Speyer Line on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
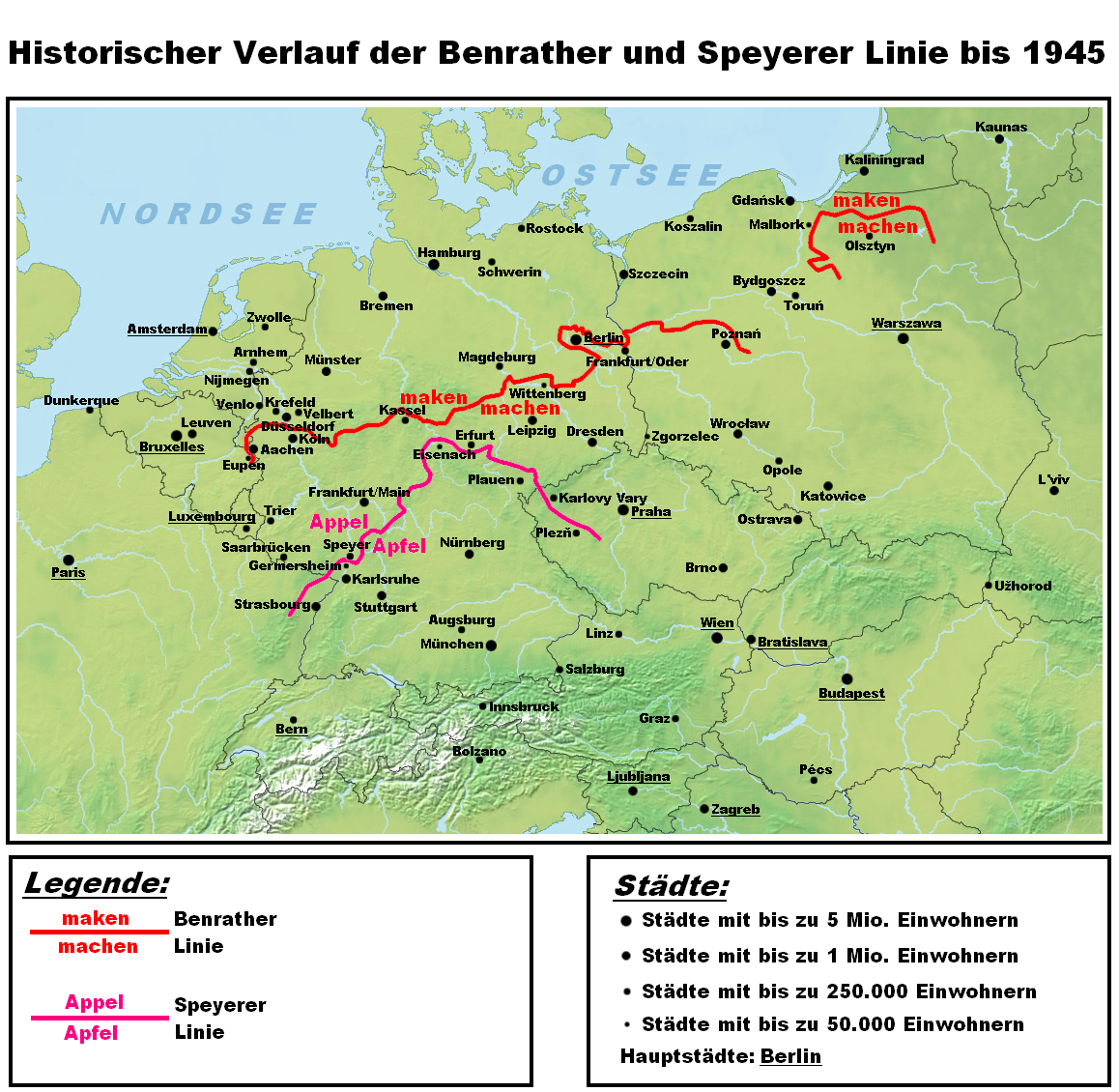 In German dialectology, the Speyer line or Main line ( Main River) is an
In German dialectology, the Speyer line or Main line ( Main River) is an
 In German dialectology, the Speyer line or Main line ( Main River) is an
In German dialectology, the Speyer line or Main line ( Main River) is an isogloss
An isogloss, also called a heterogloss (see Etymology below), is the geographic boundary of a certain linguistic feature, such as the pronunciation of a vowel, the meaning of a word, or the use of some morphological or syntactic feature. Major ...
separating the Central German dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety of a language that ...
s to the north, which have a stop in words like ''Appel'' "apple", from the Upper German
Upper German (german: Oberdeutsch ) is a family of High German dialects spoken primarily in the southern German-speaking area ().
History
In the Old High German time, only Alemannic and Bairisch are grouped as Upper German. In the Middle High ...
dialects to the south, which have an affricate: ''Apfel''. The line begins in Alsace near Strasbourg, and runs north-east to Thüringen, crossing the Rhine at Speyer
Speyer (, older spelling ''Speier'', French: ''Spire,'' historical English: ''Spires''; pfl, Schbaija) is a city in Rhineland-Palatinate in Germany with approximately 50,000 inhabitants. Located on the left bank of the river Rhine, Speyer li ...
. After passing close to Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits ...
, it turns south-east and continues into the formerly German-speaking parts of Bohemia. The line is exemplified by place-names containing an uncombined /p/ phoneme, which lie north of the line (Paderborn
Paderborn (; Westphalian: ''Patterbuorn'', also ''Paterboärn'') is a city in eastern North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, capital of the Paderborn district. The name of the city derives from the river Pader and ''Born'', an old German term for th ...
, Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and, with around 183,000 inhabitants, largest city of the German state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of B ...
, Wuppertal
Wuppertal (; "'' Wupper Dale''") is, with a population of approximately 355,000, the seventh-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia as well as the 17th-largest city of Germany. It was founded in 1929 by the merger of the cities and to ...
), while those with an affricate /pf/ ( Pfaffenhofen, Pforzheim) lie mostly to the south.
See also
*Benrath line
In German linguistics, the Benrath line (german: Benrather Linie) is the ''maken–machen'' isogloss: dialects north of the line have the original in ''maken'' (to make), while those to the south have the innovative (''machen''). The Line runs ...
* Uerdingen line
* High German consonant shift
In historical linguistics, the High German consonant shift or second Germanic consonant shift is a phonological development ( sound change) that took place in the southern parts of the West Germanic dialect continuum in several phases. It probably ...
References
Isoglosses German language {{Germanic-lang-stub