South African Army Infantry Formation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The South African Army Infantry Formation supervises all infantry within the
 In 1915, the defence forces established the South African Overseas Expeditionary Force for war service outside Southern Africa. It included the ''South African Infantry'', comprising twelve battalions, and the ''Cape Corps'', comprising two battalions of
In 1915, the defence forces established the South African Overseas Expeditionary Force for war service outside Southern Africa. It included the ''South African Infantry'', comprising twelve battalions, and the ''Cape Corps'', comprising two battalions of  The Infantry Branch was enlarged in 1934, and the mounted rifles regiments were converted to infantry in 1935.
In 1943, the Infantry Branch was incorporated into the new South African Armoured Corps, which was divided into armour and infantry branches after
The Infantry Branch was enlarged in 1934, and the mounted rifles regiments were converted to infantry in 1935.
In 1943, the Infantry Branch was incorporated into the new South African Armoured Corps, which was divided into armour and infantry branches after
File:SADF Infantry Beret Springbok ver 1.jpg, Old SADF Republic Defence Force Infantry Corps emblem ver 1
File:SADF Infantry emblem.jpg, Old SADF Republic Defence Force Infantry Corps emblem ver 2
Despite representations made by some of the units affected, the reorganisation went ahead from January 1954. In 1956 a further reorganisation was made necessary by the considerable increase in the number of citizens balloted for training in some areas. The Army was accordingly reorganised to consist of 32 Afrikaner-speaking units (including five infantry regiments, five tank units, and four armoured car units) and 20 English medium units (including ten infantry regiments, four tank units, and one armoured car unit). The changes were implemented with effect from 22 September 1956.
In 1954, the SA-AC's Infantry Branch, and the personnel of the South African Instructional Corps, were formed into the ''South African Infantry Corps''.
In 1972, continuous national service was increased to twelve months and by 1974, there were ten full-time motorised infantry
battalions, besides the parachute battalion. The infantry reserve comprised 42 citizen force infantry battalions, a parachute regiment and over 200 commando internal defence units.

 Since 1994, South Africa's Infantry units have supported numerous operations for the United Nations and the African Union across the continent, including in the
Since 1994, South Africa's Infantry units have supported numerous operations for the United Nations and the African Union across the continent, including in the
