Solomon Islands Civil War on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The human history of Solomon Islands begins with the first Papuan settlement at least 30,000 years ago from
The human history of Solomon Islands begins with the first Papuan settlement at least 30,000 years ago from
Ambassador
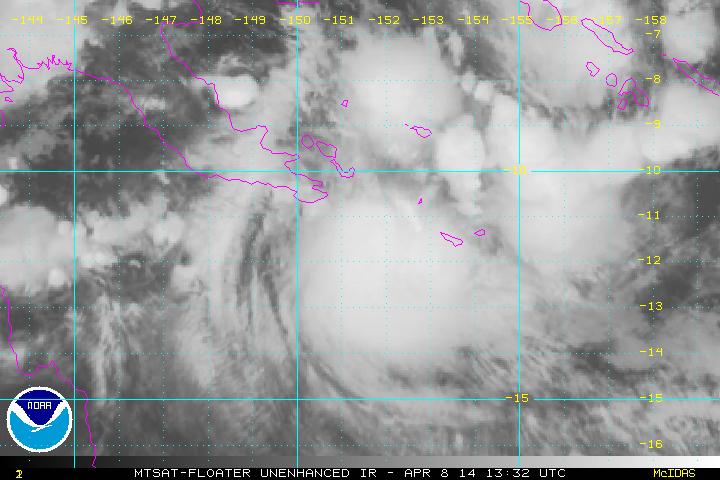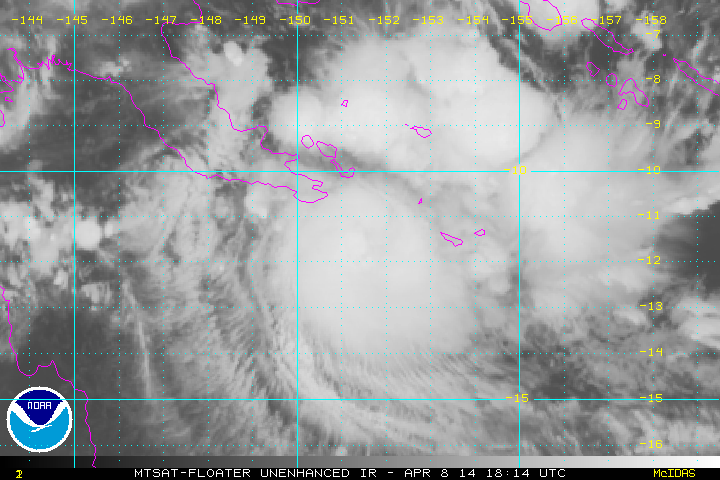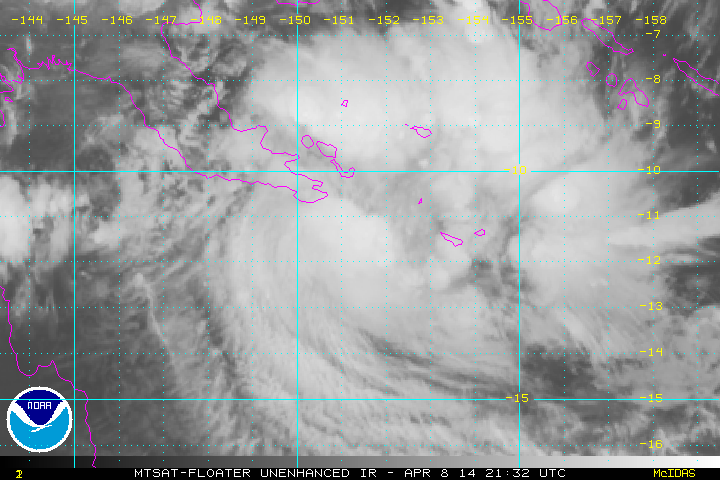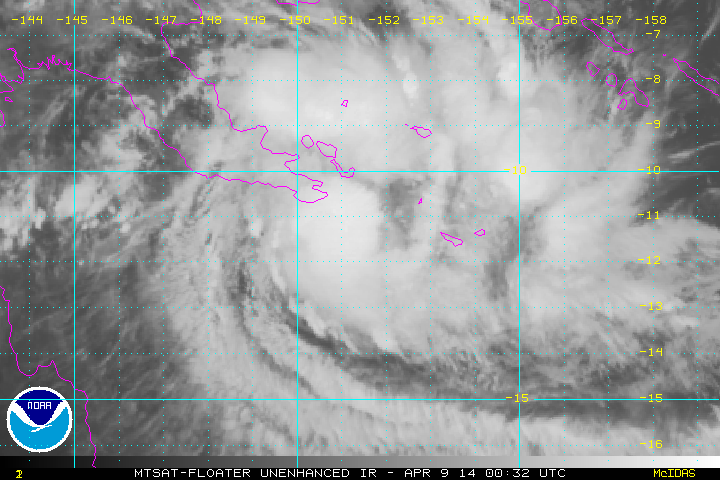 In April 2014 the islands were struck by the tropical low that later became Cyclone Ita.
