South Koreans on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 According to Worldometers' South Korea Population Forecast statistics, South Korea is supposed to have a 0.36% yearly change increase by 2020, a 0.28% yearly change increase by 2025, a 0.18% yearly change increase by 2030, and a 0.04% yearly change increase by 2035. According to those same statistics, the years from 2040 to 2050 are supposed to have a steady decline of yearly change percentages.
The population of South Korea showed robust growth since the republic's establishment in 1948, and then dramatically slowed down with the effects of its economic growth. In the first official census, taken in 1949, the total population of South Korea was calculated at 20,188,641 people. The 1985 census total was 40,466,577. Population growth was slow, averaging about 1.1% annually during the period from 1949 to 1955, when the population registered at 21.5 million. Growth accelerated between 1955 and 1966 to 29.2 million or an annual average of 2.8%, but declined significantly during the period 1966 to 1985 to an annual average of 1.7%. Thereafter, the annual average growth rate was estimated to be less than 1%, similar to the low growth rates of most industrialized countries and to the target figure set by the Ministry of Health and Social Affairs for the 1990s. As of January 1, 1989, the population of South Korea was estimated to be approximately 42,200,000.
The proportion of the total population under fifteen years of age has risen and fallen with the growth rate. In 1955 approximately 41.2% of the population was under fifteen years of age, a percentage that rose to 43.5% in 1966 before falling to 38.3% in 1975, 34.2% in 1980, and 29.9% in 1985. In the past, the large proportion of children relative to the total population put great strains on the country's economy, particularly because substantial resources were invested in education facilities. With the slowdown in the population growth rate and a rise in the median age (from 18.7 years to 21.8 years between 1960 and 1980), the age structure of the population has begun to resemble the columnar pattern typical of developed countries, rather than the pyramidal pattern found in most parts of the Third World.
The decline in the population growth rate and in the proportion of people under fifteen years of age after 1966 reflected the success of official and unofficial birth control programs. The government of President Syngman Rhee (1948–60) was conservative in such matters. Although Christian churches initiated a family planning campaign in 1957, it was not until 1962 that the government of Park Chung Hee, alarmed at the way in which the rapidly increasing population was undermining economic growth, began a nationwide family planning program. Other factors that contributed to a slowdown in population growth included
According to Worldometers' South Korea Population Forecast statistics, South Korea is supposed to have a 0.36% yearly change increase by 2020, a 0.28% yearly change increase by 2025, a 0.18% yearly change increase by 2030, and a 0.04% yearly change increase by 2035. According to those same statistics, the years from 2040 to 2050 are supposed to have a steady decline of yearly change percentages.
The population of South Korea showed robust growth since the republic's establishment in 1948, and then dramatically slowed down with the effects of its economic growth. In the first official census, taken in 1949, the total population of South Korea was calculated at 20,188,641 people. The 1985 census total was 40,466,577. Population growth was slow, averaging about 1.1% annually during the period from 1949 to 1955, when the population registered at 21.5 million. Growth accelerated between 1955 and 1966 to 29.2 million or an annual average of 2.8%, but declined significantly during the period 1966 to 1985 to an annual average of 1.7%. Thereafter, the annual average growth rate was estimated to be less than 1%, similar to the low growth rates of most industrialized countries and to the target figure set by the Ministry of Health and Social Affairs for the 1990s. As of January 1, 1989, the population of South Korea was estimated to be approximately 42,200,000.
The proportion of the total population under fifteen years of age has risen and fallen with the growth rate. In 1955 approximately 41.2% of the population was under fifteen years of age, a percentage that rose to 43.5% in 1966 before falling to 38.3% in 1975, 34.2% in 1980, and 29.9% in 1985. In the past, the large proportion of children relative to the total population put great strains on the country's economy, particularly because substantial resources were invested in education facilities. With the slowdown in the population growth rate and a rise in the median age (from 18.7 years to 21.8 years between 1960 and 1980), the age structure of the population has begun to resemble the columnar pattern typical of developed countries, rather than the pyramidal pattern found in most parts of the Third World.
The decline in the population growth rate and in the proportion of people under fifteen years of age after 1966 reflected the success of official and unofficial birth control programs. The government of President Syngman Rhee (1948–60) was conservative in such matters. Although Christian churches initiated a family planning campaign in 1957, it was not until 1962 that the government of Park Chung Hee, alarmed at the way in which the rapidly increasing population was undermining economic growth, began a nationwide family planning program. Other factors that contributed to a slowdown in population growth included
 In the past 20 years, South Korea has recorded some of the lowest fertility and marriage levels in the world. As of 2020, it is the country with the world's lowest total fertility rate—0.84.
In the past 20 years, South Korea has recorded some of the lowest fertility and marriage levels in the world. As of 2020, it is the country with the world's lowest total fertility rate—0.84.
