Spinning Mirror System on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Spinning mirror systems are used to build interactive
Spinning mirror systems are used to build interactive

 In this section we describe how to render a scene to the
In this section we describe how to render a scene to the
 In advance of that, we have implemented a two-channel field-sequential color system using a two-sided tent-shaped diffusing mirror. For each side of the tent, we place a color filter between the holographic diffusing film and the first-surface mirror, which avoids introducing specular first-surface reflections. We chose a cyan filter for one side and an orange filter for the other, dividing the
In advance of that, we have implemented a two-channel field-sequential color system using a two-sided tent-shaped diffusing mirror. For each side of the tent, we place a color filter between the holographic diffusing film and the first-surface mirror, which avoids introducing specular first-surface reflections. We chose a cyan filter for one side and an orange filter for the other, dividing the
Video depicting a spinning mirror system �
Type of Display obtained thanks to the described technology �
Article about the use of the system in 3D Teleconferencing �
Paper about spinning mirror systems {{DEFAULTSORT:Spinning Mirror System Stereoscopy
3D graphics
3D computer graphics, or “3D graphics,” sometimes called CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional computer graphics are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian) that is stored in the computer for th ...
and autostereoscopic
Autostereoscopy is any method of displaying stereoscopic images (adding binocular perception of 3D depth) without the use of special headgear, glasses, something that affects vision, or anything for eyes on the part of the viewer. Because headg ...
visuals visible to multiple simultaneous viewers, since a different view can be perceived by each viewer depending on the angle of vision.
Because these mirrors spin, they can reflect light from a projector to any outside point. Therefore, such systems can create omnidirectional projections. Because light is reflected directly from the projector to the audience and not projected onto a fixed plane, spinning mirror systems create a correct interpretation of the field of light The Field of Light is a large-scale site-specific light-based installation created by British artist Bruce Munro.
The sculpture slowly changes colour, creating a shimmering field of light.
History
Field of Light was originally conceived in 19 ...
regardless of a spectator's position relative to the system.
Because such systems are tied to a high speed video projector, the system's maximum resolution of unique angles is limited by the projector's maximum framerate.
A similar system was commercially released in 1981 for the Entex Adventure Vision
Adventure Vision is a cartridge-based video game console released by Entex Industries in either August or October 1982. The launch price of the system was $79.95. The monitor, game controls, and computer hardware are all contained within a sing ...
game console. The console, however, didn't aim for 3D visualization, but instead used the spinning mirror to project a 2D picture from a row of LEDs.
Motivation
Previous volumetric systems projected the images in a diffuse plane of rotation, thus, the light was remaining dispersed in all directions. Unfortunately, these displays could not recreate dependent effects such asocclusion
Occlusion may refer to:
Health and fitness
* Occlusion (dentistry), the manner in which the upper and lower teeth come together when the mouth is closed
* Occlusion miliaria, a skin condition
* Occlusive dressing, an air- and water-tight trauma ...
. This produced the need to create a system that was capable of settling misadventures as this one, but in turn, it had an easy implementation and was doing that his installation on systems was simple. Thus, create a system of gyratory mirrors covered by a holographic diffuser anisotropic.
Functioning
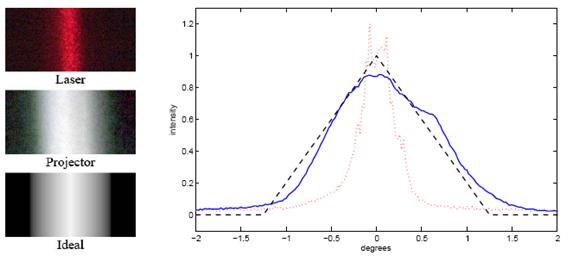
The mirrored surface reflects each projector pixel to a narrow range of viewpoints. The holographic diffuser provides control over the width and height of this region. The characteristics of the diffuser are such that the relative diffusion between x and y is approximately 1:200. Horizontally, the surface is sharplyspecular
Specular reflection, or regular reflection, is the mirror-like reflection of waves, such as light, from a surface.
The law of reflection states that a reflected ray of light emerges from the reflecting surface at the same angle to the surf ...
to maintain a 1.25-degree separation between views. Vertically, the mirror scatters widely so the projected image can be viewed from essentially any height.
The horizontal profile of the specular lobe approximates a bilinear interpolation
In mathematics, bilinear interpolation is a method for interpolating functions of two variables (e.g., ''x'' and ''y'') using repeated linear interpolation. It is usually applied to functions sampled on a 2D rectilinear grid, though it can be ge ...
between adjacent viewpoints; the motion of the mirror adds some additional blur which improves the reproduction of halftoned imagery at the expense of angular resolution
Angular resolution describes the ability of any image-forming device such as an Optical telescope, optical or radio telescope, a microscope, a camera, or an Human eye, eye, to distinguish small details of an object, thereby making it a major det ...
.
Montage
The anisotropic holographic diffuser and mirror assembly are mounted on acarbon fiber
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (American English), carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers (Commonwealth English), carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic (CFRP, CRP, CFRTP), also known as carbon fiber, carbon compo ...
panel and attached to an aluminum flywheel
A flywheel is a mechanical device which uses the conservation of angular momentum to store rotational energy; a form of kinetic energy proportional to the product of its moment of inertia and the square of its rotational speed. In particular, assu ...
at 45°. The flywheel spins synchronously relative to the images displayed by the projector.
