Somerville, MA on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Somerville ( ) is a city located directly to the northwest of
masshist.org. Accessed November 30, 2022. The location was the site where the executed body of a local slave known as "Mark", owned by John Codman, was publicly Defeated and in retreat, the British army passed again through Somerville en route back to Boston. Upon reaching Union Square, the British marched down Washington Street as far as the base of Prospect Hill, where a skirmish took place. The handful of rebellious locals, having heard of the storied battles at Lexington and Concord earlier that day, caught an exhausted retreating British contingent off guard. As the story goes, 65-year-old minuteman James Miller lost his life in the scuffle while standing his ground against the British. He was shot thirteen times after famously telling a retreating colleague, "I am too old to run."
Somerville occupied a conspicuous position during the entire
Defeated and in retreat, the British army passed again through Somerville en route back to Boston. Upon reaching Union Square, the British marched down Washington Street as far as the base of Prospect Hill, where a skirmish took place. The handful of rebellious locals, having heard of the storied battles at Lexington and Concord earlier that day, caught an exhausted retreating British contingent off guard. As the story goes, 65-year-old minuteman James Miller lost his life in the scuffle while standing his ground against the British. He was shot thirteen times after famously telling a retreating colleague, "I am too old to run."
Somerville occupied a conspicuous position during the entire
 The Late Industrial Period (1870–1915) was a time of phenomenal growth for Somerville in all spheres including civic and commercial ventures. Infrastructure such as rail, water lines, telegraph and electricity were established and connected to surrounding towns. The population soared from 15,000 to 90,000. While brickmaking had taken a hold in the area after the railroads first arrived in the 1830s, Somerville's brickyards boomed through 1870. Meatpacking soon displaced brickmaking as the primary industry in the city, dubbed "The Chicago of New England". Additionally, Somerville's location adjacent to Boston and proximity to rail and road transportation made it an ideal location for distribution facilities.
It was in this period that Irish immigrants moved to Somerville to work in the brickyards and on the railroad. At the same time, older residents of East Boston and Charlestown moved to Somerville to seek a more bucolic setting than that of more densely populated areas. They also worked to maintain political control over immigrant groups, using slogans such as "Keep Somerville Republican" and establishing a local branch of the anti-Catholic
The Late Industrial Period (1870–1915) was a time of phenomenal growth for Somerville in all spheres including civic and commercial ventures. Infrastructure such as rail, water lines, telegraph and electricity were established and connected to surrounding towns. The population soared from 15,000 to 90,000. While brickmaking had taken a hold in the area after the railroads first arrived in the 1830s, Somerville's brickyards boomed through 1870. Meatpacking soon displaced brickmaking as the primary industry in the city, dubbed "The Chicago of New England". Additionally, Somerville's location adjacent to Boston and proximity to rail and road transportation made it an ideal location for distribution facilities.
It was in this period that Irish immigrants moved to Somerville to work in the brickyards and on the railroad. At the same time, older residents of East Boston and Charlestown moved to Somerville to seek a more bucolic setting than that of more densely populated areas. They also worked to maintain political control over immigrant groups, using slogans such as "Keep Somerville Republican" and establishing a local branch of the anti-Catholic
 According to the
According to the
 Somerville's commercial property is not concentrated in a recognized downtown
Somerville's commercial property is not concentrated in a recognized downtown
 Somerville's industrial past left behind many legacies, including the invention of Marshmallow creme, Marshmallow Fluff by Archibald Query. In 1914, the city became the home of the original Economy Grocery Store, which later grew into the Stop & Shop grocery chain. Two related food service chains, Steve's Ice Cream and Bertucci's, sprung from adjacent lots in
Somerville's industrial past left behind many legacies, including the invention of Marshmallow creme, Marshmallow Fluff by Archibald Query. In 1914, the city became the home of the original Economy Grocery Store, which later grew into the Stop & Shop grocery chain. Two related food service chains, Steve's Ice Cream and Bertucci's, sprung from adjacent lots in
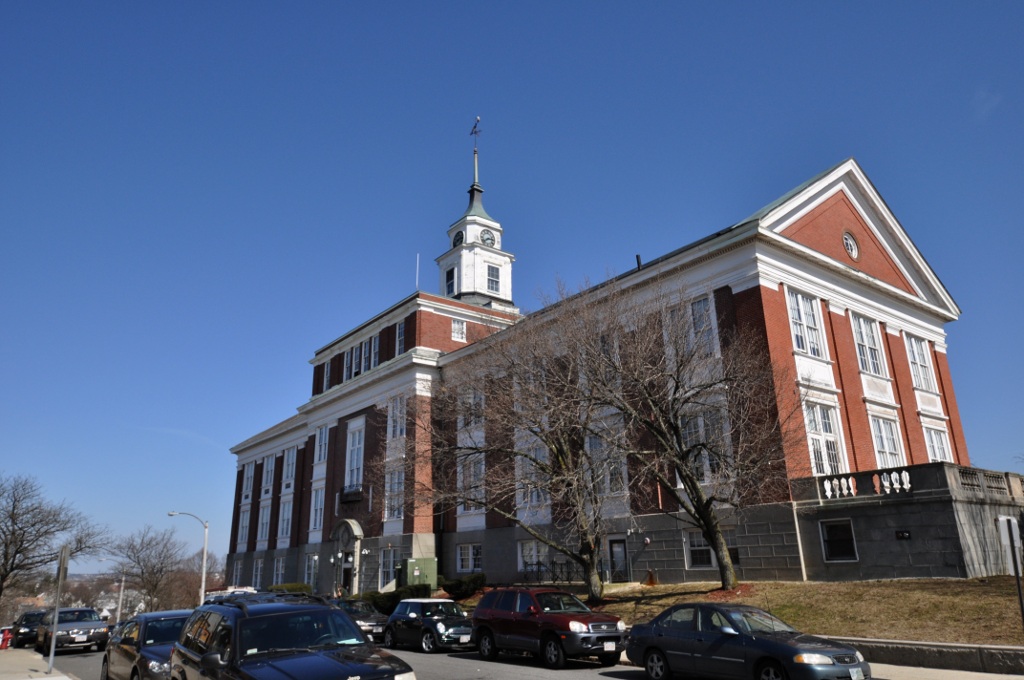


 The School Committee has seven independently elected officials as well as the Mayor and the President of the Board of Aldermen. The budget is approved by both the School Committee and the Board of Aldermen. The Chair is Adam Sweeting from Ward 3 and the Vice-Chair is Carrie Normand from Ward 7.
Also included in the school district is the Somerville Center for Adult Learning Experiences. The former Powder House Community School (which closed due to low enrollment in 2004) is being considered for redevelopment, either as a consolidated location for city offices if funding is obtained under the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 or as some other type of development.
Though formally listed as being located in Medford,
The School Committee has seven independently elected officials as well as the Mayor and the President of the Board of Aldermen. The budget is approved by both the School Committee and the Board of Aldermen. The Chair is Adam Sweeting from Ward 3 and the Vice-Chair is Carrie Normand from Ward 7.
Also included in the school district is the Somerville Center for Adult Learning Experiences. The former Powder House Community School (which closed due to low enrollment in 2004) is being considered for redevelopment, either as a consolidated location for city offices if funding is obtained under the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 or as some other type of development.
Though formally listed as being located in Medford,
 The city is served by a number of news sources, including:
*Somerville Neighborhood News (website)
*Somerville Community Access Television
*Boston Free Radio (an all-volunteer free-speech community radio station in Somerville)
*''
The city is served by a number of news sources, including:
*Somerville Neighborhood News (website)
*Somerville Community Access Television
*Boston Free Radio (an all-volunteer free-speech community radio station in Somerville)
*''

 Somerville, originally built as a streetcar suburb of Boston, has a framework and layout ideal for public transit. Its traditionally designed neighborhoods, set among grid-like street networks, connect in a walkable, transit-friendly system. Transit systems shrunk and all but disappeared as automobiles became the primary mode of transportation, however, and streetcars left the city several decades ago. The City of Somerville is serviced by the Massachusetts Bay Transit Authority, Massachusetts Bay Transit Authority (MBTA) transit service.
Somerville, originally built as a streetcar suburb of Boston, has a framework and layout ideal for public transit. Its traditionally designed neighborhoods, set among grid-like street networks, connect in a walkable, transit-friendly system. Transit systems shrunk and all but disappeared as automobiles became the primary mode of transportation, however, and streetcars left the city several decades ago. The City of Somerville is serviced by the Massachusetts Bay Transit Authority, Massachusetts Bay Transit Authority (MBTA) transit service.
 Although only 43.6% of Somerville commuters drove alone to work in 2013, several major arteries pass through the city.
McGrath Highway is a major north–south route that represents the portion of Massachusetts Route 28 through the city of Somerville. McGrath is the continuation of Monsignor O'Brien Highway in
Although only 43.6% of Somerville commuters drove alone to work in 2013, several major arteries pass through the city.
McGrath Highway is a major north–south route that represents the portion of Massachusetts Route 28 through the city of Somerville. McGrath is the continuation of Monsignor O'Brien Highway in
''History of Middlesex County, Massachusetts'', Volume 1 (A-H) Volume 2 (L-W)
published 1879 and 1880. 572 and 505 pages
Somerville article
by E.C.Booth in volume 2 pages 309–338
Somerville Fire Local 76
. * Dutton, E.P
Chart of Boston Harbor and Massachusetts Bay with Map of Adjacent Country.
Published 1867. * * Ostrander, Susan A. ''Citizenship and Governance in a Changing City: Somerville, MA'' (Temple University Press; 2013) 190 pages; study of tensions between immigrants and a new middle class in politics and community activism * * Edward Augustus Samuels, Samuels, Edward Augustus; Kimball, Henry Hastings
"Somerville, past and present: an illustrated historical souvenir"
Boston : Samuels & Kimball, 1897 * Somerville, Arlington and Belmont Directory
186918731876
* * Wall & Gray
''1871 Atlas of Massachusetts''.Map of Massachusetts.Map of Middlesex County.