File:South Korea 1955 09 01.png, as on 1955-09-01
File:South Korea Age Sex Pyramid 1960.png, as on 1960-11-01
File:South Korea Age Sex Pyramid 1965.png, as on 1965-11-01
File:South Korea 1970 10 01.png, as on 1970-10-01
File:South Korea Age Sex Pyramid 1975.png, as on 1975-11-01
File:South Korea 1980 11 01.png, as on 1980-11-01
File:South Korea 1985 11 01.png, as on 1985-11-01
File:South Korea 1990 11 01.png, as on 1990-11-01
File:South Korea 1995 11 01.png, as on 1995-11-01
File:South Korea Demographic Pyramid 2000.png, as on 2000-11-01
File:South Korea Demographic Pyramid 2005.png, as on 2005-11-01
File:South Korea Demographic Pyramid 2010.png, as on 2010-11-01
File:South Korea Demographic Pyramid 2015.png, as on 2015-11-01
South Korea faces the problem of a rapidly aging population. In fact, the speed of aging in Korea is unprecedented in human history,Thomas Klasse
"South Korean: Ageing Tiger"
, ''Global Brief'', January 12, 2010, accessed February 13, 2011. 18 years to double aging population from 7–14% (fewest years), overtaking even
"Statistics highlight scale of the aging population"
, ''Korea JoongAng Daily'', November 21, 2009, accessed February 14, 2011. The shape of its population has changed from a pyramid in the 1990s, with more young people and fewer old people, to a diamond shape in 2010, with less young people and a large proportion of middle-age individuals.Thomas Klasse
"South Korean: Aging Tiger"
, ''Global Brief'', January 12, 2010, accessed February 13, 2011. There are several implications and issues associated with an aging population. A rapidly aging population is likely to have several negative implications on the labour force. In particular, experts predict that this might lead to a shrinking of the labour force. As an increasing proportion of people enter their 50s and 60s, they either choose to retire or are forced to retire by their companies. As such, there would be a decrease in the percentage of economically active people in the population. Also, with rapid aging, it is highly likely that there would be an imbalance in the young-old percentage of the workforce. This might lead to a lack of vibrancy and innovation in the labour force, since it is helmed mainly by the middle-age workers. Data shows that while there are fewer young people in society, the percentage of economically active population, made up of people ages 15–64, has gone up by 20% from 55.5% to 72.5%. This shows that the labour force is indeed largely made up of middle-aged workers.
A possible consequence might be that South Korea would be a less attractive candidate for investment. Investors might decide to relocate to countries like Vietnam, where there is an abundance of cheaper, younger labour. If employers were to choose to maintain operations in South Korea, there is a possibility that they might incur higher costs in retraining or upgrading the skills of this group of middle-age workers. On top of that, higher healthcare costs might also be incurred and the government would need to set aside more money to maintain a good healthcare system to cater to the elderly.
Due to the very low birth rate, South Korea is predicted to enter a Russian Cross pattern once the large generation born in the 1960s starts to die off, with potentially decades of population decline.
Since 2016, the number of elderly people (+65 years old) outnumbered children (0–14 years) and the country became an "aged society". People older than 65 make up more than 14% of the total population.
There are several implications and issues associated with an aging population. A rapidly aging population is likely to have several negative implications on the labour force. In particular, experts predict that this might lead to a shrinking of the labour force. As an increasing proportion of people enter their 50s and 60s, they either choose to retire or are forced to retire by their companies. As such, there would be a decrease in the percentage of economically active people in the population. Also, with rapid aging, it is highly likely that there would be an imbalance in the young-old percentage of the workforce. This might lead to a lack of vibrancy and innovation in the labour force, since it is helmed mainly by the middle-age workers. Data shows that while there are fewer young people in society, the percentage of economically active population, made up of people ages 15–64, has gone up by 20% from 55.5% to 72.5%. This shows that the labour force is indeed largely made up of middle-aged workers.
A possible consequence might be that South Korea would be a less attractive candidate for investment. Investors might decide to relocate to countries like Vietnam, where there is an abundance of cheaper, younger labour. If employers were to choose to maintain operations in South Korea, there is a possibility that they might incur higher costs in retraining or upgrading the skills of this group of middle-age workers. On top of that, higher healthcare costs might also be incurred and the government would need to set aside more money to maintain a good healthcare system to cater to the elderly.
Due to the very low birth rate, South Korea is predicted to enter a Russian Cross pattern once the large generation born in the 1960s starts to die off, with potentially decades of population decline.
Since 2016, the number of elderly people (+65 years old) outnumbered children (0–14 years) and the country became an "aged society". People older than 65 make up more than 14% of the total population.
 Like other newly industrializing economies, South Korea experienced rapid growth of urban areas caused by the migration of large numbers of people from the countryside. In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries,
Like other newly industrializing economies, South Korea experienced rapid growth of urban areas caused by the migration of large numbers of people from the countryside. In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries,

 Sources:
Sources:
Korean Statistical Information System
South Korea: Balancing Labor Demand with Strict Controls
Park Young-bum, Migration Information Source, December 2004.
HelpAge International
HelpAge Korea (in Korean)
Basic Korean Language Act
{{DEFAULTSORT:Demographics Of South Korea Society of South Korea pt:Coreia do Sul#Demografia
Demographic
Demography () is the statistics, statistical study of human populations: their size, composition (e.g., ethnic group, age), and how they change through the interplay of fertility (births), mortality (deaths), and migration.
Demographic analy ...
features of the population
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and pl ...
of South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
include population density
Population density (in agriculture: Standing stock (disambiguation), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geog ...
, ethnicity
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they Collective consciousness, collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, ...
, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations, and other aspects of the population. The common language and especially culture are viewed as important elements by South Koreans in terms of identity, more than citizenship.
In June 2012, South Korea's population reached 50 million, and by the end of 2016, South Korea's population peaked at about 51 million people. However, in recent years the total fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
(TFR) of South Korea has plummeted, leading some researchers to suggest that if current trends continue, the country's population will shrink to approximately 28 million people by the end of the 21st century. In 2018, fertility in South Korea became a topic of international debate after only 26,500 babies were born in October and an estimated 325,000 babies for the year, causing the country to achieve the lowest birth rate in the world. In a further indication of South Korea's dramatic decline in fertility, in 2020 the country recorded more deaths than births, resulting in a population decline for the first time since modern records began.
Analysts have attributed South Korea's population decline resulting from low birth rates to the country's high economic inequality; including the high cost of living
The cost of living is the cost of maintaining a certain standard of living for an individual or a household. Changes in the cost of living over time can be measured in a cost-of-living index. Cost of living calculations are also used to compare t ...