Throughout the Solomons, at least 23 people were killed while up to 40 others remained unaccounted for as of 6 April. An estimated 49,000 people were affected by the floods, of whom 9,000 were left homeless.
As the precursor tropical low to Ita affected the Islands, local authorities issued heavy flood warnings, tropical disturbance and cyclone watches.
Nearly two days of continuous heavy rains from the storm caused flash flooding in the Islands. Over a four-day span, more than fell at the Gold Ridge (mine), Gold Ridge mine in
In April 2014 the islands were struck by the tropical low that later became Cyclone Ita.
Throughout the Solomons, at least 23 people were killed while up to 40 others remained unaccounted for as of 6 April. An estimated 49,000 people were affected by the floods, of whom 9,000 were left homeless.
As the precursor tropical low to Ita affected the Islands, local authorities issued heavy flood warnings, tropical disturbance and cyclone watches.
Nearly two days of continuous heavy rains from the storm caused flash flooding in the Islands. Over a four-day span, more than fell at the Gold Ridge (mine), Gold Ridge mine in
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands, also known simply as the Solomons,John Prados, ''Islands of Destiny'', Dutton Caliber, 2012, p,20 and passim is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 1000 smaller islands in Melanesia, part of Oceania, t ...
is a sovereign state in the Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from New Guinea in the west to the Fiji Islands in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Vanu ...
subregion of Oceania
Oceania ( , ) is a region, geographical region including Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Outside of the English-speaking world, Oceania is generally considered a continent, while Mainland Australia is regarded as its co ...
in the western Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
.
This page is about the history of the nation state rather than the broader geographical area of the Solomon Islands archipelago, which covers both Solomon Islands and Bougainville Island
Bougainville Island (; Tok Pisin: ''Bogenvil'') is the main island of the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, which is part of Papua New Guinea. Its land area is . The highest point is Mount Balbi, on the main island, at .
The much smaller Buk ...
, a province of Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n ...
. For the history of the archipelago not covered here refer to the former administration of the British Solomon Islands Protectorate, the North Solomon Islands and the History of Bougainville
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categ ...
.
Earliest inhabitants in Solomon Islands
 The human history of Solomon Islands begins with the first Papuan settlement at least 30,000 years ago from
The human history of Solomon Islands begins with the first Papuan settlement at least 30,000 years ago from New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is ...
. They represented the furthest expansion of humans into the Pacific until the expansion of Austronesian-language speakers through the area around 4000 BC, bringing new agricultural and maritime technology. Most of the languages spoken today in Solomon Islands derive from this era, but some thirty languages of the pre-Austronesian settlers survive. Most of the people that settled there back then were Papuans ''(see East Papuan languages
The East Papuan languages is a defunct proposal for a family of Papuan languages spoken on the islands to the east of New Guinea, including New Britain, New Ireland, Bougainville, Solomon Islands, and the Santa Cruz Islands. There is no eviden ...
).''
There are preserved numerous pre-European cultural monuments in Solomon Islands, notably Bao megalithic shrine complex (13th century AD), Nusa Roviana fortress and shrines (14th – 19th century), Vonavona Skull island – all in Western province. Nusa Roviana fortress, shrines and surrounding villages served as a hub of regional trade networks in 17th – 19th centuries. Skull shrines of Nusa Roviana are sites of legends. Better known is Tiola shrine – site of legendary stone dog which turned towards the direction where enemy of Roviana was coming from. This complex of archaeological monuments characterises fast development of local Roviana culture, through trade and head hunting expeditions turning into regional power in 17th – 18th centuries.
European contact
Ships of the Spanish explorerÁlvaro de Mendaña de Neira
Álvaro de Mendaña y Neira (or Neyra) (1 October 1542 – 18 October 1595) was a Spanish navigator, explorer, and cartographer, best known for two of the earliest recorded expeditions across the Pacific Ocean in 1567 and 1595. His voyages led t ...
first sighted Santa Isabel island on 7 February 1568. Finding signs of alluvial gold on Guadalcanal, Mendaña believed he had found the source of King Solomon
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a constitutional monarch if his power is restrained by f ...
's wealth, and consequently named the islands "The Islands of Solomon".
In 1595 and 1605 Spain again sent several expeditions to find the islands and establish a colony; however these were unsuccessful. In 1767, Commander
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank as well as a job title in many army, armies. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countri ...
Philip Carteret
Rear-Admiral Philip Carteret, Seigneur of Trinity (22 January 1733 – 21 July 1796) was a Royal Navy officer and explorer who participated in two of the British navy's circumnavigation expeditions in 1764–66 and 1766–69.
Biography
Carte ...
of HMS ''Swallow'' rediscovered the Santa Cruz Islands
The Santa Cruz Islands form an archipelago in Temotu Province, Solomon Islands. They lie approximately to the southeast of the Solomon Islands (archipelago), Solomon Islands archipelago, just north of the archipelago of Vanuatu and are con ...
and Malaita
Malaita is the primary island of Malaita Province in Solomon Islands. Malaita is the most populous island of the Solomon Islands, with a population of 161,832 as of 2021, or more than a third of the entire national population. It is also the se ...
