Sonometer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A monochord, also known as sonometer (see
A monochord, also known as sonometer (see
 The monochord can be used to illustrate the mathematical properties of musical pitch and to illustrate
The monochord can be used to illustrate the mathematical properties of musical pitch and to illustrate  "As the name implies, only one string is needed to do the experiments; but, since ancient times, several strings were used, all tuned in exact unison, each with a moveable bridge, so that various intervals can be compared to each other ." A "bichord instrument" is one, "having two strings in unison for each note
"As the name implies, only one string is needed to do the experiments; but, since ancient times, several strings were used, all tuned in exact unison, each with a moveable bridge, so that various intervals can be compared to each other ." A "bichord instrument" is one, "having two strings in unison for each note
 Parts of a monochord include a
Parts of a monochord include a

 The monochord is mentioned in Sumerian writings, and, according to some, was reinvented by
The monochord is mentioned in Sumerian writings, and, according to some, was reinvented by
Pianos and Their Makers Volume 1: A comprehensive history of the development of the piano from the monochord to the concert grand player piano
', p.28. Covina. . In 1618,
 A sonometer is a diagnostic instrument used to measure the tension, frequency or density of vibrations. They are used in medical settings to test both hearing and bone density. A sonometer, or audiometer, is used to determine hearing sensitivity, while a clinical bone sonometer measures bone density to help determine such conditions as the risk of osteoporosis.
In audiology, the device is used to test for hearing loss and other disorders of the ear. The audiometer measures the ability to hear sounds at frequencies normally detectable by the human ear. Several test are usually conducted using the audiometer which will then be used to assess hearing ability. Results typically are recorded on a chart known as an audiogram.
A clinical bone sonometer is a device which tests for the risk of bone fractures associated with osteoporosis. This test, called an ultrasound bone densitometry screening, is not typically used for diagnostic purposes; it is generally used as a risk assessment tool. Testing is often recommended for those whose personal history indicates a possible high risk for osteoporosis. Testing is usually conducted by an orthopedist, rheumatologist or neurologist specializing in the treatment of osteoporosis. The patient simply places his or her heel in the sonometer, and it is then scanned using ultrasound to determine bone density. This is a fast and low-cost procedure generally lasting 30 seconds or less. Results typically are available immediately following the procedure. Two score results are possible: a T-score, which compares a patient's scan against that of a young person of the same gender; and a Z-score, which compares the scan against someone of similar age, weight and gender. The T-scores results are used to assess the risk of osteoporosis. A score above -1 indicates a low risk for osteoporosis; below -1 to -2.5 indicates a risk of developing osteoporosis; and a score below -2.5 indicates more intensive testing should be performed and that osteoporosis is likely present. The Z-score reports how much bone the patient has as compared to others his age. If this number is high or low, further testing may be ordered.
A sonometer is a diagnostic instrument used to measure the tension, frequency or density of vibrations. They are used in medical settings to test both hearing and bone density. A sonometer, or audiometer, is used to determine hearing sensitivity, while a clinical bone sonometer measures bone density to help determine such conditions as the risk of osteoporosis.
In audiology, the device is used to test for hearing loss and other disorders of the ear. The audiometer measures the ability to hear sounds at frequencies normally detectable by the human ear. Several test are usually conducted using the audiometer which will then be used to assess hearing ability. Results typically are recorded on a chart known as an audiogram.
A clinical bone sonometer is a device which tests for the risk of bone fractures associated with osteoporosis. This test, called an ultrasound bone densitometry screening, is not typically used for diagnostic purposes; it is generally used as a risk assessment tool. Testing is often recommended for those whose personal history indicates a possible high risk for osteoporosis. Testing is usually conducted by an orthopedist, rheumatologist or neurologist specializing in the treatment of osteoporosis. The patient simply places his or her heel in the sonometer, and it is then scanned using ultrasound to determine bone density. This is a fast and low-cost procedure generally lasting 30 seconds or less. Results typically are available immediately following the procedure. Two score results are possible: a T-score, which compares a patient's scan against that of a young person of the same gender; and a Z-score, which compares the scan against someone of similar age, weight and gender. The T-scores results are used to assess the risk of osteoporosis. A score above -1 indicates a low risk for osteoporosis; below -1 to -2.5 indicates a risk of developing osteoporosis; and a score below -2.5 indicates more intensive testing should be performed and that osteoporosis is likely present. The Z-score reports how much bone the patient has as compared to others his age. If this number is high or low, further testing may be ordered.