Somerville Chamber of Commerce
{{authority control Somerville, Massachusetts, Cities in Massachusetts Irish-American neighborhoods Populated places established in 1630 Cities in Middlesex County, Massachusetts 1630 establishments in Massachusetts
Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the capital city, state capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financ ...
, and north of Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge beca ...
, in Middlesex County, Massachusetts
Middlesex County is located in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, in the United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 1,632,002, making it the most populous county in both Massachusetts and New England and the 22nd most populous cou ...
, United States. As of the 2020 United States Census, the city had a total population of 81,045 people. With an area of , the city has a density of , making it the most densely populated municipality in New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian province ...
and the 16th most densely populated incorporated municipality in the country. Somerville was established as a town in 1842, when it was separated from Charlestown. In 2006, the city was named the best-run city in Massachusetts by ''The Boston Globe
''The Boston Globe'' is an American daily newspaper founded and based in Boston, Massachusetts. The newspaper has won a total of 27 Pulitzer Prizes, and has a total circulation of close to 300,000 print and digital subscribers. ''The Boston Glob ...
''. In 1972, 2009, and 2015, the city received the All-America City Award
The All-America City Award is a community recognition program in the United States given by the National Civic League. The award recognizes the work of communities in using inclusive civic engagement to address critical issues and create strong ...
. It is home to Tufts University
Tufts University is a private research university on the border of Medford and Somerville, Massachusetts. It was founded in 1852 as Tufts College by Christian universalists who sought to provide a nonsectarian institution of higher learnin ...
, which has its campus along the Somerville and Medford border.
History
Early settlement
The territory now comprising the city of Somerville was first settled by Europeans in 1629 as part of Charlestown. In 1629, English surveyor Thomas Graves led a scouting party of 100Puritans
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Catholic Church, Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become m ...
from the settlement of Salem to prepare the site for the Great Migration of Puritans
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Catholic Church, Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become m ...
from England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
. Graves was attracted to the narrow Mishawum Peninsula between the Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was ...
and Mystic rivers, linked to the mainland at the present-day Sullivan Square
Sullivan Square is a traffic circle located at the north end of the Charlestown neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. It is named after James Sullivan, an early 19th-century Governor of Massachusetts. Sullivan Square station on the MBTA Orang ...
. The area of earliest settlement was based at City Square on the peninsula, though the territory of Charlestown officially included all of what is now Somerville, as well as Medford, Everett, Malden, Stoneham, Melrose Melrose may refer to:
Places
United Kingdom
* Melrose, Scottish Borders, a town in the Scottish Borders, Scotland
** Melrose Abbey, ruined monastery
** Melrose RFC, rugby club
Australia
* Melrose, Queensland, a locality in the South Burnet ...
, Woburn, Burlington, and parts of Arlington and Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge beca ...
. From that time until 1842, the area of present-day Somerville was referred to as "beyond the Neck" in reference to the thin spit of land, the Charlestown Neck, that connected it to the Charlestown Peninsula.
The first European settler in Somerville of whom there is any record was John Woolrich, an Indian trader who came from the Charlestown Peninsula in 1630, and settled near what is now Dane Street. Others soon followed Woolrich, locating in the vicinity of present-day Union Square
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
. In 1639 colonists officially acquired the land in what is now Somerville from the Squaw Sachem of Mistick
Squaw Sachem of Mistick (c. 1590-1650 or 1667) was a prominent leader of a Massachusett tribe who deeded large tracts of land in eastern Massachusetts to early colonial settlers.
Squaw Sachem was the widow of Nanepashemet, the Sachem of the Pawtuc ...
. The population continued to slowly increase, and by 1775 there were about 500 inhabitants scattered across the area. Otherwise, the area was mostly used as grazing and farmland. It was once known as the "Stinted Pasture" or "Cow Commons", as early settlers of Charlestown had the right to pasture a certain number of cows in the area.
John Winthrop
John Winthrop (January 12, 1587/88 – March 26, 1649) was an English Puritan lawyer and one of the leading figures in founding the Massachusetts Bay Colony, the second major settlement in New England following Plymouth Colony. Winthrop led ...
, the first colonial governor of the Massachusetts Bay Colony
The Massachusetts Bay Colony (1630–1691), more formally the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, was an English settlement on the east coast of North America around the Massachusetts Bay, the northernmost of the several colonies later reorganized as the ...
, was granted of land in the area in 1631. Named for the ten small knolls located on the property, Ten Hills Farm extended from the Cradock Bridge in present-day Medford Square to Convent Hill in East Somerville. Winthrop lived, planted, and raised cattle on the farm. It is also where he launched the first ship in Massachusetts, the "Blessing of the Bay
''Blessing of the Bay'' was the second oceangoing, non-fishing vessel built in what is now the United States, preceded only by the ''Virginia'', in 1607.
Construction
The ''Blessing of the Bay'' was a thirty-ton barque or a pinnace, built larg ...
". Built for trading purposes in the early 1630s, it was soon armed for use as a patrol boat for the New England coast. It is seen as a precursor to the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
. The "Ten Hills
Ten Hills is a neighborhood in the northeastern part of the city of Somerville, Massachusetts. The area is roughly wedge-shaped, about in size, and is bounded by the Mystic River to the north, McGrath Highway to the east, and is largely separ ...
" neighborhood, located in the northeastern part of the city, has retained the name for over 300 years. New research has found that less than a decade after John Winthrop moved to the farm in 1631, there were enslaved Native American prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
on the property. Each successive owner of Ten Hills Farm would depend upon slavery's profits until the 1780s, when Massachusetts abolished the practice.
In a short time, the settlers began laying out roads in all directions in search of more land for planting and trade with various Native American tribes in the area. Laid out as early as the mid-1630s, the earliest highway in Somerville was probably what is now Washington Street, and led from present-day Sullivan Square to Harvard Square
Harvard Square is a triangular plaza at the intersection of Massachusetts Avenue, Brattle Street and John F. Kennedy Street near the center of Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. The term "Harvard Square" is also used to delineate the busin ...
. In its earliest days, Washington Street was known as the "Road to Newtowne" (renamed Cambridge in 1638). During the 1700s and early 1800s, Washington Street, together with Somerville Avenue, comprised "Milk Row", a route favored by Middlesex County dairy farmers as the best way to get to the markets of Charlestown and Boston.
Laid out in 1636, Broadway was likely the second highway built in the area. Originally called "Menotomie's Road", it ran from the Charlestown Neck to the settlement at Menotomy (present-day Arlington). Initially bordered by farmsteads, Broadway would come into its own as a commercial thoroughfare after horse-drawn trolleys were
introduced to the highway in 1858.
Role in the Revolutionary War
Somerville was home to one of the first hostile acts of theAmerican Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of ...
. The removal of gunpowder by British soldiers from a powder magazine in 1774, and the massive popular reaction that ensued, are considered to be a turning point in the events leading up to war.
First built by settlers for use as a windmill in the early 1700s, the Old Powder House
Powder House Square is a neighborhood and landmark rotary in Somerville, Massachusetts, United States. It is also known locally as Powder House Circle. It is the 6-way intersection of College Avenue, Broadway, Warner Street, and Powder House Bo ...
was sold to the colonial government of Massachusetts for use as a gunpowder magazine
A gunpowder magazine is a magazine (building) designed to store the explosive gunpowder in wooden barrels for safety. Gunpowder, until superseded, was a universal explosive used in the military and for civil engineering: both applications req ...
in 1747. Located at the intersection of Broadway and College Avenue in present-day Powder House Square
Powder House Square is a neighborhood and landmark rotary in Somerville, Massachusetts, United States. It is also known locally as Powder House Circle. It is the 6-way intersection of College Avenue, Broadway, Warner Street, and Powder House Bo ...
, the Old Powder House held the largest supply of gunpowder in all of Massachusetts. General Thomas Gage
General Thomas Gage (10 March 1718/192 April 1787) was a British Army general officer and colonial official best known for his many years of service in North America, including his role as British commander-in-chief in the early days of the ...
, who had become the military governor of Massachusetts in May 1774, was charged with enforcement of the highly unpopular Intolerable Acts
The Intolerable Acts were a series of punitive laws passed by the British Parliament in 1774 after the Boston Tea Party. The laws aimed to punish Massachusetts colonists for their defiance in the Tea Party protest of the Tea Act, a tax measure ...
, which British Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the Parliamentary sovereignty in the United Kingdom, supreme Legislature, legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of We ...
had passed in response to the Boston Tea Party
The Boston Tea Party was an American political and mercantile protest by the Sons of Liberty in Boston, Massachusetts, on December 16, 1773. The target was the Tea Act of May 10, 1773, which allowed the British East India Company to sell ...
. Seeking to prevent the outbreak of war, he believed that the best way to accomplish this was by secretly removing military stores from storehouses and arsenals in New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian province ...
.
Just after dawn on September 1, 1774, a force of roughly 260 British regulars from the 4th Regiment, under the command of Lieutenant Colonel George Maddison, were rowed in secrecy up the Mystic River
The Mystic River is a riverU.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed April 1, 2011 in Massachusetts, in the United States. In Massachusett, means "large estuary," alluding to t ...
from Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the capital city, state capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financ ...
to a landing point near Winter Hill. From there they marched about to the Powder House, and after sunrise removed all of the gunpowder. Most of the regulars then returned to Boston the way they had come, but a small contingent marched on to Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge beca ...