. Later, Dutch, French and British navigators visited the islands; their reception was often hostile.
Christian missionaries began visiting the Solomons from the 1840s, beginning with an attempt by French Catholics under Jean-Baptiste Epalle to establish a mission on Santa Isabel Island, which was abandoned after Epalle was killed by islanders in 1845. Anglican missionaries began arriving from the 1850s, followed by other denominations, over time gaining a large number of converts.
Museums with significant collections of Solomon Islands artifacts include the Bishop Museum
The Bernice Pauahi Bishop Museum, designated the Hawaii State Museum of Natural and Cultural History, is a museum of history and science in the historic Kalihi district of Honolulu, Hawaii, Honolulu on the Hawaiian island of Oʻahu. Founded in 1 ...
, the Peabody Museum of Salem
The Peabody Museum of Salem (1915–1992), formerly the Peabody Academy of Science (1865–1915), was a museum and antiquarian society based in Salem, Massachusetts. The academy was organized in part as a successor to the East India Marine Socie ...
, South Sea Islands Museum and National Museum of Ireland
The National Museum of Ireland () is Ireland's leading museum institution, with a strong emphasis on national and some international archaeology, Irish history, Irish art, culture, and natural history. It has three branches in Dublin, the arch ...
.
Colonisation
Sikaiana
Sikaiana (formerly called the Stewart Islands) is a small atoll NE of Malaita in Solomon Islands in the south Pacific Ocean. It is almost in length and its lagoon, known as Te Moana, is totally enclosed by the coral reef. Its total land surfa ...
, then known as the Stewart Islands, was annexed to the Hawaiian Kingdom in 1856. Hawai'i did not formalize the annexation, and the United States refused to recognize Hawaiian sovereignty over Sikaiana when the United States annexed Hawai'i in 1898.
The colonial ambitions of Imperial Germany
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperia ...
led to the establishment of a German Protectorate over the North Solomon Islands, which covered parts of what is now Solomon Islands, following the Anglo-German Declarations about the Western Pacific Ocean In 1886, the British Empire and the German Empire made two declarations about their spheres of interest in the Western Pacific Ocean. Their complete names are:
*Declaration between the Governments of Great Britain and the German Empire relating to ...
(1886), which established "spheres of influence" that Germany and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
agreed, with Germany giving up its claim to the southern Solomon Islands.
In June 1893, Captain Herbert Gibson of , declared the southern Solomon Islands a British protectorate
British protectorates were protectorates under the jurisdiction of the British government. Many territories which became British protectorates already had local rulers with whom the Crown negotiated through treaty, acknowledging their status wh ...
.
No immediate steps to place administrators in the Solomon Islands, which were made part of the British Western Pacific Territories
The British Western Pacific Territories (BWPT) was a colonial entity created in 1877 for the administration of a series of Pacific islands in Oceania under a single representative of the British Crown, styled the High Commissioner for the Weste ...
(BWPT), which was administered by a high commissioner who resided in Fiji
Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about ...
.
The Colonial Office appointed Charles Morris Woodford
Charles Morris Woodford (30 October 1852 – 4 October 1927) was a British naturalist and government minister active in the Solomon Islands. He became the first Resident Commissioner of the Solomon Islands Protectorate, serving from 1896 (thr ...
as the Resident Commissioner in the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands, also known simply as the Solomons,John Prados, ''Islands of Destiny'', Dutton Caliber, 2012, p,20 and passim is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 1000 smaller islands in Melanesia, part of Oceania, t ...
on 17 February 1897. He was directed to control the labour trade operating in the Solomon Island waters and to stop the illegal trade in firearms. Arthur Mahaffy was appointed as the Deputy Commissioner to Woodford in January 1898. In January 1900, Mahaffy established a government station at Gizo, as Woodford considered Mahaffy’s military training as making him suitable for the role of suppressing headhunting
Headhunting is the practice of hunting a human and collecting the severed head after killing the victim. More portable body parts (such as ear, nose, or scalp) can be taken as trophies, instead. Headhunting was practiced in historic times ...
in New Georgia
New Georgia, with an area of , is the largest of the islands in Western Province (Solomon Islands), Western Province, Solomon Islands, and the List of islands by area, 203rd-largest island in the world. Since July 1978, the island has been par ...
and neighbouring islands.
In 1898 Britain annexed the Santa Cruz and the Rennell and Bellona Islands.
In 1900, under the terms of the Treaty of Berlin (14 November 1899), Germany transferred Choiseul, Santa Isabel, the Shortlands and Ontong Java Atoll Islands to the British Solomon Islands Protectorate, but retained Bougainville and its surrounding islands. Germany granted this claim in exchange for the British giving up all claims to Western Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa and known until 1997 as Western Samoa, is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania, in the South Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu), two smaller, inhabit ...
