Split and merge segmentation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Split and merge segmentation is an
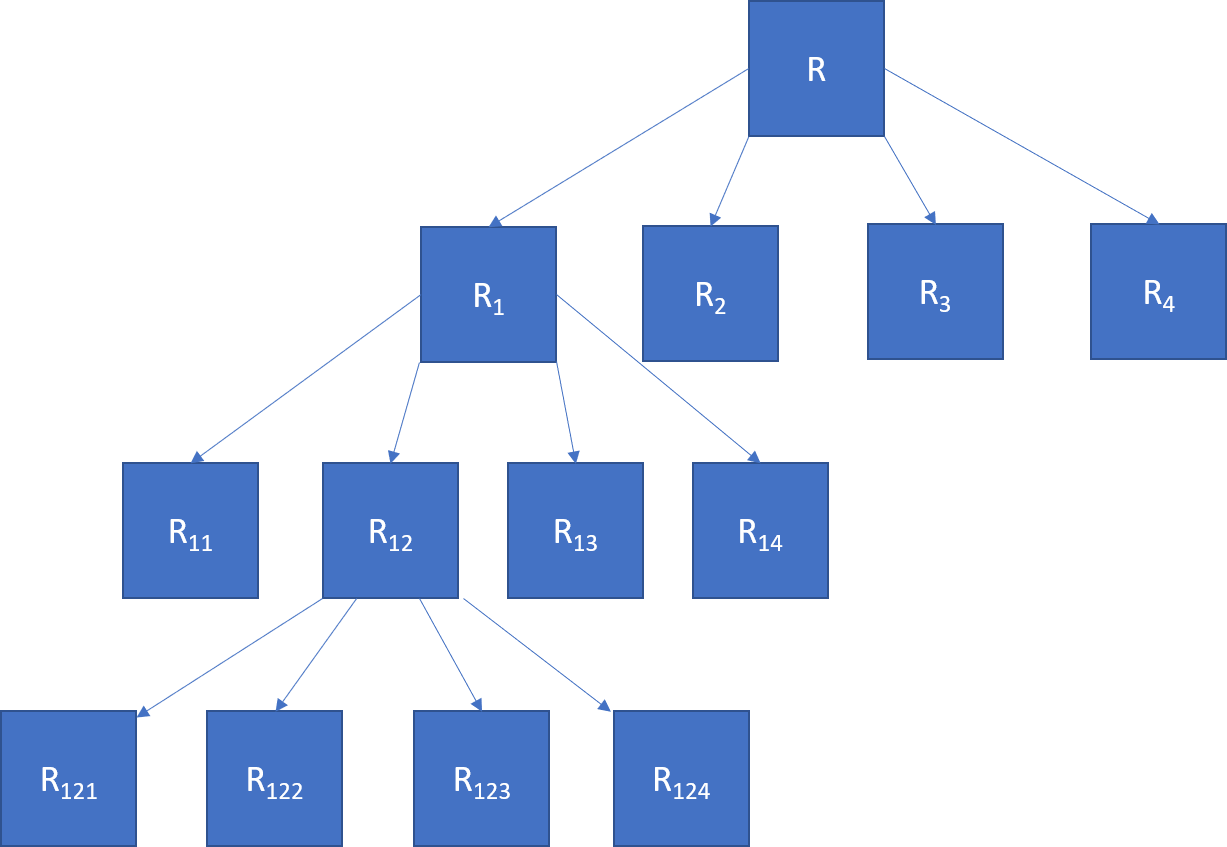
 Each level of partitioning can be represented in a tree-like structure.
Each level of partitioning can be represented in a tree-like structure.
 The blocks created during splitting are shown in the following picture:
The blocks created during splitting are shown in the following picture:
 And the segmented image is below.
And the segmented image is below.

image processing
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensiona ...
technique used to segment an image
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensiona ...
. The image is successively split into quadrants based on a homogeneity
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts often used in the sciences and statistics relating to the uniformity of a substance or organism. A material or image that is homogeneous is uniform in composition or character (i.e. color, shape, siz ...
criterion and similar regions are merged to create the segmented result. The technique incorporates a quadtree
A quadtree is a tree data structure in which each internal node has exactly four children. Quadtrees are the two-dimensional analog of octrees and are most often used to partition a two-dimensional space by recursively subdividing it into four q ...
data structure, meaning that there is a parent-child node relationship. The total region is a parent, and each of the four splits is a child.
Algorithm
* Define the criterion to be used for homogeneity * Split the image into equal size regions * Calculate homogeneity for each region * If the region is homogeneous, then merge it with neighbors * The process is repeated until all regions pass the homogeneity testHomogeneity
After each split, a test is necessary to determine whether each new region needs further splitting. The criterion for the test is the homogeneity of the region. There are several ways to define homogeneity, some examples are: * Uniformity- the region is homogeneous if its gray scale levels are constant or within a given threshold. * Local mean vs global mean - if the mean of a region is greater than the mean of the global image, then the region is homogeneous * Variance - thegray level
In digital photography, computer-generated imagery, and colorimetry, a grayscale image is one in which the value of each pixel is a single sample representing only an ''amount'' of light; that is, it carries only intensity information. Grayscal ...
variance is defined as
where r and c are row and column, N is the number of pixels in the region and
An example incorporation would be that the variance of a region be less than a specified value in order to be considered homogeneous.
Data structure
The splitting results in a partitioned image as shown below to 3 levels. Each level of partitioning can be represented in a tree-like structure.
Each level of partitioning can be represented in a tree-like structure.

Example
The following example shows the segmentation of a gray scale image using matlab.{{Cite web, url=https://www.mathworks.com/help/images/ref/qtdecomp.html?s_tid=srchtitle, title=Quadtree decomposition - MATLAB qtdecomp, website=www.mathworks.com, access-date=2018-04-24 The homogeneity criterion is thresholding, max(region)-min(region) < 10 for a region to be homogeneous. The blocks created during splitting are shown in the following picture:
The blocks created during splitting are shown in the following picture:
 And the segmented image is below.
And the segmented image is below.

References