, seizing two field pieces
Field may refer to:
Expanses of open ground
* Field (agriculture), an area of land used for agricultural purposes
* Airfield, an aerodrome that lacks the infrastructure of an airport
* Battlefield
* Lawn, an area of mowed grass
* Meadow, a ...
from the Cambridge Common.Fischer
Fischer is a German occupational surname, meaning fisherman. The name Fischer is the fourth most common German surname. The English version is Fisher.
People with the surname A
* Abraham Fischer (1850–1913) South African public official
* ...
, pp. 44–45 The field pieces and powder were then taken from Boston to the British stronghold on Castle Island, then known as Castle William (renamed Fort Independence in 1779).
In response to the raid, amid rumors that blood had been shed, alarm spread through the countryside as far as Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its cap ...
and beyond, and American Patriots
Patriots, also known as Revolutionaries, Continentals, Rebels, or American Whigs, were the colonists of the Thirteen Colonies who rejected British rule during the American Revolution, and declared the United States of America an independent na ...
sprang into action, fearing that war was at hand. Thousands of militiamen began streaming toward Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the capital city, state capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financ ...
and Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge beca ...
, and mob action forced Loyalists
Loyalism, in the United Kingdom, its overseas territories and its former colonies, refers to the allegiance to the British crown or the United Kingdom. In North America, the most common usage of the term refers to loyalty to the British Crow ...
and some government officials to flee to the protection of the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gur ...
. This action provided a "dress rehearsal" for the Battles of Lexington and Concord
The Battles of Lexington and Concord were the first military engagements of the American Revolutionary War. The battles were fought on April 19, 1775, in Middlesex County, Province of Massachusetts Bay, within the towns of Lexington, Concor ...
seven months later in the famous "shot heard 'round the world", and inflamed already heated feelings on both sides, spurring actions by both British and American forces to remove powder and cannon to secure locations.
After the raid on the Powder House, the colonists took action to conceal arms and munitions of war in Concord. When General Gage found out, he was resolved to take the powder by force if necessary. The Americans learned that the British intended to start for Concord on April 18, 1775, and couriers Paul Revere
Paul Revere (; December 21, 1734 O.S. (January 1, 1735 N.S.)May 10, 1818) was an American silversmith, engraver, early industrialist, Sons of Liberty member, and Patriot and Founding Father. He is best known for his midnight ride to al ...
and William Dawes
William Dawes Jr. (April 6, 1745 – February 25, 1799) was one of several men who in April 1775 alerted colonial minutemen in Massachusetts of the approach of British army troops prior to the Battles of Lexington and Concord at the outset ...
set out on their famous ride to warn the farmers and militiamen in between Boston and Concord, including Sam Adams and John Hancock
John Hancock ( – October 8, 1793) was an American Founding Father, merchant, statesman, and prominent Patriot of the American Revolution. He served as president of the Second Continental Congress and was the first and third Governor of ...
. That night, he set out from the North End through Charlestown towards East Somerville. In Revere's own written account of his ride, he mentions a specific location in Somerville (then part of Charlestown).Focus on: Paul Revere's ridemasshist.org. Accessed November 30, 2022. The location was the site where the executed body of a local slave known as "Mark", owned by John Codman, was publicly
gibbet
A gibbet is any instrument of public execution (including guillotine, executioner's block, impalement stake, hanging gallows, or related scaffold). Gibbeting is the use of a gallows-type structure from which the dead or dying bodies of crimi ...
ed and displayed for several years after his execution. The location is probably near the site of the present day Holiday Inn on Washington Street. Revere wrote "nearly opposite where Mark was hung in chains, I saw two men on Horse back, under a Tree", which he then realized were two British officers stationed on Washington Street. They immediately pursued him, and Revere galloped up Broadway towards Winter Hill and eventually eluded them. His warning gave the militia enough time to prepare for battle, and launch the American Revolution.
Shortly after Paul Revere set out on his ride, Lieutenant Colonel Francis Smith and 700 British Army regulars landed near Lechmere Square
Lechmere Square ( ) is located at the intersection of Cambridge Street and First Street in East Cambridge, Massachusetts. It was originally named for the Colonial-era landowner Richard Lechmere, a Loyalist who returned to England at the beginnin ...
. As it was nearly high tide, East Cambridge was an island and the troops, skirting the marshes, were obliged to wade "thigh deep" to reach Somerville. They probably came through Prospect Street into Washington Street, and through Union Square.
 Defeated and in retreat, the British army passed again through Somerville en route back to Boston. Upon reaching Union Square, the British marched down Washington Street as far as the base of Prospect Hill, where a skirmish took place. The handful of rebellious locals, having heard of the storied battles at Lexington and Concord earlier that day, caught an exhausted retreating British contingent off guard. As the story goes, 65-year-old minuteman James Miller lost his life in the scuffle while standing his ground against the British. He was shot thirteen times after famously telling a retreating colleague, "I am too old to run."
Somerville occupied a conspicuous position during the entire
Defeated and in retreat, the British army passed again through Somerville en route back to Boston. Upon reaching Union Square, the British marched down Washington Street as far as the base of Prospect Hill, where a skirmish took place. The handful of rebellious locals, having heard of the storied battles at Lexington and Concord earlier that day, caught an exhausted retreating British contingent off guard. As the story goes, 65-year-old minuteman James Miller lost his life in the scuffle while standing his ground against the British. He was shot thirteen times after famously telling a retreating colleague, "I am too old to run."
Somerville occupied a conspicuous position during the entire Siege of Boston
The siege of Boston (April 19, 1775 – March 17, 1776) was the opening phase of the American Revolutionary War. New England militiamen prevented the movement by land of the British Army, which was garrisoned in what was then the peninsular tow ...
, which lasted nine months, and Prospect Hill became the central position of the Continental Army's chain of emplacements north of Boston. Its height and commanding view of Boston and the harbor had tremendous strategic value and the fortress became known as the "Citadel". Originally occupied by just 400 men, Prospect Hill became a primary encampment for American forces after General Israel Putnam
Israel Putnam (January 7, 1718 – May 29, 1790), popularly known as "Old Put", was an American military officer and landowner who fought with distinction at the Battle of Bunker Hill during the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783). He als ...
's retreat from the Battle of Bunker Hill
The Battle of Bunker Hill was fought on June 17, 1775, during the Siege of Boston in the first stage of the American Revolutionary War. The battle is named after Bunker Hill in Charlestown, Massachusetts, which was peripherally involved in ...
. It is believed that on January 1, 1776, the Grand Union Flag
The "Grand Union Flag" (also known as the "Continental Colours", the "Congress Flag", the
"Cambridge Flag", and the "First Navy Ensign") is considered to be the first national flag of the United States of America.
Similar to the current U.S. ...
flew for the first time at the Citadel, the first official raising of an American flag.
Independence, urbanization and rapid growth
With the Revolutionary War over, the residents of Somerville were able once again to devote their energies wholeheartedly to the business of making a living. From the 1780s until Somerville's separation from Charlestown in 1842, material progress was continuous, if a bit slow. As transportation infrastructure gradually transformed the area, new industries sprang up, such as brickmaking, quarrying and dairy farming. Transportation improvements in the early to mid-1800s factored significantly in the growth of a more urban residential form and Somerville's incorporation as a City in 1872. These improvements included the opening of theMiddlesex Canal
The Middlesex Canal was a 27-mile (44-kilometer) barge canal connecting the Merrimack River with the port of Boston. When operational it was 30 feet (9.1 m) wide, and 3 feet (0.9 m) deep, with 20 locks, each 80 feet (24 m) long and between 10 and ...
through Somerville in 1803, various turnpikes such as Medford and Beacon streets, built during the 1810s and 1820s, and especially the introduction of rail lines. In 1841, the Fitchburg Railroad
The Fitchburg Railroad is a former railroad company, which built a railroad line across northern Massachusetts, United States, leading to and through the Hoosac Tunnel. The Fitchburg was leased to the Boston and Maine Railroad in 1900. The main li ...
was built between Boston and Fresh Pond in Cambridge, paralleling the route of Somerville Avenue. This led to the establishment of industries along its path. Soon after, in 1843 the Fitchburg Railroad commenced passenger service and enabled residential development along the southern slopes of Prospect and Spring hills. By the early 1840s, the population of present-day Somerville topped 1,000 for the first time.
Despite the growth, however, discontent was growing steadily outside the "neck". The area's rural farmers paid taxes to the local government in Charlestown, but received little in return. By 1842, the area had no churches, few schools, no taverns, and suffered from poor and impassable roads. For many years after the Revolution the two parts of Charlestown styled "within" and "without the neck" were nearly equal in population; the former had by this time completely outstripped the latter. With this growth of population and trade came the need of city institutions, and consequently greater expenses were involved. Therefore, the rural part of Charlestown found herself contributing to the paving of the streets, the maintenance of a night watch, to the building of engine houses, and various other improvements from which they derived little benefit.
In 1828, a petition was presented to the Legislature
A legislature is an deliberative assembly, assembly with the authority to make laws for a Polity, political entity such as a Sovereign state, country or city. They are often contrasted with the Executive (government), executive and Judiciary, ...
asking that a part of
Charlestown be set off as a separate town, to be known as Warren. This petition was subsequently withdrawn. The desire for a separate township continued to spread, and by 1841, becoming impatient at the neglect of the government to adequately provide for their needs, the inhabitants again agitated a division of the town, and a meeting in reference to the matter was held November 22 in the Prospect Hill school house.
A petition was accordingly drawn up and signed by Guy C. Hawkins and 151 others, and a committee deputed to further its passage through the Legislature, then in session. A bill incorporating a new town was signed by the governor on March 3, 1842. The original choice for the city's new name, after breaking away from Charlestown, was Walford, after the first settler of Charlestown, Thomas Walford. However, this name was not adopted by the separation committee. Charles Miller, a member of this committee, proposed the name "Somerville", which was ultimately chosen. It was not derived from any one person's name, and a report commissioned by the Somerville Historical Society found that Somerville was a "purely fanciful name".
