Space Surveillance Telescope on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Space Surveillance Telescope (SST) is a Southern Hemisphere-based
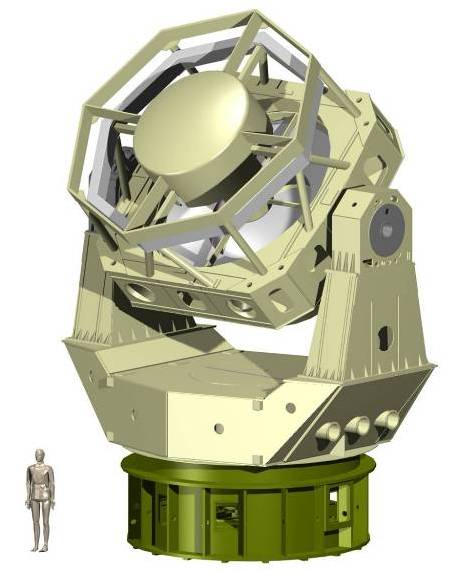
Asteroid Detection with the Space Surveillance Telescope
{{United States Missile Defense Reflecting telescopes United States Space Surveillance Network Military equipment introduced in the 2010s
United States Space Force
The United States Space Force (USSF) is the space force branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces, armed forces of the United States and one of the eight uniformed services of the Unite ...
telescope used for detecting, tracking, and cataloguing satellites
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scientif ...
, near-Earth objects
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body orbiting the Sun whose closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 times the Earth–Sun distance (astronomical unit, AU). This definition applies to the object's orbit aro ...
, and space debris
Space debris (also known as space junk, space pollution, space waste, space trash, space garbage, or cosmic debris) are defunct human-made objects in spaceprincipally in Earth orbitwhich no longer serve a useful function. These include dere ...
.
In 2011, SST achieved first light at the White Sands Missile Range
White Sands Missile Range (WSMR) is a United States Army military testing area and firing range located in the US state of New Mexico. The range was originally established in 1941 as the Alamogordo Bombing and Gunnery Range, where the Trinity t ...
, New Mexico, United States. In 2017, the SST was dismantled and moved to the Harold E. Holt Naval Communication Station, Exmouth, Western Australia to a site with an altitude of around . From there it began observing the Southern Celestial Hemisphere and collecting data for the US Space Surveillance Network. The repositioned SST achieved first light in Australia on 5 March 2020. The SST entered initial operational capability on 4 October 2022 and is operated by the Royal Australian Air Force
The Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) is the principal Air force, aerial warfare force of Australia, a part of the Australian Defence Force (ADF) along with the Royal Australian Navy and the Australian Army. Constitutionally the Governor-Gener ...
, 1 Remote Sensor Unit under the command and control (C2) of the U.S. Space Force.
Purpose
The SST primarily enables the military to track and identify objects and threats in space including space debris, as well as predict and avoid potential collisions. Whether it is space traffic management or the protection of critical space-based capabilities, SST maintains real-time awareness of the space domain of both the U.S. and Australia. The discovery and tracking of space debris is a growing problem. Among the 20–30 thousand large objects in orbit that are tracked, an estimated 100 million objects some as small as paint flecks are harder to track than the larger objects, but large enough to shield against if they collide with a space asset. Paint flecks are known to cause damage mainly due to the extreme velocity that they travel in orbit. In other words, there are objects too big to easily shield against, but too small to track. Another concern is theKessler syndrome
The Kessler syndrome, also known as the Kessler effect, collisional cascading, or ablation cascade, is a scenario proposed by NASA scientists Donald J. Kessler and Burton G. Cour-Palais in 1978. It describes a situation in which the density of o ...
, a chain reaction of collisions, creating far more space debris dangerous to working satellites. Another concern are near-Earth asteroids
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body orbiting the Sun whose closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 times the Earth–Sun distance (astronomical unit, AU). This definition applies to the object's orbit aro ...
, that the SST also tracks as part of its mission.

Design
The SST was sponsored byDARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military. Originally known as the Adva ...
and designed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Lincoln Laboratory.
SST has a mirror. Two noted design features include a Mersenne-Schmidt type optics and curved CCD. The large curved focal surface array sensors are considered to be an innovative design. It encompasses improvements in detection sensitivity, has short focal length
The focal length of an Optics, optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the Multiplicative inverse, inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system Converge ...
, wide field of view, and improvements in step-and-settle abilities.
SST detects, tracks, and can discern small, obscure objects, in deep space with a "wide field of view system". It is a single telescope with the dual abilities. First the telescope is sensitive enough to allow for detection, also, of small, dimly lit objects (low reflectivity). Second it is capable of quickly searching the visible sky. This combination is a difficult achievement in a single telescope design.
It is a Mersenne-Schmidt design with an F/1.0 aperture
In optics, the aperture of an optical system (including a system consisting of a single lens) is the hole or opening that primarily limits light propagated through the system. More specifically, the entrance pupil as the front side image o ...
and a primary mirror. It uses an array of charge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a ...
(CCD) sensors, arranged on a curved focal plane array. The SST mount uses an advanced servo-control technology, that makes it one of the quickest and most agile telescopes of its size. It has a field of view of 6 square degrees and can scan the visible sky at night on clear nights down to apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the Irradiance, brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction (astronomy), ...
20.5. These features allow the system to conduct multiple searches throughout the night, including the entire geostationary belt within its field.
As a telescope system, it can give precise locations of discovered objects, extrapolate the courses of individual objects and determine their stability.
The SST is notable in the number of observations it makes and is currently listed by the Minor Planet Center
The Minor Planet Center (MPC) is the official body for observing and reporting on minor planets under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Founded in 1947, it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory.
Funct ...
as the world record holder for making the most observations in a single year. In 2015 it made a record 6.97 million observations, significantly more than any other telescope, including Pan-STARRS
The Panoramic Survey Telescope and Rapid Response System (Pan-STARRS1; List of observatory codes, obs. code: IAU code#F51, F51 and Pan-STARRS2 obs. code: IAU code#F52, F52) located at Haleakala Observatory, Hawaii, US, consists of astronomical ...
which is currently in second place, having recorded 5.25 million observations in its best year so far (2014).
See also
* United States Space Surveillance Network *List of largest optical reflecting telescopes
This list of the largest optical reflecting telescopes with Objective (optics), objective diameters of or greater is sorted by aperture, which is a measure of the light-gathering power and resolution of a reflecting telescope. The mirrors themse ...
*Space debris
Space debris (also known as space junk, space pollution, space waste, space trash, space garbage, or cosmic debris) are defunct human-made objects in spaceprincipally in Earth orbitwhich no longer serve a useful function. These include dere ...
*Near-earth objects
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body orbiting the Sun whose closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 times the Earth–Sun distance (astronomical unit, AU). This definition applies to the object's orbit aro ...
*Satellites
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scientif ...
* Asteroid impact prediction
Notes
References
External links
Asteroid Detection with the Space Surveillance Telescope
{{United States Missile Defense Reflecting telescopes United States Space Surveillance Network Military equipment introduced in the 2010s