The Monochord in the Medieval and Modern Classrooms
, ''JMHP''. {{Authority control Continuous pitch instruments Box zithers Measuring instruments Pythagorean philosophy
 A monochord, also known as sonometer (see
A monochord, also known as sonometer (see below
Below may refer to:
*Earth
* Ground (disambiguation)
* Soil
* Floor
* Bottom (disambiguation)
* Less than
*Temperatures below freezing
* Hell or underworld
People with the surname
* Ernst von Below (1863–1955), German World War I general
* Fr ...
), is an ancient musical
Musical is the adjective of music
Music is generally defined as the The arts, art of arranging sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Exact def ...
and scientific laboratory instrument
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physicia ...
, involving one (mono-
Numeral or number prefixes are prefixes derived from numerals or occasionally other numbers. In English and many other languages, they are used to coin numerous series of words. For example:
* unicycle, bicycle, tricycle (1-cycle, 2-cycle, 3-cyc ...
) string (chord
Chord may refer to:
* Chord (music), an aggregate of musical pitches sounded simultaneously
** Guitar chord a chord played on a guitar, which has a particular tuning
* Chord (geometry), a line segment joining two points on a curve
* Chord ( ...
). The term ''monochord'' is sometimes used as the class-name for any musical stringed instrument having only one string and a stick shaped body, also known as musical bow
The musical bow (bowstring or string bow, a subset of bar zithers) is a simple string instrument used by a number of South African peoples, which is also found in the Americas via slave trade. It consists of a flexible, usually wooden, stick ...
s. According to the Hornbostel–Sachs
Hornbostel–Sachs or Sachs–Hornbostel is a system of musical instrument classification devised by Erich Moritz von Hornbostel and Curt Sachs, and first published in the in 1914. An English translation was published in the '' Galpin Society ...
system, string bows are bar zithers (311.1) while monochords are traditionally board zithers (314). The "harmonical canon", or monochord is, at its least, "merely a string having a board
Board or Boards may refer to:
Flat surface
* Lumber, or other rigid material, milled or sawn flat
** Plank (wood)
** Cutting board
** Sounding board, of a musical instrument
* Cardboard (paper product)
* Paperboard
* Fiberboard
** Hardboa ...
under it of exactly the same length, upon which may be delineated the points at which the string must be stopped to give certain notes," allowing comparison.
A string
String or strings may refer to:
*String (structure), a long flexible structure made from threads twisted together, which is used to tie, bind, or hang other objects
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* ''Strings'' (1991 film), a Canadian anim ...
is fixed at both ends and stretched over a sound box. One or more movable bridges
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually somethi ...
are then manipulated to demonstrate mathematical relationships among the frequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from '' angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is e ...
produced. "With its single string, movable bridge and graduated rule
Rule or ruling may refer to:
Education
* Royal University of Law and Economics (RULE), a university in Cambodia
Human activity
* The exercise of political or personal control by someone with authority or power
* Business rule, a rule pert ...
, the monochord (''kanōn'' reek: law straddled the gap between notes
Note, notes, or NOTE may refer to:
Music and entertainment
* Musical note, a pitched sound (or a symbol for a sound) in music
* ''Notes'' (album), a 1987 album by Paul Bley and Paul Motian
* ''Notes'', a common (yet unofficial) shortened version ...
and numbers, intervals and ratio
In mathematics, a ratio shows how many times one number contains another. For example, if there are eight oranges and six lemons in a bowl of fruit, then the ratio of oranges to lemons is eight to six (that is, 8:6, which is equivalent to the ...
s, sense-perception and mathematical reason." However, "music, mathematics, and astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest ...
were lsoinexorably linked in the monochord."Terpstra, Siemen (1993). "An Introduction to the Monochord", ''Alexandria 2: The Journal of the Western Cosmological Traditions, Volume 2'', p.137-9. David Fideler, ed. Red Wheel/Weiser. . As a pedagogical tool for demonstrating mathematical relationships between intervals, the monochord remained in use throughout the middle ages.
