Spring Campaign on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Spring CampaignIstván Lázár, An illustrated history of Hungary, Corvina, 1999, p. 90, (), named also the ''Glorious Spring Campaign''Tarján Tamás
1849. április 26. , A komáromi csata
Rubicon () is the military campaign of the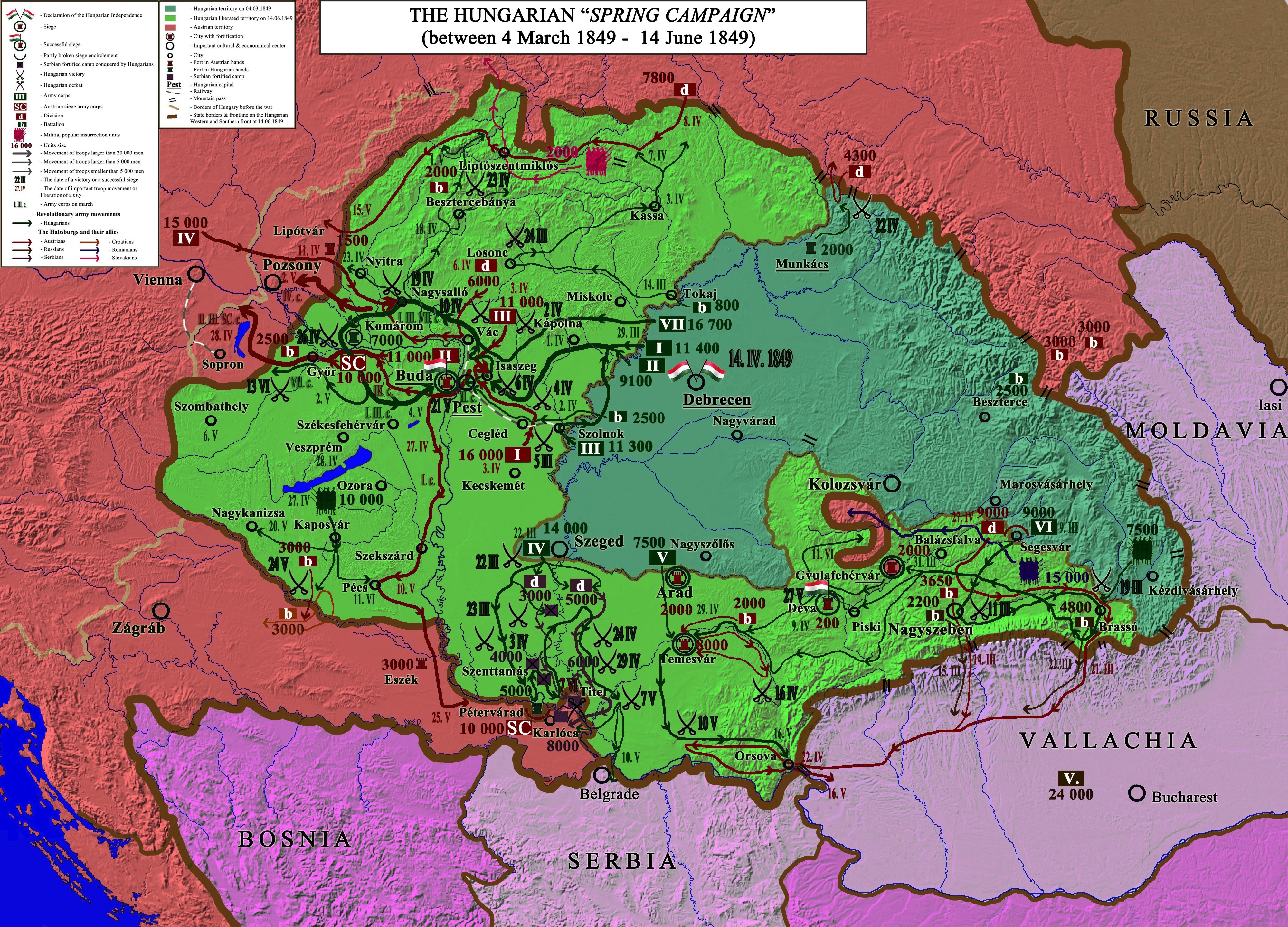 The spring campaign's commander-in-chief was General Artúr Görgey, whose army (47 500 men, 198 cannons) defeated the numerically, technologically and tactically superior (55 000 soldiers and 214 cannons and rockets) imperial armies led by
The spring campaign's commander-in-chief was General Artúr Görgey, whose army (47 500 men, 198 cannons) defeated the numerically, technologically and tactically superior (55 000 soldiers and 214 cannons and rockets) imperial armies led by
Video animation showing the Spring Campaign's main military operations on the map
Military history of Hungary Military campaigns Battles of the Hungarian Revolution of 1848
1849. április 26. , A komáromi csata
Rubicon () is the military campaign of the
Hungarian Revolutionary Army
The Hungarian Defence Forces (, ) is the national defence force of Hungary. Since 2007, the Hungarian Armed Forces has been under a unified command structure. The Ministry of Defence maintains political and civil control over the army. A subordi ...