Before Somerville became a township in 1842 the area was primarily populated by British farmers and brick makers who sold their wares in the markets of Boston, Cambridge and Charlestown. As the markets grew, the population of Somerville increased six-fold between the years of 1842 and 1870 to 14,685. With the sharp influx of immigrants to the Somerville area, industry boomed and brick manufacturing became the predominant trade. Before mechanical presses were invented, Somerville produced 1.3 million bricks a year. Thereafter, production increased rapidly to 5.5 million bricks a year, and the success of the brickyards began to attract numerous other industries. In 1851, American Tubes Works opened, followed by meat processing and packaging plants. Other Somerville factories came to produce steam engines, boilers, household appliances, glass, and iron.
Shortly thereafter Somerville incorporated as a city in 1872. The population growth was due in part to improvements in pre-existing transportation lines, as well as a new rail line, the Lexington and Arlington Railroad
Lexington may refer to:
Places England
* Laxton, Nottinghamshire, formerly Lexington
Canada
* Lexington, a district in Waterloo, Ontario
United States
* Lexington, Kentucky, the largest city with this name
* Lexington, Massachusetts, the old ...
, introduced through Davis Square
Davis Square is a major intersection in the northwestern section of Somerville, Massachusetts where several streets meet: Holland Street, Dover Street, Day Street, Elm Street, Highland Avenue, and College Avenue. The name is often used to refer ...
in 1870. At its height, Somerville was served by eight passenger rail stations. Somerville's buoyant economy during this period was tied to industries that tended to locate at the periphery of the residential core, near freight rail corridors. By the mid 1870s meat packing
The meat-packing industry (also spelled meatpacking industry or meat packing industry) handles the slaughtering, processing, packaging, and distribution of meat from animals such as cattle, pigs, sheep and other livestock. Poultry is general ...
plants were the primary employers and profit centers of the community.
 The Late Industrial Period (1870–1915) was a time of phenomenal growth for Somerville in all spheres including civic and commercial ventures. Infrastructure such as rail, water lines, telegraph and electricity were established and connected to surrounding towns. The population soared from 15,000 to 90,000. While brickmaking had taken a hold in the area after the railroads first arrived in the 1830s, Somerville's brickyards boomed through 1870. Meatpacking soon displaced brickmaking as the primary industry in the city, dubbed "The Chicago of New England". Additionally, Somerville's location adjacent to Boston and proximity to rail and road transportation made it an ideal location for distribution facilities.
It was in this period that Irish immigrants moved to Somerville to work in the brickyards and on the railroad. At the same time, older residents of East Boston and Charlestown moved to Somerville to seek a more bucolic setting than that of more densely populated areas. They also worked to maintain political control over immigrant groups, using slogans such as "Keep Somerville Republican" and establishing a local branch of the anti-Catholic
The Late Industrial Period (1870–1915) was a time of phenomenal growth for Somerville in all spheres including civic and commercial ventures. Infrastructure such as rail, water lines, telegraph and electricity were established and connected to surrounding towns. The population soared from 15,000 to 90,000. While brickmaking had taken a hold in the area after the railroads first arrived in the 1830s, Somerville's brickyards boomed through 1870. Meatpacking soon displaced brickmaking as the primary industry in the city, dubbed "The Chicago of New England". Additionally, Somerville's location adjacent to Boston and proximity to rail and road transportation made it an ideal location for distribution facilities.
It was in this period that Irish immigrants moved to Somerville to work in the brickyards and on the railroad. At the same time, older residents of East Boston and Charlestown moved to Somerville to seek a more bucolic setting than that of more densely populated areas. They also worked to maintain political control over immigrant groups, using slogans such as "Keep Somerville Republican" and establishing a local branch of the anti-Catholic American Protective Association
The American Protective Association (APA) was an American anti-Catholic secret society established in 1887 by Protestants. The organization was the largest anti-Catholic movement in the United States during the later part of the 19th century, sho ...
.
Between 1915 and 1930 population growth slowed slightly as Somerville's industries consolidated rather than expanded, and the period's most important enterprises were meat packing, dairy processing, ice and food distribution. In 1920, 73% of meatpacking in Massachusetts occurred in Somerville. Construction of the McGrath Highway in 1925 marked the turning point of Somerville as an industrial city, which accelerated when the Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company (commonly known as Ford) is an American multinational automobile manufacturer headquartered in Dearborn, Michigan, United States. It was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. The company sells automobiles ...
built a plant in Assembly Square in 1926. In the years that followed, Somerville would see itself transformed into a major industrial center as automobile assembly surpassed meat packing as Somerville's most important industry.
By 1930, 70% of Somerville residents had either been born outside of the United States or had parents who were. The population was then estimated to be 60% Catholic.
Although Union Square and Davis Square continued to be the largest commercial areas during the first decades of the 20th century, smaller, less-developed squares grew as well. Ball Square, Magoun Square
Magoun Square is a neighborhood centered on the intersection of Broadway and Medford Streets on the border of Medford and Somerville, Massachusetts. It is located between the neighborhoods of Ball Square and Winter Hill. It is a mixed-use urb ...
and Teele Square were developed with one- or two-story masonry commercial buildings, and the public green at Gilman Square was surrounded by multiple four-story commercial buildings. Retail development and banking facilities also spread. During this time of industrial prosperity, continuing through World War II, the city of Somerville reached its population apex at 105,883 residents in 1940. The building boom continued until the 1940s, creating the dense residential fabric the "city of homes" is known for.
Deindustrialization and decline
By mid-century, powerful social and economic forces precipitated a period of industrial and population decline that lasted into the 1980s. The postwar period was characterized by the ascent of the private automobile, which carried significant implications for Somerville. Streetcar lines that had crisscrossed the city since 1890 were systematically ripped out and commuter rail service was discontinued at the city's eight railway stations, one by one. Passenger rail service along the Fitchburg and Lowell lines had been declining for some time, and stations such as theWinter Hill station
Gilman Square station is a light rail station on the Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (MBTA) Green Line located at Gilman Square in Somerville, Massachusetts. The accessible station has a single island platform serving the two tracks ...
at Gilman Square were removed as early as the late 1940s. Passenger rail service stopped altogether by 1958.
The number of cars on Somerville's streets continued to rise, and road construction projects proliferated. The Alewife Brook Parkway
Alewife Brook Parkway is a short parkway in Cambridge and Somerville, Massachusetts. It is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. It begins at Fresh Pond in Cambridge (linking to Fresh Pond Parkway via Concord Avenue), and heads nor ...
, Mystic Valley Parkway and the Fells Connector Parkways, originally conceived in the 1890s as a means for city residents to reach the metropolitan parks, evolved into congested commuter routes for suburban drivers. Highway projects were advanced in the wake of the Federal Highway Aid Act (1956), in some instances displacing entire neighborhoods. The Brickbottom neighborhood was razed in 1950 to prepare for a proposed Inner Belt Expressway, and construction of Interstate 93
Interstate 93 (I-93) is an Interstate Highway in the New England states of Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Vermont in the United States. Spanning approximately along a north–south axis, it is one of three primary Interstate Highways ...
resulted in demolition of homes in The States neighborhood during the late 1960s.
Industry slowly moved outward to the metropolitan fringes, encouraged by highway access and cheap, undeveloped land. The Ford Motor Plant in Assembly Square, which had been one of the region's largest employers, closed its doors in 1958 with severe consequences for the local economy. From the late 1950s through the early 1970s, Finast Supermarkets used the building that had earlier housed the Ford assembly plant on Middlesex Avenue, but in 1976 it too closed its doors. By 1976, Assembly Square was becoming a ghost town: Finast Stores, the Boston and Maine Railroad
The Boston and Maine Railroad was a U.S. Class I railroad in northern New England. Originally chartered in 1835, it became part of what was the Pan Am Railways network in 1983 (most of which was purchased by CSX in 2022).
At the end of 1970 ...
, and Ford Motor Company, which had each paid the city over $1 million in annual taxes, were gone. By the late 1970s, Somerville was losing population, revenue and jobs.
Somerville also has a history of racial tension. It only hired its first black police officer, a person named Francis Moore, in 1974. Moore subsequently won a suit charging that the police department was "blatantly discriminatory" against him, including an episode in which he was told to patrol the East Somerville neighborhood of Glen Park at night without his issued firearm, night stick, Mace, or communication devices. Moore's name had been written on a barrel in the neighborhood and used for target practice by local youth.
Contemporary revitalization
In the last years of the 20th century, the situation in Somerville stabilized and growth returned—first to West Somerville, and then the rest of the city. Almost thirty years after passenger rail service to Somerville was halted, the Red Line Northwest Extension reachedDavis Square
Davis Square is a major intersection in the northwestern section of Somerville, Massachusetts where several streets meet: Holland Street, Dover Street, Day Street, Elm Street, Highland Avenue, and College Avenue. The name is often used to refer ...
in 1984. The city and community used the creation of the new station as a catalyst for revitalizing the faded square, promoting new commercial development and sponsoring other physical and infrastructural improvements. However, when the new transit station opened, business around Davis Square did not immediately thrive. The number of retail stores in the area declined from 68 in 1977 to 56 in 1987.
However many non-retail uses, such as beauty salons and real estate offices, had already begun to fill the empty retail spaces. With the Boston area's emergence from its long recession, the area truly began to revive. Clearly, the community's vision of a rebirth of commercial and retail activity has, in the past few years, been fully realized. All benefit from their proximity to the MBTA station, with connections to Cambridge and Boston. Retail vacancy rates around the square were close to zero as of 2013.