Experimental use
 The monochord can be used to illustrate the mathematical properties of musical pitch and to illustrate
The monochord can be used to illustrate the mathematical properties of musical pitch and to illustrate Mersenne's laws
Mersenne's laws are laws describing the frequency of oscillation of a stretched string or monochord, useful in musical tuning and musical instrument construction.
Overview
The equation was first proposed by French mathematician and music theori ...
regarding string length and tension: "essentially a tool for measuring musical intervals". For example, when a monochord's string is open it vibrates at a particular frequency and produces a pitch. When the length of the string is halved, and plucked, it produces a pitch an octave
In music, an octave ( la, octavus: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is the interval between one musical pitch and another with double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been refer ...
higher and the string vibrates at twice the frequency of the original (2:1) . Half of this length will produce a pitch two octaves higher than the original—four times the initial frequency (4:1)—and so on. Standard diatonic Pythagorean tuning
Pythagorean tuning is a system of musical tuning in which the frequency ratios of all intervals are based on the ratio 3:2.Bruce Benward and Marilyn Nadine Saker (2003). ''Music: In Theory and Practice'', seventh edition, 2 vols. (Boston: M ...
(Ptolemy's Diatonic Ditonic) is easily derived starting from superparticular ratios, (n+1)/n, constructed from the first four counting numbers, the tetractys
The tetractys ( el, τετρακτύς), or tetrad, or the tetractys of the decad is a triangular figure consisting of ten points arranged in four rows: one, two, three, and four points in each row, which is the geometrical representation of the ...
, measured out on a monochord. The mathematics involved include the multiplication table
In mathematics, a multiplication table (sometimes, less formally, a times table) is a mathematical table used to define a multiplication operation for an algebraic system.
The decimal multiplication table was traditionally taught as an essen ...
, least common multiple
In arithmetic and number theory, the least common multiple, lowest common multiple, or smallest common multiple of two integers ''a'' and ''b'', usually denoted by lcm(''a'', ''b''), is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by bo ...
s, and prime
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only way ...
and composite number
A composite number is a positive integer that can be formed by multiplying two smaller positive integers. Equivalently, it is a positive integer that has at least one divisor other than 1 and itself. Every positive integer is composite, prime, ...
s.
 "As the name implies, only one string is needed to do the experiments; but, since ancient times, several strings were used, all tuned in exact unison, each with a moveable bridge, so that various intervals can be compared to each other ." A "bichord instrument" is one, "having two strings in unison for each note
"As the name implies, only one string is needed to do the experiments; but, since ancient times, several strings were used, all tuned in exact unison, each with a moveable bridge, so that various intervals can be compared to each other ." A "bichord instrument" is one, "having two strings in unison for each note course
Course may refer to:
Directions or navigation
* Course (navigation), the path of travel
* Course (orienteering), a series of control points visited by orienteers during a competition, marked with red/white flags in the terrain, and corresponding ...
]," such as the mandolin. With two strings one can easily demonstrate how various musical interval (musical), intervals sound. Both open strings are tuned to the same pitch, and then the movable bridge is put in a mathematical position on the second string to demonstrate, for instance, the major third
In classical music, a third is a musical interval encompassing three staff positions (see Interval number for more details), and the major third () is a third spanning four semitones. Forte, Allen (1979). ''Tonal Harmony in Concept and P ...
(at 4/5th of the string length) or the minor third
In music theory, a minor third is a musical interval that encompasses three half steps, or semitones. Staff notation represents the minor third as encompassing three staff positions (see: interval number). The minor third is one of two com ...
(at 5/6th of the string length) .
Many contemporary composers focused on microtonality
Microtonal music or microtonality is the use in music of microtones— intervals smaller than a semitone, also called "microintervals". It may also be extended to include any music using intervals not found in the customary Western tuning of ...
and just intonation
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is the tuning of musical intervals as whole number ratios (such as 3:2 or 4:3) of frequencies. An interval tuned in this way is said to be pure, and is called a just interval. Just intervals (and ...
such as Harry Partch
Harry Partch (June 24, 1901 – September 3, 1974) was an American composer, music theorist, and creator of unique musical instruments. He composed using scales of unequal intervals in just intonation, and was one of the first 20th-century co ...
