Spanish speaking world on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Hispanophone refers to anything related to the
Hispanophone refers to anything related to the
 There are an estimated 474.7 million native Spanish speakers and about 100 million second and foreign language speakers around the world as of 2022, totaling 574 million Hispanophones in total. This makes Spanish the second most natively spoken language and fourth most spoken language overall globally. The vast majority of Hispanophones are concentrated in the Hispanosphere, the countries and territories where Spanish is a native or significant language.
There are an estimated 474.7 million native Spanish speakers and about 100 million second and foreign language speakers around the world as of 2022, totaling 574 million Hispanophones in total. This makes Spanish the second most natively spoken language and fourth most spoken language overall globally. The vast majority of Hispanophones are concentrated in the Hispanosphere, the countries and territories where Spanish is a native or significant language.
 During the Spanish period between 1492 and 1898, many people from Spain migrated to the new lands they had conquered. The
During the Spanish period between 1492 and 1898, many people from Spain migrated to the new lands they had conquered. The
 The modern-day nationalities that live in the region of ancient
The modern-day nationalities that live in the region of ancient

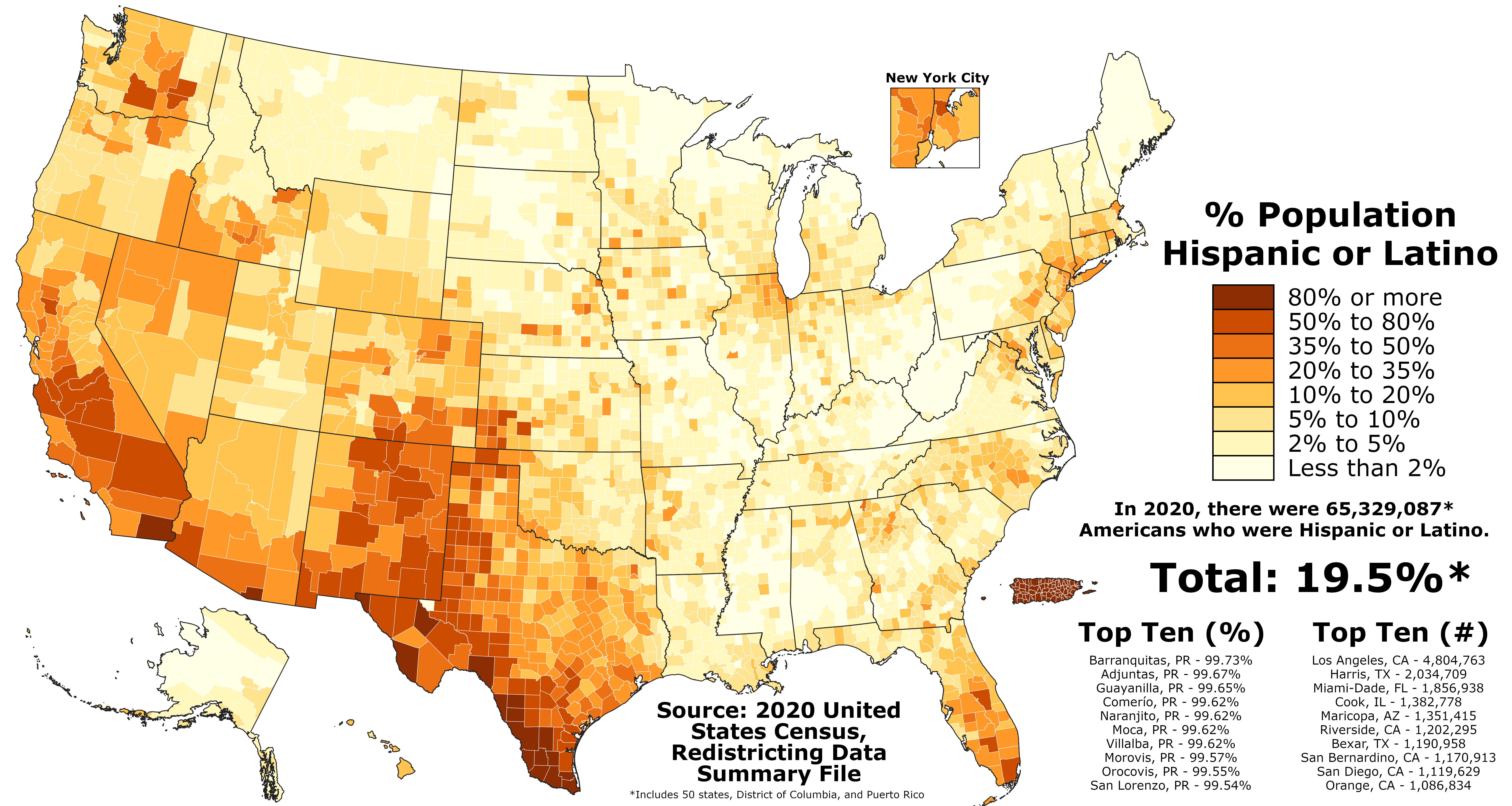 U.S. Hispanics are citizens of the United States whose ancestry or national origin is of any of the nations composing the Hispanosphere. A Hispanic person's status is independent from whether or not he or she speaks the Spanish language, for not all Hispanic Americans speak Spanish. A Hispanic person may be of any race (White, Amerindian, mixed, Black, Asian or Pacific Islander). Hispanics accounted for 17.1% of the population, around 53.2 million people. This was an increase of 29% since 2004, when Hispanics were 14.1% of the population (around 41.3 million people). The Hispanic growth rate over the July 1, 2003 to July 1, 2004, period was 3.6% — higher than any other ancestral group in the United States — and more than three times the rate of the nation's total population (at 1.0%). The projected Hispanic population of the United States for July 1, 2050, is 105.6 million people. According to this projection, Hispanics will constitute 25% of the nation's total population by the year 2050.
Historically, a continuous Hispanic presence in the territory of the United States has existed since the 16th century, earlier than any other group after the