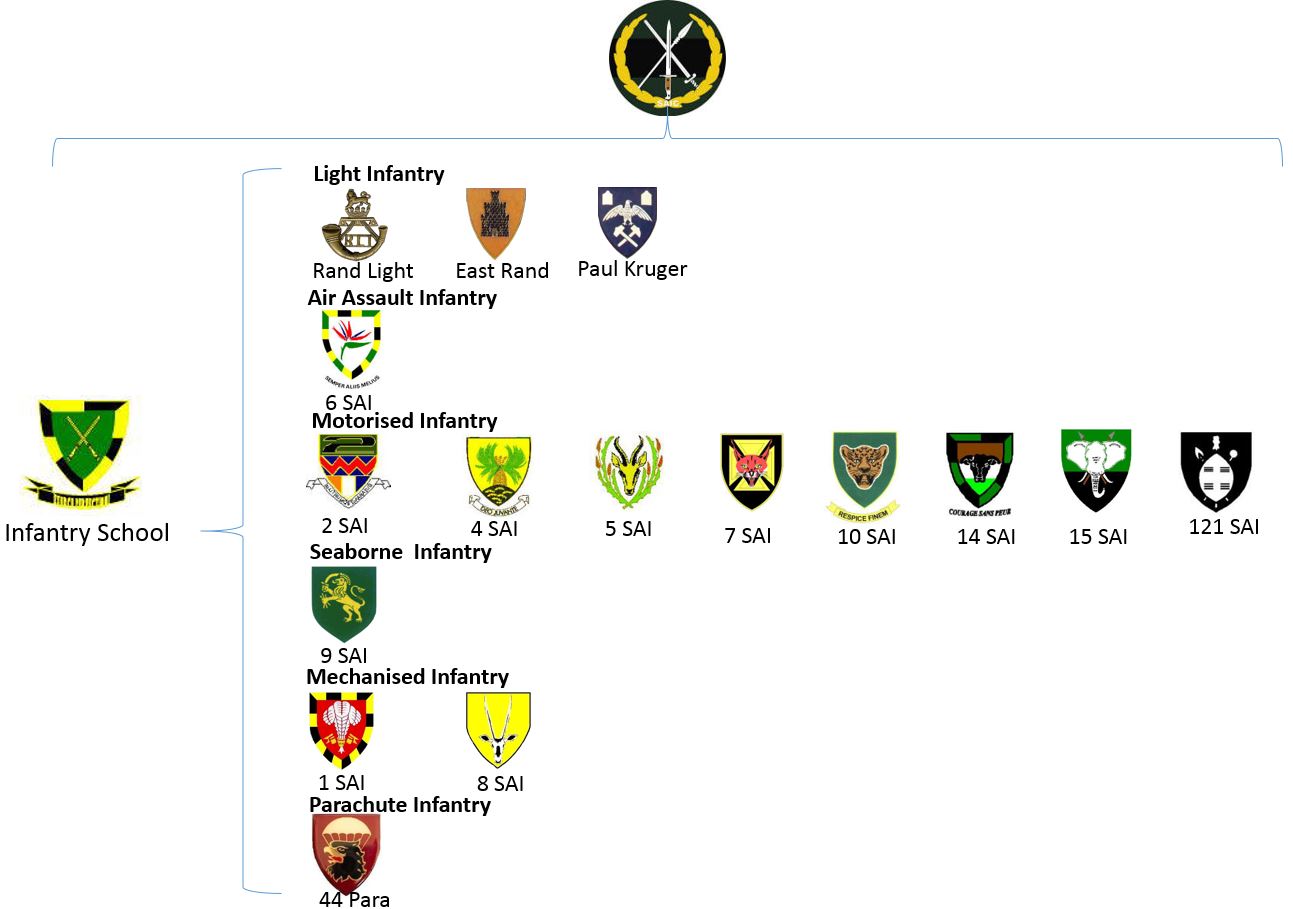 The infantry corps contains a total of 15 regular battalions in a variety of different roles:
*
The infantry corps contains a total of 15 regular battalions in a variety of different roles:
*
;Regular Force * 1 Parachute Battalion, (
 ;Reserve Force
* Chief Makhanda Regiment (
;Reserve Force
* Chief Makhanda Regiment (
 ;Reserve Force
*
;Reserve Force
*
 ;Reserve Force
* Rand Light Infantry (
;Reserve Force
* Rand Light Infantry (
 ;Regular Force
*
;Regular Force
*
 * 4 South African Infantry Battalion ( Middelburg, Mpumalanga)
* 5 South African Infantry Battalion ( Ladysmith)
* 7 South African Infantry Battalion (
* 4 South African Infantry Battalion ( Middelburg, Mpumalanga)
* 5 South African Infantry Battalion ( Ladysmith)
* 7 South African Infantry Battalion (
 All basic infantry training is done at 3 South African Infantry Battalion Training Depot at
All basic infantry training is done at 3 South African Infantry Battalion Training Depot at  More specialized training is done on an ad-hoc basis.
More specialized training is done on an ad-hoc basis. 

South African Army
The South African Army is the principal Army, land warfare force of South Africa, a part of the South African National Defence Force (SANDF), along with the South African Air Force, South African Navy and South African Military Health Servi ...
.
History
Origins: Union Defence Force
South African Infantry originated as the ''Infantry Branch'' of the Union Defence Forces in 1913. In 1915, the defence forces established the South African Overseas Expeditionary Force for war service outside Southern Africa. It included the ''South African Infantry'', comprising twelve battalions, and the ''Cape Corps'', comprising two battalions of
In 1915, the defence forces established the South African Overseas Expeditionary Force for war service outside Southern Africa. It included the ''South African Infantry'', comprising twelve battalions, and the ''Cape Corps'', comprising two battalions of Coloured
Coloureds () are multiracial people in South Africa, Namibia and, to a smaller extent, Zimbabwe and Zambia. Their ancestry descends from the interracial mixing that occurred between Europeans, Africans and Asians. Interracial mixing in South ...
volunteers. These units were disbanded in 1919.
 The Infantry Branch was enlarged in 1934, and the mounted rifles regiments were converted to infantry in 1935.
In 1943, the Infantry Branch was incorporated into the new South African Armoured Corps, which was divided into armour and infantry branches after
The Infantry Branch was enlarged in 1934, and the mounted rifles regiments were converted to infantry in 1935.
In 1943, the Infantry Branch was incorporated into the new South African Armoured Corps, which was divided into armour and infantry branches after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.