, Ivor Darreg, Tony Conrad
Anthony Schmalz Conrad (March 7, 1940 – April 9, 2016) was an American video artist, experimental filmmaker, musician, composer, sound artist, teacher, and writer. Active in a variety of media since the early 1960s, he was a pioneer of both d ...
, Glenn Branca Glenn may refer to:
Name or surname
* Glenn (name)
* John Glenn, U.S. astronaut
Cultivars
* Glenn (mango)
* a 6-row barley variety
Places
In the United States:
* Glenn, California
* Glenn County, California
* Glenn, Georgia, a settlement ...
, Bart Hopkin, and Yuri Landman
Yuri Landman (born 1 February 1973) is a Dutch inventor of musical instruments and musician who has made several experimental electric string instruments for a number of artists including Lee Ranaldo of Sonic Youth, Liars, Jad Fair of Half Japa ...
constructed multistring variants of sonometers with movable bridges.
Instruments
 Parts of a monochord include a
Parts of a monochord include a tuning peg
A variety of methods are used to tune different stringed instruments. Most change the pitch produced when the string is played by adjusting the tension of the strings.
A tuning peg in a pegbox is perhaps the most common system. A peg has ...
, nut, string, moveable bridge, fixed bridge, calibration marks, belly or resonating box, and an end pin.
Instruments derived from the monochord (or its moveable bridge) include the guqin
The ''guqin'' (; ) is a plucked seven-string Chinese musical instrument. It has been played since ancient times, and has traditionally been favoured by scholars and literati as an instrument of great subtlety and refinement, as highlighted b ...
, dan bau, koto
Koto may refer to:
* Koto (band), an Italian synth pop group
* Koto (instrument), a Japanese musical instrument
* Koto (kana), a ligature of two Japanese katakana
* Koto (traditional clothing), a traditional dress made by Afro-Surinamese women
* ...
, vina, hurdy-gurdy
The hurdy-gurdy is a string instrument that produces sound by a hand-crank-turned, rosined wheel rubbing against the strings. The wheel functions much like a violin bow, and single notes played on the instrument sound similar to those of a v ...
, and clavichord
The clavichord is a stringed rectangular keyboard instrument that was used largely in the Late Middle Ages, through the Renaissance, Baroque and Classical eras.
Historically, it was mostly used as a practice instrument and as an aid to composit ...
("hence all keyboard instruments"). A monopipe is the wind instrument version of a monochord; a variable open pipe
Pipe(s), PIPE(S) or piping may refer to:
Objects
* Pipe (fluid conveyance), a hollow cylinder following certain dimension rules
** Piping, the use of pipes in industry
* Smoking pipe
** Tobacco pipe
* Half-pipe and quarter pipe, semi-circul ...
which can produce variable pitches, a sliding cylinder with the numbers of the monochord marked. End correction must be used with this method, to achieve accuracy.
Monochord practitioners


 The monochord is mentioned in Sumerian writings, and, according to some, was reinvented by
The monochord is mentioned in Sumerian writings, and, according to some, was reinvented by Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos ( grc, Πυθαγόρας ὁ Σάμιος, Pythagóras ho Sámios, Pythagoras the Samian, or simply ; in Ionian Greek; ) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His politic ...
(sixth century BCE). Dolge attributes the invention of the moveable bridge to Guido of Arezzo
Guido of Arezzo ( it, Guido d'Arezzo; – after 1033) was an Italian music theorist and pedagogue of High medieval music. A Benedictine monk, he is regarded as the inventor—or by some, developer—of the modern staff notation that had ...
around 1000 CE.Dolge, Alfred (1911). Pianos and Their Makers Volume 1: A comprehensive history of the development of the piano from the monochord to the concert grand player piano
', p.28. Covina. . In 1618,
Robert Fludd
Robert Fludd, also known as Robertus de Fluctibus (17 January 1574 – 8 September 1637), was a prominent English Paracelsian physician with both scientific and occult interests. He is remembered as an astrologer, mathematician, cosmologis ...