.
In 1927 District Commissioner William R. Bell was killed on Malaita
Malaita is the primary island of Malaita Province in Solomon Islands. Malaita is the most populous island of the Solomon Islands, with a population of 161,832 as of 2021, or more than a third of the entire national population. It is also the se ...
, along with a cadet named Lillies and 13 Solomon Islanders in his charge. A massive punitive expedition
A punitive expedition is a military journey undertaken to punish a political entity or any group of people outside the borders of the punishing state or union. It is usually undertaken in response to perceived disobedient or morally wrong beha ...
, known as the Malaita massacre, ensued; at least 60 Kwaio were killed, nearly 200 detained in Tulagi
Tulagi, less commonly known as Tulaghi, is a small island in Solomon Islands, just off the south coast of Ngella Sule. The town of the same name on the island (pop. 1,750) was the capital of the British Solomon Islands Protectorate from 1896 t ...
(the protectorate capital), and many sacred sites and objects were destroyed or desecrated. Basiana, who had killed Bell, was hanged publicly on 29 June 1928.
World War II
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
ese forces occupied the North Solomon Islands, part of the Australian Territory of New Guinea
The Territory of New Guinea was an Australian-administered League of Nations and then United Nations trust territory on the island of New Guinea from 1914 until 1975. In 1949, the Territory and the Territory of Papua were established in an adm ...
, in January 1942, going South to Tulagi
Tulagi, less commonly known as Tulaghi, is a small island in Solomon Islands, just off the south coast of Ngella Sule. The town of the same name on the island (pop. 1,750) was the capital of the British Solomon Islands Protectorate from 1896 t ...
. The counter-attack was led by the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
; the 1st Division of the US Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines or simply the Marines, is the Marines, maritime land force service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is responsible for conducting expedi ...
landed on Guadalcanal
Guadalcanal (; indigenous name: ''Isatabu'') is the principal island in Guadalcanal Province of Solomon Islands, located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, northeast of Australia. It is the largest island in the Solomons by area and the second- ...
and Tulagi
Tulagi, less commonly known as Tulaghi, is a small island in Solomon Islands, just off the south coast of Ngella Sule. The town of the same name on the island (pop. 1,750) was the capital of the British Solomon Islands Protectorate from 1896 t ...
in August 1942. Some of the most bitter fighting of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
took place on the islands for almost three years.
Tulagi, the seat of the British administration on the island of Nggela Sule in Central Province was destroyed in the heavy fighting following landings by the US Marines. Then the tough battle for Guadalcanal, which was centred on the capture of the airfield, Henderson field, led to the development of the adjacent town of Honiara
Honiara () is the capital and largest city of Solomon Islands, situated on the northwestern coast of Guadalcanal. , it had a population of 92,344 people. The city is served by Honiara International Airport and the seaport of Point Cruz, and lies ...
as the United States logistics centre.
Biuku Gasa and Eroni Kumana
Islanders Biuku Gasa (deceased 2005) and Eroni Kumana (Gizo) (deceased 2014) were indigenous Allied scouts during the war. They became famous when they were noted byNational Geographic
''National Geographic'' (formerly ''The National Geographic Magazine'', sometimes branded as ''Nat Geo'') is an American monthly magazine published by National Geographic Partners. The magazine was founded in 1888 as a scholarly journal, nine ...
for being the first men to find the shipwrecked John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), also known as JFK, was the 35th president of the United States, serving from 1961 until his assassination in 1963. He was the first Roman Catholic and youngest person elected p ...
and his crew of the PT-109 using a traditional dugout canoe
A dugout canoe or simply dugout is a boat made from a hollowed-out tree. Other names for this type of boat are logboat and monoxylon. ''Monoxylon'' (''μονόξυλον'') (pl: ''monoxyla'') is Greek''mono-'' (single) + '' ξύλον xylon'' (tr ...
. They suggested the idea of using a coconut which was later kept on the desk of the president to write a rescue message for delivery. Their names had not been credited in most movie and historical accounts, and they were turned back before they could visit President Kennedy's inauguration, though the Australian coastwatcher would also meet the president.
Gasa and Kumana were interviewed by ''National Geographic'' in 2002, and can be seen on the DVD of the television special. They were presented a bust by Max Kennedy
Matthew Maxwell Taylor Kennedy (born January 11, 1965) is an American lawyer and author. He is the ninth child of Robert F. Kennedy and Ethel Skakel Kennedy.
Early life and education
Max Kennedy was born in New York City on January 11, 1965 ...
, a son of Robert F. Kennedy. The ''National Geographic'' had gone there as part of an expedition by Robert Ballard
Robert Duane Ballard (born June 30, 1942) is an American retired Navy officer and a professor of oceanography at the University of Rhode Island who is noted for his work in underwater archaeology (maritime archaeology and archaeology of ...