, low wages for an OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; , OCDE) is an international organization, intergovernmental organization with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and international trade, wor ...
member country, lack of job opportunities, as well as rising housing costs. South Korea also has the highest suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death.
Risk factors for suicide include mental disorders, physical disorders, and substance abuse. Some suicides are impulsive acts driven by stress (such as from financial or ac ...
rate in the OECD and the wider developed world.
In South Korea, a variety of different Asian people had migrated to the Korean Peninsula in past centuries, however few have remained permanently. South Korea is a highly homogenous nation, but has in recent decades become home to a number of foreign residents (4.37%), whereas North Korea has not experienced this trend. However, many of them are ethnic Koreans with a foreign citizenship. Many residents from China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, post-Soviet states
The post-Soviet states, also referred to as the former Soviet Union or the former Soviet republics, are the independent sovereign states that emerged/re-emerged from the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Prior to their independence, they ...
, the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
are, in fact, repatriated ethnic Koreans (labelled "Overseas Koreans") who may meet criteria for expedited acquisition of South Korean citizenship. For example, migrants from China (PRC) make up 56.5% of foreign nationals, but approximately 70% of the Chinese citizens in Korea are (), PRC citizens of Korean ethnicity. The total population of Korea is estimated to be 80 million, which includes the population of North Korea.
Population trends
urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from Rural area, rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. ...
, later marriage ages for both men and women, higher education levels, a greater number of women in the labor force, and better health standards.
Public and private agencies involved in family planning included the Ministry of Health and Social Affairs, the Ministry of Home Affairs, the Planned Parenthood Federation of Korea, and the Korea Institute of Family Planning. In the late 1980s, their activities included distribution of free birth control devices and information, classes for women on family planning methods, and the granting of special subsidies and privileges (such as low-interest housing loans) to parents who agreed to undergo sterilization. There were 502,000 South Koreans sterilized in 1984, as compared with 426,000 in the previous year.
The 1973 Maternal and Child Health Law legalized abortion. In 1983 the government began suspending medical insurance benefits for maternal care for pregnant women with three or more children. It also denied tax deductions for education expenses to parents with two or more children.
As in China, cultural attitudes posed problems for family planning programs. A strong preference for sons—who in Korea's traditional Confucian value system are expected to care for their parents in old age and carry on the family name—means that parents with only daughters usually continued to have children until a son is born. The government encouraged married couples to have only one child. This has been a prominent theme in public service advertising, which stresses "have a single child and raise it well."
Total fertility rates (the average number of births a woman will have during her lifetime) fell from 6.1 births per female in 1960 to 4.2 in 1970, 2.8 in 1980, and 2.4 in 1984. The number of live births, recorded as 711,810 in 1978, grew to a high of 917,860 in 1982. This development stirred apprehensions among family planning experts of a new "baby boom." By 1986, however, the number of live births had declined to 806,041.
Decline in population growth continued, and between 2005 and 2010 total fertility rate for South Korean women was 1.21, one of the world's lowest according to the United Nations. Fertility rate well below the replacement level of 2.1 births per female has triggered a national alarm, with some predicting an aging society unable to grow or support its elderly. Recent Korean governments have prioritized the issue on its agenda, promising to enact social reforms that will encourage women to have children.
The country's population increased to 46 million by the end of the twentieth century, with growth rates ranging between 0.9% and 1.2%. The population is expected to stabilize (that is, cease to grow) in the year 2023 at around 52.6 million people. In the words of ''Asiaweek'' magazine, the "stabilized tally will approximate the number of Filipinos in 1983, but squeezed into less than a third of their he Philippines'space."
As of early 2019, the birth rate of South Korea reached a very low number. In February 2019, the Korean TFR fell to 0.98, well below the replacement level of 2.1 births. South Korea is now the fastest aging developed country in the world. The Korean government (and their failing actions against the birth rate issue) and the worsening economic environment for young people are blamed as the main cause.
Population settlement patterns
South Korea is one of the world's most densely populated countries, with an estimated 425 people per square kilometer in 1989—over sixteen times the average population density of the United States in the late 1980s. By comparison, China had an estimated 114 people, the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany) 246 people, and Japan 323 people per square kilometer in the late 1980s. Because about 70% of South Korea's land area is mountainous and the population is concentrated in the lowland areas, actual population densities were in general greater than the average. As early as 1975, it was estimated that the density of South Korea's thirty-five cities, each of which had a population of 50,000 or more inhabitants, was 3,700 people per square kilometer. Because of continued migration to urban areas, the figure was higher in the late 1980s. In 1988 Seoul had a population density of 17,030 people per square kilometer as compared with 13,816 people per square kilometer in 1980. The second largest city, Busan, had a density of 8,504 people per square kilometer in 1988 as compared with 7,272 people in 1980. Gyeonggi Province, which surrounds the capital and contains Incheon, the country's fourth largest city, was the most densely populated province; Gangwon Province in the northeast was the least densely populated province. According to the government's Economic Planning Board, the population density will be 530 people per square kilometer by 2023, the year the population is expected to stabilize. Rural areas in South Korea consist of agglomerated villages in river valleys and range from a few houses to several hundred. These villages are located in the south that are backed by hills and give strong protection from winter winds. Since 1960, the pace of urbanization in South Korea has hit a considerable decline in population of rural areas and the traditional rural lifestyle has been slowly fading away.Fertility
Seoul
Seoul, officially Seoul Special Metropolitan City, is the capital city, capital and largest city of South Korea. The broader Seoul Metropolitan Area, encompassing Seoul, Gyeonggi Province and Incheon, emerged as the world's List of cities b ...
has a TFR of 0.64, probably the lowest level anywhere in the world.