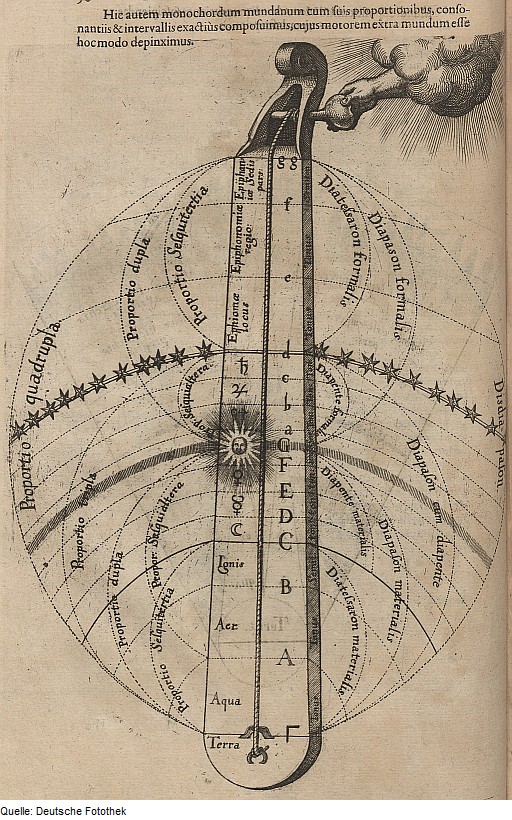
devised a mundane monochord (also celestial or divine monochord) that linked the Ptolemaic universe to musical intervals. "Was it ersenne's discoveries through use of the monochord (1637)physical intuition or a Pythagorean confidence in the importance of small whole numbers? ... It was the latter."Gozza, Paolo; ed. (2013). ''Number to Sound: The Musical Way to the Scientific Revolution'', p.279. Springer. . Gozza is referring to statements by Sigalia Dostrovsky's "Early Vibration Theory", p.185-187.
The psalmodicon
The psalmodicon (psalmodikon or salmodikon) is a stringed musical instrument; the most common variants have a single string. It was developed in Scandinavia for simplifying music in churches and schools, and as an alternative to the fiddle for ...
, a similar instrument but with a chromatic fret board replacing the moveable bridge, was developed in Denmark in the 1820s and became widespread throughout Scandinavia in churches as an alternative to the organ. Scandinavian immigrants also brought it to the United States. It became quite rare by the latter 20th century, but more recently has been revived by folk musicians.
An image of the celestial monochord was used on the 1952 cover of '' Anthology of American Folk Music'' by Harry Everett Smith
Harry Everett Smith (May 29, 1923 – November 27, 1991) was an American polymath, who was credited variously as an artist, experimental filmmaker, bohemian, mystic, record collector, hoarder, student of anthropology and a Neo-Gnostic bish ...
and in the 1977 book ''The Cosmographical Glass: Renaissance Diagrams of the Universe'' (p. 133) by S. K. Heninger Jr.
S is the nineteenth letter of the English alphabet.
S may also refer to:
History
* an Anglo-Saxon charter's number in Peter Sawyer's, catalogue Language and linguistics
* Long s (ſ), a form of the lower-case letter s formerly used where "s ...
, . A reproduction of the monochordum mundanum (mundane monochord) illustration from page 90 of Robert Fludd's "Utriusque Cosmi, Maioris scilicet et Minoris, Metaphysica, Physica, Atque Technica Historia" ("Tomus Primus"), 1617, was used as the cover art for Kepler Quartet's 2011 audio CD, '' Ben Johnston: String Quartets Nos. 1, 5 & 10'' (New World Records
New World Records is a record label that was established in 1975 through a Rockefeller Foundation grant to celebrate America's bicentennial (1976) by producing a 100-LP anthology, with American music from many genres.experimental rock
Experimental rock, also called avant-rock, is a subgenre of rock music that pushes the boundaries of common composition and performance technique or which experiments with the basic elements of the genre. Artists aim to liberate and innovate, with ...
as well as contemporary classical music
Contemporary classical music is classical music composed close to the present day. At the beginning of the 21st century, it commonly referred to the post-1945 modern forms of post-tonal music after the death of Anton Webern, and included se ...
is 3rd bridge. This technique shares the same mechanism as used on the monochord, by dividing the string into two sections with an additional bridge.
