in Argentina, Uruguay, southern Brazil, and Venezuela, and in Canada and the United States, where they formed a physical and cultural presence.
In some cases, colonies were established where variants of regional
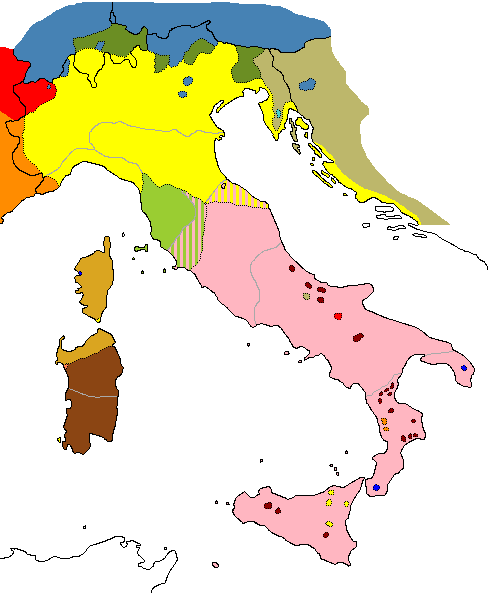
 In Italy, almost all the other languages spoken as the vernacular—other than standard Italian and some languages spoken among immigrant communities—are often called " Italian dialects", a label that can be very misleading if it is understood to mean "dialects of Italian". The Romance dialects of Italy are local evolutions of spoken Latin that pre-date the establishment of Italian, and as such are sister languages to the Tuscan that was the historical source of Italian. They can be quite different from Italian and from each other, with some belonging to different linguistic branches of Romance. The only exceptions to this are twelve groups considered " historical language minorities", which are officially recognised as distinct
In Italy, almost all the other languages spoken as the vernacular—other than standard Italian and some languages spoken among immigrant communities—are often called " Italian dialects", a label that can be very misleading if it is understood to mean "dialects of Italian". The Romance dialects of Italy are local evolutions of spoken Latin that pre-date the establishment of Italian, and as such are sister languages to the Tuscan that was the historical source of Italian. They can be quite different from Italian and from each other, with some belonging to different linguistic branches of Romance. The only exceptions to this are twelve groups considered " historical language minorities", which are officially recognised as distinct
' ''; ''i'' is the plural of ''il''; and ''le'' is the plural of feminine ''la'' and ''l''
Accademia della Crusca
*
Treccani
Il Nuovo De Mauro
* Italian proverbs *
Learn Italian
,
Xeno Italia
at ''Omniglot'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Italian Language Fusional languages Languages attested from the 10th century Languages of Italy Languages of Monaco Languages of San Marino Languages of Sicily Languages of Switzerland Languages of Vatican City Languages of Slovenia Languages of Croatia Subject–verb–object languages Syllable-timed languages
Niçard Italians
Niçard Italians ( ) are Italians who have full or partial County of Nice, Nice heritage by birth or ethnicity.
History
Niçard Italians have roots in Nice and the County of Nice. They often speak the Ligurian language after Nice joined the Genoa ...
to Italy, and the Niçard Vespers. Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as (). In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as () or (). 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, revolutionary and republican. H ...
complained about the referendum that allowed France to annex Savoy and Nice, and a group of his followers (among the Italian Savoyards) took refuge in Italy in the following years. Corsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
passed from the Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( ; ; ) was a medieval and early modern Maritime republics, maritime republic from the years 1099 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italy, Italian coast. During the Late Middle Ages, it was a major commercial power in ...
to France in 1769 after the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
. Italian was the official language of Corsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
until 1859. Giuseppe Garibaldi called for the inclusion of the " Corsican Italians" within Italy when Rome was annexed to the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
, but King Victor Emmanuel II did not agree to it. Italian is generally understood in Corsica by the population resident therein who speak Corsican, which is an Italo-Romance language similar to Tuscan. Francization
Francization (in American English, Canadian English, and Oxford English) or Francisation (in other British English), also known as Frenchification, is the expansion of French language use—either through willful adoption or coercion—by more an ...
occurred in Nice case, and caused a near-disappearance of the Italian language as many of the Italian speakers in these areas migrated to Italy. In Corsica, on the other hand, almost everyone still speaks the Corsican language
Corsican (, , or , ) is a Romance languages, Romance language consisting of the Dialect continuum, continuum of the Tuscan dialect, Tuscan Italo-Dalmatian languages, Italo-Dalmatian dialects spoken on the Mediterranean island of Corsica, a Singl ...
, which, due to its linguistic proximity to the Italian standard language, appears both linguistically as an Italian dialect and therefore as a carrier of Italian culture, despite the French government's decades-long efforts to cut Corsica off from the Italian motherland. Italian was the official language in Monaco
Monaco, officially the Principality of Monaco, is a Sovereign state, sovereign city-state and European microstates, microstate on the French Riviera a few kilometres west of the Regions of Italy, Italian region of Liguria, in Western Europe, ...
until 1860, when it was replaced by the French. This was due to the annexation of the surrounding County of Nice to France following the Treaty of Turin (1860).
 It formerly had official status in
It formerly had official status in Montenegro
, image_flag = Flag of Montenegro.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Montenegro.svg
, coa_size = 80
, national_motto =
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map = Europe-Mont ...
(because of the Venetian Albania), parts of Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
and Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
(because of the Venetian Istria and Venetian Dalmatia), parts of Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
(because of the Venetian rule in the Ionian Islands and by the Kingdom of Italy in the Dodecanese). Italian is widely spoken in Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
, where nearly two-thirds of the population can speak it fluently (see Maltese Italian). Italian served as Malta's official language until 1934, when it was abolished by the British colonial administration amid strong local opposition. Italian language in Slovenia is an officially recognised minority language
A minority language is a language spoken by a minority of the population of a territory. Such people are termed linguistic minorities or language minorities. With a total number of 196 sovereign states recognized internationally (as of 2019) and ...
in the country. The official census, carried out in 2002, reported 2,258 ethnic Italians ( Istrian Italians) in Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
(0.11% of the total population). Italian language in Croatia is an official minority language in the country, with many schools and public announcements published in both languages. The 2001 census in Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
reported 19,636 ethnic Italians (Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians) in the country (some 0.42% of the total population). Their numbers dropped dramatically after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
following the Istrian–Dalmatian exodus, which caused the emigration of between 230,000 and 350,000 Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians. Italian was the official language of the Republic of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa, or the Republic of Dubrovnik, was an maritime republics, aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost ...
from 1492 to 1807.
Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
due to the annexation of the country to the Kingdom of Italy (1939–1943). Albania has a large population of non-native speakers, with over half of the population having some knowledge of the Italian language. The Albanian government has pushed to make Italian a compulsory second language in schools. The Italian language is well-known and studied in Albania, due to its historical ties and geographical proximity to Italy and to the diffusion of Italian television in the country.
Due to heavy Italian influence during the Italian colonial period, Italian is still understood by some in former colonies such as Libya. Although it was the primary language in Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–L ...
since colonial rule
Colonialism is the control of another territory, natural resources and people by a foreign group. Colonizers control the political and tribal power of the colonised territory. While frequently an imperialist project, colonialism can also take ...
, Italian greatly declined under the rule of Muammar Gaddafi, who expelled the Italian Libyan population and made Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
the sole official language of the country. A few hundred Italian settlers returned to Libya in the 2000s.
Italian was the official language of Eritrea
Eritrea, officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa, with its capital and largest city being Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia in the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, south, Sudan in the west, and Dj ...
during Italian colonisation. Italian is today used in commerce, and it is still spoken especially among elders; besides that, Italian words are incorporated as loan words in the main language spoken in the country (Tigrinya). The capital city of Eritrea, Asmara
Asmara ( ), or Asmera (), is the capital and most populous city of Eritrea, in the country's Central Region (Eritrea), Central Region. It sits at an elevation of , making it the List of capital cities by altitude, sixth highest capital in the wo ...
, still has several Italian schools, established during the colonial period. In the early 19th century, Eritrea was the country with the highest number of Italians abroad, and the Italian Eritreans grew from 4,000 during World War I to nearly 100,000 at the beginning of World War II. In Asmara there are two Italian schools, the Istituto Italiano Statale Omnicomprensivo di Asmara (Italian primary school with a Montessori department) and the Liceo Sperimentale "G. Marconi" (Italian international senior high school).
Italian was also introduced to Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th ...
through colonialism and was the sole official language of administration and education during the colonial period but fell out of use after government, educational and economic infrastructure were destroyed in the Somali Civil War
The Somali Civil War (; ) is an List of ongoing armed conflicts, ongoing civil war that is taking place in Somalia. It grew out of resistance to the military junta which was led by Siad Barre during the 1980s. From 1988 to 1990, the Somali Armed ...
.
varieties of Chinese
There are hundreds of local Chinese language varieties forming a branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages, Sino-Tibetan language family, many of which are not Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible. Variation is particularly strong in the m ...
are not grouped together, with 375,645 claiming Italian as their mother tongue in 2016.
Italian immigrants to South America have also brought a presence of the language to that continent. According to some sources, Italian is the second most spoken language in Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
after the official language of Spanish, although its number of speakers, mainly of the older generation, is decreasing. Italian bilingual speakers can be found scattered across the southeast of Brazil and in the south. In Venezuela
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It com ...
, Italian is the most spoken language after Spanish and Portuguese, with around 200,000 speakers. In Uruguay
Uruguay, officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast, while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the A ...
, people who speak Italian as their home language are 1.1% of the total population of the country. In Australia, Italian is the second most spoken foreign language after Chinese, with 1.4% of the population speaking it as their home language.
The main Italian-language newspapers published outside Italy are the ''L'Osservatore Romano
''L'Osservatore Romano'' is the daily newspaper of Vatican City which reports on the activities of the Holy See and events taking place in the Catholic Church and the world. It is owned by the Holy See but is not an official publication, a role ...
'' (Vatican City
Vatican City, officially the Vatican City State (; ), is a Landlocked country, landlocked sovereign state and city-state; it is enclaved within Rome, the capital city of Italy and Bishop of Rome, seat of the Catholic Church. It became inde ...
), the ''L'Informazione di San Marino'' (San Marino
San Marino, officially the Republic of San Marino, is a landlocked country in Southern Europe, completely surrounded by Italy. Located on the northeastern slopes of the Apennine Mountains, it is the larger of two European microstates, microsta ...
), the '' Corriere del Ticino'' and the '' laRegione Ticino'' (Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
), the '' La Voce del Popolo'' (Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
), the ''Corriere d'Italia'' (Germany), the ''L'italoeuropeo'' (United Kingdom), the ''Passaparola'' (Luxembourg
Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France on the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembour ...
), the (United States), the '' Corriere Canadese'' and the '' Corriere Italiano'' (Canada), the ''Il punto d'incontro'' (Mexico), the ''L'Italia del Popolo'' (Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
), the ''Fanfulla'' (Brazil), the ''Gente d'Italia'' (Uruguay
Uruguay, officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast, while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the A ...
), the ''La Voce d'Italia'' (Venezuela
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It com ...
), the '' Il Globo'' (Australia) and the ''La gazzetta del Sud Africa'' (South Africa).
Education
 Italian is widely taught in many schools around the world, but rarely as the first foreign language. In the 21st century, technology also allows for the continual spread of the Italian language, as people have new ways to learn how to speak, read, and write languages at their own pace and at any given time. For example, the free website and application
Italian is widely taught in many schools around the world, but rarely as the first foreign language. In the 21st century, technology also allows for the continual spread of the Italian language, as people have new ways to learn how to speak, read, and write languages at their own pace and at any given time. For example, the free website and application Duolingo
Duolingo, Inc. is an American educational technology company that produces learning Mobile app, apps and provides Language assessment, language certification. Duolingo offers courses on 43 languages, ranging from English language, English, Fre ...
has 4.94 million English speakers learning the Italian language.
According to the Italian Ministry of Foreign Affairs, every year there are more than 200,000 foreign students who study the Italian language; they are distributed among the 90 Institutes of Italian Culture that are located around the world, in the 179 Italian schools located abroad, or in the 111 Italian lecturer sections belonging to foreign schools where Italian is taught as a language of culture.
As of 2022, Australia had the highest number of students learning Italian in the world. This occurred because of support by the Italian community in Australia and the Italian Government and also because of successful educational reform efforts led by local governments in Australia.
Influence and derived languages
languages of Italy
The languages of Italy include Italian language, Italian, which serves as the country's national language, in its standard and Regional Italian, regional forms, as well as numerous local and regional languages, most of which, like Italian, ...
were used, and some continue to use this regional language. Examples are Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul (, ; ; "Great River of the South") is a Federative units of Brazil, state in the South Region, Brazil, southern region of Brazil. It is the Federative units of Brazil#List, fifth-most populous state and the List of Brazilian s ...
, Brazil, where Talian is used, and the town of Chipilo near Puebla, Mexico; each continues to use a derived form of Venetian dating back to the 19th century. Other examples are Cocoliche
Cocoliche is an Italian language, Italian–Spanish language, Spanish Macaronic language, contact language or pidgin that was spoken by Italian settlement in Argentina, Italian immigrants between 1870 and 1970 in Argentina (especially in Gran Bu ...