U.S. Hispanics are citizens of the United States whose ancestry or national origin is of any of the nations composing the Hispanosphere. A Hispanic person's status is independent from whether or not he or she speaks the Spanish language, for not all Hispanic Americans speak Spanish. A Hispanic person may be of any race (White, Amerindian, mixed, Black, Asian or Pacific Islander). Hispanics accounted for 17.1% of the population, around 53.2 million people. This was an increase of 29% since 2004, when Hispanics were 14.1% of the population (around 41.3 million people). The Hispanic growth rate over the July 1, 2003 to July 1, 2004, period was 3.6% — higher than any other ancestral group in the United States — and more than three times the rate of the nation's total population (at 1.0%). The projected Hispanic population of the United States for July 1, 2050, is 105.6 million people. According to this projection, Hispanics will constitute 25% of the nation's total population by the year 2050.
Historically, a continuous Hispanic presence in the territory of the United States has existed since the 16th century, earlier than any other group after the
, Stanford University The populations of Iberia (both Spain and Portugal), like all European populations, have received multiple other influences, even though they are still largely descended from the prehistoric European populations, and to a greater degree than any other major group.

 In the
In the
 Spanish is the official language of Easter Island, a territorial possession of Chile in
Spanish is the official language of Easter Island, a territorial possession of Chile in
 In
In
Spanish language
Spanish () or Castilian () is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin spoken on the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. Today, it is a world language, gl ...
.
In a cultural, rather than merely linguistic sense, the notion of "Hispanophone" goes further than the above definition. The Hispanic culture
The term Hispanic () are people, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or broadly. In some contexts, especially within the United States, "Hispanic" is used as an ethnic or meta-ethnic term.
The term commonly applie ...
is the legacy of the vast and prolonged Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered ...
, and so the term can refer to people whose cultural background is primarily associated with Spain, regardless of racial
Race is a categorization of humans based on shared physical or social qualities into groups generally viewed as distinct within a given society. The term came into common usage during the 16th century, when it was used to refer to groups of va ...
or geographical differences. The whole sense of identity of the Hispanic population and the Hispanophones is sometimes referred by the term ''Hispanidad
(, typically translated as "Hispanicity") is a Spanish term describing a shared cultural, linguistic, or political identity among speakers of the Spanish language or members of the Hispanic diaspora. The term can have various, different implicat ...