against the forces of the Habsburg Empire
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
in Middle and Western Hungary during the Hungarian Revolution of 1848
The Hungarian Revolution of 1848, also known in Hungary as Hungarian Revolution and War of Independence of 1848–1849 () was one of many Revolutions of 1848, European Revolutions of 1848 and was closely linked to other revolutions of 1848 in ...
between 2 April and 21 May 1849, which resulted in the liberation of almost the whole territory of Hungary from the Habsburg forces.
 The spring campaign's commander-in-chief was General Artúr Görgey, whose army (47 500 men, 198 cannons) defeated the numerically, technologically and tactically superior (55 000 soldiers and 214 cannons and rockets) imperial armies led by
The spring campaign's commander-in-chief was General Artúr Görgey, whose army (47 500 men, 198 cannons) defeated the numerically, technologically and tactically superior (55 000 soldiers and 214 cannons and rockets) imperial armies led by Alfred I, Prince of Windisch-Grätz
General Alfred Candidus Ferdinand, Prince of Windischgrätz (; 11 May 178721 March 1862), a member of an old Austro- Bohemian House of Windischgrätz, was a Field Marshal in the Austrian army. He is most noted for his service during the Napo ...
and after his dismissal, Ludwig von Welden, in a series of victories. The Hungarians won the battles of Hatvan
Hatvan ( German: ''Hottwan)'' is a town in Heves County, Hungary. Hatvan is the Hungarian word for "sixty". It is the county's third most populous town following Eger and Gyöngyös.
Etymology
Hatvan is the Hungarian word for "sixty". It is a com ...
(2 April), Tápióbicske (4 April), Isaszeg (6 April), Vác
Vác (; ; ; ) is a thousand-year old city in Pest county in Hungary with approximately 35,000 inhabitants. The archaic spelling of the name is ''Vácz''.
Location
Vác is located north of Budapest on the eastern bank of the Danube river, below t ...
(10 April), Nagysalló (19 April), on 26 April relieved the fortress of Komárom from a long Austrian siege, then on 21 May 1849 liberated the Castle of Buda, concluding the Spring Campaign.
On the other theaters of operations, the Hungarians also scored victories against the enemies of the revolution.
In Transylvania, the Hungarian army led by Józef Bem
Józef Zachariasz Bem (, ; 14 March 1794 – 10 December 1850) was a Polish engineer and general, an Ottoman pasha and a national hero of Poland and Hungary, and a figure intertwined with other European patriotic movements. Like Tadeusz Kościus ...
, after the victory against the Austro-Russian forces in the Battle of Nagyszeben from 11 March, liberated most of the provinces territory (excepting the fortresses of Gyulafehérvár, Déva, with imperial garrison and the Erdélyi-középhegység mountains, held by the Romanian insurgents).
In southern Hungary the Hungarians led by Mór Perczel and Józef Bem defeated the Serbian insurgents and Austrian troops, liberating the provinces of Bácska and Bánság, except the fortress of Temesvár and Titel
Titel ( sr-Cyrl, Тител, ) is a town and municipality located in the South Bačka District of the province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The town of Titel has a population of 4,522, while the population of the municipality of Titel is 13,984 (2022 ...
.
In southern Transdanubia
Transdanubia ( ; , or ', ) is a traditional region of Hungary. It is also referred to as Hungarian Pannonia, or Pannonian Hungary.
Administrative divisions Traditional interpretation
The borders of Transdanubia are the Danube River (north and ...
, the popular uprising led by Gáspár Noszlopy also led to the liberation of this region from imperial occupation.
During the Spring Campaign, the Hungarians liberated much of their country from Habsburg rule. The Habsburg armies and their allies, besides the fortresses and mountains mentioned above, remained only in the westernmost territory strip of Hungary, Croatia and the fortress of Arad. Also the result of the victories of the Spring Campaign was the Hungarian Declaration of Independence on 14 April 1849, resulting in total Hungarian independence for some months before the Russian intervention brought the defeat of the Hungarian revolution and war of independence in the Summer Campaign
Summer or summertime is the hottest and brightest of the four temperate seasons, occurring after spring and before autumn. At or centred on the summer solstice, daylight hours are the longest and darkness hours are the shortest, with day ...
.
References
External links
*{{in lang, huVideo animation showing the Spring Campaign's main military operations on the map
Military history of Hungary Military campaigns Battles of the Hungarian Revolution of 1848