, an Italian–Spanish pidgin
A pidgin , or pidgin language, is a grammatically simplified form of contact language that develops between two or more groups of people that do not have a language in common: typically, its vocabulary and grammar are limited and often drawn f ...
once spoken in Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
and especially in Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires, controlled by the government of the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Argentina. It is located on the southwest of the Río de la Plata. Buenos Aires is classified as an Alpha− glob ...
, and Lunfardo
Lunfardo (; from the Italian ) is an argot originated and developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries in the lower classes in the Río de la Plata region (encompassing the port cities of Buenos Aires in Argentina and Montevideo in Uruguay) ...
. The Rioplatense Spanish
Rioplatense Spanish ( , ), also known as Rioplatense Castilian, or River Plate Spanish, is a variety of SpanishAlvar, Manuel, "''Manual de dialectología hispánica. El español de América''", ("Handbook of Hispanic Dialectology. Spanish Lan ...
dialect of Argentina and Uruguay today has thus been heavily influenced by both standard Italian and Italian regional languages as a result.
Lingua franca
Starting in latemedieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
times in much of Europe and the Mediterranean, Latin was replaced as the primary commercial language by languages of Italy, especially Tuscan and Venetian. These varieties were consolidated during the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
with the strength of Italy and the rise of humanism
Humanism is a philosophy, philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential, and Agency (philosophy), agency of human beings, whom it considers the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The me ...
and the arts
The arts or creative arts are a vast range of human practices involving creative expression, storytelling, and cultural participation. The arts encompass diverse and plural modes of thought, deeds, and existence in an extensive range of m ...
.
Italy came to enjoy increasing artistic prestige within Europe. A mark of the educated gentlemen was to make the Grand Tour, visiting Italy to see its great historical monuments and works of art. It was expected that the visitor would learn at least some Italian, understood as language based on Florentine. In England, while the classical languages Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
and Greek were the first to be learned, Italian became the second most common modern language after French, a position it held until the late 18th century when it tended to be replaced by German. John Milton, for instance, wrote some of his early poetry in Italian.
Within the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, Italian is known by a large part of the ecclesiastical hierarchy and is used in substitution for Latin in some official documents.
Italian loanword
A loanword (also a loan word, loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language (the recipient or target language), through the process of borrowing. Borrowing is a metaphorical term t ...
s continue to be used in most languages in matters of art and music (especially classical music including opera), in the design and fashion industries, in some sports such as football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kick (football), kicking a football (ball), ball to score a goal (sports), goal. Unqualified, football (word), the word ''football'' generally means the form of football t ...
and especially in culinary terms.
Languages and dialects

minority language
A minority language is a language spoken by a minority of the population of a territory. Such people are termed linguistic minorities or language minorities. With a total number of 196 sovereign states recognized internationally (as of 2019) and ...
s by the law. On the other hand, Corsican (a language spoken on the French island of Corsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
) is closely related to medieval Tuscan, from which standard Italian derives and evolved.
The differences in the evolution of Latin in the different regions of Italy can be attributed to the natural changes
Changes may refer to:
Books
* '' Changes: A Love Story'', 1991 novel by Ama Ata Aidoo
* ''Changes'' (The Dresden Files) (2010), the 12th novel in Jim Butcher's ''The Dresden Files'' Series
* ''Changes'', a 1983 novel by Danielle Steel
* ''Chan ...
that all languages in regular use are subject to, and to some extent to the presence of three other types of languages: substrata, superstrata, and adstrata. The most prevalent were substrata (the language of the original inhabitants), as the Italian dialects were most probably simply Latin as spoken by native cultural groups. Superstrata and adstrata were both less important. Foreign conquerors of Italy that dominated different regions at different times left behind little to no influence on the dialects. Foreign cultures with which Italy engaged in peaceful relations with, such as trade, had no significant influence either.
Throughout Italy, regional varieties of standard Italian, called Regional Italian
Regional Italian (, ) is any regional"Regional" in the broad sense of the word; not to be confused with the Italian endonym , for Italy's administrative units. variety of the Italian language.
Such vernacular varieties and standard Italian exi ...
, are spoken. Regional differences can be recognised by various factors: the openness of vowels, the length of the consonants, and influence of the local language (for example, in informal situations ', ' and ' replace the standard Italian ' in the area of Tuscany, Rome and Venice respectively for the infinitive 'to go').
There is no definitive date when the various Italian variants of Latin—including varieties that contributed to modern standard Italian—began to be distinct enough from Latin to be considered separate languages. One criterion for determining that two language variants are to be considered separate languages rather than variants of a single language is that they have evolved so that they are no longer mutually intelligible
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between different but related language varieties in which speakers of the different varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. Mutual intellig ...
; this diagnostic is effective if mutual intelligibility is minimal or absent (e.g. in Romance, Romanian and Portuguese), but it fails in cases such as Spanish-Portuguese or Spanish-Italian, as educated native speakers of either pairing (particularly Spanish-Portuguese) can understand each other well if they choose to do so; however, the level of intelligibility is markedly lower between Italian-Spanish, and considerably higher between the Iberian sister languages of Portuguese-Spanish. Speakers of this latter pair can communicate with one another with remarkable ease, each speaking to the other in his own native language, without slang/jargon.
Nevertheless, on the basis of accumulated differences in morphology, syntax, phonology, and to some extent lexicon, it is not difficult to identify that for the Romance varieties of Italy, the first extant written evidence of languages that can no longer be considered Latin comes from the 9th and 10th centuries CE. These written sources demonstrate certain vernacular characteristics and sometimes explicitly mention the use of the vernacular in Italy.
Full literary manifestations of the vernacular began to surface around the 13th century in the form of various religious texts and poetry.Although these are the first written records of Italian varieties separate from Latin, the spoken language had probably diverged long before the first written records appeared since those who were literate generally wrote in Latin even if they spoke other Romance varieties in person.
Throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, the use of standard Italian became increasingly widespread and was mirrored by a decline in the use of the dialects. An increase in literacy was one of the main driving factors (one can assume that only literates were capable of learning standard Italian, whereas those who were illiterate had access only to their native dialect). The percentage of literates rose from 25% in 1861 to 60% in 1911, and then on to 78.1% in 1951. Tullio De Mauro, an Italian linguist, has asserted that in 1861, only 2.5% of the population of Italy could speak standard Italian. He reports that in 1951, that percentage had risen to 87%. The ability to speak Italian did not necessarily mean that it was in everyday use, and most people (63.5%) still usually spoke their native dialects. In addition, other factors such as mass emigration, industrialization, and urbanization, and internal migrations after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, contributed to the proliferation of standard Italian. The Italians who emigrated during the Italian diaspora
The Italian diaspora (, ) is the large-scale emigration of Italians from Italy.
