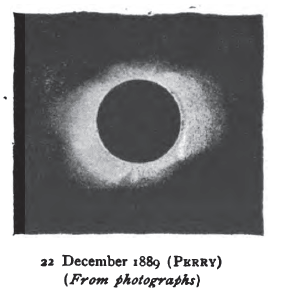
Solar Eclipse Of December 22, 1889 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A total
NASA graphic
*
Googlemap
*
NASA Besselian elements
Lick Observatory Plate Archive, Mt. Hamilton.
by Albert Bergman (A Man Before the Mast), New York, 1890 * * {{Solar eclipses 1889 12 22 1889 12 22 1889 in science December 1889
solar eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs approximately every six months, during the eclipse season i ...
occurred at the Moon's descending node
An orbital node is either of the two points where an orbit intersects a plane of reference to which it is inclined. A non-inclined orbit, which is contained in the reference plane, has no nodes.
Planes of reference
Common planes of referenc ...
of orbit on Sunday, December 22, 1889, with a magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
of 1.0449. A solar eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs approximately every six months, during the eclipse season i ...
occurs when the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
passes between Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
and the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter
The angular diameter, angular size, apparent diameter, or apparent size is an angular separation (in units of angle) describing how large a sphere or circle appears from a given point of view. In the vision sciences, it is called the '' visual ...
is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 12.5 hours before perigee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values.
Apsides perta ...
(on December 23, 1889, at 1:30 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.
The path of totality was visible from parts of modern-day Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago, officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean, comprising the main islands of Trinidad and Tobago, along with several List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, smaller i ...
, northern French Guiana
French Guiana, or Guyane in French, is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France located on the northern coast of South America in the Guianas and the West Indies. Bordered by Suriname to the west ...
, Angola
Angola, officially the Republic of Angola, is a country on the west-Central Africa, central coast of Southern Africa. It is the second-largest Portuguese-speaking world, Portuguese-speaking (Lusophone) country in both total area and List of c ...
, the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is t ...
, Rwanda
Rwanda, officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of East Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equator, Rwanda is bordered by ...
, Burundi
Burundi, officially the Republic of Burundi, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is located in the Great Rift Valley at the junction between the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa, with a population of over 14 million peop ...
, Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t ...
, Kenya
Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country located in East Africa. With an estimated population of more than 52.4 million as of mid-2024, Kenya is the 27th-most-populous country in the world and the 7th most populous in Africa. ...
, and Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th ...
. A partial solar eclipse was also visible for parts of the eastern Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
, northern and central South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
, and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
.
The eclipse was the focus of a 242-day United States scientific expedition, roughly 70 miles south of Luanda
Luanda ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Angola, largest city of Angola. It is Angola's primary port, and its major industrial, cultural and urban centre. Located on Angola's northern Atlantic coast, Luanda is Ang ...
.
Observations
The eclipse was the focus of a scientific expedition from the United States, led by David P. Todd of Amherst College and including a team of at least six. Among the members was E. J. Loomis from theAmerican Ephemeris and Nautical Almanac
''The American Ephemeris and Nautical Almanac'' was published for the years 1855 to 1980, containing information necessary for astronomers, surveyors, and navigators. It was based on the original British publication, '' The Nautical Almanac and Ast ...
office. It set sail October 16 on the USS Pensacola
There have been four United States Navy ships named USS ''Pensacola'':
*The first was a steamer launched in 1859 and was decommissioned in 1911.
*The second was a German steamer seized when the United States entered World War I and used as a tra ...
and set up the eclipse base camp in December, roughly 70 miles south of Luanda
Luanda ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Angola, largest city of Angola. It is Angola's primary port, and its major industrial, cultural and urban centre. Located on Angola's northern Atlantic coast, Luanda is Ang ...
in Cape Ledo. Totality was completely obscured by cloud cover. The ship returned to New York after 242 days, with the expedition performing a variety of other scientific studies along the way.

Eclipse details
Shown below are two tables displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. The first table outlines times at which the moon's penumbra or umbra attains the specific parameter, and the second table describes various other parameters pertaining to this eclipse.Eclipse season
This eclipse is part of aneclipse season
An eclipse season is a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Eclipse seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of the Orbit of the Moon, Moon's orbital plane (orbital inclination, tilted five degrees to the ecliptic, Earth ...
, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later; thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. In the sequence below, each eclipse is separated by a fortnight
A fortnight is a unit of time equal to 14 days (two weeks). The word derives from the Old English term , meaning "" (or "fourteen days", since the Anglo-Saxons counted by nights).
Astronomy and tides
In astronomy, a ''lunar fortnight'' is hal ...
.
Related eclipses
Eclipses in 1889
* A total solar eclipse on January 1. * A partial lunar eclipse on January 17. * An annular solar eclipse on June 28. * A partial lunar eclipse on July 12. * A total solar eclipse on December 22.Metonic
* Preceded by:Solar eclipse of March 5, 1886
Solar may refer to:
Astronomy
* Of or relating to the Sun
** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun
** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels")
** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate t ...
* Followed by: Solar eclipse of October 9, 1893
Solar may refer to:
Astronomy
* Of or relating to the Sun
** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun
** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels")
** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate t ...
Tzolkinex
* Preceded by:Solar eclipse of November 10, 1882
Solar may refer to:
Astronomy
* Of or relating to the Sun
** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun
** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels")
** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate t ...
* Followed by: Solar eclipse of February 1, 1897
Solar may refer to:
Astronomy
* Of or relating to the Sun
** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun
** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels")
** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate t ...
Half-Saros
* Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of December 16, 1880 * Followed by: Lunar eclipse of December 27, 1898Tritos
* Preceded by:Solar eclipse of January 22, 1879
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's Lunar node, ascending node of orbit on Wednesday January 22, 1879, with a Magnitude of eclipse, magnitude of 0.9700. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby tot ...
* Followed by: Solar eclipse of November 22, 1900
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of orbit on Thursday, November 22, 1900, with a magnitude of 0.9421. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the imag ...
Solar Saros 130
* Preceded by: Solar eclipse of December 12, 1871 * Followed by:Solar eclipse of January 3, 1908
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's Lunar node, descending node of orbit between Friday, January 3 and Saturday, January 4, 1908, with a Magnitude of eclipse, magnitude of 1.0437. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth ...
Inex
* Preceded by:Solar eclipse of January 11, 1861
Solar may refer to:
Astronomy
* Of or relating to the Sun
** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun
** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels")
** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate t ...
* Followed by: Solar eclipse of December 3, 1918
Triad
* Preceded by: Solar eclipse of February 21, 1803 * Followed by:Solar eclipse of October 23, 1976
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's Lunar node, ascending node of orbit on Saturday, October 23, 1976, with a Magnitude of eclipse, magnitude of 1.0572. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totall ...
Solar eclipses of 1888–1891
The partial solar eclipses on February 11, 1888 and August 7, 1888 occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set.Saros 130
Metonic series
Tritos series
Inex series
References
NASA graphic
*
Googlemap
*
NASA Besselian elements
Lick Observatory Plate Archive, Mt. Hamilton.
by Albert Bergman (A Man Before the Mast), New York, 1890 * * {{Solar eclipses 1889 12 22 1889 12 22 1889 in science December 1889