Soviet–Japanese Neutrality Pact on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The , also known as the , was a non-aggression pact between the
The , also known as the , was a non-aggression pact between the
April 13, 1941. (
April 5, 1945. (
 The , also known as the , was a non-aggression pact between the
The , also known as the , was a non-aggression pact between the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
and the Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent for ...
signed on April 13, 1941, two years after the conclusion of the Soviet-Japanese Border War. The agreement meant that for most of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, the two nations fought against each other's allies but not against each other. In 1945, late in the war, the Soviets scrapped the pact and joined the Allied campaign against Japan.
Background
After theFall of France
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the German invasion of France during the Second Wo ...
and then the expansion of the Axis Powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
wished to mend its diplomatic relations in the Far East
The ''Far East'' was a European term to refer to the geographical regions that includes East and Southeast Asia as well as the Russian Far East to a lesser extent. South Asia is sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.
The te ...
to safeguard its eastern border and to concentrate on the European Theatre of World War II
The European theatre of World War II was one of the two main Theater (warfare), theatres of combat during World War II. It saw heavy fighting across Europe for almost six years, starting with Nazi Germany, Germany's invasion of Poland on 1 Sept ...
. On the other hand, the Empire of Japan
The also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was a historical nation-state and great power that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent for ...
was bogged down in a seemingly-interminable war against China and had rapidly-deteriorating diplomatic relations with the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
. Those factors made the Japanese seek an accommodation with the Soviet Union to improve its international standing and to secure the northern border of Manchukuo
Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of (Great) Manchuria after 1934, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in Manchuria from 1932 until 1945. It was founded as a republic in 1932 after the Japanese in ...
from a possible Soviet invasion.
Soviet Premier Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secreta ...
was initially unaware of Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
's briefing to his generals that an attack on the Soviet Union by the European Axis Powers would let Japan overtly challenge the United States. That briefing was based on the belief that if such an attack occurred, the Soviet Union would be too preoccupied with fighting Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
. That would make Japan feel less threatened by any possible Soviet invasion of Manchukuo and allow Japan to have enough provisions and capabilities to start a war against the United States. The pact would allow both Japan and the Soviet Union to avoid fighting on multiple fronts.