Low birth rates have discouraged South Korean doctors from entering pediatrics
Pediatrics (American English) also spelled paediatrics (British English), is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, Adolescence, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, pediatrics covers many o ...
out of the fear that the field has no future. Due to how medical insurance is structured in South Korea, pediatric care relies especially on volume to compensate for its low reimbursement rates. The number of pediatric facilities in Seoul fell by 12.5 percent between 2018 and 2022, compared to an increase of 76.8 percent for psychiatry clinics and a 41.2 percent rise for anesthesiology centers. Conditions such as overcrowded waiting rooms and a shortage of hospital beds have led to the death of at least one child. The difficulty in obtaining pediatric care is causing many South Korean couples to reconsider having babies.
Age structure
Population of South Korea by age and sex (demographic pyramid)"South Korean: Ageing Tiger"
, ''Global Brief'', January 12, 2010, accessed February 13, 2011. 18 years to double aging population from 7–14% (fewest years), overtaking even
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
. Statistics support this observation, the percentage of elderly aged 65 and above, has sharply risen from 3.3% in 1955 to 10.7% in 2009.Jung Ha-wo"Statistics highlight scale of the aging population"
, ''Korea JoongAng Daily'', November 21, 2009, accessed February 14, 2011. The shape of its population has changed from a pyramid in the 1990s, with more young people and fewer old people, to a diamond shape in 2010, with less young people and a large proportion of middle-age individuals.Thomas Klasse
"South Korean: Aging Tiger"
, ''Global Brief'', January 12, 2010, accessed February 13, 2011.
 There are several implications and issues associated with an aging population. A rapidly aging population is likely to have several negative implications on the labour force. In particular, experts predict that this might lead to a shrinking of the labour force. As an increasing proportion of people enter their 50s and 60s, they either choose to retire or are forced to retire by their companies. As such, there would be a decrease in the percentage of economically active people in the population. Also, with rapid aging, it is highly likely that there would be an imbalance in the young-old percentage of the workforce. This might lead to a lack of vibrancy and innovation in the labour force, since it is helmed mainly by the middle-age workers. Data shows that while there are fewer young people in society, the percentage of economically active population, made up of people ages 15–64, has gone up by 20% from 55.5% to 72.5%. This shows that the labour force is indeed largely made up of middle-aged workers.
A possible consequence might be that South Korea would be a less attractive candidate for investment. Investors might decide to relocate to countries like Vietnam, where there is an abundance of cheaper, younger labour. If employers were to choose to maintain operations in South Korea, there is a possibility that they might incur higher costs in retraining or upgrading the skills of this group of middle-age workers. On top of that, higher healthcare costs might also be incurred and the government would need to set aside more money to maintain a good healthcare system to cater to the elderly.
Due to the very low birth rate, South Korea is predicted to enter a Russian Cross pattern once the large generation born in the 1960s starts to die off, with potentially decades of population decline.
Since 2016, the number of elderly people (+65 years old) outnumbered children (0–14 years) and the country became an "aged society". People older than 65 make up more than 14% of the total population.
There are several implications and issues associated with an aging population. A rapidly aging population is likely to have several negative implications on the labour force. In particular, experts predict that this might lead to a shrinking of the labour force. As an increasing proportion of people enter their 50s and 60s, they either choose to retire or are forced to retire by their companies. As such, there would be a decrease in the percentage of economically active people in the population. Also, with rapid aging, it is highly likely that there would be an imbalance in the young-old percentage of the workforce. This might lead to a lack of vibrancy and innovation in the labour force, since it is helmed mainly by the middle-age workers. Data shows that while there are fewer young people in society, the percentage of economically active population, made up of people ages 15–64, has gone up by 20% from 55.5% to 72.5%. This shows that the labour force is indeed largely made up of middle-aged workers.
A possible consequence might be that South Korea would be a less attractive candidate for investment. Investors might decide to relocate to countries like Vietnam, where there is an abundance of cheaper, younger labour. If employers were to choose to maintain operations in South Korea, there is a possibility that they might incur higher costs in retraining or upgrading the skills of this group of middle-age workers. On top of that, higher healthcare costs might also be incurred and the government would need to set aside more money to maintain a good healthcare system to cater to the elderly.
Due to the very low birth rate, South Korea is predicted to enter a Russian Cross pattern once the large generation born in the 1960s starts to die off, with potentially decades of population decline.
Since 2016, the number of elderly people (+65 years old) outnumbered children (0–14 years) and the country became an "aged society". People older than 65 make up more than 14% of the total population.
Urbanization
 Like other newly industrializing economies, South Korea experienced rapid growth of urban areas caused by the migration of large numbers of people from the countryside. In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries,
Like other newly industrializing economies, South Korea experienced rapid growth of urban areas caused by the migration of large numbers of people from the countryside. In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, Seoul
Seoul, officially Seoul Special Metropolitan City, is the capital city, capital and largest city of South Korea. The broader Seoul Metropolitan Area, encompassing Seoul, Gyeonggi Province and Incheon, emerged as the world's List of cities b ...
, by far the largest urban settlement, had a population of about 190,000 people. There was a striking contrast with Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, where Edo (Tokyo
Tokyo, officially the Tokyo Metropolis, is the capital of Japan, capital and List of cities in Japan, most populous city in Japan. With a population of over 14 million in the city proper in 2023, it is List of largest cities, one of the most ...
