Solid Pseudopapillary Tumour on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A solid pseudopapillary tumour is a low-grade malignant neoplasm of the pancreas of papillary architecture that typically afflicts young women.
 The gold standard for diagnosing solid pseudopapillary tumour of the pancreas is cytopathology by endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) guided fine needle aspiration (FNA) of the lesion. After surgical excision, the tumor can undergo
The gold standard for diagnosing solid pseudopapillary tumour of the pancreas is cytopathology by endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) guided fine needle aspiration (FNA) of the lesion. After surgical excision, the tumor can undergo
Signs and symptoms
Solid pseudopapillary tumours are often asymptomatic and are identified incidentally on imaging performed for unrelated reasons. Less often, they may cause abdominal pain. Solid pseudopapillary tumours tend to occur in women, and most often present in the third decade of life.Anatomy
Gross morphology
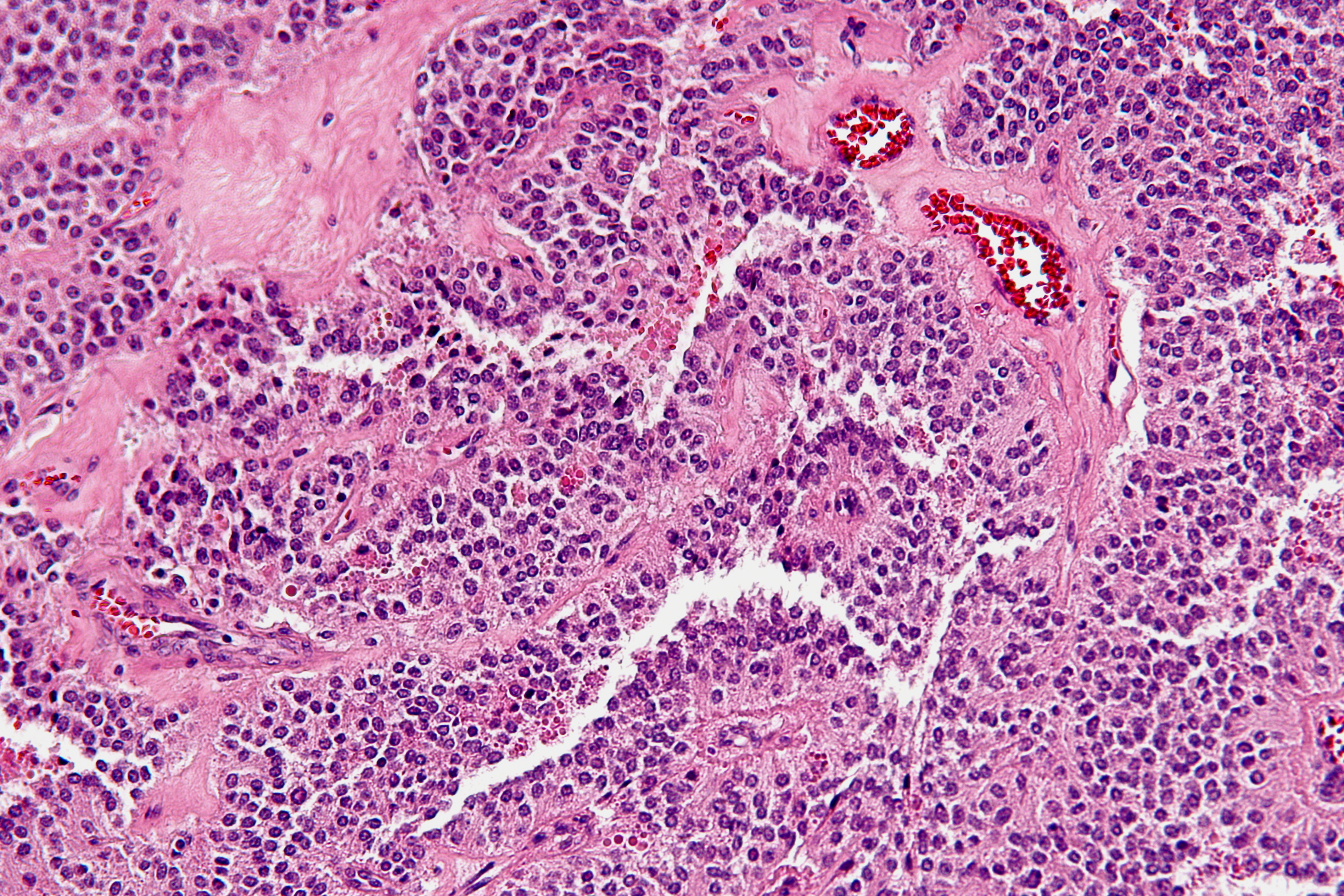
Solid pseudopapillary tumours are typically round, well-demarcated, measuring 2–17 cm in diameter (average 8 cm), with solid and cystic areas with hemorrhage on cut sections.Histomorphology
Solid pseudopapillary tumours consist of solid sheets of cells that are focally dyscohesive. The cells in the lesion usually have uniform nuclei with occasional nuclear grooves, eosinophilic or clear cytoplasm and PAS positive eosinophilic intracytoplasmic globules. Necrosis is usually present and, as cell death preferentially occurs distant from blood vessels, lead to the formation of pseudopapillae.Immunohistochemistry
Solid pseudopapillary tumours show positive nuclear staining for beta catenin, as well as positive immunostaining for CD10, CD56, vimentin,alpha 1-antitrypsin
Alpha-1 antitrypsin or α1-antitrypsin (A1AT, α1AT, A1A, or AAT) is a protein belonging to the serpin superfamily. It is encoded in humans by the ''SERPINA1'' gene. A protease inhibitor, it is also known as alpha1–proteinase inhibitor (A1PI) ...
, and neuron specific enolase; they are negative for chromogranin and pancreatic enzymes.
Diagnosis

 The gold standard for diagnosing solid pseudopapillary tumour of the pancreas is cytopathology by endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) guided fine needle aspiration (FNA) of the lesion. After surgical excision, the tumor can undergo
The gold standard for diagnosing solid pseudopapillary tumour of the pancreas is cytopathology by endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) guided fine needle aspiration (FNA) of the lesion. After surgical excision, the tumor can undergo histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: ''histos'' "tissue", πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", and -λογία '' -logia'' "study of") refers to the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Spe ...
evaluation for cancer staging.
Management
In most cases, solid pseudopapillary tumours should be resected surgically, as there is a risk of malignancy (cancer).See also
*Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer arises when cell (biology), cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a Neoplasm, mass. These cancerous cells have the malignant, ability to invade other parts of t ...
* Pancreatic mucinous cystic neoplasm
* Serous cystadenoma of the pancreas
References
{{Digestive system neoplasia Digestive system neoplasia Pancreatic cancer