Republic Defence Force (SADF)
Separated by language
Based on the findings of a committee led by Brigadier H.B. Popper in late 1953, it was recommended that some English-speaking units be converted to Afrikaans medium units, while other regiments should be amalgamated or contracted.Separated by race (Black Infantry)
Plans were in place to establish volunteer black infantry units along ethnic lines, comparable to the Cape Corps. The volunteer black infantry unit plans eventually bore fruit with the formation of 21, 111,113 113 may refer to:
*113 (number), a natural number
*AD 113, a year
*113 BC, a year
*113 (band), a French hip hop group
*113 (MBTA bus), Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority bus route
*113 (New Jersey bus), Ironbound Garage in Newark and run to ...
, 115, 116 (Northern Sooth, Messina
Messina ( , ; ; ; ) is a harbour city and the capital city, capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of 216,918 inhabitants ...
), 117, 118, 121 and 151 Battalions. Another battalion, 114 Battalion, was planned but not actually formed.
Many of their members were Service Volunteers, members of all the population groups who were not compelled to do National Service (hence excluding white males). Eventually, the various black battalions amounted to about 16,000 troops, and some of the members of these battalions became Auxiliary or Permanent Force members.

National Defence Force (SANDF) post 1994
In the post-apartheid era, no ethnic or language-based infantry exists at all. By 1997, several units were reorganised: * 13 SAI was amalgamated into 14 SAI at Umtata, * 151 Battalion was amalgamated into 1 SAI * 113 Battalion was amalgamated into 7 SAI * 61 Mechanised Battalion Group was disbanded and elements incorporated into 8 SAI * 16 SAI was disbanded 1997. In the 1980s Regiment Port Natal appears to have been a component of 84 Motorised Brigade. It was amalgamated with the Durban Light Infantry about 1999.From Corps to Formation
In 2000 the Corps became known as the South African Army Infantry Formation. The first female battalion commander appears to have been appointed in 2001. The specialised horse/motorcycle/dog-using battalion, 12 South African Infantry Battalion, was disbanded in April 2005. The previousGeneral Officer Commanding
General officer commanding (GOC) is the usual title given in the armies of the United Kingdom and the Commonwealth (and some other nations, such as Ireland) to a general officer who holds a command appointment.
Thus, a general might be the GOC ...
up to 2012 was Lieutenant General Themba Nkabinde.
 Since 1994, South Africa's Infantry units have supported numerous operations for the United Nations and the African Union across the continent, including in the
Since 1994, South Africa's Infantry units have supported numerous operations for the United Nations and the African Union across the continent, including in the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is t ...
(MONUC/MONUSCO), the Force Intervention Brigade in particular, Burundi (South African Protection Support Detachment, and African Union Mission in Burundi), in the Comores, and with AMIS/UNMIS in Sudan.
Formation structure and units
 The infantry corps contains a total of 15 regular battalions in a variety of different roles:
*
The infantry corps contains a total of 15 regular battalions in a variety of different roles:
*Mechanised Infantry
Mechanized infantry are infantry units equipped with Armoured personnel carrier, armored personnel carriers (APCs) or infantry fighting vehicles (IFVs) for transport and combat (see also armoured corps).
As defined by the United States Army, me ...
– 2 battalions
* Motorised Infantry – 8 battalions
*Light Infantry
Light infantry refers to certain types of lightly equipped infantry throughout history. They have a more mobile or fluid function than other types of infantry, such as heavy infantry or line infantry. Historically, light infantry often fought ...
– 1 battalion
* Parachute Infantry – 1 battalion
*Air Assault Infantry
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
– 1 battalion
* Seaborne Infantry – 1 battalion
*Basic Training
Military recruit training, commonly known as basic training or boot camp, refers to the initial instruction of new military personnel. It is a physically and psychologically intensive process, which resocializes its subjects for the unique dema ...
– 1 battalion
*The Oudtshoorn army base houses the South African Infantry School.
The infantry corps contains a total of 26 reserve battalions in the following roles:
*Mechanised Infantry – 6 battalions
*Motorised Infantry – 14 battalions
*Light Infantry – 3 battalions
*Parachute Infantry – 1 battalion
*Air Assault Infantry – 2 battalions
Infantry Types
Within the South African Army, there are six main types of infantry:Type 1: Parachute Infantry
44 Parachute Regiment (Bloemfontein
Bloemfontein ( ; ), also known as Bloem, is the capital and the largest city of the Free State (province), Free State province in South Africa. It is often, and has been traditionally, referred to as the country's "judicial capital", alongsi ...