) had as many as 1 million inhabitants and the urban population comprised as much as 10% to 15% of the total during the Tokugawa Period (1600–1868). During the closing years of the Joseon
Joseon ( ; ; also romanized as ''Chosun''), officially Great Joseon (), was a dynastic kingdom of Korea that existed for 505 years. It was founded by Taejo of Joseon in July 1392 and replaced by the Korean Empire in October 1897. The kingdom w ...
period and the first years of Japanese colonial rule, the urban population of Korea was no more than 3% of the total. After 1930, when the Japanese began industrial development on the Korean Peninsula, particularly in the northern provinces adjacent to Manchuria, the urban portion of the population began to grow, reaching 11.6% for all of Korea in 1940.
Between 1945 and 1985, the urban population of South Korea grew from 14.5% to 65.4% of the total population. In 1988 the Economic Planning Board estimated that the urban portion of the population will reach 78.3% by the end of the twentieth century. Most of this urban increase was attributable to migration rather than to natural growth of the urban population. Urban birth rates have generally been lower than the national average. The extent of urbanization in South Korea, however, is not fully revealed in these statistics. Urban population was defined in the national census as being restricted to those municipalities with 50,000 or more inhabitants. Although many settlements with fewer than 50,000 inhabitants were satellite towns of Seoul or other large cities or mining communities in northeastern Gangwon Province, which would be considered urban in terms of the living conditions and occupations of the inhabitants, they still were officially classified as rural.
The dislocation caused by the Korean War accounted for the rapid increase in urban population during the early 1950s. Hundreds of thousands of refugees, many of them from North Korea, streamed into the cities. During the post-Korean War period, rural people left their ancestral villages in search of greater economic and educational opportunities in the cities. By the late 1960s, migration had become a serious problem, not only because cities were terribly overcrowded, but also because the rural areas were losing the most youthful and productive members of their labor force.
In 1970, the Park Chung Hee government launched the Saemaul Undong (New Community Movement) as a rural reconstruction and self-help movement to improve economic conditions in the villages, close the wide gap in income between rural and urban areas, and stem urban migration—as well as to build a political base. Despite a huge amount of government sponsored publicity, especially during the Park era, it was not clear by the late 1980s that the Saemaul undong had achieved its objectives. By that time many, if not most, farming and fishing villages consisted of older persons; relatively few able-bodied men and women remained to work in the fields or to fish. This trend was apparent in government statistics for the 1986–87 period: the proportion of people fifty years old or older living in farming communities grew from 28.7% in 1986 to 30.6% in 1987, while the number of people in their twenties living in farming communities declined from 11.3% to 10.8%. The nationwide percentages for people fifty years old or older and in their twenties were, in 1986, 14.9% and 20.2%, respectively.
In 1985 the largest cities were Seoul (9,645,932 inhabitants), Busan (3,516,807), Daegu (2,030,672), Incheon (1,387,491), Gwangju (906,129), and Daejeon (866,695). According to government statistics, the population of Seoul, one of the world's largest cities, surpassed 10 million people in late 1988. Seoul's average annual population growth rate during the late 1980s was more than 3%. Two-thirds of this growth was attributable to migration rather than to natural increase. Surveys revealed that "new employment or seeking a new job," "job transfer," and "business" were major reasons given by new immigrants for coming to the capital. Other factors cited by immigrants included "education" and "a more convenient area to live."
To alleviate overcrowding in Seoul's downtown area, the city government drew up a master plan in the mid-1980s that envisioned the development of four "core zones" by 2000: the original downtown area, Yongdongpo-Yeouido, Yongdong, and Jamsil. Satellite towns also would be established or expanded. In the late 1980s, statistics revealed that the daytime or commuter population of downtown Seoul was as much as six times the officially registered population. If the master plan is successful, many commuters will travel to work in a core area nearer their homes, and the downtown area's daytime population will decrease. Many government ministries have been moved out of Seoul, and the army, navy, and air force headquarters have been relocated to Daejeon
Daejeon (; ) is South Korea's list of cities in South Korea, fifth-largest metropolis, with a population of nearly 1.5 million. Located in a central lowland valley between the Sobaek Mountains and the Geum River, the city is known both as a ...
.
In 1985 the population of Seoul constituted 23.8% of the national total. Provincial cities, however, experienced equal and, in many cases, greater expansion than the capital. Growth was particularly spectacular in the southeastern coastal region, which encompasses the port cities of Busan, Masan, Yosu, Jinhae, Ulsan, and Pohang. Census figures show that Ulsan's population increased eighteenfold, growing from 30,000 to 551,300 inhabitants between 1960 and 1985. With the exception of Yosu, all of these cities are in South Gyeongsang Province, a region that has been an especially favored recipient of government development projects. By comparison, the population of Gwangju, capital of South Jeolla Province, increased less than threefold between 1960 and 1985, growing from 315,000 to 906,129 inhabitants.
Rapid urban growth has brought familiar problems to developed and developing countries alike. The construction of large numbers of high-rise apartment complexes in Seoul and other large cities alleviated housing shortages to some extent. But it also imposed hardship on the tens of thousands of people who were obliged to relocate from their old neighborhoods because they could not afford the rents in the new buildings. In the late 1980s, squatter areas consisting of one-story shacks still existed in some parts of Seoul. Housing for all but the wealthiest was generally cramped. The concentration of factories in urban areas, the rapid growth of motorized traffic, and the widespread use of coal for heating during the severe winter months caused dangerous levels of air and water pollution, issues that still persist today even after years of environmentally friendly policies.
In 2016, 82.59 percent of South Korea's total population lived in urban areas and cities.
Vital statistics
Total fertility rate from 1900 to 1924
Thetotal fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
is the number of children born per woman. It is based on fairly good data for the entire period. Sources: Our World In Data
Our World in Data (OWID) is a scientific online publication that focuses on large global problems such as poverty, disease, hunger, war, climate change, population growth, existential risks, and inequality.