The telecommunication and biotechnology booms of the mid-to-late 1990s significantly contributed to Somerville's revitalization. As with the housing boom a century earlier, the sudden increase in the number of jobs available in the cities of Somerville, Boston, and particularly Cambridge—as well in as the other communities immediately surrounding Somerville—led to a new surge in the demand for housing. Additionally, the end of rent control
Rent regulation is a system of laws, administered by a court or a public authority, which aims to ensure the affordability of housing and tenancies on the rental market for dwellings. Generally, a system of rent regulation involves:
* Price co ...
in Cambridge coincided with the economic recovery in 1995, increasing demand for Somerville's affordable housing options.
The city also had a very high car theft rate, once being the car theft capital of the country, and its Assembly Square area was especially infamous for this. However, after the gentrification
Gentrification is the process of changing the character of a neighborhood through the influx of more affluent residents and businesses. It is a common and controversial topic in urban politics and planning. Gentrification often increases the ...
period the city went through in the 1990s, and an influx of artists to the area, this name has mostly faded from use and the city has instead gained a reputation for its active arts community and effective government, including being named the best-run city in Massachusetts in 2006. Nowadays lobbying by grassroots organizations is attempting to revive and preserve Somerville's "small-town" neighborhood environments by supporting local business, public transit and gardens.
Geography
 According to the
According to the United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy
An economy is an area of th ...
, Somerville has a total area of , of which is land and , or 2.61%, is water. Somerville is bordered by the cities of Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge beca ...
, Medford, Everett, Arlington and the Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the capital city, state capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financ ...
neighborhood of Charlestown. It is located on the west bank of the Mystic River
The Mystic River is a riverU.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed April 1, 2011 in Massachusetts, in the United States. In Massachusett, means "large estuary," alluding to t ...
.
Millennia ago, glaciation left a series of drumlins
A drumlin, from the Irish word ''droimnín'' ("littlest ridge"), first recorded in 1833, in the classical sense is an elongated hill in the shape of an inverted spoon or half-buried egg formed by glacial ice acting on underlying unconsolidated ...
running west to east across the landscape of what would become Somerville. These ridges would later become known as the "Seven Hills" of Somerville (like many other cities claiming to be built on seven hills, following the seven hills of Rome
The seven hills of Rome ( la, Septem colles/montes Romae, it, Sette colli di Roma ) east of the river Tiber form the geographical heart of Rome, within the walls of the city.
Hills
The seven hills are:
* Aventine Hill (Latin: ''Collis Aventi ...
):
# Central Hill
# Clarendon Hill
# Cobble Hill
# Ploughed Hill (or Mount Benedict)
# Prospect Hill (or Mount Pisgah)
# Spring Hill
# Winter Hill
These hills rise from the floodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river which stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls, and which experiences flooding during periods of high discharge.Goudi ...
of the Mystic River, and generally run west to east, providing for beautiful vistas of Boston to the south and Medford/Everett to the north. Physical boundaries are also defined by prominent waterways: the Mystic River to the north, its tributary Alewife Brook to the west, and the Miller's River to the southeast.
Land in early Somerville was used primarily as grazing commons and small farms. After the proliferation of the railroads in the area during the mid-1800s, industrialization transformed the landscape. In the 1800s, the Millers River was used as a sewer and dumping ground for local industry and would be ordered filled by the Commonwealth before the end of the century, for health reasons. As a result of landfill and the elimination of former Cobble Hill, the Millers River marsh was turned into railyard
A rail yard, railway yard, railroad yard (US) or simply yard, is a series of tracks in a rail network for storing, sorting, or loading and unloading rail vehicles and locomotives. Yards have many tracks in parallel for keeping rolling stock or ...
s, slaughterhouse
A slaughterhouse, also called abattoir (), is a facility where animals are slaughtered to provide food. Slaughterhouses supply meat, which then becomes the responsibility of a packaging facility.
Slaughterhouses that produce meat that is not ...
s and other large-scale land uses.
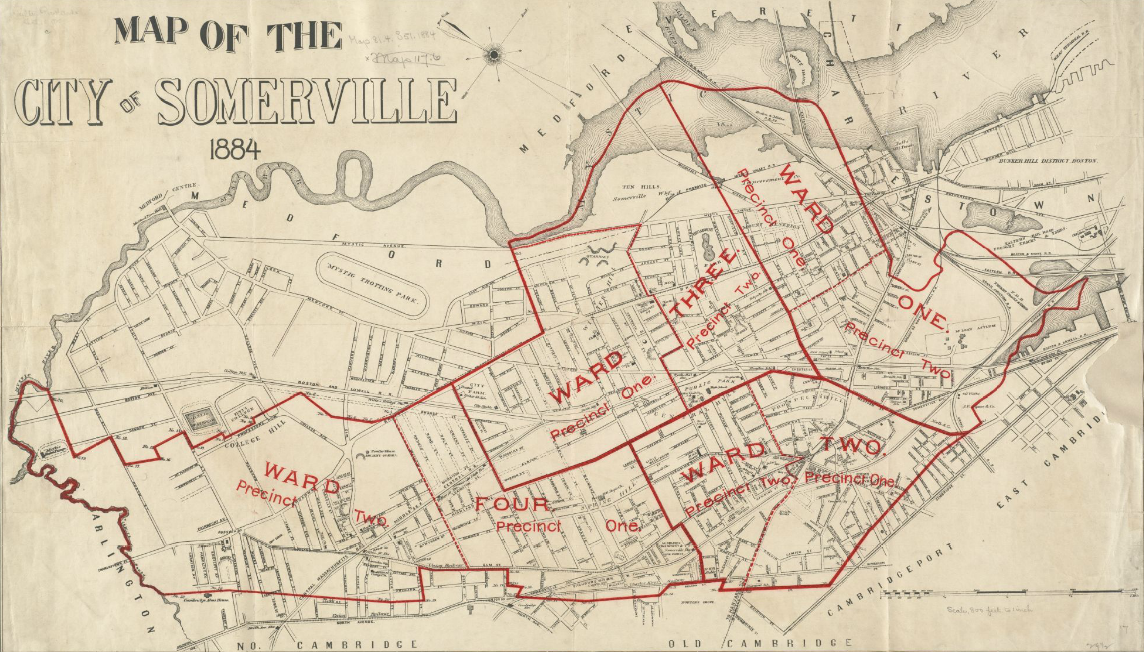
Squares and neighborhoods
 Somerville's commercial property is not concentrated in a recognized downtown
Somerville's commercial property is not concentrated in a recognized downtown central business district
A central business district (CBD) is the commercial and business centre of a city. It contains commercial space and offices, and in larger cities will often be described as a financial district. Geographically, it often coincides with the " cit ...
but instead is spread over many different nodes or corridors of business activity. The difference in character ranges from the vibrant nightlife, live music and theaters of Davis Square
Davis Square is a major intersection in the northwestern section of Somerville, Massachusetts where several streets meet: Holland Street, Dover Street, Day Street, Elm Street, Highland Avenue, and College Avenue. The name is often used to refer ...
to the large scale retail and highway access of Assembly Square. This spatial allocation is directly related to the early influence of rail and streetcar systems which caused economic activity to occur at stops. The other key factor in the creation of commercial squares is the area's topography. The numerous hills making up Somerville's landscape determined where road networks would allow neighborhood commercial development.
Somerville has a number of squares that are centers for business and entertainment, as well as a number of other neighborhoods:
* Assembly Square
* Ball Square
* Brickbottom (north of McGrath Highway
Route 28 is a nominally south–north state highway in the U.S. state of Massachusetts, running from the town of Eastham via Boston to the New Hampshire state line in Methuen. Following the route from its nominally southern end, Route 28 i ...
, south of Inner Belt District)
* Clarendon Hill (near Broadway and Arlington border)
* Davis Square
Davis Square is a major intersection in the northwestern section of Somerville, Massachusetts where several streets meet: Holland Street, Dover Street, Day Street, Elm Street, Highland Avenue, and College Avenue. The name is often used to refer ...
(considered West Somerville)
* Duck Village (north of Beacon Street, just west of Union Square)
* East Somerville (East of McGrath Highway, between Washington and Broadway Streets)
* Gilman Square (at the junction of Medford Street, Pearl Street, and Marshall Street)
* Inner Belt District
* Magoun Square
Magoun Square is a neighborhood centered on the intersection of Broadway and Medford Streets on the border of Medford and Somerville, Massachusetts. It is located between the neighborhoods of Ball Square and Winter Hill. It is a mixed-use urb ...
* Nunnery Grounds (Mount Benedict)
* Powder House Square
Powder House Square is a neighborhood and landmark rotary in Somerville, Massachusetts, United States. It is also known locally as Powder House Circle. It is the 6-way intersection of College Avenue, Broadway, Warner Street, and Powder House Bo ...
* Prospect Hill (part of Union Square)
* Spring Hill
* The States (streets named after U.S. states, between Broadway in East Somerville and I-93 near Assembly Square)
* Teele Square
* Ten Hills
Ten Hills is a neighborhood in the northeastern part of the city of Somerville, Massachusetts. The area is roughly wedge-shaped, about in size, and is bounded by the Mystic River to the north, McGrath Highway to the east, and is largely separ ...
* Tufts
Tufts University is a private research university on the border of Medford and Somerville, Massachusetts. It was founded in 1852 as Tufts College by Christian universalists who sought to provide a nonsectarian institution of higher learning. ...
* Union Square
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
* Wilson Square (Elm Street and Somerville Avenue), known as Oak Square before 1920
* Winter Hill
Sullivan Square
Sullivan Square is a traffic circle located at the north end of the Charlestown neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. It is named after James Sullivan, an early 19th-century Governor of Massachusetts. Sullivan Square station on the MBTA Orang ...