, who found the remains of the PT-109. The special was called '' The Search for Kennedy's PT 109''."JFK's PT-109 Found, U.S. Navy Confirms"Ambassador
Caroline Kennedy
Caroline Bouvier Kennedy (born November 27, 1957) is an American author, diplomat, and attorney who served as the List of ambassadors of the United States to Australia, United States ambassador to Australia from 2022 to 2024. She previously serv ...
met John Koloni, the son of Kumana, and Nelma Ane, daughter of Gasa at a ceremony in August 2023 in Honiara
Honiara () is the capital and largest city of Solomon Islands, situated on the northwestern coast of Guadalcanal. , it had a population of 92,344 people. The city is served by Honiara International Airport and the seaport of Point Cruz, and lies ...
to mark the 80th anniversary of the battle of Guadalcanal. She also visited the places that her father had swum after the sinking of PT 109.
War consequences
The impact of the war on islanders was profound. The destruction caused by the fighting and the longer-term consequences of the introduction of modern materials, machinery and western cultural artefacts, transformed traditional isolated island ways of life. The reconstruction was slow in the absence of war reparations and with the destruction of the pre-war plantations, formerly the mainstay of the economy. Significantly, Solomon Islanders' experience as labourers with the Allies led some to a new appreciation of the importance of economic organisation and trade as the basis for material advancement. Some of these ideas were put into practice in the early post-war political movement "Maasina Ruru
Maasina Ruru was an emancipation movement for self-government and self-determination in the British Solomon Islands during and after World War II, 1945–1950, credited with creating the movement towards independence for the Solomon Islands. The ...
" – often corrupted to "Marching Rule".
Post war (1945–1978)
In 1956 a movement for social economic and political improvement using co-operatives economic enterprises in combination with a regard for custom and tradition to synthesise a new social order called Moro Movement began on Guadalcanal. Stability was restored during the 1950s, as the British colonial administration built a network of official local councils. On this platform Solomon Islanders with experience on the local councils started participation in central government, initially through the bureaucracy and then, from 1960, through the newly established Legislative and Executive Councils. Positions on both Councils were initially appointed by the High Commissioner of the British Protectorate but progressively more of the positions were directly elected or appointed by electoral colleges formed by the local councils. The first national election was held in 1964 for the seat of Honiara, and by 1967 the first general election was held for all but one of the 15 representative seats on the Legislative Council (the one exception was the seat for the Eastern Outer Islands, which was again appointed by electoral college). Elections were held again in 1970 and a new constitution was introduced. The 1970 constitution replaced the Legislative and Executive Councils with a single Governing Council. It also established a 'committee system of government' where all members of the Council sat on one or more of five committees. The aim of this system was to reduce divisions between elected representatives and the colonial bureaucracy, provide opportunities for training new representatives in managing the responsibilities of government. It was also claimed that this system was more consistent with the Melanesian style of government. However this was quickly undermined by opposition to the 1970 constitution and the committee system by elected members of the council. As a result, a new constitution was introduced in 1974 which established a standard Westminster form of government and gave the Islanders both Chief Ministerial and Cabinet responsibilities.Solomon Mamaloni
Solomon Sunaone Mamaloni (23 January 1943 – 11 January 2000) was a Solomon Islands politician. He was the first chief minister of the islands, and later served as the prime minister for three spells in the 1980s and 1990s.
Biography
Mamaloni ...
became the country's first Chief Minister in July 1974.
Independence (1978)
As late as 1970, the British Protectorate did not envisage independence for Solomon Islands in the foreseeable future. Shortly thereafter, the financial costs of supporting the Protectorate became more trying, as the world economy was hit by the first oil price shock of 1973. The imminent independence of Papua New Guinea (in 1975) was also thought to have influenced the Protectorate's administrators. Outside of a very small educated elite in Honiara, there was little in the way of an indigenous independence movement in the Solomons. Self-government was granted in January 1976 and after July 1976, SirPeter Kenilorea
Sir Peter Kenilorea (23 May 1943 – 24 February 2016) was a Solomon Islander politician, officially styled The Rt Hon. Sir Peter Kenilorea as a member of the Privy Council of the United Kingdom. He was the first prime minister of an independ ...
became the Chief Minister who would lead the country to independence. Independence was granted on 7 July 1978, and Kenilorea automatically became the country's first Prime Minister.
Ethnic violence (1999–2003)
Before WWII the provincial capital of Guadalcanal was located at Aola, further down the coast from the present capital, Honiara. That area was then still occupied by the tribal owners of the land. Unfortunately for them Point Cruz had a deep-water harbour and was only a few miles away from the Guadalcanal Plains, where Henderson airfield was built by the Americans during WWII. The landowners accepted the need for such military effort based on their land, presuming it would be returned to them afterwards. In the meantime they moved out, over to the Weather Coast on the opposite side of the island, settling in and around an area called Bambanakira. But they were never compensated. Efforts to resolve this issue as late as 1998 by Ezekiel Alebua, then Guadalcanal Premier, were thwarted and for just a few million dollars ($SBD). Ethnic bias within the bureaucracy and authorities at the time was well known. As well, in the late 90s suburban development had been accelerating on the outskirts of Honiara, whole suburbs of squatters mainly of Malaitan origin. Exacerbating the problem, the police had refused to properly investigate a growing series of violent murders, all of Guadalcanal men in and around Honiara. In early 1999 long-simmering tensions between the local Guale people onGuadalcanal
Guadalcanal (; indigenous name: ''Isatabu'') is the principal island in Guadalcanal Province of Solomon Islands, located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, northeast of Australia. It is the largest island in the Solomons by area and the second- ...
