Special School (Netherlands) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
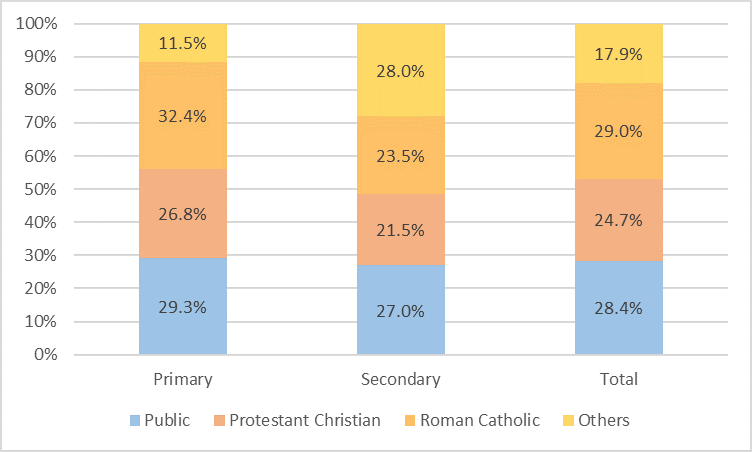 In the
In the
 In the
In the Dutch education system
Dutch or Nederlands commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
** Dutch people as an ethnic group ()
** Dutch nationality law, history and regulations of Dutch citizenship ()
** Dutch language ()
* In specific terms, i ...
, particular education ("bijzonder onderwijs") refers to a separate category of education distinct from both public
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociology, sociological concept of the ''Öf ...
and private
Private or privates may refer to:
Music
* "In Private", by Dusty Springfield from the 1990 album ''Reputation''
* Private (band), a Denmark-based band
* "Private" (Ryōko Hirosue song), from the 1999 album ''Private'', written and also recorded ...
education, in which a school is administered by an independent board, as opposed to a government authority, while still receiving government funding.
About two thirds of pupils in the Netherlands attend particular education. Particular schools are comparable to the concept of a charter school
A charter school is a school that receives government funding but operates independently of the established state school system in which it is located. It is independent in the sense that it operates according to the basic principle of autono ...
, with the additional characteristic of being grounded in a particular religious denomination
A religious denomination is a subgroup within a religion that operates under a common name and tradition, among other activities.
The term refers to the various Christian denominations (for example, Oriental Orthodox Churches, non-Chalcedonian, E ...
or educational philosophy
The philosophy of education is the branch of applied philosophy that investigates the nature of education as well as its aims and problems. It also examines the concepts and presuppositions of education theories. It is an interdisciplinary fiel ...
, although confusingly many state-operated schools also have chosen a distinct educational philosophy. Particular education is not to be confused with " speciaal onderwijs", which refers to schools specialized to deal with physical and/or learning disabilities.
Definition
Particular education schools teach on the basis of religion, philosophy of life or a vision of education. Public school lessons are not based on religion or belief. The government pays for both types of education. For this, schools must meet conditions. For example, education must be of sufficient quality. There are also requirements, for example, for the minimum number of pupils, the competence of teachers and the number of hours of education. Particular schools differ from both public and private schools in the way they are funded and run. While privately run, particular schools are not altogether outside the control of the Dutch Ministry of Education, as they are subsidized on equal footing with public schools, and cannot charge tuition over the statutory rate. They are therefore also distinct from private schools—of which there are a small but increasing number in the country—which get no subsidies and can charge market tuition.Public schools
Public schools are open to every student and teacher. Education is not based on religion or belief. There are public schools that teach from certain educational principles. The municipality must ensure that there is enough public education. This is also stated in Article 23 of theDutch Constitution
The Constitution of the Kingdom of the Netherlands of 24 August 1815 () is one of two fundamental documents governing the Kingdom of the Netherlands as well as the Constitution, fundamental law of the Netherlands, Netherlands proper (the territo ...
on freedom of education. When there are not enough public schools in the area, then the municipality ensures that children receive public education in a different way. For example, by arranging transport to a public school.
Particular schools
Special schools teach from a certain direction, which is a religious or philosophical belief. A special school is usually created, because parents need a school of a particular religious or pedagogical direction.Subcategories
Particular education can be further subdivided into two categories: * Denominational Particular Education ("confessioneel bijzonder onderwijs") refers to schools grounded in a religious denomination, often founded by or linked to church boards or religious foundations. Examples of denominational schools areChristian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
schools, including Roman Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
, Evangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide, interdenominational movement within Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes evangelism, or the preaching and spreading of th ...
, and Protestant Reformed, as well as Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
ic, Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
, and Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
schools. Denominational schools represent the majority of particular schools.
* General Particular Education ("algemeen bijzonder onderwijs") refers to a minority of particular schools not rooted in religion but operating on a particular educational concept, such as Dalton education, Montessori education
The Montessori method of education is a type of educational method that involves children's natural interests and activities rather than formal teaching methods. A Montessori classroom places an emphasis on hands-on learning and developing ...
, Jenaplan education, and Waldorf education
Waldorf education, also known as Steiner education, is based on the educational philosophy of Rudolf Steiner, the founder of anthroposophy. Its educational style is holistic, intended to develop pupils' intellectual, artistic, and practical sk ...
.
In practice, classification is complicated by schools that combine aspects of denominational and general, as well as public and particular education, for instance schools that adhere to an educational philosophy while lacking an independent school board, and schools combining denominational and educational philosophy in their teaching.
History
The distinction between particular and public education arose from the hugely influential school struggle, which dominated Dutch politics from the mid-19th century until thePacification of 1917
The Pacification of 1917 was a political agreement between liberals and socialists on the left and some Christian parties on the right in the Netherlands, ending both the suffrage issue and the School struggle (Netherlands), school struggle. The ...
, when public and religious schools were granted equal rights to government funding under article 23 of the Dutch constitution.
Criticism
Since the post-World War II decline of the pillarization of Dutch society along ideological lines, and the rapidsecularization
In sociology, secularization () is a multilayered concept that generally denotes "a transition from a religious to a more worldly level." There are many types of secularization and most do not lead to atheism or irreligion, nor are they automatica ...
of Dutch society, government funding of particular schools has in recent years become a topic of debate once again, with several political parties calling for an amendment or revoking of article 23 of the constitution.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Special School (Netherlands) School types Education in the Netherlands Special education in the Netherlands