Solar Saros 133 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Saros cycle 133 - Information and visualization
{{Solar eclipses Solar saros series 1219 establishments 25th century

Saros cycle
The saros () is a period of exactly 223 synodic months, approximately 6585.3211 days, or 18 years, 10, 11, or 12 days (depending on the number of leap years), and 8 hours, that can be used to predict eclipses of the Sun and Moon. One saros perio ...
series 133 for solar eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of the Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six mo ...
s occurs at the Moon's ascending node, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 72 events. All eclipses in this series occurs at the Moon's ascending node.
Solar Saros 133 is one of the saros series of solar eclipse cycle
Eclipses may occur repeatedly, separated by certain intervals of time: these intervals are called eclipse cycles. The series of eclipses separated by a repeat of one of these intervals is called an eclipse series.
Eclipse conditions
Eclips ...
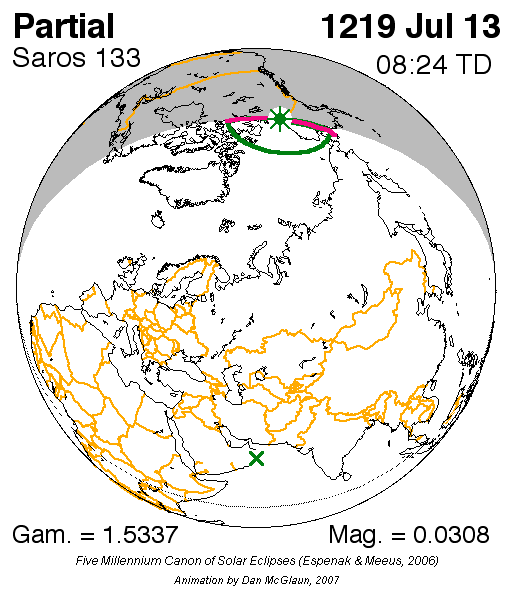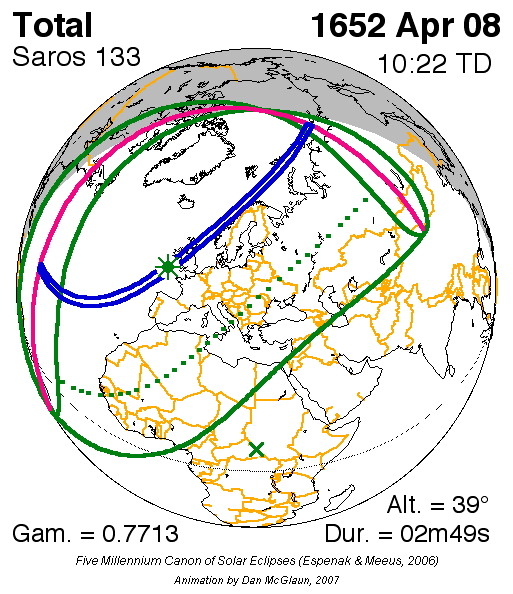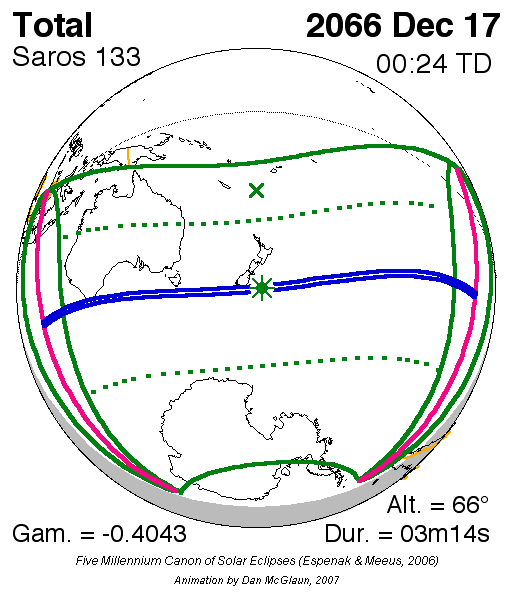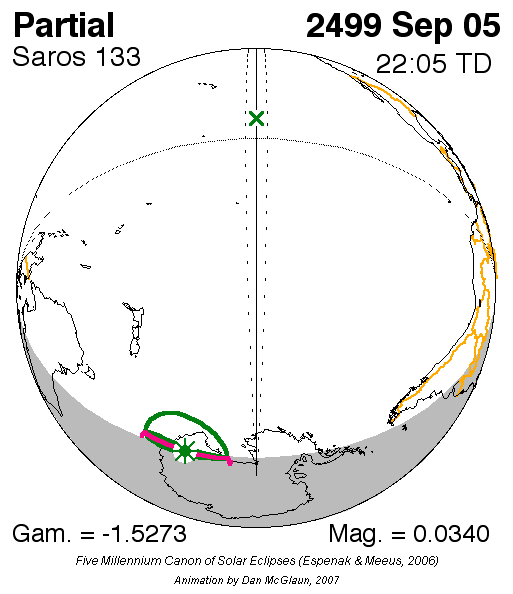
s. It began on July 13, 1219 with a partial eclipse occurring in northern Yukon at , about east of Canada's present-day Vuntut National Park. The final eclipse in the series will be on September 5, 2499. All eclipses in this series occurs at the Moon's ascending node.
The period separating each of the 72 eclipses in the series is approximately 6585.3 days (18 years, 11 days); that period was first called a saros by astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, moons, comets and galaxies – in either o ...
Edmond Halley
Edmond (or Edmund) Halley (; – ) was an English astronomer, mathematician and physicist. He was the second Astronomer Royal in Britain, succeeding John Flamsteed in 1720.
From an observatory he constructed on Saint Helena in 1676–77, Hal ...
. This solar saros is linked to Lunar Saros 126.
20th and 21st century
Five of the series ofsolar eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of the Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six mo ...
s occur during the 21st century: November 13, 2012, November 25, 2030, December 5, 2048, December 17, 2066, and December 27, 2084.
Umbral eclipses
Umbral eclipses (annular, total and hybrid) can be further classified as either: 1) Central (two limits), 2) Central (one limit) or 3) Non-Central (one limit). The statistical distribution of these classes in Saros series 133 appears in the following table.List
In the following list, theJulian calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematics, Greek mathematicians and Ancient Greek astronomy, as ...
is used for the first 21 members of the series; the Gregorian calendar
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It was introduced in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years di ...
is used for all the rest,
starting with the solar eclipse of March 7, 1598.
References
External links
Saros cycle 133 - Information and visualization
{{Solar eclipses Solar saros series 1219 establishments 25th century