'' (Hispanicity).
When used in terms to refer to speakers of the Spanish language and the Spanish-speaking world, the Hispanosphere encompasses the following geographical areas: Spain, Hispanic America
Hispanic America ( or ), historically known as Spanish America () or Castile (historical region), Castilian America (), is the Spanish-speaking countries and territories of the Americas. In all of these countries, Spanish language, Spanish is th ...
, Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea, officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea, is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. It has an area of . Formerly the colony of Spanish Guinea, its post-independence name refers to its location both near the Equ ...
, and portions of the United States (namely the Southwest
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A '' compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west— ...
and Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
).El español: una lengua viva - Informe 2022Instituto Cervantes
Instituto Cervantes (, the Cervantes Institute) is a worldwide nonprofit organization created by the Spanish government in 1991. It is named after Miguel de Cervantes (1547–1616), the author of ''Don Quixote'' and perhaps the most important fi ...
. Retrieved 29 March 2022. (in Spanish) When used in the broader sense to include areas where the local culture has been heavily impacted by Hispanic influences, the former Spanish East Indies
The Spanish East Indies were the colonies of the Spanish Empire in Asia-Pacific, Asia and Oceania from 1565 to 1901, governed through the Captaincy General of the Philippines, captaincy general in Manila for the Monarchy of Spain, Spanish Crown, i ...
colonies of Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
and to a lesser extent, Guam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, Guam, Hagåtña, and the most ...
are also included.
The terms are derived from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
word ''Hispanicus'' ("Spanish") which refers to anything pertaining to the Roman province of Hispania
Hispania was the Ancient Rome, Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two Roman province, provinces: Hispania Citerior and Hispania Ulterior. During the Principate, Hispania Ulterior was divide ...
("Spain"). In addition to the general definition of Hispanophone, some groups in the Hispanic world make a distinction between Castilian-speaking and Spanish-speaking, with the former term denoting the speakers of the Spanish language— also known as Castilian—and the latter the speakers of the Spanish or Hispanic languages (i.e. the languages of Spain
The majority of languages of Spain belong to the Romance languages, Romance language family, of which Spanish language, Spanish is the only one with Official languages of Spain, official status in the whole country. Others, including Catalan l ...
or the languages of the Hispanic nations).
The Hispanosphere
Countries
 During the Spanish period between 1492 and 1898, many people from Spain migrated to the new lands they had conquered. The
During the Spanish period between 1492 and 1898, many people from Spain migrated to the new lands they had conquered. The Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance-speaking ethnic group native to the Iberian Peninsula, primarily associated with the modern nation-state of Spain. Genetically and ethnolinguistically, Spaniards belong to the broader Southern a ...
took with them their language and culture, and integrated within the society they had settled, creating a large empire that stretched all over the world and producing several multiracial populations. Their influences are found in the following continents and countries that were originally colonized by the Spaniards.
Geographic distribution of Spanish speakers
Europe
Spain
Hispania
Hispania was the Ancient Rome, Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two Roman province, provinces: Hispania Citerior and Hispania Ulterior. During the Principate, Hispania Ulterior was divide ...
are the Portuguese, Spanish, Andorran and Gibraltarian people. Historically, the modern country of Spain was formed by the accretion of several independent Iberian kingdoms through dynastic inheritance, conquest and the will of the local elites. These kingdoms had their own nationalistic loyalties and political borders.
Today, there is no single Castilian–Spanish identity for the whole country. Spain is a ''de facto'' plurinational state. Many Spanish citizens feel no conflict in recognising their multiple ethnic identities at the same time. Spain is a culturally heterogeneous country, home to a wide range of cultures, each one with its own customs and traditions. Some such cultures have their own language. Since the beginning of the transition to democracy in Spain and the creation of the Spanish '' autonomous communities'', after Francoist Spain
Francoist Spain (), also known as the Francoist dictatorship (), or Nationalist Spain () was the period of Spanish history between 1936 and 1975, when Francisco Franco ruled Spain after the Spanish Civil War with the title . After his death i ...