It is a project of the Global Cha ...
and Gapminder Foundation.
UN estimates
Source:Registered births and deaths
Source:Current vital statistics
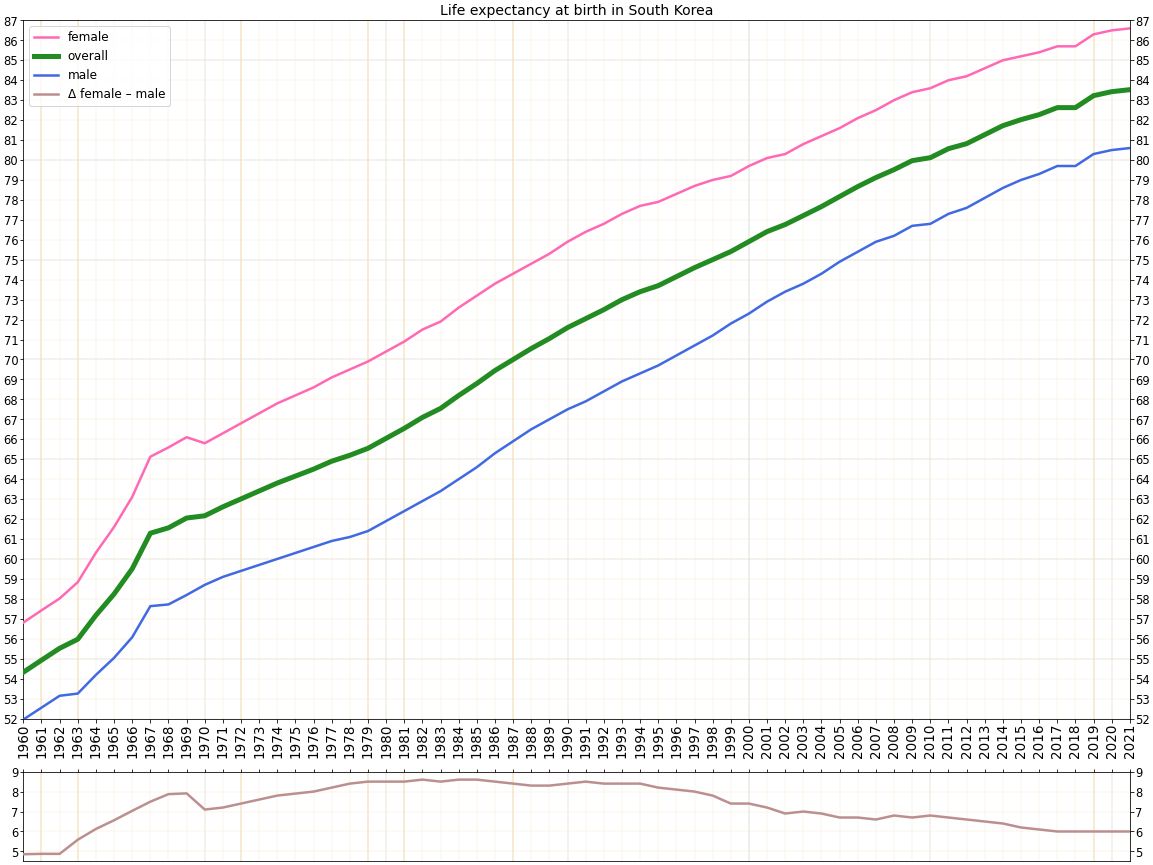
Life expectancy at birth
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, organisation, metabolism, growth, adaptation, respons ...
from 1908 to 2015
 Sources:
Sources: Our World In Data
Our World in Data (OWID) is a scientific online publication that focuses on large global problems such as poverty, disease, hunger, war, climate change, population growth, existential risks, and inequality.
It is a project of the Global Cha ...
and the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
.
1865–1950
1950–2015
Source: ''UN World Population Prospects''
Ethnic groups
South Korea is a largely ethnically homogeneous country with an absolute majority of the Korean ethnicity from estimates but the country itself does collect ethnic or racial data formally. However, with its emergence as an economic powerhouse, demand for foreign immigrants increased and in 2007 the number of foreign citizen residents in South Korea passed the one million mark for the first time in history, and the number reached 2 million in 2016. Of those, 1,016,000 came fromChina
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, with more than half of them being ethnic Koreans of Chinese citizenship. The next largest group was from Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
with 149,000 residents. The third largest group was from the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
with 117,000 residents, excluding the American troops stationed in the country. Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
and other countries followed. Many of the foreign residents from China and the former Soviet Union, including Russia and Kazakhstan, are ethnic Koreans (see Koreans in China
Koreans in China include both ethnic Koreans with Chinese nationality and non-Chinese nationalities such as South Korean ( zh, s=在华韩国人·韩裔) and North Korean ( zh, s=在华朝鲜人·朝鲜裔) people living in China. For this re ...
, Koryo-saram
Koryo-saram (; ) or Koryoin () are ethnic Koreans of the post-Soviet states, former Soviet Union, who descend from Koreans that were living in the Russian Far East.
Koreans first began settling in the Russian Far East in the late 19th century. ...
).
Chinese in South Korea
Since The People's Republic of China and South Korea established their diplomatic relationship in 1992, the number of Chinese immigrants, majorly Joseonjok, has continued to increase. In the early 1990s, a trade agreement allowed merchants from China to conduct business trades in South Korea. There are alsoChaoxianzu in Korea
Korean Chinese in Korea ( zh, , p=Zàihán Cháoxiǎnzú, s=在韩朝鲜族), also called Jaehan Joseonjok () are Chinese nationals of Korean ethnicity who live in Korea, primarily South Korea, with a visa or after having changed their nationality ...