and more recent migrants from the neighbouring island of Malaita
Malaita is the primary island of Malaita Province in Solomon Islands. Malaita is the most populous island of the Solomon Islands, with a population of 161,832 as of 2021, or more than a third of the entire national population. It is also the se ...
erupted into violence. The 'Guadalcanal Revolutionary Army', later called Isatabu Freedom Movement (IFM), began terrorising Malaitans in the rural areas of the island to make them leave their homes. About 20,000 Malaitans fled to the capital and others returned to their home island; Guale residents of Honiara fled. The city became a Malaitan enclave.
Meanwhile, the Malaita Eagle Force (MEF) was formed to uphold Malaitan interests. The Government appealed to the Commonwealth Secretary General for assistance. The Honiara Peace Accord was agreed on 28 June 1999. Despite this apparent success the underlying problems remained unresolved and had already resulted in the death or serious injury of 30,000 civilians. The accord soon broke down and fighting broke out again in June 2000.
Malaitans took over some armouries at their home island and Honiara
Honiara () is the capital and largest city of Solomon Islands, situated on the northwestern coast of Guadalcanal. , it had a population of 92,344 people. The city is served by Honiara International Airport and the seaport of Point Cruz, and lies ...
and helped by that, on 5 June 2000 the MEF seized the parliament by force. Through their spokesman Andrew Nori, they claimed that the government of the then Prime Minister, Bartholomew Ulufa'alu, had failed to secure compensation for loss of Malaitan life and property. Ulufa’alu was forced to step down.
On 30 June 2000 Parliament elected by a narrow margin a new Prime Minister, Manasseh Sogavare
Manasseh Damukana Sogavare (born 17 January 1955) is a Solomon Islander politician serving as Minister of Finance since 2024. He served as the prime minister of Solomon Islands for a total of nine years from 2000–2001, 2006–2007, 2014–2017 ...
. He established a Coalition for National Unity, Reconciliation and Peace, which released a program of action focused on resolving the ethnic conflict, restoring the economy and distributing the benefits of development more equally. However, Sogavare's government was deeply corrupt and its actions led to the downward economic spiral and the deterioration of law and order.
The conflict was foremost about access to land and other resources and was centered on Honiara. Since the beginning of the civil war it is estimated that 100 have been killed. About 30,000 refugees, mainly Malaitans, had to leave their homes, and economic activity on Guadalcanal was severely disrupted.
Continuing civil unrest led to an almost complete breakdown in normal activity: civil servants remained unpaid for months at a time, and cabinet meetings had to be held in secret to prevent local warlord
Warlords are individuals who exercise military, Economy, economic, and Politics, political control over a region, often one State collapse, without a strong central or national government, typically through informal control over Militia, local ...
s from interfering. The security forces were unable to reassert control, largely because many police and security personnel were associated with one or another of the rival gangs.
In July 2003 the Governor General of Solomon Islands issued an official request for international help, which was subsequently endorsed by a unanimous vote of the parliament. Technically, only the Governor General's request for troops was necessary. However, the government then passed legislation to provide the international force with greater powers and resolve some legal ambiguities.
On 6 July 2003, in response to a proposal to send 300 police and 2,000 troops from Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
, Fiji
Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about ...
and Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n ...
to Guadalcanal
Guadalcanal (; indigenous name: ''Isatabu'') is the principal island in Guadalcanal Province of Solomon Islands, located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, northeast of Australia. It is the largest island in the Solomons by area and the second- ...
, warlord Harold Keke announced a ceasefire
A ceasefire (also known as a truce), also spelled cease-fire (the antonym of 'open fire'), is a stoppage of a war in which each side agrees with the other to suspend aggressive actions often due to mediation by a third party. Ceasefires may b ...
by faxing a signed copy of the announcement to the Solomons Prime Minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
, Allan Kemakeza. Keke ostensibly leads the Guadalcanal Liberation Front, but has been described as marauding bandits based on the isolated southwestern coast (Weather Coast) of Guadalcanal. Despite this ceasefire, on 11 July 2003 the Solomon Islands Broadcasting Corporation broadcast unconfirmed reports that supporters of Harold Keke razed two villages.
In mid-July 2003, the Solomons parliament voted unanimously in favour of the proposed intervention. The international force began gathering at a training facility in Townsville
The City of Townsville is a city on the north-eastern coast of Queensland, Australia. With a population of 201,313 as of 2024, it is the largest settlement in North Queensland and Northern Australia (specifically, the parts of Australia north of ...