, there have been many movements towards more autonomy ( delegation of powers) in certain territories of the country, some with the aim of achieving full independence and others with the goal of improving the system of devolution and the state of the autonomies (or self-government entities).
The existence of multiple distinct cultures in Spain allows an analogy to be drawn to the United Kingdom. Using the term Spanish for someone of Spanish descent would then be expected to be equivalent to using Briton
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs modern British citizenship and nationality, w ...
to describe someone descending from some part of the United Kingdom. Cultures within the United Kingdom, such as English, Irish, Scottish, and Welsh, would then correspond in this analogy to cultures within Spain such as Castilian, Catalan, Galician and Basque
Basque may refer to:
* Basques, an ethnic group of Spain and France
* Basque language, their language
Places
* Basque Country (greater region), the homeland of the Basque people with parts in both Spain and France
* Basque Country (autonomous co ...
among others. In contrast with Spain, because of centuries of gradual and mutual consolidation across the Iberian Peninsula, such distinctions tend to be blurred. It is a subtle, yet important, distinction.
In Spain, as in the United Kingdom, the economically dominant territories— Castile and England—spread their language for mutual communication. However, the political dominance in the United Kingdom tends to be sharper compared to Spain, where most of medieval realms do not correspond with the actual boundaries of the autonomous communities, and the crown was unified into a sole monarch
A monarch () is a head of stateWebster's II New College Dictionary. "Monarch". Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest ...
.
Americas
Hispanic America
Spanish is the most widely-spoken language of the Americas, as well as the official language in a great part of the Americas.United States
Origins and demography
 U.S. Hispanics are citizens of the United States whose ancestry or national origin is of any of the nations composing the Hispanosphere. A Hispanic person's status is independent from whether or not he or she speaks the Spanish language, for not all Hispanic Americans speak Spanish. A Hispanic person may be of any race (White, Amerindian, mixed, Black, Asian or Pacific Islander). Hispanics accounted for 17.1% of the population, around 53.2 million people. This was an increase of 29% since 2004, when Hispanics were 14.1% of the population (around 41.3 million people). The Hispanic growth rate over the July 1, 2003 to July 1, 2004, period was 3.6% — higher than any other ancestral group in the United States — and more than three times the rate of the nation's total population (at 1.0%). The projected Hispanic population of the United States for July 1, 2050, is 105.6 million people. According to this projection, Hispanics will constitute 25% of the nation's total population by the year 2050.
Historically, a continuous Hispanic presence in the territory of the United States has existed since the 16th century, earlier than any other group after the
U.S. Hispanics are citizens of the United States whose ancestry or national origin is of any of the nations composing the Hispanosphere. A Hispanic person's status is independent from whether or not he or she speaks the Spanish language, for not all Hispanic Americans speak Spanish. A Hispanic person may be of any race (White, Amerindian, mixed, Black, Asian or Pacific Islander). Hispanics accounted for 17.1% of the population, around 53.2 million people. This was an increase of 29% since 2004, when Hispanics were 14.1% of the population (around 41.3 million people). The Hispanic growth rate over the July 1, 2003 to July 1, 2004, period was 3.6% — higher than any other ancestral group in the United States — and more than three times the rate of the nation's total population (at 1.0%). The projected Hispanic population of the United States for July 1, 2050, is 105.6 million people. According to this projection, Hispanics will constitute 25% of the nation's total population by the year 2050.
Historically, a continuous Hispanic presence in the territory of the United States has existed since the 16th century, earlier than any other group after the Amerindians
In the Americas, Indigenous peoples comprise the two continents' pre-Columbian inhabitants, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with them in the 15th century, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with the pre-Columbian population of ...
. Spaniards pioneered the present-day United States. The first confirmed European landing on the continent was that of Juan Ponce de León, who landed in 1513 on the shore he christened '' La Florida''. Within three decades of Ponce de León's landing, the Spanish became the first Europeans to reach the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain ...