: Chinese nationals of Korean ethnicity living in South Korea.
North Americans in South Korea
South Korea is a country with one of the largest American immigrant populations in the world, numbering over 100,000. Most Americans tend to beKorean Americans
Korean Americans () are Americans of full or partial Korean ethnicity, Korean ethnic descent. While the broader term Overseas Korean in America () may refer to all ethnic Koreans residing in the United States, the specific designation of Kore ...
who have returned to South Korea. About 43,000 Korean Americans reported living in South Korea in 2020, more than twice the number in 2005. South Korea also has a Canadian population of over 20,000.
Vietnamese in South Korea
The relationship between Vietnamese and Koreans date back to when Lý Dương Côn left for ''Goryeo'' after succession of power dispute. Likewise in 1226, Lý Long Tường, a prince of theLý dynasty
The Lý dynasty (, , chữ Nôm: 茹李, chữ Hán: 朝李, Vietnamese language, Vietnamese: ''triều Lý''), officially Đại Cồ Việt (chữ Hán: 大瞿越) from 1009 to 1054 and Đại Việt (chữ Hán: 大越) from 1054 to 1225, was ...
of Đại Việt
Đại Việt (, ; literally Great Việt), was a Vietnamese monarchy in eastern Mainland Southeast Asia from the 10th century AD to the early 19th century, centered around the region of present-day Hanoi. Its early name, Đại Cồ Việt,(ch ...
(in modern-day Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
), later became Yi Yongsang () of Hwasan, a general of Korea. He is an ancestor of one branch of the Lee (or Rhee) family today in South Korea. Nowadays, most Vietnamese immigrants are either manual labor workers, marriage immigrants, or cooks in Vietnamese cuisines.
Filipinos in South Korea
Relationship betweenFilipinos
Filipinos () are citizens or people identified with the country of the Philippines. Filipinos come from various Austronesian peoples, all typically speaking Filipino language, Filipino, Philippine English, English, or other Philippine language ...
and South Koreans can be traced back to 1950s during the Korean War
The Korean War (25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953) was an armed conflict on the Korean Peninsula fought between North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea; DPRK) and South Korea (Republic of Korea; ROK) and their allies. North Korea was s ...
. Over 7,500 Filipino soldiers fought on the United Nations' side to help South Korea. As of 2019, there were more than 55,000 Filipino immigrants living in South Korea. Population decline in rural regions led to shortage of young people especially young women in those areas and it led many Koreans to marry Filipino brides.
Multiracial people in South Korea
Languages
TheKorean language
Korean is the first language, native language for about 81 million people, mostly of Koreans, Korean descent. It is the national language of both South Korea and North Korea. In the south, the language is known as () and in the north, it is kn ...
is the native language spoken by the vast majority of the population. English is widely taught in both public and private schools as a foreign language. However, general fluency in English in the country is relatively low compared to other industrialized developed countries. There is a Chinese minority who speak Mandarin and Cantonese
Cantonese is the traditional prestige variety of Yue Chinese, a Sinitic language belonging to the Sino-Tibetan language family. It originated in the city of Guangzhou (formerly known as Canton) and its surrounding Pearl River Delta. While th ...
. Some elderly may still be able to speak Japanese, which was de facto (1910–1938) and de jure (1938–1945) official during the Japanese rule in Korea.
In different areas of South Korea, different dialects are spoken. For example, the Gyeongsang dialect
The Gyeongsang dialects (), also known as Southeastern Korean (), are dialects of the Korean language from the historical region of Gyeongsang Province. Today, that region is divided into Daegu, Busan, Ulsan, North Gyeongsang Province, and Sou ...
spoken around Busan and Daegu to the south is often perceived to sound quite rough and aggressive compared to standard Korean.
Religion
Koreans have historically lived under the religious influences of Korean shamanism, Buddhism, Daoism, or Confucianism. Korea is a country where three of the world's major religions, Christianity, Buddhism, and Confucianism, peacefully coexist. According to 2015 statistics, 43.1% of Korean population has a religion and 2008 statistics show that over 510 religious organizations were in the South Korea population. * Irreligious: 51% *Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
: 31%
*Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
: 17%
*Other religions: 1%
Migration
Emigration
Large-scaleemigration
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanentl ...
from Korea began around 1904 and continued until the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. During the Japanese rule, many Koreans emigrated to Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical region in northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day northeast China and parts of the modern-day Russian Far East south of the Uda (Khabarovsk Krai), Uda River and the Tukuringra-Dzhagdy Ranges. The exact ...
(present-day China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
's northeastern provinces of Liaoning
)
, image_skyline =
, image_alt =
, image_caption = Clockwise: Mukden Palace in Shenyang, Xinghai Square in Dalian, Dalian coast, Yalu River at Dandong
, image_map = Liaoning in China (+all claims hatched).svg
, ...
, Jilin
)
, image_skyline = Changbaishan Tianchi from western rim.jpg
, image_alt =
, image_caption = View of Heaven Lake
, image_map = Jilin in China (+all claims hatched).svg
, mapsize = 275px
, map_al ...
, and Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang is a province in northeast China. It is the northernmost and easternmost province of the country and contains China's northernmost point (in Mohe City along the Amur) and easternmost point (at the confluence of the Amur and Us ...
), other parts of China, the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
, and the contiguous United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
.