, in the Charlestown neighborhood of Boston, is just over the border from East Somerville; Inman Square
Inman Square is a neighborhood and historic district in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It lies north of Central Square, at the junction of Cambridge, Hampshire, and Inman Streets near the Cambridge– Somerville border.
Location
Like many square ...
and Lechmere Square
Lechmere Square ( ) is located at the intersection of Cambridge Street and First Street in East Cambridge, Massachusetts. It was originally named for the Colonial-era landowner Richard Lechmere, a Loyalist who returned to England at the beginnin ...
, both in Cambridge, are also just outside Somerville. Porter Square is in both Somerville and Cambridge.
Demographics
Somerville has experienced dramatic growth since the Red Line of Boston'sMBTA
The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority (abbreviated MBTA and known colloquially as "the T") is the public agency responsible for operating most public transportation services in Greater Boston, Massachusetts. The MBTA transit network in ...
subway system was extended through Somerville in 1985, especially in the area between Harvard and Tufts. This was especially accelerated by the dot-com bubble
The dot-com bubble (dot-com boom, tech bubble, or the Internet bubble) was a stock market bubble in the late 1990s, a period of massive growth in the use and adoption of the Internet.
Between 1995 and its peak in March 2000, the Nasdaq Comp ...
of the late 90s, rising incomes, and concomitant rises in demand for urban housing.
Tensions between long-time residents and recent arrivals exist, with many of the former accusing the latter of ignoring problems such as drugs and gang violence. Incidents such as anti-"yuppie
Yuppie, short for "young urban professional" or "young upwardly-mobile professional", is a term coined in the early 1980s for a young professional person working in a city. The term is first attested in 1980, when it was used as a fairly ne ...
" graffiti
Graffiti (plural; singular ''graffiti'' or ''graffito'', the latter rarely used except in archeology) is art that is written, painted or drawn on a wall or other surface, usually without permission and within public view. Graffiti ranges from s ...
, appearing around town in 2005, highlighting this rift. The economic clash between several areas of the city of Somerville and its neighboring cities of Boston, and in particular Cambridge, has created an underlying tension between residents that has persisted for multiple generations.
Due to Somerville's proximity to various institutions of higher education
Higher education is tertiary education leading to award of an academic degree. Higher education, also called post-secondary education, third-level or tertiary education, is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after compl ...
, the city has a constant influx of college students and young professionals, who reside in sections near Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge beca ...
where Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of high ...
, Lesley University
Lesley University is a private university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. It is accredited by the New England Commission of Higher Education. As of 2018-19 Lesley University enrolled 6,593 students (2,707 undergraduate and 3,886 graduate).
Histor ...
, and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a Private university, private Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern t ...
are located and near Tufts University
Tufts University is a private research university on the border of Medford and Somerville, Massachusetts. It was founded in 1852 as Tufts College by Christian universalists who sought to provide a nonsectarian institution of higher learnin ...
, which straddles the Somerville-Medford city line. The city is inhabited by blue collar
A blue-collar worker is a working class person who performs manual labor. Blue-collar work may involve skilled or unskilled labor. The type of work may involving manufacturing, warehousing, mining, excavation, electricity generation and ...
Irish American
, image = Irish ancestry in the USA 2018; Where Irish eyes are Smiling.png
, image_caption = Irish Americans, % of population by state
, caption = Notable Irish Americans
, population =
36,115,472 (10.9%) alone ...
, Italian American
Italian Americans ( it, italoamericani or ''italo-americani'', ) are Americans who have full or partial Italian ancestry. The largest concentrations of Italian Americans are in the urban Northeast and industrial Midwestern metropolitan area ...
, Greek American
Greek Americans ( el, Ελληνοαμερικανοί ''Ellinoamerikanoí'' ''Ellinoamerikánoi'' ) are Americans of full or partial Greek ancestry. The lowest estimate is that 1.2 million Americans are of Greek descent while the highest ...
, and Portuguese American
Portuguese Americans ( pt, português-americanos), also known as Luso-Americans (''luso-americanos''), are citizens and residents of the United States who are connected to the country of Portugal by birth, ancestry, or citizenship.
Americans and ...
families, who are spread throughout the city.
In November 1997, the ''Utne Reader
''Utne Reader'' (also known as ''Utne'') ( ) is a digital digest that collects and reprints articles on politics, culture, and the environment, generally from alternative media sources including journals, newsletters, weeklies, zines, music, and ...
'' named Davis Square
Davis Square is a major intersection in the northwestern section of Somerville, Massachusetts where several streets meet: Holland Street, Dover Street, Day Street, Elm Street, Highland Avenue, and College Avenue. The name is often used to refer ...
in Somerville one of the 15 hippest places to live in the U.S.
Somerville is home to a thriving arts community and boasts the second highest number of artists per capita in America.
Statistics
As of the 2010 census, there were 75,754 people, 33,720 households, and 14,673 families residing in the city. Thepopulation density
Population density (in agriculture: Stock (disambiguation), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical ...
was . There were 32,105 housing units at an average density of . The racial makeup of the city was 73.92% White
White is the lightness, lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully diffuse reflection, reflect and scattering, scatter all the ...
, 6.8% African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an Race and ethnicity in the United States, ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American ...
, 0.3% Native American (U.S. Census), Native American, 8.7% Asian (U.S. Census), Asian (2.7% Chinese American, Chinese, 2.3% Indian American, Indian, 1.0% Nepalese American, Nepalese, 0.6% Korean American, Korean), 0.06% Pacific Islander (U.S. Census), Pacific Islander, 6.67% from Race (United States Census), other races, and 3.6% were multiracial. Hispanic (U.S. Census), Hispanic or Latino (U.S. Census), Latino of any race were 10.6% of the population (4.2% Salvadoran American, Salvadoran, 1.2% Puerto Ricans in the United States, Puerto Rican, 1.0% Mexican American, Mexican, 0.5% Guatemalan American, Guatemalan). The city regularly provides translation services and alerts into Spanish language, Spanish, Portuguese language, Portuguese, Haitian Creole, and Nepali language, Nepali.
There were 31,555 households, out of which 18.8% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 32.2% were Marriage, married couples living together, 10.3% had a female householder with no husband present, and 53.5% were non-families. 31% of all households were made up of individuals, and 8.8% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.38 and the average family size was 3.06.
The population was spread out, with 14.8% under the age of 18, 15.9% from 18 to 24, 42.6% from 25 to 44, 16.2% from 45 to 64, and 10.5% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 31 years. For every 100 females, there were 94.9 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 93.2 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $46,315, and the median income for a family was $51,243. Males had a median income of $36,333 versus $31,418 for females. The per capita income for the city was $23,628. About 8.4% of families and 12.5% of the population were below the poverty line, including 14.3% of those under age 18 and 13.6% of those age 65 or over.
Economy
Companies based in Somerville include Gentle Giant Moving Company and Candlewick Press.Top employers
According to Somerville's 2013 Comprehensive Annual Financial Report, the top employers in the city are:Arts and culture
 Somerville's industrial past left behind many legacies, including the invention of Marshmallow creme, Marshmallow Fluff by Archibald Query. In 1914, the city became the home of the original Economy Grocery Store, which later grew into the Stop & Shop grocery chain. Two related food service chains, Steve's Ice Cream and Bertucci's, sprung from adjacent lots in
Somerville's industrial past left behind many legacies, including the invention of Marshmallow creme, Marshmallow Fluff by Archibald Query. In 1914, the city became the home of the original Economy Grocery Store, which later grew into the Stop & Shop grocery chain. Two related food service chains, Steve's Ice Cream and Bertucci's, sprung from adjacent lots in Davis Square
Davis Square is a major intersection in the northwestern section of Somerville, Massachusetts where several streets meet: Holland Street, Dover Street, Day Street, Elm Street, Highland Avenue, and College Avenue. The name is often used to refer ...
.
Davis Square
Davis Square is a major intersection in the northwestern section of Somerville, Massachusetts where several streets meet: Holland Street, Dover Street, Day Street, Elm Street, Highland Avenue, and College Avenue. The name is often used to refer ...
is home to the Somerville Theatre, which formerly housed the Museum of Bad Art and plays host to the Independent Film Festival of Boston each spring. P.A.'s Lounge, Union Tavern and the Crystal Ballroom are live music venues in the city.
Two major art studios, the Brickbottom Artists Building and the Joy Street Studios, are located in former industrial buildings in the Brickbottom district. The Brickbottom Artists Association has been hosting annual open studio events in the fall since 1987. Starlab Studios, a multimedia artist studio space and the host of Somerville's annual Starlabfest, opened in Union Square
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
in 2009. Additionally, Artisan's Asylum on Tyler Street between Union Square (Somerville), Union and Porter squares is a hackerspace, where 150 members and 200 students have been participating in the maker culture since 2011.
The Somerville Public Library has three branches.
The Somerville Arts Council and Somerville Open Studios both host annual events involving the community in homegrown arts. The Boston chapter of the Dorkbot community meets in Somerville at the Willoughby & Baltic studio, in the Brickbottom district. Starting in 2006, an annual Fluff Festival has been held to celebrate the invention of Fluff in Somerville. "What the Fluff?" is produced by Union Square Main Streets and includes vendors, activities, entertainment and the crowning of the Pharaoh of Fluff. It has been described in food journal ''Gastronomica'' as an "orgiastic frenzy of all things fluffy--old-world village celebration meets American kitsch." Somerville mayor Joseph Curtatone attended in 2006 and declared, "My house always has been, and always will be, stocked with fluff."