. In August 2003, an international peacekeeping force, known as the Regional Assistance Mission to Solomon Islands (RAMSI) and Operation Helpem Fren, entered the islands. Australia committed the largest number of security personnel, but with substantial numbers also from other South Pacific Forum countries such as New Zealand, Fiji, and Papua New Guinea (PNG). It acts as an interim police force and is responsible for restoring law and order in the country because the Royal Solomon Islands Police force failed to do so for a variety of reasons. Peacekeeping forces have been successful in improving the country's overall security conditions, including brokering the surrender of a notorious warlord Harold Keke in August 2003.
In 2006, riots
A riot or mob violence is a form of civil disorder commonly characterized by a group lashing out in a violent public disturbance against authority, property, or people.
Riots typically involve destruction of property, public or private. The p ...
broke out following the election of Snyder Rini as Prime Minister, destroying part of Chinatown and displacing more than 1,000 Chinese residents; the large Pacific Casino Hotel was also totally gutted. The commercial heart of Honiara was virtually reduced to rubble and ashes. Three National Parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
members, Charles Dausabea, Nelson Ne'e, and Patrick Vahoe, were arrested during or as a result of the riots. The Regional Assistance Mission to Solomon Islands (RAMSI), the 16-country Pacific Islands Forum initiative set up in 2003 with assistance from Australia, intervened, sending in additional police and army officers to bring the situation under control. A vote of no confidence was passed against the Prime Minister. Following his resignation, a five-party Grand Coalition for Change Government was formed in May 2006, with Manasseh Sogavare as Prime Minister, quelling the riots and running the government. The military part of RAMSI was withdrawn in 2013 and rebuilding took shape.
In 2009, the government is scheduled to set up a Truth and Reconciliation Commission
A truth commission, also known as a truth and reconciliation commission or truth and justice commission, is an official body tasked with discovering and revealing past wrongdoing by a government (or, depending on the circumstances, non-state ac ...
, with the assistance of South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
n Archbishop Desmond Tutu
Desmond Mpilo Tutu (7 October 193126 December 2021) was a South African Anglican bishop and theologian, known for his work as an anti-apartheid and human rights activist. He was Bishop of Johannesburg from 1985 to 1986 and then Archbishop ...
, to "address people’s traumatic experiences during the five-year ethnic conflict on Guadalcanal".
The government continues to face serious problems, including an uncertain economic outlook, deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
, and malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
control. At one point, prior to the deployment of RAMSI forces, the country was facing a serious financial crisis. While economic conditions are improving, the situation remains unstable.
2021 unrest
In 2019, the central government under Prime MinisterManasseh Sogavare
Manasseh Damukana Sogavare (born 17 January 1955) is a Solomon Islander politician serving as Minister of Finance since 2024. He served as the prime minister of Solomon Islands for a total of nine years from 2000–2001, 2006–2007, 2014–2017 ...
withdrew recognition of the Republic of China (Taiwan)
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
and established relations with the mainland People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
. Malaita Province
Malaita Province is the most populous of the nine provinces of Solomon Islands. The population of the province is 122,620 (1999). The area of the province is .
It is named after its largest island, Malaita (also known as "Big Malaita" or " ...
, however, continued to be supported by Taiwan and the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, the latter sending US$25 million of aid to the island in 2020. The premier of Malaita Province, Daniel Suidani, also held an independence referendum in 2020 which the national government has dismissed as illegitimate. Rising unemployment and poverty, worsened by the border closure during the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
, have also been cited as a cause of the unrest. Chinese businesses were also accused of giving jobs to foreigners instead of locals.
The protests were initially peaceful, but turned violent on 24 November 2021 after buildings adjoining the Solomon Islands Parliament Building were burnt down. Schools and businesses were closed down as police and government forces clashed with protesters. Violence escalated as Honiara's Chinatown
Chinatown ( zh, t=唐人街) is the catch-all name for an ethnic enclave of Chinese people located outside Greater China, most often in an urban setting. Areas known as "Chinatown" exist throughout the world, including Europe, Asia, Africa, O ...
was looted. Most of the protesters came from Malaita Province
Malaita Province is the most populous of the nine provinces of Solomon Islands. The population of the province is 122,620 (1999). The area of the province is .
It is named after its largest island, Malaita (also known as "Big Malaita" or " ...
.
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
responded to the unrest by deploying Australian Federal Police
The Australian Federal Police (AFP) is the principal Federal police, federal law enforcement agency of the Australian Government responsible for investigating Crime in Australia, crime and protecting the national security of the Commonwealth ...
and Australian Defence Force
The Australian Defence Force (ADF) is the Armed forces, military organisation responsible for the defence of Australia and its national interests. It consists of three branches: the Royal Australian Navy (RAN), Australian Army and the Royal Aus ...
personnel following a request from the Sogavare government under the Australia–Solomon Islands Bilateral Security Treaty. Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n ...
, Fiji
Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about ...
and New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
also sent peacekeepers.