Stalin believed that his "problems can be solved in a natural way if the Soviets and the Japanese cooperate". After concluding the nonaggression treaty, Stalin, in an unprecedented gesture, saw Japanese Foreign Minister Yosuke Matsuoka off at the train station. That was symbolic of the importance that Stalin, who rarely appeared before foreign diplomats, attached to the treaty. It also provided him with the occasion, in the presence of the entire diplomatic corps, to invite negotiations with Germany and to flaunt his increased bargaining power.
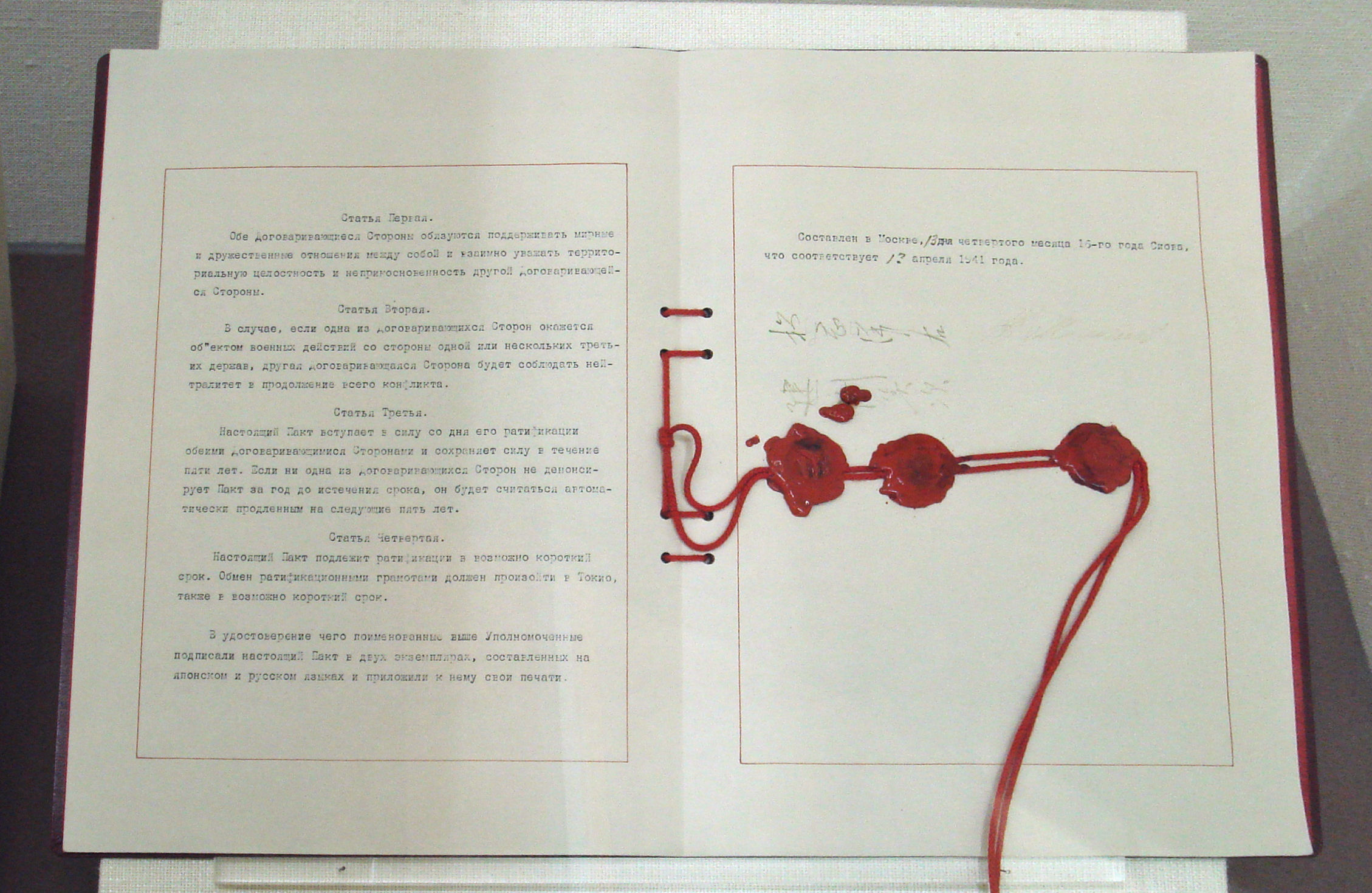
Signing
The treaty was signed inMoscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
on April 13, 1941, by Foreign Minister Yosuke Matsuoka and Ambassador Yoshitsugu Tatekawa for Japan and Foreign Minister Vyacheslav Molotov
Vyacheslav Mikhaylovich Molotov. ; (;. 9 March O. S. 25 February">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Old Style and New Style dates">O. S. 25 February1890 – 8 November 1986) was a Russian politician and diplomat, an Old Bol ...
for the Soviet Union.
The same day, all three men also signed a declaration regarding Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 millio ...
and Manchukuo
Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of (Great) Manchuria after 1934, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in Manchuria from 1932 until 1945. It was founded as a republic in 1932 after the Japanese in ...
.Declaration Regarding MongoliaApril 13, 1941. (
Avalon Project
The Avalon Project is a digital library of documents relating to law, history and diplomacy. The project is part of the Yale Law School Lillian Goldman Law Library.
The project contains online electronic copies of documents dating back to the ...
at Yale University
Yale University is a Private university, private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. Established in 1701 as the Collegiate School, it is the List of Colonial Colleges, third-oldest institution of higher education in the United Sta ...
) The Soviet Union pledged to respect the territorial integrity and the inviolability of Manchukuo, and Japan did the same for Mongolia.
Effects
Later in 1941, Japan, as a signatory of theTripartite Pact
The Tripartite Pact, also known as the Berlin Pact, was an agreement between Germany, Italy, and Japan signed in Berlin on 27 September 1940 by, respectively, Joachim von Ribbentrop, Galeazzo Ciano and Saburō Kurusu. It was a defensive militar ...
, considered denouncing the Soviet–Japanese Neutrality Pact, especially after the German invasion of the Soviet Union
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after ...
, but it made the crucial decision to keep the pact and to expand southwards by instead invading the European colonies in Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
. That had a direct bearing on the Battle of Moscow
The Battle of Moscow was a military campaign that consisted of two periods of strategically significant fighting on a sector of the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front during World War II. It took place between September 1941 and January ...
since the absence of a Japanese threat allowed the Soviets to move large forces from Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
and to send them to the front against the Germans.
It is possible that if the Germans had won the Battle of Stalingrad
The Battle of Stalingrad (23 August 19422 February 1943) was a major battle on the Eastern Front of World War II where Nazi Germany and its allies unsuccessfully fought the Soviet Union for control of the city of Stalingrad (later re ...