Synchronization in a system
Because the outputframe rate
Frame rate (expressed in or FPS) is the frequency (rate) at which consecutive images ( frames) are captured or displayed. The term applies equally to film and video cameras, computer graphics, and motion capture systems. Frame rate may also ...
of the PC graphics card is relatively constant and cannot be fine-tuned on the fly, The PC video output rate is used as the master signal for system synchronization. The projector's FPGA also creates signals encoding the current frame rate. These control signals interface directly to an Animatics SM3420D ”Smart Motor" which contains firmware and motion control parameters resulting in a stable, velocity-based control loop that ensures the motor velocity stays in sync with the signals from the projector.
Projection of graphs on the screen
3D display
A 3D display is a display device capable of conveying depth to the viewer. Many 3D displays are stereoscopic displays, which produce a basic 3D effect by means of stereopsis, but can cause eye strain and visual fatigue. Newer 3D displays such ...
with correct perspective, using either scanline rendering
Scanline rendering (also scan line rendering and scan-line rendering) is an algorithm for visible surface determination, in 3D computer graphics, that works on a row-by-row basis rather than a polygon-by-polygon or pixel-by-pixel basis. All of t ...
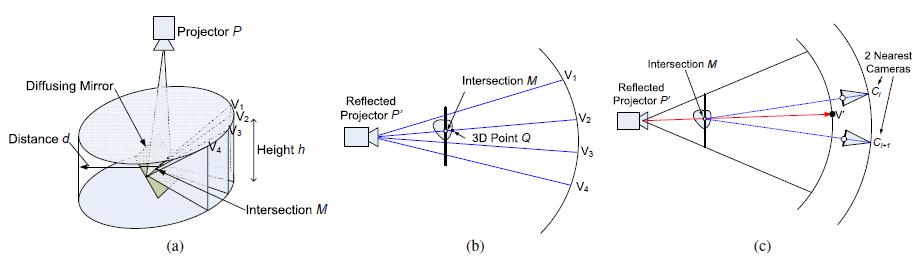
or ray tracing. We assume that the spinning mirror is centered at the origin and that its axis of rotation is the vertical y-axis, with the video projector
A video projector is an image projector that receives a video signal and projects the corresponding image on a projection screen using a lens system. Video projectors use a very bright ultra-high-performance lamp (a special mercury arc lamp), ...
at the nodal point P above the mirror as in top figure. We further assume that the viewpoint for which the correct perspective should be obtained is at a height h and a distance d from the y axis.
By the rotation
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional ...
al symmetry of our system, we can produce perspective-correct imagery for any viewing position on the circle V defined by h and d, yielding binocular
Binocular may refer to:
Science and technology
* Binocular vision, seeing with two eyes
* Binoculars, a telescopic tool
* Binocular microscope, binocular viewing of objects through a single objective lens
Other uses
* Binocular (horse), a thoroug ...
images for a viewer facing the display since h and d will be similar for both eyes. We denote a particular viewpoint on the circle V as V'. In practice, the set of perspective-correct viewpoints V need not be a continuous planar circle and can pass through a variety of tracked viewer positions at different distances and heights.
Double spinning mirror system
visible spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called ''visible light'' or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wav ...
approximately evenly into short and long wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tr ...
s.
We convert RGB colors to Orange-Cyan colors by projecting the linear RGB vector onto the plane spanned by the Orange and Cyan colors.
To render in color, we calibrate each plane of the tent mirror independently as in Section 5. Then, we render the 3D scene twice for each sub-frame, once for the orange side and once for the cyan side, and the calibration process ensures that each side is rendered toward the appropriate set of viewpoints. The effect for the viewer is similar to the Kinemacolor
Kinemacolor was the first successful colour motion picture process, used commercially from 1908 to 1914. It was invented by George Albert Smith in 1906. He was influenced by the work of William Norman Lascelles Davidson and, more directly, Ed ...
, 2-color cinema system and the choice of filters allows for useful color reproduction for many scenes.
Applications
* System Maeda aeda, 2003'': it is based on a system of a monitor of gyratoryLCD
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but i ...
. The weight of this monitor limits the rate of update, allowing only five revolutions per second, obtaining only five independent points of view.
*System Transport tsuka, 2006'': it realizes 24 images in the foreign edge of the projected video and reflects these images on a screen anisotropic of rapid rotation using a circle created by different faces of mirrors.
* 3D Videoconference alifornia, 2009'': It is based on a structure composed of two mirrors on those who reflect the images and create different perspectives about his 360 degrees.
Articles and books
*TRAVIS, A. R. L. 1997. The display of three-dimensional video images. *ENDO, T., KAJIKI, Y., HONDA, T., AND SATO, M. 2000. Cylindrical 3D video display observable from all directions. *DODGSON, N. A. 2005. Autostereoscopic 3D displays. *MCDOWALL, I., AND BOLAS, M. 2005. Display, sensing, and control applications for digital micromirror displays. *FAVALORA, G. E. 2005. Volumetric 3D displays and application infrastructure. *OTSUKA, R., HOSHINO, T., AND HORRY, Y. 2006. Transpost: A novel approach to the display and transmission of 360 degreesviewable 3D solid images. *AGOCS, T., BALOGH, T., FORGACS, T., BETTIO, F., GOBBETTI, E., ZANETTI, G., AND BOUVIER, E. 2006. A large scale interactive holographic display.External links
�Video depicting a spinning mirror system �
Type of Display obtained thanks to the described technology �
Article about the use of the system in 3D Teleconferencing �
Paper about spinning mirror systems {{DEFAULTSORT:Spinning Mirror System Stereoscopy