There were two major Italian diasporas in Italian history. The first diaspora began around 1880, two decades after the Risorgimento, Unification of Italy, and ended ...
beginning in 1861 were often of the uneducated lower class, and thus the emigration had the effect of increasing the percentage of literates, who often knew and understood the importance of standard Italian back home in Italy. A large percentage of those who had emigrated also eventually returned to Italy, often more educated than when they had left.
Although use of the Italian dialects has declined in the modern era
The modern era or the modern period is considered the current historical period of human history. It was originally applied to the history of Europe and Western history for events that came after the Middle Ages, often from around the year 1500 ...
, as Italy unified under standard Italian and continues to do so aided by mass media from newspapers to radio to television, diglossia
In linguistics, diglossia ( , ) is where two dialects or languages are used (in fairly strict compartmentalization) by a single language community. In addition to the community's everyday or vernacular language variety (labeled "L" or "low" v ...
is still frequently encountered in Italy and triglossia is not uncommon in emigrant communities among older speakers. Both situations normally involve some degree of code-switching
In linguistics, code-switching or language alternation occurs when a speaker alternates between two or more languages, or language varieties, in the context of a single conversation or situation. These alternations are generally intended to ...
and code-mixing
Code-mixing is the mixing of two or more languages or Variety (linguistics), language varieties in speech.
Some scholars use the terms "code-mixing" and "code-switching" interchangeably, especially in studies of syntax, Morphology (linguistics) ...
.
Phonology
Italian has a seven-vowel system, consisting of , and 23 consonants. Compared with most other Romance languages, Italian phonology is conservative, preserving many words nearly unchanged fromVulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Colloquial, Popular, Spoken or Vernacular Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. ''Vulgar Latin'' a ...
. Some examples:
* Italian ' 'fourteen' < Latin (cf. Spanish ', French ' , Catalan and Portuguese )
* Italian ''settimana'' 'week' < Latin (cf. Romanian ''săptămână'', Spanish and Portuguese ''semana'', French ''semaine'' , Catalan ''setmana'')
* Italian ''medesimo'' 'same' < Vulgar Latin * (cf. Spanish ''mismo'', Portuguese ''mesmo'', French ''même'' , Catalan ''mateix''; Italian usually prefers the shorter ''stesso'')
* Italian ''guadagnare'' 'to win, earn, gain' < Vulgar Latin * < Germanic (cf. Spanish ''ganar'', Portuguese ''ganhar'', French ''gagner'' , Catalan ''guanyar'').
The conservative nature of Italian phonology is partly explained by its origin. Italian stems from a literary language that is derived from the 13th-century speech of the city of Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
in the region of Tuscany
Tuscany ( ; ) is a Regions of Italy, region in central Italy with an area of about and a population of 3,660,834 inhabitants as of 2025. The capital city is Florence.
Tuscany is known for its landscapes, history, artistic legacy, and its in ...
, and has changed little in the last 700 years or so. Furthermore, the Tuscan dialect is the most conservative of all Italian dialects, radically different from the Gallo-Italian languages
The Gallo-Italic, Gallo-Italian, Gallo-Cisalpine or simply Cisalpine languages constitute the majority of the Romance languages of northern Italy: Piedmontese, Lombard, Emilian, Ligurian, and Romagnol. In central Italy they are spoken in th ...
less than to the north (across the La Spezia–Rimini Line).
The following are some of the conservative phonological features of Italian, as compared with the common Western Romance languages (French, Spanish, Portuguese, Galician, Catalan). Some of these features are also present in Romanian.
* Little or no phonemic
A phoneme () is any set of similar speech sounds that are perceptually regarded by the speakers of a language as a single basic sound—a smallest possible phonetic unit—that helps distinguish one word from another. All languages con ...
lenition
In linguistics, lenition is a sound change that alters consonants, making them "weaker" in some way. The word ''lenition'' itself means "softening" or "weakening" (from Latin 'weak'). Lenition can happen both synchronically (within a language ...
of consonants between vowels, e.g. > ''vita'' 'life' (cf. Romanian ''viață'', Spanish ''vida'' , French ''vie''), > ''piede'' 'foot' (cf. Spanish ''pie'', French ''pied'' ).
** Words that are an exception to this rule exist, such as: > ''scodella'' 'bowl', > ''ricevere'' 'receive', > ''lago'' 'lake', > ''ago'' 'needle', (only in the Tuscan accent and historical standard Italian) > ''viso'' 'face'.
* Preservation of geminate consonants, e.g. > 'year' (cf. Spanish , French , Romanian , Portuguese ).
* Preservation of all Proto-Romance final vowels, e.g. > 'peace' (cf. Romanian , Spanish , French ), > 'eight' (cf. Romanian , Spanish , French ), > 'I did' (cf. Romanian dialectal , Spanish , French ).
* Preservation of most intertonic vowels (those between the stressed syllable and either the beginning or ending syllable). This accounts for some of the most noticeable differences, as in the forms ''quattordici'' and ''settimana'' given above.
* Slower consonant development, e.g. > Italo-Western > ''foglia'' 'leaf' (cf. Romanian ''foaie'' , Spanish ''hoja'' , French ''feuille'' ; but note Portuguese ''folha'' ).
Compared with most other Romance languages, Italian has many inconsistent outcomes, where the same underlying sound produces different results in different words, e.g. > ''lasciare'' and ''lassare'', > ''cacciare'' and ''cazzare'', > ''sdrucciolare'', ''druzzolare'' and ''ruzzolare'', > ''regina'' and ''reina''. Although in all these examples the second form has fallen out of usage, the dimorphism is thought to reflect the several-hundred-year period during which Italian developed as a literary language divorced from any native-speaking population, with an origin in 12th/13th-century Tuscan but with many words borrowed from languages
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing. Human language is ch ...
farther to the north, with different sound outcomes. (The La Spezia–Rimini Line, the most important isogloss
An isogloss, also called a heterogloss, is the geographic boundary of a certain linguistics, linguistic feature, such as the pronunciation of a vowel, the meaning of a word, or the use of some morphological or syntactic feature. Isoglosses are a ...
in the entire Romance-language area, passes only about north of Florence.) Dual outcomes of Latin between vowels, such as > ''luogo'' but > ''fuoco'', was once thought to be due to borrowing of northern voiced forms, but is now generally viewed as the result of early phonetic variation within Tuscany.
Some other features that distinguish Italian from the Western Romance languages:
* Latin becomes rather than .
* Latin becomes rather than or : > ''otto'' 'eight' (cf. Spanish ''ocho'', French ''huit,'' Portuguese ''oito'').