Sonometer
 A sonometer is a diagnostic instrument used to measure the tension, frequency or density of vibrations. They are used in medical settings to test both hearing and bone density. A sonometer, or audiometer, is used to determine hearing sensitivity, while a clinical bone sonometer measures bone density to help determine such conditions as the risk of osteoporosis.
In audiology, the device is used to test for hearing loss and other disorders of the ear. The audiometer measures the ability to hear sounds at frequencies normally detectable by the human ear. Several test are usually conducted using the audiometer which will then be used to assess hearing ability. Results typically are recorded on a chart known as an audiogram.
A clinical bone sonometer is a device which tests for the risk of bone fractures associated with osteoporosis. This test, called an ultrasound bone densitometry screening, is not typically used for diagnostic purposes; it is generally used as a risk assessment tool. Testing is often recommended for those whose personal history indicates a possible high risk for osteoporosis. Testing is usually conducted by an orthopedist, rheumatologist or neurologist specializing in the treatment of osteoporosis. The patient simply places his or her heel in the sonometer, and it is then scanned using ultrasound to determine bone density. This is a fast and low-cost procedure generally lasting 30 seconds or less. Results typically are available immediately following the procedure. Two score results are possible: a T-score, which compares a patient's scan against that of a young person of the same gender; and a Z-score, which compares the scan against someone of similar age, weight and gender. The T-scores results are used to assess the risk of osteoporosis. A score above -1 indicates a low risk for osteoporosis; below -1 to -2.5 indicates a risk of developing osteoporosis; and a score below -2.5 indicates more intensive testing should be performed and that osteoporosis is likely present. The Z-score reports how much bone the patient has as compared to others his age. If this number is high or low, further testing may be ordered.
A sonometer is a diagnostic instrument used to measure the tension, frequency or density of vibrations. They are used in medical settings to test both hearing and bone density. A sonometer, or audiometer, is used to determine hearing sensitivity, while a clinical bone sonometer measures bone density to help determine such conditions as the risk of osteoporosis.
In audiology, the device is used to test for hearing loss and other disorders of the ear. The audiometer measures the ability to hear sounds at frequencies normally detectable by the human ear. Several test are usually conducted using the audiometer which will then be used to assess hearing ability. Results typically are recorded on a chart known as an audiogram.
A clinical bone sonometer is a device which tests for the risk of bone fractures associated with osteoporosis. This test, called an ultrasound bone densitometry screening, is not typically used for diagnostic purposes; it is generally used as a risk assessment tool. Testing is often recommended for those whose personal history indicates a possible high risk for osteoporosis. Testing is usually conducted by an orthopedist, rheumatologist or neurologist specializing in the treatment of osteoporosis. The patient simply places his or her heel in the sonometer, and it is then scanned using ultrasound to determine bone density. This is a fast and low-cost procedure generally lasting 30 seconds or less. Results typically are available immediately following the procedure. Two score results are possible: a T-score, which compares a patient's scan against that of a young person of the same gender; and a Z-score, which compares the scan against someone of similar age, weight and gender. The T-scores results are used to assess the risk of osteoporosis. A score above -1 indicates a low risk for osteoporosis; below -1 to -2.5 indicates a risk of developing osteoporosis; and a score below -2.5 indicates more intensive testing should be performed and that osteoporosis is likely present. The Z-score reports how much bone the patient has as compared to others his age. If this number is high or low, further testing may be ordered.
See also
* *Beat (acoustics)
In acoustics, a beat is an Interference (wave propagation), interference pattern between two sounds of slightly different frequency, frequencies, ''perceived'' as a periodic variation in amplitude (music), volume whose rate is the Difference (math ...
* Harmonic Canon
*Long-string instrument
The long-string instrument is a musical instrument in which the string is of such a length that the fundamental transverse wave is below what a person can hear as a tone (±20 Hz). If the tension and the length result in sounds with such ...
References
External links
The Monochord in the Medieval and Modern Classrooms
, ''JMHP''. {{Authority control Continuous pitch instruments Box zithers Measuring instruments Pythagorean philosophy