Since 2024
In May 2024, Jeremiah Manel was elected as the Solomon Islands new prime minister to succeed Manasseh Sogavare.Cyclones
In 1992, Cyclone Tia struck the island ofTikopia
Tikopia is a volcanic island in Temotu Province, in the independent nation of Solomon Islands, southwestern Pacific Ocean. Although most of Solomon Islands is Melanesian, Tikopia is culturally Polynesian. Its remoteness has enabled much of its c ...
, wiping out most housing and food crops.
In 1997, the Government asked for help from the US and Japan to clean up more than 50 sunken World War II shipwreck
A shipwreck is the wreckage of a ship that is located either beached on land or sunken to the bottom of a body of water. It results from the event of ''shipwrecking'', which may be intentional or unintentional. There were approximately thre ...
s polluting coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in group ...
s and killing marine life.
In December 2002, Severe Tropical Cyclone Zoe struck the island of Tikopia and Anuta, cutting off contact with the 3,000 inhabitants. Due to funding problems, the Solomon Islands government could not send relief until the Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
n government provided funding.
Cyclone Ita
 In April 2014 the islands were struck by the tropical low that later became Cyclone Ita.
Throughout the Solomons, at least 23 people were killed while up to 40 others remained unaccounted for as of 6 April. An estimated 49,000 people were affected by the floods, of whom 9,000 were left homeless.
As the precursor tropical low to Ita affected the Islands, local authorities issued heavy flood warnings, tropical disturbance and cyclone watches.
Nearly two days of continuous heavy rains from the storm caused flash flooding in the Islands. Over a four-day span, more than fell at the Gold Ridge (mine), Gold Ridge mine in
In April 2014 the islands were struck by the tropical low that later became Cyclone Ita.
Throughout the Solomons, at least 23 people were killed while up to 40 others remained unaccounted for as of 6 April. An estimated 49,000 people were affected by the floods, of whom 9,000 were left homeless.
As the precursor tropical low to Ita affected the Islands, local authorities issued heavy flood warnings, tropical disturbance and cyclone watches.
Nearly two days of continuous heavy rains from the storm caused flash flooding in the Islands. Over a four-day span, more than fell at the Gold Ridge (mine), Gold Ridge mine in Guadalcanal
Guadalcanal (; indigenous name: ''Isatabu'') is the principal island in Guadalcanal Province of Solomon Islands, located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, northeast of Australia. It is the largest island in the Solomons by area and the second- ...
, with falling in a 24‑hour span. The Matanikau River, which runs through the capital city Honiara
Honiara () is the capital and largest city of Solomon Islands, situated on the northwestern coast of Guadalcanal. , it had a population of 92,344 people. The city is served by Honiara International Airport and the seaport of Point Cruz, and lies ...
, broke its banks on 3 April and devastated nearby communities. Thousands of homes along with the city's two main bridges were washed away, stranding numerous residents. The national hospital had to evacuate 500 patients to other facilities due to flooding. Graham Kenna from Save the Children stated that, "the scale of destruction is like something never seen before in the Solomon Islands." According to Permanent Secretary Melchoir Mataki, the majority of homes destroyed in Honiara were built on a flood plain where construction was not allowed.
Severe flooding took place on Guadalcanal. Immediately following the floods, Honiara and Guadalcanal were declared disaster areas by the Solomon Government. Debris left behind by the floods initially hampered relief efforts, with the runway at Honiara International Airport blocked by two destroyed homes. Food supplies started running low as the Red Cross provided aid to the thousands homeless. The airport was reopened on 6 April, allowing for supplies from Australia and New Zealand to be delivered. Roughly 20 percent of Honiara's population relocated to evacuation centers as entire communities were swept away. There were fears that the flooding could worsen an already ongoing dengue fever outbreak and cause outbreaks of diarrhea and conjunctivitis.
New Zealand offered an immediate New Zealand dollar, NZ$300,000 in funds and deployed a Lockheed C-130 Hercules, C-130 Hercules with supplies and emergency response personnel. Australia donated Australian dollar, A$250,000 on 6 April and sent engineers and response teams to aid in relief efforts. On 8 April, Australia increased its aid package to A$3 million while New Zealand provided an additional NZ$1.2 million. Taiwan provided US$200,000 in funds.
See also
*History of Oceania *Politics of Solomon Islands *Prime Minister of Solomon IslandsReferences
Further reading
* Golden, Graeme A., The Early European Settlers of the Solomon Islands, Graeme A. Golden, Melbourne, (1993). * Lawrence, David Russell, The Naturalist and his 'Beautiful Islands': Charles Morris Woodford in the Western Pacific, ANU Press, Canberra, (2014). * Richards, Rhys, Head Hunters Black and White: Three Collectors in the Western Solomon Islands 1893 to 1914, and the Diary of Graham Officer, Collector of Museum Objects in the Solomon Islands in 1901 for Museum Victoria in Melbourne, Paremata Press, Wellington, (2012). * * {{DEFAULTSORT:History of the Solomon Islands History of the Solomon Islands,