* Vulgar Latin becomes ''cchi'' rather than : > ''occhio'' 'eye' (cf. Portuguese ''olho'' , French ''œil'' < ); but Romanian ''ochi'' .
* Final is not preserved, and vowel changes rather than are used to mark the plural: ''amico'', ''amici'' 'male friend(s)', ''amica'', ''amiche'' 'female friend(s)' (cf. Romanian ''amic'', ''amici'' and ''amică'', ''amice''; Spanish ''amigo(s)'' 'male friend(s)', ''amiga(s)'' 'female friend(s)'); → ''tre, sei'' 'three, six' (cf. Romanian ''trei'', ''șase''; Spanish ''tres'', ''seis'').
Standard Italian also differs in some respects from most nearby Italian languages:
* Perhaps most noticeable is the total lack of metaphony, although metaphony is a feature characterizing nearly every other Italian language
Italian (, , or , ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family. It evolved from the colloquial Latin of the Roman Empire. Italian is the least divergent language from Latin, together with Sardinian language, Sardinian. It is ...
.
* No simplification of original , (which often became elsewhere).
Assimilation
Italianphonotactics
Phonotactics (from Ancient Greek 'voice, sound' and 'having to do with arranging') is a branch of phonology that deals with restrictions in a language on the permissible combinations of phonemes. Phonotactics defines permissible syllable struc ...
do not usually permit verbs and polysyllabic nouns to end with consonants, except in poetry and song, so foreign words may receive extra terminal vowel sounds.
Writing system
Italian has ashallow orthography
A phonemic orthography is an orthography (system for writing a language) in which the graphemes (written symbols) correspond consistently to the language's phonemes (the smallest units of speech that can differentiate words), or more generally ...
, meaning very regular spelling with an almost one-to-one correspondence between letters and sounds. In linguistic terms, the writing system is close to being a phonemic orthography. The most important of the few exceptions are the following (see below for more details):
* The letter c represents the sound at the end of words and before the letters a, o, and u but represents the sound (as the first sound in the English word ''chair'') before the letters e and i.
* The letter g represents the sound at the end of words and before the letters a, o, and u but represents the sound (as the first sound in the English word ''gem'') before the letters e and i.
* The letter n represents the phoneme , which is pronounced (as in the English word ''sing'') before the letters c and g when these represent velar plosives or , as in ''banco'' , ''fungo'' . The letter q represents pronounced thus n also represents in the position preceding it: ''cinque'' . Elsewhere the letter n represents pronounced , including before the affricate
An affricate is a consonant that begins as a stop and releases as a fricative, generally with the same place of articulation (most often coronal). It is often difficult to decide if a stop and fricative form a single phoneme or a consonant pai ...
s or spelt with c or g before the letters i and e : ''mancia'' , ''mangia'' .
* The letter ''h'' is always silent: ''hotel'' ; ''hanno'' 'they have' and ''anno'' 'year' both represent . It is used to form a digraph with ''c'' or ''g'' to represent or before ''i'' or ''e'': ''chi'' 'who', ''che'' 'what'; ''aghi'' 'needles', ''ghetto'' .
* The spellings ''ci'' and ''gi'' before another vowel represent only or with no /i/ sound (''ciuccio'' 'pacifier', ''Giorgio'' ) unless ''c'' or ''g'' precede stressed (''farmacia'' 'pharmacy', ''biologia'' 'biology'). Elsewhere ''ci'' and ''gi'' represent and followed by : ''cibo'' 'food', ''baci'' 'kisses'; ''gita'' 'trip', ''Tamigi'' 'Thames'.*
The Italian alphabet is typically considered to consist of 21 letters. The letters j, k, w, x, y are traditionally excluded, although they appear in loanwords such as ''jeans'', ''whisky'', ''taxi'',, ''xilofono''. The letter has become common in standard Italian with the prefix ''extra-'', although ''(e)stra-'' is traditionally used; it is also common to use the Latin particle ''ex(-)'' to mean 'former(ly)' as in ''la mia ex'' ('my ex-girlfriend'), "Ex-Jugoslavia" ('Former Yugoslavia'). The letter appears in the first name ''Jacopo'' and in some Italian place-names, such as Bajardo, Bojano
Bojano or Boiano is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Campobasso, Molise, south-central Italy.
History
Originally named Bovianum, it was settled by the 7th century BC. As the capital of the Pentri, a tribe of the Samnites, it played a majo ...
, Joppolo, Jerzu
Jerzu (sardinian language, Sardinian: Jersu), is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Nuoro in the Italy, Italian region Sardinia, located about northeast of Cagliari and about southwest of Tortolì. As of 31 December 2004, it had a pop ...
, Jesolo, Jesi, Ajaccio
Ajaccio (, , ; French language, French: ; or ; , locally: ; ) is the capital and largest city of Corsica, France. It forms a communes of France, French commune, prefecture of the Departments of France, department of Corse-du-Sud, and head o ...
, among others, and in ''Mar Jonio'', an alternative spelling of ''Mar Ionio'' (the Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea (, ; or , ; , ) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including Basilicata, Calabria, Sicily, and the Salento peninsula to the west, ...
). The letter may appear in dialectal words, but its use is discouraged in contemporary standard Italian. Letters used in foreign words can be replaced with phonetically equivalent native Italian letters and digraphs: , , or for ; or for (including in the standard prefix ''kilo-''); , or for ; , , , or for ; and or for .
* The acute accent
The acute accent (), ,
is a diacritic used in many modern written languages with alphabets based on the Latin alphabet, Latin, Cyrillic script, Cyrillic, and Greek alphabet, Greek scripts. For the most commonly encountered uses of the accen ...
is used over word-final to indicate a stressed front close-mid vowel, as in ''perché'' 'why, because'. In dictionaries, it is also used over to indicate a stressed back close-mid vowel (''azióne''). The grave accent
The grave accent () ( or ) is a diacritical mark used to varying degrees in French, Dutch, Portuguese, Italian, Catalan and many other Western European languages as well as for a few unusual uses in English. It is also used in other ...
is used over word-final and to indicate a front open-mid vowel and a back open-mid vowel respectively, as in ''tè'' 'tea', and ''può'' '(he) can'. The grave accent is used over any vowel to indicate word-final stress, as in ''gioventù'' 'youth'. Unlike , which is a ''close''-mid vowel, a stressed final is almost always a back open-mid vowel (''andrò''), with a few exceptions, such as ''metró'', with a stressed final back close-mid vowel, making for the most part unnecessary outside of dictionaries. Most of the time, the penultimate syllable is stressed. But if the stressed vowel is the final letter of the word, the accent is mandatory, otherwise, it is virtually always omitted. Exceptions are typically either in dictionaries, where all or most stressed vowels are commonly marked. Accents can optionally be used to disambiguate words that differ only by stress, as for ''prìncipi'' 'princes' and ''princìpi'' 'principles', or ''àncora'' 'anchor' and ''ancóra'' 'still''/''yet'. For monosyllabic words, the rule is different: when two orthographically identical monosyllabic words with different meanings exist, one is accented and the other is not (example: ''è'' 'is', ''e'' 'and').