Points of interest

Dilboy Stadium
George Dilboy Memorial Stadium is a multi-purpose public stadium in city. It is known as the home of the Boston Renegades women's tackle football team. It was also the home field of the Boston Militia women's tackle football team from 2008 to 2014. The Boston Breakers women's soccer club made Dilboy Stadium their home in 2012 and 2013. The stadium is named after George Dilboy, who was awarded the Medal of Honor during World War I.Historic places
Somerville has eighty-three sites listed on the National Register of Historic Places listings in Somerville, Massachusetts, National Register of Historic Places. These places include various houses, libraries, parkways, churches, among other places, and have been declared landmarks within the city.Somerville Museum
The Somerville Museum preserves memorabilia chronicling the city's roots, with historical and artistic exhibits. It is located at 1 Westwood Road, on the corner of Central Street.Parks and recreation
The Somerville Community Path is a tree-lined rail trail that runs from Lowell Street to the Cambridge border nearDavis Square
Davis Square is a major intersection in the northwestern section of Somerville, Massachusetts where several streets meet: Holland Street, Dover Street, Day Street, Elm Street, Highland Avenue, and College Avenue. The name is often used to refer ...
. It connects with the Alewife Linear Park, which in turn connects with the Minuteman Bikeway and the Fitchburg Cutoff Path. Community activists hope to extend the path eastward to Lechmere Square
Lechmere Square ( ) is located at the intersection of Cambridge Street and First Street in East Cambridge, Massachusetts. It was originally named for the Colonial-era landowner Richard Lechmere, a Loyalist who returned to England at the beginnin ...
, which would connect with the Charles River Bike Paths and the proposed East Coast Greenway. In May 2013, construction began on an extension of the path between Cedar and Lowell streets, which was completed in 2015. , the city has a total of 63 parks, playgrounds, playing fields, and community gardens.
With the establishment of the Playground Association of America in 1906, many cities, including Somerville, began to sponsor supervised playgrounds for the children of the city during the summer months. Though the Recreation Department was not formally established in Somerville until 1917, supervised play, sponsored in part by the city and the Playground Association of America, began in 1909.
The Recreation Department provides many recreational and play activities for residents of all ages, including Summertime Playgrounds, outdoor games and sports leagues, theater groups, and an active Senior Citizens Club.
Government
City government
Somerville has a Mayor–council government, mayor-city council form of municipality, municipal government. The City Council (formerly a Alderman, Board of Aldermen) consists of four at-large (citywide) positions and seven ward representatives, where each ward is a specific section of the city. The change from Aldermen to Council came in 2018 when gender equity was honored. As of January 3, 2022, the City Council compromised the following councilors: The first United States Democratic Party, Democratic mayor of the city was John J. Murphy in 1929. Every mayor prior, since 1872, had been unaffiliated with a party or United States Republican Party, Republican. Murphy succeeded on his seventh try by uniting the Irish people, Irish, Italians, Italian, Greeks, Greek, and Portuguese people, Portuguese communities. There were candlelit processions with thousands marching in rallies in the middle of Union Square and other squares in the city. The current List of mayors of Somerville, Massachusetts, mayor of Somerville is Katjana Ballantyne. In July 2020, the Somerville City Council voted to recognize polyamorous domestic partnerships in the city, becoming the first city in the United States to do so. This measure was passed in order to allow those in a polyamorous relationship easier access to their partners' health insurance. Alongside these, Somerville boasts a large Subsidized housing in the United States, subsidized housing program with 1400 units and 4,328 people (5% of the population) living in them. There are 13 developments, the largest being theMystic River
The Mystic River is a riverU.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed April 1, 2011 in Massachusetts, in the United States. In Massachusett, means "large estuary," alluding to t ...
Projects and Clarendon Hill Apartments.
* Mystic River Development (Winter Hill – 240 units)
* Clarendon Hill Apartments (Teele Square – 216 units)
* Mystic View Development (Winter Hill – 215 units)
* Bryant Towers (East Somerville – 134 units)
* Properzi Manor (Union Square – 110 units)
* Brady Towers (Inner Belt District – 84 units)
* Weston Manor (Teele Square – 80 units)
* Ciampa Manor (Davis Square – 53 units)
* Highland Gardens (Winter Hill – 42 units)
* Corbett Apartments (Winter Hill – 31 units)
* Hagan Manor (Union Square – 24 units)
* Waterworks Apartments (Alewife – 21 units)
Federal and state representation
Somerville is part of Massachusetts's 7th congressional district for purposes of elections to the United States House of Representatives. It is represented by Representative Ayanna Pressley. For representation to the Massachusetts Senate, Somerville is entirely within the Massachusetts Senate's 2nd Middlesex district, Second Middlesex district. For representation to the Massachusetts House of Representatives, Somerville is part of the Massachusetts House of Representatives' 26th Middlesex district, 26th, Massachusetts House of Representatives' 27th Middlesex district, 27th and Massachusetts House of Representatives' 34th Middlesex district, 34th Middlesex districts. The 26th Middlesex district includes East Somerville, Brickbottom, and a portion of the Union Square area, as well as portions ofCambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge beca ...
, The 34th Middlesex district includes Winter Hill and Teele Square, as well as portions of Medford. The remainder of the city, just over half, comprises the 27th Middlesex district, which does not extend outside Somerville.

Education
 The School Committee has seven independently elected officials as well as the Mayor and the President of the Board of Aldermen. The budget is approved by both the School Committee and the Board of Aldermen. The Chair is Adam Sweeting from Ward 3 and the Vice-Chair is Carrie Normand from Ward 7.
Also included in the school district is the Somerville Center for Adult Learning Experiences. The former Powder House Community School (which closed due to low enrollment in 2004) is being considered for redevelopment, either as a consolidated location for city offices if funding is obtained under the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 or as some other type of development.
Though formally listed as being located in Medford,
The School Committee has seven independently elected officials as well as the Mayor and the President of the Board of Aldermen. The budget is approved by both the School Committee and the Board of Aldermen. The Chair is Adam Sweeting from Ward 3 and the Vice-Chair is Carrie Normand from Ward 7.
Also included in the school district is the Somerville Center for Adult Learning Experiences. The former Powder House Community School (which closed due to low enrollment in 2004) is being considered for redevelopment, either as a consolidated location for city offices if funding is obtained under the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 or as some other type of development.
Though formally listed as being located in Medford, Tufts University
Tufts University is a private research university on the border of Medford and Somerville, Massachusetts. It was founded in 1852 as Tufts College by Christian universalists who sought to provide a nonsectarian institution of higher learnin ...
is also located in Somerville. The Somerville–Medford line runs through the Tufts campus, splitting the university's Tisch Library. The school employs many local residents and has many community service projects that benefit the city, especially those run through the Leonard Carmichael Society and the Jonathan M. Tisch College of Citizenship and Public Service.
Somerville Public Schools
Somerville Public Schools (SPS) operates ten schools from pre-kindergarten to secondary schools. The majority of the schools in Somerville (with exception of Somerville High School, Benjamin G. Brown School, Capuano Early Childhood Center, and Next Wave/Full Circle) are schools that go from kindergarten through 8th grade. There are 4,691 students enrolled in Somerville Public Schools. * Somerville High School (Massachusetts), Somerville High School * East Somerville Community School * Arthur D. Healey School * John F. Kennedy School * Benjamin G. Brown School (K–5) * West Somerville Community School * Albert F. Argenziano School * Winter Hill Community School * Michael E. Capuano Early Childhood Center (pre-kindergarten) * Next Wave/Full Circle (6–12 grades) East Somerville Community School, which was temporarily closed after a fire in 2007, was demolished and reconstructed, reopening in fall 2013. During its closure students were transferred to the nearby Edgerly and Capuano schools. Somerville High School underwent renovations after having been the oldest un-renovated high school in the nation. Its renovations lasted from early 2012 to January 2021.Somerville High School
Somerville High School (SHS) is located right next to the Somerville City Hall at 81 Highland Avenue. It is in Winter Hill near the border of East Somerville and Union Square. Somerville High School offers a vocational program (CTE) as well as musical programs and athletics programs. It hosts roughly 1,215 students throughout 4 grades. Its student proficiency in math and science is at 73% and its proficiency for English and history is at 83%. Its student to teacher ratio is 10:1. It is in the top 20% of the state's schools composite averages. It has a graduation rate of 89.9%. The school demographics as of 2021 are 45% Hispanic or Latino, 32% White, 14% African American, 8% Asian and 1% other. 54.6% of students in the school do not have English as their first language. 48.1% of students are economically disadvantaged. 16.9% of students have a disability. Dilboy Stadium is where the SHS soccer, football, lacrosse, tennis and track teams compete. It is located on 110Alewife Brook Parkway
Alewife Brook Parkway is a short parkway in Cambridge and Somerville, Massachusetts. It is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. It begins at Fresh Pond in Cambridge (linking to Fresh Pond Parkway via Concord Avenue), and heads nor ...
, roughly from the school itself. It is close to the Dilboy Pool (which is open solely in the summer), as well as the Clarendon Hill Towers and Clarendon Hill Projects (an installment of the Somerville Housing Authority). The SHS hockey team plays at Veterans Memorial Rink at 570 Somerville Avenue next to Conway Park and Playground.
Media
 The city is served by a number of news sources, including:
*Somerville Neighborhood News (website)
*Somerville Community Access Television
*Boston Free Radio (an all-volunteer free-speech community radio station in Somerville)
*''
The city is served by a number of news sources, including:
*Somerville Neighborhood News (website)
*Somerville Community Access Television
*Boston Free Radio (an all-volunteer free-speech community radio station in Somerville)
*''The Boston Globe
''The Boston Globe'' is an American daily newspaper founded and based in Boston, Massachusetts. The newspaper has won a total of 27 Pulitzer Prizes, and has a total circulation of close to 300,000 print and digital subscribers. ''The Boston Glob ...