, the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
, the Grand Canyon
The Grand Canyon is a steep-sided canyon carved by the Colorado River in Arizona, United States. The Grand Canyon is long, up to wide and attains a depth of over a mile ().
The canyon and adjacent rim are contained within Grand Canyon Nati ...
, and the Great Plains
The Great Plains is a broad expanse of plain, flatland in North America. The region stretches east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, and grassland. They are the western part of the Interior Plains, which include th ...
. Spanish ships sailed along the East Coast, penetrating to present-day Bangor, Maine, and up the Pacific Coast as far as Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while t ...
.
In 1540 Hernando de Soto
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1497 – 21 May 1542) was a Spanish explorer and conquistador who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire in Peru, ...
undertook an extensive exploration of the present United States. In the same year Francisco Vásquez de Coronado led 2,000 Spaniards and Mexican Indians across today's Arizona
Arizona is a U.S. state, state in the Southwestern United States, Southwestern region of the United States, sharing the Four Corners region of the western United States with Colorado, New Mexico, and Utah. It also borders Nevada to the nort ...
–Mexico border and traveled as far as central Kansas
Kansas ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the west. Kansas is named a ...
, close to the exact geographic center of what is now the continental United States. Other Spanish explorers of the United States make up a long list that includes, among others, Lucas Vásquez de Ayllón, Pánfilo de Narváez, Sebastián Vizcaíno, Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo
Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo (; 1497 – January 3, 1543) was a Portuguese maritime explorer best known for investigations of the west coast of North America, undertaken on behalf of the Spanish Empire. He was the first European to explore presen ...
, Gaspar de Portolà, Pedro Menéndez de Avilés, Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca, Tristán de Luna y Arellano
Tristán de Luna y Arellano (1510 – September 16, 1573) was a Spanish explorer and conquistador of the 16th century.Herbert Ingram Priestley, Tristan de Luna: Conquistador of the Old South: A Study of Spanish Imperial Strategy (1936). http://pa ...
, and Juan de Oñate. In all, Spaniards probed half of today's lower 48 states before the first English colonization attempt at Roanoke Island in 1585.
The Spanish created the first permanent European settlement in the continental United States, at St. Augustine, Florida, in 1565. Santa Fe, New Mexico
Santa Fe ( ; , literal translation, lit. "Holy Faith") is the capital city, capital of the U.S. state of New Mexico, and the county seat of Santa Fe County. With over 89,000 residents, Santa Fe is the List of municipalities in New Mexico, fourt ...
also predates Jamestown, Virginia
The Jamestown settlement in the Colony of Virginia was the first permanent British colonization of the Americas, English settlement in the Americas. It was located on the northeast bank of the James River, about southwest of present-day Willia ...
(founded in 1607) and Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony (sometimes spelled Plimouth) was the first permanent English colony in New England from 1620 and the third permanent English colony in America, after Newfoundland and the Jamestown Colony. It was settled by the passengers on t ...
(of '' Mayflower'' and Pilgrims fame, founded in 1620). Later came Spanish settlements in San Antonio
San Antonio ( ; Spanish for " Saint Anthony") is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in Greater San Antonio. San Antonio is the third-largest metropolitan area in Texas and the 24th-largest metropolitan area in the ...
, Tucson, San Diego
San Diego ( , ) is a city on the Pacific coast of Southern California, adjacent to the Mexico–United States border. With a population of over 1.4 million, it is the List of United States cities by population, eighth-most populous city in t ...
, Los Angeles, and San Francisco, to name just a few. The Spanish even established a Jesuit
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
mission in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
's Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Ea ...
37 years before the founding of Jamestown.
Two iconic American stories have Spanish antecedents, too. Almost 80 years before John Smith's alleged rescue by Pocahontas
Pocahontas (, ; born Amonute, also known as Matoaka and Rebecca Rolfe; 1596 – March 1617) was a Native American woman belonging to the Powhatan people, notable for her association with the colonial settlement at Jamestown, Virginia. S ...