) – a brigade sized regiment consisting of the following units:;Regular Force * 1 Parachute Battalion, (
Bloemfontein
Bloemfontein ( ; ), also known as Bloem, is the capital and the largest city of the Free State (province), Free State province in South Africa. It is often, and has been traditionally, referred to as the country's "judicial capital", alongsi ...
)
* 44 Pathfinder Platoon, (Bloemfontein)
* 44 Training Wing, (Bloemfontein)
;Reserve Force
* 3 Parachute Battalion, (Bloemfontein)
Type 2: Air Assault Infantry
Air Assault infantry are trained to be deployed using helicopters. ;Regular Force * 6 South African Infantry Battalion (Grahamstown
Makhanda, formerly known as Grahamstown, is a town of about 75,000 people in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa. It is situated about northeast of Gqeberha and southwest of East London. It is the largest town in the Makana Local Mun ...
)
 ;Reserve Force
* Chief Makhanda Regiment (
;Reserve Force
* Chief Makhanda Regiment (Grahamstown
Makhanda, formerly known as Grahamstown, is a town of about 75,000 people in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa. It is situated about northeast of Gqeberha and southwest of East London. It is the largest town in the Makana Local Mun ...
)
* Chief Maqoma Regiment (Port Elizabeth
Gqeberha ( , ), formerly named Port Elizabeth, and colloquially referred to as P.E., is a major seaport and the most populous city in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa. It is the seat of the Nelson Mandela Bay Metropolitan Municipal ...
)
Type 3: Seaborne Infantry
;Regular Force * 9 South African Infantry Battalion (Cape Town
Cape Town is the legislature, legislative capital city, capital of South Africa. It is the country's oldest city and the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. Cape Town is the country's List of municipalities in South Africa, second-largest ...
)  ;Reserve Force
*
;Reserve Force
*Chief Langalibalele Rifles
The Chief Langalibalele Rifles (formerly known as the Cape Town Rifles and Duke of Edinburgh's Own Rifles) is a reserve infantry regiment of the South African Army.
History Origin
The Regiment was founded on 28 November 1855, as the Cape Rifle ...
, (Cape Town
Cape Town is the legislature, legislative capital city, capital of South Africa. It is the country's oldest city and the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. Cape Town is the country's List of municipalities in South Africa, second-largest ...
)
Type 4: Light Infantry
Fast highly mobile skirmishers. ;Regular Force * 21 South African Infantry Battalion (Johannesburg
Johannesburg ( , , ; Zulu language, Zulu and Xhosa language, Xhosa: eGoli ) (colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, Jo'burg or "The City of Gold") is the most populous city in South Africa. With 5,538,596 people in the City of Johannesburg alon ...
)  ;Reserve Force
* Rand Light Infantry (
;Reserve Force
* Rand Light Infantry (Johannesburg
Johannesburg ( , , ; Zulu language, Zulu and Xhosa language, Xhosa: eGoli ) (colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, Jo'burg or "The City of Gold") is the most populous city in South Africa. With 5,538,596 people in the City of Johannesburg alon ...
)
* OR Tambo Regiment (Germiston
Germiston, also known as kwaDukathole, is a city in the East Rand region of Gauteng, South Africa, administratively forming part of the City of Ekurhuleni Metropolitan Municipality since the latter's establishment in 2000. It functions as the m ...
)
* Lenong Regiment (Krugersdorp
Krugersdorp (Afrikaans for ''Kruger's Town'') is a mining city in the West Rand, Gauteng Province, South Africa founded in 1887 by Marthinus Pretorius and Abner Cohen. Following the discovery of gold on the Witwatersrand, a need arose for a ...
)
Type 5: Mechanised Infantry
Mechanised infantry are equipped with the Ratel infantry combat vehicle, a wheeled vehicle that can deploy over all terrain. ;Regular Force
*
;Regular Force
*1 South African Infantry Battalion
1 South African Infantry Battalion is a mechanized infantry unit of the South African Army.
History Oudtshoorn origin
With its establishment as 1 SA Infantry Training Battalion at Oudtshoorn on 26 January 1951, the unit became part of the Sou ...
(Bloemfontein)
* 8 South African Infantry Battalion ( 61 Mechanised Infantry Battalion Group was merged into this unit) (Upington
Upington () is a town founded in 1873 and located in the Northern Cape province of South Africa, on the banks of the Orange River. The town was originally called Olijvenhoutsdrift ('Olive wood drift'), due to the abundance of olive wood trees i ...