, Japan would have invaded Siberia. General Tomoyuki Yamashita, who was known for his achievements in the Battle of Singapore
The Fall of Singapore, also known as the Battle of Singapore,; ta, சிங்கப்பூரின் வீழ்ச்சி; ja, シンガポールの戦い took place in the South–East Asian theatre of the Pacific War. The Empire o ...
, was sent to Manchuria in July 1942 and tasked with organizing troops for the invasion.
At the Yalta Conference
The Yalta Conference (codenamed Argonaut), also known as the Crimea Conference, held 4–11 February 1945, was the World War II meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union to discuss the post ...
in February 1945, Stalin secretly agreed to enter the war against Japan in exchange for American and British recognition of certain Soviet territorial claims in Asia. The Soviet offensive was to start within three months after the end of the war in Europe.
Soviet denunciation
On April 5, 1945, the Soviet Union denounced the pact with Japan by informing the Japanese government that "in accordance with Article Three of the above mentioned pact, which envisaged the right of denunciation one year before the lapse of the five-year period of operation of the pact, the Soviet Government hereby makes known to the Government of Japan its wish to denounce the pact of April 13, 1941."Denunciation of the neutrality pactApril 5, 1945. (
Avalon Project
The Avalon Project is a digital library of documents relating to law, history and diplomacy. The project is part of the Yale Law School Lillian Goldman Law Library.
The project contains online electronic copies of documents dating back to the ...
at Yale University
Yale University is a Private university, private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. Established in 1701 as the Collegiate School, it is the List of Colonial Colleges, third-oldest institution of higher education in the United Sta ...
) The wording of the denunciation suggested that the Soviet Union wished to see the treaty go out of effect immediately, and ''Time'' magazine reported that the Soviet Foreign Commissar's tone indicated that the Soviet Union might soon go to war against Japan.
The text of the treaty had stated that the pact remained "valid for five years," (April 13, 1941 - April 13, 1946). When Japanese Ambassador Naotake Sato pressed him, Molotov assured him that the treaty would remain in force until April 1946. The treaty also stated, "In case neither of the Contracting Parties denounces the Pact one year before the expiration of the term, it will be considered automatically prolonged for the next five years" (April 13, 1946 - April 13, 1951). The denunciation came on April 5, 1945, which under those terms meant that the treaty would not renew on April 13, 1946.
On May 8 or 9, 1945, the date depending on the time zone, Nazi Germany surrendered, which ended the war in Europe and started the secret three-month countdown for the Soviets to start hostilities against Japan. On August 9, 1945, just after midnight in Manchuria, the Soviets invaded Manchuria. The declaration of war against Japan followed nearly six hours later. Because of the time zone difference of 7 hours, the declaration of war could be still dated August 8, 1945 and was presented to the Japanese ambassador in Moscow at 11 p.m. Moscow time.
During the Soviet invasion, Japanese forces on the Asian mainland were unprepared to resist and were overrun relatively quickly. In the last campaign of the war, Soviet territorial gains in Asia were Manchukuo, Mengjiang
Mengjiang, also known as Mengkiang or the Mongol Border Land, and governed as the Mengjiang United Autonomous Government, was an autonomous area in Inner Mongolia, formed in 1939 as a puppet state of the Empire of Japan, then from 1940 being ...
(Inner Mongolia) and northern Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republi ...
.
Text of pact
Text of declaration
Text of denunciation
Text of declaration of war
See also
*Japan–Soviet Union relations
Relations between the Soviet Union and Japan between the Communist takeover in 1917 and the collapse of Communism in 1991 tended to be hostile. Japan had sent troops to counter the Bolshevik presence in Russia's Far East during the Russian Civil ...
*Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union that enabled those powers to partition Poland between them. The pact was signed in Moscow on 23 August 1939 by German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ri ...
* Italo-Soviet Pact
*Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference (german: Potsdamer Konferenz) was held at Potsdam in the Soviet occupation zone from July 17 to August 2, 1945, to allow the three leading Allies to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistakes of the Paris Pe ...
, Potsdam Declaration
The Potsdam Declaration, or the Proclamation Defining Terms for Japanese Surrender, was a statement that called for the surrender of all Japanese armed forces during World War II. On July 26, 1945, United States President Harry S. Truman, U ...
References
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Soviet-Japanese Neutrality Pact Military history of Japan during World War II Treaties of the Soviet Union World War II treaties Soviet Union in World War II Mongolian People's Republic History of Manchuria Germany–Soviet Union relations Treaties concluded in 1941 Treaties entered into force in 1941 1941 in Japan 1941 in the Soviet Union Japan–Russia relations Japan–Soviet Union relations Treaties of the Empire of Japan Non-aggression pacts April 1941 events 1941 in Moscow Axis powers Japan–Russia treaties