, a man by the name of Juan Ortiz told of his remarkably similar rescue from execution by an Indian girl. Spaniards also held a thanksgiving
Thanksgiving is a national holiday celebrated on various dates in October and November in the United States, Canada, Saint Lucia, Liberia, and unofficially in countries like Brazil and Germany. It is also observed in the Australian territory ...
—56 years before the famous Pilgrims festival
A festival is an event celebrated by a community and centering on some characteristic aspect or aspects of that community and its religion or cultures. It is often marked as a local or national holiday, Melā, mela, or Muslim holidays, eid. A ...
—when they feasted near St. Augustine with Florida Indians, probably on stewed pork and garbanzo beans. As late as 1783, at the end of the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
, Spain held claim to roughly half of today's continental United States (see New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
); in 1775, Spanish ships even reached Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
. From 1819 to 1848, the United States increased the nation's area by roughly a third of former Spanish and Mexican territory, including today's three most populous states: California, Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
, and Florida. Hispanics became the first American citizens in the newly acquired Southwest
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A '' compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west— ...
territory and remained the ancestral majority in several states until the 20th century, and a large minority in the 21st century.
Hispanic Americans have fought in all the wars of the United States and have earned some of the highest distinctions awarded to U.S. soldiers ( list of Hispanic Medal of Honor recipients). Historic figures in the United States have been Hispanic from early times.
National Hispanic Heritage Month
The National Hispanic Heritage Month is celebrated in the United States from September 15 to October 15.Diversity
The people of Hispanophone countries encompass many different ethnic backgrounds. Though in countries like the United States, Hispanics may often be stereotyped as having a typicalMediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
/ Amerindian/Southern European appearance - olive skin, dark hair, and dark eyes.
Most Hispanics in the United States have their origins in countries such as El Salvador
El Salvador, officially the Republic of El Salvador, is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south by the Pacific Ocean. El Salvador's capital and largest city is S ...
, Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...
, and Mexico, with 90% of Salvadorans, 95% of Paraguayans, and 70% of Mexicans identifying as mestizo, with Mexico having the largest total mestizo population at over 66 million.
In the United States, Hispanics, regardless of self-identified racial background, are labeled ''Hispanic'' by the U.S. census. They may have varying of European ancestry, such as Spanish origins, and Amerindian or African roots. From 1850 to 1920, the U.S. Census form did not distinguish between whites and Mexican Americans. In 1930, the U.S. Census form asked for "color or race", and census enumerators were instructed to write ''W'' for white and ''Mex'' for Mexican. In 1940 and 1950, the census reverted its decision and made Mexicans be classified as white again and thus the instructions were to "Report ''white'' (W) for Mexicans unless they were definitely of full Indigenous Indian or other non-white races (such as Black or Asian).")
Of the over 35 million Hispanics counted in the Federal 2000 Census, 47.9% identified as White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wa ...
(termed White Hispanic by the Census Bureau); 42.2% some other race; 6.3% two or more races; 2% Black or African American; 1.2% American Indian and Alaska Native; 0.3% Asian; and 0.1% Native Hawaiian and Other Pacific Islander. Even among those Hispanics who reported one race only, most would also possess at least some ancestral lineage from one or more other races, despite the fact that only 6.3% reported as such (this is also applicable to the non-Hispanics counted in the U.S. Census, although maybe in less proportion).
According to one study (Stephens et al. 2001), from the genetic perspective, Hispanics generally represent a differential mixture of European, Native American, and African ancestry, with the proportionate mix typically depending on country of origin.Stephens' study, Stanford University The populations of Iberia (both Spain and Portugal), like all European populations, have received multiple other influences, even though they are still largely descended from the prehistoric European populations, and to a greater degree than any other major group.
Africa

Equatorial Guinea
In the former Spanish province ofEquatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea, officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea, is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. It has an area of . Formerly the colony of Spanish Guinea, its post-independence name refers to its location both near the Equ ...
, although Portuguese and French are co-official languages, the majority of the population speak Spanish. There is a small minority of African people who possessed Spanish and other European ancestry. These individuals form less than 1% of the population.