)
;Reserve Force
* General de la Rey Regiment (Potchefstroom
Potchefstroom ( ; ), colloquially known as Potch, is an college town, academic city in the North West (South African province), North West Province of South Africa. It hosts the Potchefstroom Campus of the North-West University. Potchefstro ...
)
* Job Masego Regiment (Pretoria
Pretoria ( ; ) is the Capital of South Africa, administrative capital of South Africa, serving as the seat of the Executive (government), executive branch of government, and as the host to all foreign embassies to the country.
Pretoria strad ...
)
* Gonnema Regiment (Cape Town)
* General Jan Smuts Regiment (Cape Town)
* Bambatha Rifles (Johannesburg)
Type 6: Motorised Infantry
Motorised infantry are equipped with various Samil trucks, that can be deployed over rough terrain, but is primarily a road vehicle. Since the mid-2000s, they have been using vehicles like Mamba. ;Regular Force * 2 South African Infantry Battalion (Zeerust
Zeerust is a commercial town situated in the Ngaka Modiri Molema district of North West Province, South Africa. It lies in the Marico valley, approximately 240 kilometres northwest of Johannesburg. It lies on the N4, the main road link betwee ...
)  * 4 South African Infantry Battalion ( Middelburg, Mpumalanga)
* 5 South African Infantry Battalion ( Ladysmith)
* 7 South African Infantry Battalion (
* 4 South African Infantry Battalion ( Middelburg, Mpumalanga)
* 5 South African Infantry Battalion ( Ladysmith)
* 7 South African Infantry Battalion (Phalaborwa
Phalaborwa (translated to English as ''better than the south; phala'' means ''better than and borwa'' means ''south'') is a town in the Mopani District Municipality, Limpopo province, South Africa.
Name
The place was called "Phalaborwa" by the S ...
)
* 10 South African Infantry Battalion (Mafikeng
Mahikeng ( Tswana for "Place of Rocks"), formerly known as Mafikeng and alternatively known as Mafeking (, ), is the capital city of the North West province of South Africa.
Close to South Africa's border with Botswana, Mafikeng is northeast ...
)
* 14 South African Infantry Battalion ( Mthatha)
* 15 South African Infantry Battalion ( Thohoyandou)
* 121 South African Infantry Battalion ( Mtubatuba)
;Reserve Force
* General Botha Regiment ( Barberton)
* Mapungubwe Regiment (Polokwane
Polokwane (, meaning "Sanctuary" in Northern SothoPolokwane - The Heart of the Limpopo Provin ...
)
* Johannesburg Regiment (Johannesburg)
* Andrew Mlangeni Regiment (Johannesburg)
* Solomon Mahlangu Regiment (Johannesburg)
* Tshwane Regiment (Pretoria
Pretoria ( ; ) is the Capital of South Africa, administrative capital of South Africa, serving as the seat of the Executive (government), executive branch of government, and as the host to all foreign embassies to the country.
Pretoria strad ...
)
* Buffalo Volunteer Rifles (East London
East London is the part of London, England, east of the ancient City of London and north of the River Thames as it begins to widen. East London developed as London Docklands, London's docklands and the primary industrial centre. The expansion of ...
)
* Durban Light Infantry (Durban
Durban ( ; , from meaning "bay, lagoon") is the third-most populous city in South Africa, after Johannesburg and Cape Town, and the largest city in the Provinces of South Africa, province of KwaZulu-Natal.
Situated on the east coast of South ...
)
* King Shaka Regiment (Durban
Durban ( ; , from meaning "bay, lagoon") is the third-most populous city in South Africa, after Johannesburg and Cape Town, and the largest city in the Provinces of South Africa, province of KwaZulu-Natal.
Situated on the east coast of South ...
)
* Kimberley Regiment (Kimberley
Kimberly or Kimberley may refer to:
Places and historical events
Australia
Queensland
* Kimberley, Queensland, a coastal locality in the Shire of Douglas
South Australia
* County of Kimberley, a cadastral unit in South Australia
Ta ...
)
*Ingobamakhosi Carbineers
The Ingobamakhosi Carbineers (formerly Natal Carbineers) is an infantry unit of the South African Army.
History Origins
The regiment traces its roots to 1854 but it was formally raised on 15 January 1855 and gazetted on 13 March of that year ...
(Pietermaritzburg
Pietermaritzburg (; ) is the capital and second-largest city in the province of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa after Durban. It was named in 1838 and is currently governed by the Msunduzi Local Municipality. The town was named in Zulu after King ...