* The letter distinguishes ''ho'', ''hai'', ''ha'', ''hanno'' (present indicative of ''avere'' 'to have') from ''o'' ('or'), ''ai'' ('to the'), ''a'' ('to'), ''anno'' ('year'). In the spoken language, the letter is always silent. The in ''ho'' additionally marks the contrasting open pronunciation of the . The letter is also used in combinations with other letters. No phoneme
A phoneme () is any set of similar Phone (phonetics), speech sounds that are perceptually regarded by the speakers of a language as a single basic sound—a smallest possible Phonetics, phonetic unit—that helps distinguish one word fr ...
exists in Italian. In nativized foreign words, the is silent. For example, ''hotel'' and ''hovercraft'' are pronounced and respectively. (Where existed in Latin, it either disappeared or, in a few cases before a back vowel, changed to : ''traggo'' 'I pull' ← Lat. .)
* The letters and can symbolize voiced
Voice or voicing is a term used in phonetics and phonology to characterize speech sounds (usually consonants). Speech sounds can be described as either voiceless (otherwise known as ''unvoiced'') or voiced.
The term, however, is used to refe ...
or voiceless
In linguistics, voicelessness is the property of sounds being pronounced without the larynx vibrating. Phonologically, it is a type of phonation, which contrasts with other states of the larynx, but some object that the word phonation implies v ...
consonants. symbolizes or depending on context, with few minimal pairs. For example: ''zanzara'' 'mosquito' and ''nazione'' 'nation'. symbolizes word-initially before a vowel, when clustered with a voiceless consonant (), and when doubled; it symbolizes when between vowels and when clustered with voiced consonants. Intervocalic varies regionally between and , with being more dominant in northern Italy and in the south.
* The letters and vary in pronunciation between plosives and affricates depending on following vowels. The letter symbolizes when word-final and before the back vowels . It symbolizes as in ''chair'' before the front vowels . The letter symbolizes when word-final and before the back vowels . It symbolizes as in ''gem'' before the front vowels . Other Romance languages and, to an extent, English have similar variations for . Compare hard and soft C
In the Latin-based orthographies of many European languages, including English, a distinction between hard and soft occurs in which represents two distinct phonemes. The sound of a hard often precedes the non-front vowels , and , and is th ...
, hard and soft G. (See also palatalization.)
* The digraphs and indicate ( and ) before . The digraphs and indicate 'softness' ( and , the affricate consonant
An affricate is a consonant that begins as a stop and releases as a fricative, generally with the same place of articulation (most often coronal). It is often difficult to decide if a stop and fricative form a single phoneme or a consonant pai ...
s of English ''church'' and ''judge'') before . For example:
:
:Note: is silent in the digraphs '' '', '' ''; and is silent in the digraphs and before unless the is stressed. For example, it is silent in '' ciao'' and cielo , but it is pronounced in ''farmacia'' and ''farmacie'' .
Italian has geminate, or double, consonants, which are distinguished by length
Length is a measure of distance. In the International System of Quantities, length is a quantity with Dimension (physical quantity), dimension distance. In most systems of measurement a Base unit (measurement), base unit for length is chosen, ...
and intensity. Length is distinctive for all consonants except for , , , , , which are always geminate when between vowels, and , which is always single.
Geminate plosives and affricates are realized as lengthened closures. Geminate fricatives, nasals, and are realized as lengthened continuant
In phonetics
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that studies how humans produce and perceive sounds or, in the case of sign languages, the equivalent aspects of sign. Linguists who specialize in studying the physical properties of speech ...
s. There is only one vibrant phoneme but the actual pronunciation depends on the context and regional accent. Generally one can find a flap consonant in an unstressed position whereas is more common in stressed syllables, but there may be exceptions. Especially people from the northern part of Italy (Parma
Parma (; ) is a city in the northern Italian region of Emilia-Romagna known for its architecture, Giuseppe Verdi, music, art, prosciutto (ham), Parmesan, cheese and surrounding countryside. With a population of 198,986 inhabitants as of 2025, ...
, Aosta Valley, South Tyrol
South Tyrol ( , ; ; ), officially the Autonomous Province of Bolzano – South Tyrol, is an autonomous administrative division, autonomous provinces of Italy, province in northern Italy. Together with Trentino, South Tyrol forms the autonomo ...
) may pronounce as , , or .
Of special interest to the linguistic study of Regional Italian
Regional Italian (, ) is any regional"Regional" in the broad sense of the word; not to be confused with the Italian endonym , for Italy's administrative units. variety of the Italian language.
Such vernacular varieties and standard Italian exi ...
is the '' gorgia toscana'', or "Tuscan throat", the weakening or lenition
In linguistics, lenition is a sound change that alters consonants, making them "weaker" in some way. The word ''lenition'' itself means "softening" or "weakening" (from Latin 'weak'). Lenition can happen both synchronically (within a language ...
of intervocalic , , and in the Tuscan language.
The voiced postalveolar fricative is present as a phoneme only in loanwords: for example, ''garage'' . Phonetic is common in central and southern Italy as an intervocalic allophone of : ''gente'' 'people' but ''la gente'' 'the people', ''ragione'' 'reason'.
Grammar
Italiangrammar
In linguistics, grammar is the set of rules for how a natural language is structured, as demonstrated by its speakers or writers. Grammar rules may concern the use of clauses, phrases, and words. The term may also refer to the study of such rul ...
is typical of the grammar of Romance languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
in general. Cases exist for personal pronouns (nominative
In grammar, the nominative case ( abbreviated ), subjective case, straight case, or upright case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb, or (in Latin and formal variants of E ...
, oblique, accusative, dative), but not for nouns.