'' (specifically its local edition ''Your Town Somerville'', inactive since 2011)
*Somerville Journal (website)
*The Somerville News Weekly (daily blog, despite name)
*''The Somerville Times'' (newspaper)
*Somerville Beat (website, went mostly inactive in 2015)
*Somerville Patch (website)
*''Scout Somerville'' (bimonthly magazine)
*Somerville Voices (blog, inactive)
The public radio show ''Living on Earth'' is recorded in Davis Square. In addition, Candlewick Press, a major children's book printing company, is operated in Somerville.
Bay State Newspaper Company, Highwater Books, and Radical America were all originally published in the city.
Infrastructure
Transportation

Rail
Somerville is served by seven MBTA subway stations: Davis station (MBTA), Davis station on the Red Line, Assembly station on the Orange Line (MBTA), Orange Line, and , , , , and on the Green Line (MBTA), Green Line. Davis opened in 1984, and Assembly in 2014. The Green Line stations opened in 2022 as part of the Green Line Extension, which the state was legally obligated to build since 1990. Sullivan Square station on the Orange Line and Porter station on the Red Line and Fitchburg Line are located just outside Somerville.Road
 Although only 43.6% of Somerville commuters drove alone to work in 2013, several major arteries pass through the city.
McGrath Highway is a major north–south route that represents the portion of Massachusetts Route 28 through the city of Somerville. McGrath is the continuation of Monsignor O'Brien Highway in
Although only 43.6% of Somerville commuters drove alone to work in 2013, several major arteries pass through the city.
McGrath Highway is a major north–south route that represents the portion of Massachusetts Route 28 through the city of Somerville. McGrath is the continuation of Monsignor O'Brien Highway in Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge beca ...
to the southeast and is known as the Fellsway north of the junction with Mystic Avenue and Interstate 93 in Medford. The highway has a long and complex history that hints to the changing nature of transportation throughout Somerville and the greater Boston metropolitan region. Originally constructed in 1928 to create a speedier connection for Route 28 between the Charles and Mystic Rivers, McGrath was elevated in the 1950s to further facilitate increased travel speed. The result was to cut off East Somerville and the Inner Belt District from Winter Hill and the rest of the city. When Route 28 was built, its primary purpose was to serve regional commuters traveling into Boston. However, it soon became clear that McGrath would need to be replaced by a larger and safer highway. The construction of the elevated Interstate 93, Northern Expressway (Massachusetts), part of Interstate 93
Interstate 93 (I-93) is an Interstate Highway in the New England states of Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Vermont in the United States. Spanning approximately along a north–south axis, it is one of three primary Interstate Highways ...
, was completed in the early 1970s and essentially rendered McGrath redundant. Today, the infrastructure of the two raised portions (the McCarthy Overpass, running from Somerville Avenue to Medford Street, and the Squires Bridge, running above the MBTA Fitchburg line near Twin City Plaza) are decaying and decrepit. In 2013, the Massachusetts Department of Transportation recommended that the McCarthy Overpass that crosses over several streets in Somerville be torn down, and proposed a boulevard-syle reconstruction with bike lanes and sidewalks for pedestrians. No date has been set for construction to begin.
Interstate 93, Northern Expressway (Massachusetts) runs northwest and southeast through Somerville, separating Ten Hills
Ten Hills is a neighborhood in the northeastern part of the city of Somerville, Massachusetts. The area is roughly wedge-shaped, about in size, and is bounded by the Mystic River to the north, McGrath Highway to the east, and is largely separ ...
and Assembly Square from the rest of the city. The massive elevated "Northern Expressway" was completed in the early 1970s and passes directly through Somerville running alongside and/or above Mystic Avenue (Massachusetts Route 38). Commonly referred to as the "upper and lower decks of 93", the Somerville-Charlestown section of the Northern Expressway carries three lanes of northbound traffic on the upper deck, and three lanes of southbound traffic on the lower deck. The highway also serves to cut off East Somerville from Charlestown.
Walking and cycling
Somerville is considered to be a highly walkable and bikeable city. In 2013, 7.8% of all commutes were made by bicycle, ranking Somerville 5th among U.S. cities for its share of bicycling. In 2013, 49.8% of Somerville commuters either walked, biked or used public transit. Somerville launched its first Bluebikes (originally Hubway) stations during the summer of 2012 and now hosts 21 stations. The Somerville Community Path is a mixed-use path that runs along the old Boston and Lowell Railroad right-of-way fromDavis Square
Davis Square is a major intersection in the northwestern section of Somerville, Massachusetts where several streets meet: Holland Street, Dover Street, Day Street, Elm Street, Highland Avenue, and College Avenue. The name is often used to refer ...
across Somerville to the Cambridge border near Lechmere Square
Lechmere Square ( ) is located at the intersection of Cambridge Street and First Street in East Cambridge, Massachusetts. It was originally named for the Colonial-era landowner Richard Lechmere, a Loyalist who returned to England at the beginnin ...
. Roughly of the path is finished and in use. The two finished segments feature pavement interspersed with brick and surrounded by grass, trees, pedestrian connections to nearby streets, and a community garden. The path is lit at night and snowplowed in the winter.
In 2013, the city broke ground on the first extension in almost twenty years that extended the path another east from its then-terminus at Cedar Street to Lowell Street.
Bus
Somerville has among the highest bus ridership in the Boston metro area. Nearly 40,000 passengers board the buses that pass through Somerville each day, and 15 MBTA bus routes operate in Somerville.Emergency services
Somerville is protected by the 152 paid, professional firefighters of the city of Somerville Fire Department (SFD). The Somerville Fire Department currently operates out of five firehouses, located throughout the city, and operates five engine companies, three ladder companies, and one rescue company, commanded by an on-duty district chief and deputy chief each shift.Waste
The city provides contracted trash, single-stream recycling, yard waste, and hazardous waste pickup for residents in buildings with six or fewer units, and textile recycling pickup for all residents. Single-stream recycling materials are sent to the Casella Waste Systems processing facility in neighboring Charlestown.Notable people
* James E. Barlow, civil engineer and city manager * Robert A. Bruce, noted cardiologist and professor * Mike Capuano, member of the United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives and mayor of Somerville * Richard Carle, actor * Gosder Cherilus, National Football League player * Neil Cicierega, musician, filmmaker, and animator * Hal Clement, author * Mildred Codding, medical illustrator * Mike Colman, Ice hockey player for the 1991–1992 San Jose Sharks * Hal Connolly, athlete, Olympic gold medalist in National Track and Field Hall of Fame * George Dilboy, Medal of Honor recipient * Henry F. Gilbert (1868–1928), music composer * Nick Gomez, film director and writer * Henry Kimball Hadley, composer and conducting, conductor * Henry Oliver Hansen, raised the first flag in the Battle of Iwo Jima * Hazel Heald, pulp fiction writer who collaborated on several stories with H.P. Lovecraft * Arthur Daniel Healey, Member of the U.S. House of Representatives * Alan Hovhaness, composer * James "Hutch" Hutchinson, studio musician and longtime Bonnie Raitt bassist * Jake Kilrain, noted Boxer (boxing), boxer * Howie Long, NFL Hall of Famer, actor and sports analyst * Martha Perry Lowe (1829–1902), poet, education activist * Theodore Roosevelt McElroy, telegraph operator and radio telegrapher * Jessica Meir, astronaut * Patricia Head Minaldi, United States District Court judge * Connie Morella, member of the House of Representatives * Randall Munroe, cartoonist and writer * Jack Parker (ice hockey), Jack Parker, head coach of the Boston University Terriers men's ice hockey, Boston University Terriers hockey team, 1973–2013 * Bobby Pickett, composer of "Monster Mash" * Harry Nelson Pillsbury, chess champion * Alfred M. Pride,United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
admiral and pioneer naval aviator
* Archibald Query, inventor of Marshmallow creme, Fluff
* Charles Revson, founder of Revlon
* Alex Rocco, actor
* Paul Ryan (cartoonist), Paul Ryan, born in Somerville; comic artist on ''Fantastic Four'' and ''The Phantom''
* Daniel Alfred Sanborn, a surveyor who founded the Sanborn Map Company was born in Somerville
* John Shea (playwright)
* Paul Sorrento, former Major League Baseball player
* Daniel Chapman Stillson, inventor of the modern adjustable pipe wrench
* David Foster Wallace, author
* Barbara Weeks (film actress), Barbara Weeks, actress
* Winter Hill Gang, noted crime group
* Reverend Leonard Grimes, abolitionist
* Eliza Trask Hill, women's suffrage leader and prison reformer
* Aline van Barentzen, classical pianist
Sister cities
Somerville's Sister city, sister cities are: * Gaeta, Italy * Nordeste, Azores, Nordeste, Portugal * Tiznit, Morocco * Yucuaiquín, El SalvadorReferences
Bibliography
* Drake, Samuel Adams''History of Middlesex County, Massachusetts'', Volume 1 (A-H)
published 1879 and 1880. 572 and 505 pages
Somerville article
by E.C.Booth in volume 2 pages 309–338
Somerville Fire Local 76
. * Dutton, E.P
Chart of Boston Harbor and Massachusetts Bay with Map of Adjacent Country.
Published 1867. * * Ostrander, Susan A. ''Citizenship and Governance in a Changing City: Somerville, MA'' (Temple University Press; 2013) 190 pages; study of tensions between immigrants and a new middle class in politics and community activism * * Edward Augustus Samuels, Samuels, Edward Augustus; Kimball, Henry Hastings
"Somerville, past and present: an illustrated historical souvenir"
Boston : Samuels & Kimball, 1897 * Somerville, Arlington and Belmont Directory
1869
* * Wall & Gray
''1871 Atlas of Massachusetts''.
External links
*Somerville Chamber of Commerce
{{authority control Somerville, Massachusetts, Cities in Massachusetts Irish-American neighborhoods Populated places established in 1630 Cities in Middlesex County, Massachusetts 1630 establishments in Massachusetts