)
* Mangaung Regiment (Bloemfontein)
* Nelson Mandela Regiment (Port Elizabeth
Gqeberha ( , ), formerly named Port Elizabeth, and colloquially referred to as P.E., is a major seaport and the most populous city in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa. It is the seat of the Nelson Mandela Bay Metropolitan Municipal ...
)
* Chief Albert Luthuli Regiment (Kroonstad
Kroonstad ( in Afrikaans) is a town in Free State, South Africa, consisting of the following suburbs:
Brentpark,
Constantia,
Constantia Park,
Dawid Malanville,
Elandia,
Gelukwaarts,
Goedgedacht,
Heuningspruit,
Industria,
Jordania,
Koek ...
)
Infantry Battalion internal organization
The organisation of South African motorised, mechanised, air assault and parachute infantry battalions are broadly similar, the mechanised battalion however lacks a machine gun platoon in the support company and the internal security battalion lacks the same as well as other support weapons (mortars, antitank weapons and assault pioneers). A battalion musters about 34 officers, 776 men, or 810 all ranks. A company has nine rifle sections. A battalion has nine rifle platoons and 27 rifle sections. A battalion has at its disposal the following weapons: * 8 M3 81mm mortars, * 27 M4 60mm patrol mortars, * 6 infantry antitank guns (M40A1 or Ratel 90), * 6 antitank guided missile launchers (MBDA Milan ADT3 or Ratel ZT3), * 4 Browning 12.7mm HMG and four Denel Y3 AGL (not in the mechanised infantry), * 27 7.62mm GPMG and * 9 RPG7 rocket-propelled grenade launchers (one per rifle platoon). The number of vehicles is dependent on the type of unit and role. A parachute or air assault battalion deployed by air will largely be dependent on the 104 LMT Gecko airborne amphibious 8x8 light rapid deployment logistic vehicles assigned to 44 Parachute Regiment. The number deployed will depend on the airlift available. By some accounts, a Fighting Echelon (F-Echelon) would include 88 A-Vehicles, but the numbers can be higher. In September 2008 the motorised 5 SAI Bn deployed 113 Casspir armoured personnel and weapon carriers to a force preparation exercise (Seboka) and the mechanised 8 SAI Bn deployed 107 Ratels. The A- and B-Echelons, fully mobilised, can muster up at least another 90 B-Vehicles of various types.Training
 All basic infantry training is done at 3 South African Infantry Battalion Training Depot at
All basic infantry training is done at 3 South African Infantry Battalion Training Depot at Kimberley
Kimberly or Kimberley may refer to:
Places and historical events
Australia
Queensland
* Kimberley, Queensland, a coastal locality in the Shire of Douglas
South Australia
* County of Kimberley, a cadastral unit in South Australia
Ta ...
. This is a Regular Force unit. Second phase deals with specific equipment, weapons and tactics, general and specific to the type of Infantry, and is dealt with at the unit and its training areas.
Third phase ramps up to a conventional warfare exercise usually held at Lohatla Army Battle School. Tactics such as fire and movement, as well as the amalgamation with other type formations, are done here, with expanding the scope from the squad to section to the platoon to company, battalion, and brigade exercises.  More specialized training is done on an ad-hoc basis.
More specialized training is done on an ad-hoc basis. 
Equipment
South African Infantry are trained in an assortment of equipment in addition to their personal rifles, such as:Alliances
While South Africa was part of theBritish Commonwealth
The Commonwealth of Nations, often referred to as the British Commonwealth or simply the Commonwealth, is an international association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire
The B ...
, many units formed alliances with British and other units. With the advent of the Republic in 1961, almost all of these alliances fell away either as a natural consequence of changing alliances or on instructions from the authorities. Some units have maintained the alliances unofficially.
With the change of government in 1994, South Africa once again became officially part of the Commonwealth, so alliances are once again possible.
Some examples of alliances:
* – The Rifles
The Rifles is an infantry regiment of the British Army. Formed in 2007, it consists of four Regular battalions and three Reserve battalions. Each Regular battalion was formerly an individual battalion of one of the two large regiments of the ...
; 5 Infantry Battalion
* – The Royal Welsh; 121 Infantry Battalion
Battle Honours
Many South African units have a proud history. This is particularly reflected in the many Battle Honours they have received.
Notes
References
{{SA Army Units South African administrative corps Military units and formations established in 2000