There are two basic classes of nouns in Italian, referred to as genders, masculine and feminine. Gender may be natural (''ragazzo'' 'boy', ''ragazza'' 'girl') or simply grammatical with no possible reference to biological gender (masculine ''costo'' 'cost', feminine ''costa'' 'coast'). Masculine nouns typically end in ''-o'' (''ragazzo'' 'boy'), with plural marked by ''-i'' (''ragazzi'' 'boys'), and feminine nouns typically end in ''-a'', with plural marked by ''-e'' (''ragazza'' 'girl', ''ragazze'' 'girls'). For a group composed of boys and girls, ''ragazzi'' is the plural, suggesting that ''-i'' is a general neutral plural. A third category of nouns is unmarked
In linguistics and social sciences, markedness is the state of standing out as nontypical or divergent as opposed to regular or common. In a marked–unmarked relation, one term of an opposition is the broader, dominant one. The dominant defau ...
for gender, ending in ''-e'' in the singular and ''-i'' in the plural: ''legge'' 'law, f. sg.', ''leggi'' 'laws, f. pl.'; ''fiume'' 'river, m. sg.', ''fiumi'' 'rivers, m. pl.', thus assignment of gender is arbitrary in terms of form, enough so that terms may be identical but of distinct genders: ''fine'' meaning 'aim', 'purpose' is masculine, while ''fine'' meaning 'end, ending' (e.g. of a movie) is feminine, and both are ''fini'' in the plural, a clear instance of ''-i'' as a non-gendered default plural marker. These nouns often, but not always, denote inanimates. There are a number of nouns that have a masculine singular and a feminine plural, most commonly of the pattern m. sg. ''-o'', f. pl. ''-a'' (''miglio'' 'mile, m. sg.', ''miglia'' 'miles, f. pl.'; ''paio'' 'pair, m. sg.', ''paia'' 'pairs, f. pl.'), and thus are sometimes considered neuter (these are usually derived from neuter Latin nouns). An instance of neuter gender also exists in pronouns of the third person singular.
Examples:
Nouns, adjectives, and articles inflect
In linguistic morphology, inflection (less commonly, inflexion) is a process of word formation in which a word is modified to express different grammatical categories such as tense, case, voice, aspect, person, number, gender, mood, a ...
for gender and number (singular and plural).
Like in English, common nouns are capitalized when occurring at the beginning of a sentence. Unlike English, nouns referring to languages (e.g. Italian) and adjectives pertaining to ethnicity are never capitalized, while speakers of languages, or inhabitants of an area (e.g. Italians) used to always be capitalized, but, starting from the 19th century, this convention has been subject to various changes.
There are three types of adjective
An adjective (abbreviations, abbreviated ) is a word that describes or defines a noun or noun phrase. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun.
Traditionally, adjectives are considered one of the main part of speech, parts of ...
s: descriptive, invariable and form-changing. Descriptive adjectives are the most common, and their endings change to match the number and gender of the noun they modify. Invariable adjectives are adjectives whose endings do not change. The form-changing adjectives ''buono'' 'good', ''bello'' 'beautiful', ''grande'' 'big', and ''santo'' 'saint/holy' change in form when placed before different types of nouns. Italian has three degrees for comparison of adjectives: positive, comparative, and superlative.
The order of words in the phrase is relatively free compared to most European languages. The position of the verb in the phrase is highly mobile. Word order often has a lesser grammatical function in Italian than in English. Adjectives are sometimes placed before their noun and sometimes after. Subject nouns generally come before the verb. Italian is a null-subject language, so nominative pronouns are usually absent, with subject indicated by verbal inflection
In linguistic Morphology (linguistics), morphology, inflection (less commonly, inflexion) is a process of word formation in which a word is modified to express different grammatical category, grammatical categories such as grammatical tense, ...
s (e.g. ''amo'' 'I love', ''ama'' '(s)he loves', ''amano'' 'they love'). Noun objects normally come after the verb, as do pronoun objects after imperative verbs, infinitives and gerunds, but otherwise, pronoun objects come before the verb.
There are both indefinite and definite articles in Italian. There are four indefinite articles, selected by the gender of the noun they modify and by the phonological structure of the word that immediately follows the article. ''Uno'' is masculine singular, used before ''z'' ( or ), ''s+consonant'', ''gn'' (), ''pn'' or ''ps'', while masculine singular ''un'' is used before a word beginning with any other sound. The noun ''zio'' 'uncle' selects masculine singular, thus ''uno zio'' 'an uncle' or ''uno zio anziano'' 'an old uncle,' but ''un mio zio'' 'an uncle of mine'. The feminine singular indefinite articles are ''una'', used before any consonant sound, and its abbreviated form, written ''un','' used before vowels: ''una camicia'' 'a shirt', ''una camicia bianca'' 'a white shirt', ''un'altra camicia'' 'a different shirt'. There are seven forms for definite articles, both singular and plural. In the singular: ''lo'', which corresponds to the uses of ''uno''; ''il'', which corresponds to the uses with the consonant of ''un''; ''la,'' which corresponds to the uses of ''una''; ''l','' used for both masculine and feminine singular before vowels. In the plural: ''gli'' is the masculine plural of ''lo and lpreposition
Adpositions are a part of speech, class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in, under, towards, behind, ago'', etc.) or mark various thematic relations, semantic roles (''of, for''). The most common adpositions are prepositi ...
s with subsequent articles. There are numerous productive suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns and adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can ca ...
es for diminutive
A diminutive is a word obtained by modifying a root word to convey a slighter degree of its root meaning, either to convey the smallness of the object or quality named, or to convey a sense of intimacy or endearment, and sometimes to belittle s ...
, augmentative
An augmentative (abbreviated ) is a morphological form of a word which expresses greater intensity, often in size but also in other attributes. It is the opposite of a diminutive.
Overaugmenting something often makes it grotesque and so in so ...
, pejorative, attenuating, etc., which are also used to create neologism
In linguistics, a neologism (; also known as a coinage) is any newly formed word, term, or phrase that has achieved popular or institutional recognition and is becoming accepted into mainstream language. Most definitively, a word can be considered ...
s.
There are 27 pronouns, grouped in clitic
In morphology and syntax, a clitic ( , backformed from Greek "leaning" or "enclitic"Crystal, David. ''A First Dictionary of Linguistics and Phonetics''. Boulder, CO: Westview, 1980. Print.) is a morpheme that has syntactic characteristics of a ...
and tonic pronouns. Personal pronouns are separated into three groups: subject, object (which takes the place of both direct and indirect objects), and reflexive. Second-person subject pronouns have both a polite and a familiar form. These two different types of addresses are very important in Italian social distinctions. All object pronouns have two forms: stressed and unstressed (clitics). Unstressed object pronouns are much more frequently used, and come before a verb conjugated for subject-verb (''la vedi'': 'you see her'), after (in writing, attached to) non-conjugated verbs (''vedendola'': 'seeing her'). Stressed object pronouns come after the verb, and are used when the emphasis is required, for contrast, or to avoid ambiguity (''vedo lui, ma non lei'': 'I see him, but not her'). Aside from personal pronouns, Italian also has demonstrative, interrogative, possessive, and relative pronouns. There are two types of demonstrative pronouns: relatively near (this) and relatively far (that); there exists a third type of demonstrative denoting vicinity only to the listener, but it has fallen out of use. Demonstratives in Italian are repeated before each noun, unlike in English.