Morocco
Portions of the north coast ofMorocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
were a former Spanish protectorate and Spanish remains spoken by about 1.7 million people as of 2018. This makes Morocco the country with the most Spanish speakers outside the Hispanophone world unless the United States is excluded. However, demand for Spanish and overall competency in the language has fallen since the start of the 21st century and the most popular foreign language is now English (as French is considered a second and mandatory language in the country).
Spanish territories in North Africa
Since theReconquista
The ''Reconquista'' (Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese for ) or the fall of al-Andalus was a series of military and cultural campaigns that European Christian Reconquista#Northern Christian realms, kingdoms waged ag ...
, Spain has held numerous emplacements in North Africa. Most of them were promptly lost, but to date, with an approximate population of 143,000 people, the autonomous cities of Ceuta
Ceuta (, , ; ) is an Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous city of Spain on the North African coast. Bordered by Morocco, it lies along the boundary between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. Ceuta is one of th ...
and Melilla, which constitute the two ''plazas de soberanía mayores'' (Major Territories under panishSovereignty) remained Spanish, and the Chafarinas Islands, the Peñón de Alhucemas and the Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, which constitute the three ''plazas de soberanía menores'' (Minor Territories under panishSovereignty), still forming part of Spain. The Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the cont ...
, a constituent part of Spain's main territorial subdivisions, are also located in North Africa.
Western Sahara
Spanish is maintained as a secondary language alongside the official Arabic in the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, a partially recognized state that claimsWestern Sahara
Western Sahara is a territorial dispute, disputed territory in Maghreb, North-western Africa. It has a surface area of . Approximately 30% of the territory () is controlled by the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR); the remaining 70% is ...
, whose territory formerly comprised the Spanish colony of Spanish Sahara and now is mostly occupied by Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
. However, Spanish is not a native language in the territory, and the Moroccan government uses Arabic and French in its administration of Western Sahara and the number of Spanish speakers in the territory itself is rather trivial compared to the former two languages.
Asia
Philippines
 In the
In the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, the Spanish Filipino population which mostly descends from those Spanish colonists who arrived during the Spanish colonial period remains influential in Filipino society despite its small numbers. However, the vast majority of Spanish Filipinos today no longer speak Spanish. Instead, most now exclusively speak Tagalog or other local Philippine languages and English. Nevertheless, the only Spanish-based creole language in Asia called Chavacano
Chavacano or Chabacano () is a group of Spanish-based creole language varieties spoken in the Philippines. The variety spoken in Zamboanga City, located in the southern Philippine island group of Mindanao, has the highest concentration of spea ...
was developed on the islands and is spoken by roughly a million people.
Section 7, Article XIV of the 1987 Philippine Constitution specifies Spanish (along with Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
) a language to "be promoted on a voluntary and optional basis", while the Philippine Academy of the Spanish Language () remains the state regulating body for the language. Castilian Spanish
In English, Castilian Spanish can mean the variety of Peninsular Spanish spoken in northern and central Spain, the standard form of Spanish, or Spanish from Spain in general. In Spanish, the term (Castilian) can either refer to the Spanish langu ...
is the sole dialectal standard taught in schools, while Philippine Spanish
Philippine Spanish ( or ) is the variety of standard Spanish spoken in the Philippines, used primarily by Spanish Filipinos.
Spanish as spoken in the Philippines contains a number of features that distinguishes it from other varieties of ...
(the local variant of the language which developed during the colonial era) currently has a few thousand native speakers left and is close to extinction.
Despite its rapid decline in the 20th century, there has been a revival of interest in the Spanish language since the first decade of the 21st century among select circles. Under the rule of President Gloria Macapagal Arroyo (herself a fluent speaker), Spanish was re-introduced into the educational system as an elective language in secondary schools. Nevertheless, the Spanish language's presence in the country and its cultural influence continues to decline and is no longer present in daily life outside the numerous loanwords of Spanish origin in Philippine languages.
Pacific Islands
Easter Island (Rapa Nui)
 Spanish is the official language of Easter Island, a territorial possession of Chile in
Spanish is the official language of Easter Island, a territorial possession of Chile in Polynesia
Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in ...
.