Most emigrated for economic reasons; employment opportunities were scarce, and many Korean farmers lost their land after the Japanese introduced a system of land registration and private land tenure, imposed higher land taxes, and promoted the growth of an absentee landlord class charging exorbitant rents. Koreans from the northern provinces of Korea migrated mainly to Manchuria, China, and Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
. Most people from the southern provinces went to Japan or the United States. Koreans were conscripted into Japanese labor battalions or the Japanese army, especially during World War II. In the 1940–44 period, nearly 2 million Koreans lived in Japan, 1.4 million in Manchuria, 600,000 in Siberia, and 130,000 in China. An estimated 40,000 Koreans were scattered among other countries, mainly the United States. At the end of World War II, approximately 2 million Koreans were repatriated from Japan and Manchuria.
More than 4 million ethnic Koreans lived outside the peninsula during the early 1980s. The largest group, about 1.7 million people, lived in China, the descendants of the Korean farmers who had left the country during the Japanese occupation. Most had assumed Chinese citizenship. The Soviet Union had about 430,000 ethnic Koreans, known as the Koryo-saram
Koryo-saram (; ) or Koryoin () are ethnic Koreans of the post-Soviet states, former Soviet Union, who descend from Koreans that were living in the Russian Far East.
Koreans first began settling in the Russian Far East in the late 19th century. ...
, scattered in several Soviet republics.
By contrast, many of Japan's approximately 700,000 Koreans had below-average standards of living. This situation occurred partly because of discrimination by the Japanese majority and partly because a large number of resident Koreans, loyal to the North Korean regime of Kim Il Sung
Kim Il Sung (born Kim Song Ju; 15 April 1912 – 8 July 1994) was a North Korean politician and the founder of North Korea, which he led as its first Supreme Leader (North Korean title), supreme leader from North Korea#Founding, its establishm ...
, preferred to remain separate from and hostile to the Japanese mainstream. The pro–North Korea Chongryon (General Association of Korean Residents in Japan) initially was more successful than the pro–South Korea Mindan (Association for Korean Residents in Japan) in attracting adherents among residents in Japan. Since diplomatic relations were established between Seoul
Seoul, officially Seoul Special Metropolitan City, is the capital city, capital and largest city of South Korea. The broader Seoul Metropolitan Area, encompassing Seoul, Gyeonggi Province and Incheon, emerged as the world's List of cities b ...
and Tokyo
Tokyo, officially the Tokyo Metropolis, is the capital of Japan, capital and List of cities in Japan, most populous city in Japan. With a population of over 14 million in the city proper in 2023, it is List of largest cities, one of the most ...
in 1965, however, the South Korean government has taken an active role in promoting the interests of their residents in Japan in negotiations with the Japanese government. It also has provided subsidies to Korean schools in Japan and other community activities.
By the end of 1988, the South Korean diaspora was estimated at around two million people. North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
was home to over 1.2 million. Smaller Korean communities formed in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
(100,000), Central and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
(45,000), the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
(12,000), Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean ...
(40,000), New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
(30,000), other Asian countries (27,000), and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
(25,000). A limited number of South Korean government-sponsored migrants settled in Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
, Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
, and other Latin American
Latin Americans (; ) are the citizenship, citizens of Latin American countries (or people with cultural, ancestral or national origins in Latin America).
Latin American countries and their Latin American diaspora, diasporas are Metroethnicity, ...
countries.
Because of South Korea's rapid economic expansion, an increasing number of its citizens reside abroad on a temporary basis as business executives, technical personnel, foreign students, and construction workers. A large number of formerly expatriate South Koreans have returned to South Korea primarily because of the country's much improved economic conditions and the difficulties they experienced in adjusting to living abroad.
Immigration
There are 2 650 783 foreign residents in South Korea as of December 2024, i.e. 5.18% of the total population. Roughly half of this population was Chinese (958,959), followed by Vietnamese (305,936), Thai (188,770) and American (170,251). Out of the total foreign population, 557,057 were short-term residents on fixed-term employment contracts. These figures exclude foreign-born citizens who have naturalized and obtained South Korean citizenship; the total number of naturalized South Korean citizens surpassed 200,000 in 2019. Fair amount of the foreign residents from some countries are Korean descendants. Two thirds of Chinese, half of Russian, one fourth of Uzbeks are repatriated ethnic Koreans (labelled "Overseas Koreans") who may meet criteria for expedited acquisition of South Korean citizenship. They are Korean Chinese andKoryo-saram
Koryo-saram (; ) or Koryoin () are ethnic Koreans of the post-Soviet states, former Soviet Union, who descend from Koreans that were living in the Russian Far East.
Koreans first began settling in the Russian Far East in the late 19th century. ...
.
Also, sizeable number of migrants from countries with primarily multicultural immigrant population, such as Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, and Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
are also of Korean ethnic descent.
Number of Foreign Residents in South Korea of Different Ethnicity
See also
*Demographics of North Korea
The demographics of North Korea are determined through national censuses and international estimates. The Central Bureau of Statistics (North Korea), Central Bureau of Statistics of North Korea conducted the 2008 North Korea Census, most recent ...
* Koreans
Koreans are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula. The majority of Koreans live in the two Korean sovereign states of North and South Korea, which are collectively referred to as Korea. As of 2021, an estimated 7.3 m ...
* Chinese people in Korea
* Vietnamese people in South Korea
Vietnamese people in Korea, also known as Vietnamese Koreans, have a history dating back to the 12th century. After the division of Korea and the Korean War, Vietnamese people, ethnic Vietnamese had various contacts with both North Korea, North an ...
* Filipinos in South Korea
Notes
References
Works cited
*External links
Korean Statistical Information System
South Korea: Balancing Labor Demand with Strict Controls
Park Young-bum, Migration Information Source, December 2004.
HelpAge International
HelpAge Korea (in Korean)
Basic Korean Language Act
{{DEFAULTSORT:Demographics Of South Korea Society of South Korea pt:Coreia do Sul#Demografia