There are three regular sets of verbal conjugations, and various verbs are irregularly conjugated. Within each of these sets of conjugations, there are four simple (one-word) verbal conjugations by person/number in the indicative mood
A realis mood ( abbreviated ) is a grammatical mood which is used principally to indicate that something is a statement of fact; in other words, to express what the speaker considers to be a known state of affairs, as in declarative sentences. Mo ...
( present tense; past tense
The past tense is a grammatical tense whose function is to place an action or situation in the past. Examples of verbs in the past tense include the English verbs ''sang'', ''went'' and ''washed''. Most languages have a past tense, with some hav ...
with imperfective aspect, past tense with perfective aspect
The perfective aspect ( abbreviated ), sometimes called the aoristic aspect, is a grammatical aspect that describes an action viewed as a simple whole, i.e., a unit without interior composition. The perfective aspect is distinguished from the ...
, and future tense
In grammar, a future tense ( abbreviated ) is a verb form that generally marks the event described by the verb as not having happened yet, but expected to happen in the future. An example of a future tense form is the French ''achètera'', mea ...
), two simple conjugations in the subjunctive mood
The subjunctive (also known as the conjunctive in some languages) is a grammatical mood, a feature of an utterance that indicates the speaker's attitude toward it. Subjunctive forms of verbs are typically used to express various states of unreali ...
(present tense and past tense), one simple conjugation in the conditional mood
The conditional mood (abbreviated ) is a grammatical mood used in conditional sentences to express a proposition whose validity is dependent on some condition, possibly counterfactual.
It may refer to a distinct verb form that expresses the condit ...
, and one simple conjugation in the imperative mood
The imperative mood is a grammatical mood that forms a command or request.
The imperative mood is used to demand or require that an action be performed. It is usually found only in the present tense, second person. They are sometimes called ' ...
. Corresponding to each of the simple conjugations, there is a compound conjugation involving a simple conjugation of "to be" or "to have" followed by a past participle
In linguistics, a participle (; abbr. ) is a nonfinite verb form that has some of the characteristics and functions of both verbs and adjectives. More narrowly, ''participle'' has been defined as "a word derived from a verb and used as an adject ...
. "To have" is used to form compound conjugation when the verb is transitive (''ha detto, ha fatto'': 'he/she has said, he/she has made/done'), while "to be" is used in the case of verbs of motion and some other intransitive verbs (''è andato, è stato'': 'he has gone, he has been'). "To be" may be used with transitive verbs, but in such a case it makes the verb passive (''è detto, è fatto'': 'it is said, it is made/done'). This rule is not absolute, and some exceptions do exist.
Words
Conversation
Note: the plural form of verbs could also be used as an extremely formal (for example to noble people in monarchies) singular form (seeroyal we
The royal ''we'', majestic plural (), or royal plural, is the use of a plural pronoun (or corresponding plural-inflected verb forms) used by a single person who is a monarch or holds a high office to refer to themself. A more general term fo ...
).
Question words
Time
Numbers
Days of the week
Months of the year
Example text
Article 1 of theUniversal Declaration of Human Rights
The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the Human rights, rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN Drafting of the Universal D ...
in Italian:
: ''Tutti gli esseri umani nascono liberi ed eguali in dignità e diritti. Essi sono dotati di ragione e di coscienza e devono agire gli uni verso gli altri in spirito di fratellanza.''
Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights in English:
: ''All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.''
International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standard written representation ...
transcription:
: [ˈtut.ti‿ʎ.ʎ‿ˈɛs.seri̯‿uˈmaːni ˈnaskono ˈliːberi e.d‿eˈgwaːli̯‿in diɲ.ɲiˈta e‿diˈrit.ti ‖ ˈɛs.si ˈsoːno doˈtaːti di raˈd͡ʒoːn‿e‿di koʃˈʃɛnt͡sa e‿ˈdɛːvono aˈd͡ʒiːre‿ʎ.ʎ‿ˈuːni ˈvɛr.so‿ʎ.ʎ‿ˈaltri̯‿in ˈspiːrito di fratelˈlant͡sa ‖]
Nobel Prizes for Italian language literature
See also
* Languages of Italy (includes "Italian dialects", ) * CELI * CILS (Qualification) * Italian alphabet *Regional Italian
Regional Italian (, ) is any regional"Regional" in the broad sense of the word; not to be confused with the Italian endonym , for Italy's administrative units. variety of the Italian language.
Such vernacular varieties and standard Italian exi ...
* Italian exonyms
* Italian grammar
* Italian honorifics
* List of countries and territories where Italian is an official language
* The Italian Language Foundation
The Italian Language Foundation (ILF) was established on July 3, 2008, to promote and support Italian language education in the United States and specifically to reinstate the Advanced Placement program (AP) of the College Board for Advanced Placem ...
(in the United States)
* Italian language in Brazil
* Italian language in Croatia
* Italian language in Slovenia
* Italian language in the United States
* Italian language in Venezuela
* Italian literature
* Italian musical terms
* Italian phonology
* Italian profanity
* Italian Sign Language
Italian Sign Language (, LIS) is the visual language used by deaf people in Italy. Deep analysis of it began in the 1980s, along the lines of William Stokoe's research on American Sign Language in the 1960s. Until the beginning of the 21st cen ...
* Italian Studies
* Italian-language international radio stations
* '' Lessico etimologico italiano''
* Sicilian School
* Veronese Riddle
* Languages of the Vatican City
* Talian
* List of English words of Italian origin
* List of Italian musical terms used in English
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * M. Vitale, ''Studi di Storia della Lingua Italiana'', LED Edizioni Universitarie, Milano, 1992, * S. Morgana, ''Capitoli di Storia Linguistica Italiana'', LED Edizioni Universitarie, Milano, 2003, * J. Kinder, ''CLIC: Cultura e Lingua d'Italia in CD-ROM / Culture and Language of Italy on CD-ROM'', Interlinea, Novara, 2008, * (with a similar list of other Italian-modern languages dictionaries)External links
Accademia della Crusca
*
Treccani
Il Nuovo De Mauro
* Italian proverbs *
Learn Italian
,
BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
* Swadesh list in English and Italian
Xeno Italia
at ''Omniglot'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Italian Language Fusional languages Languages attested from the 10th century Languages of Italy Languages of Monaco Languages of San Marino Languages of Sicily Languages of Switzerland Languages of Vatican City Languages of Slovenia Languages of Croatia Subject–verb–object languages Syllable-timed languages