Mariana Islands
TheMariana Islands
The Mariana Islands ( ; ), also simply the Marianas, are a crescent-shaped archipelago comprising the summits of fifteen longitudinally oriented, mostly dormant volcanic mountains in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, between the 12th and 21st pa ...
(today split between the United States territory of Guam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, Guam, Hagåtña, and the most ...
and the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands) were formerly governed as a part of the Spanish East Indies
The Spanish East Indies were the colonies of the Spanish Empire in Asia-Pacific, Asia and Oceania from 1565 to 1901, governed through the Captaincy General of the Philippines, captaincy general in Manila for the Monarchy of Spain, Spanish Crown, i ...
, and thus many Chamorros possess some degree of Spanish admixture.
While most people living on these islands no longer speak Spanish, the native Chamorro language exhibits a noticeable Spanish influence in its vocabulary. Many Chamorros have also preserved Hispanic cultural elements such as fiestas, cockfighting, and the Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
faith despite having integrated with the American way of life.
Spanish surnames are still prevalent on Guam, it is spoken by Catholic people and Puerto Ricans
Puerto Ricans (), most commonly known as Puerto Rico#Etymology, Boricuas, but also occasionally referred to as '':es:Anexo:Gentilicios de Puerto Rico#Lista general, Borinqueños'', '':es:Anexo:Gentilicios de Puerto Rico#Lista general, Borincan ...
, and the custom of women keeping their maiden names after marriage is a both byproduct of Spanish culture on these islands as well as the matrilineal
Matrilineality, at times called matriliny, is the tracing of kinship through the female line. It may also correlate with a social system in which people identify with their matriline, their mother's lineage, and which can involve the inheritan ...
structure of indigenous Chamorro culture.
Antarctica
 In
In Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
, there are only two civilian localities and both are inhabited primarily by native Spanish speakers. One of them is the Argentine Fortín Sargento Cabral, which has 66 inhabitants. The other is the Chilean town of Villa Las Estrellas, which has a population of 150 inhabitants in summer and 80 inhabitants in winter. In each of them there is a school where students study and do research in Spanish. The Orcadas Base, an Argentine scientific station, is the oldest base in all of Antarctica still in operation and the oldest with a permanent population (since 1907).
The following countries operate scientific bases in Antarctica:
Religion
The Spanish and the Portuguese took the Christian faith to their colonies in the Americas, Africa, and Asia;Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
remains the predominant religion amongst most Hispanics. A significant minority of Spanish speakers are also either Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
Latinobarometro, Opinion Publica Latinoamericana, Enero 2018. or not affiliated with any religion.
See also
* List of countries and territories where Spanish is an official language * Spanish-based creole languages * Flag of the Hispanic People *Hispanic
The term Hispanic () are people, Spanish culture, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or broadly. In some contexts, Hispanic and Latino Americans, especially within the United States, "Hispanic" is used as an Ethnici ...
* Hispanicity
* Hispanism
Hispanism (sometimes referred to as Hispanic studies or Spanish studies) is the study of the literature and culture of the Spanish-speaking world, principally that of Spain and Hispanic America. It may also entail studying Spanish language ...
and Panhispanism
* Hispanophobia
* Latino
* Language geography and '' Sprachraum''
* ''Lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
'' and World language
* Anglophone, Francophone
The Francophonie or Francophone world is the whole body of people and organisations around the world who use the French language regularly for private or public purposes. The term was coined by Onésime Reclus in 1880 and became important a ...
, Lusophone
The Portuguese-speaking world, also known as the Lusophone world () or the Lusophony (''Lusofonia''), comprises the countries and territories in which the Portuguese language is an official, administrative, cultural, or secondary language. This ...
, the corresponding words relating to use of the English, French, and Portuguese languages, respectively
* List of link languages
* Dialect continuum
A dialect continuum or dialect chain is a series of Variety (linguistics), language varieties spoken across some geographical area such that neighboring varieties are Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible, but the differences accumulat ...
* Geolinguistics
* Language geography
Notes
References
External links
{{Countries and languages lists * * Country classifications Cultural regions Spanish diaspora