Solar barque on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 According to Egyptian myth, when Ra became too old and weary to reign on earth he relinquished and went to the skies. Ra was said to travel through the sky on the barge, providing light to the world. Each twelfth of his journey formed one of the twelve Egyptian hours of the day, each overseen by a protective deity. When the sun set and twilight came, he and his vessel passed through the ''akhet'', the horizon, in the west, and traveled to the underworld.
According to Egyptian myth, when Ra became too old and weary to reign on earth he relinquished and went to the skies. Ra was said to travel through the sky on the barge, providing light to the world. Each twelfth of his journey formed one of the twelve Egyptian hours of the day, each overseen by a protective deity. When the sun set and twilight came, he and his vessel passed through the ''akhet'', the horizon, in the west, and traveled to the underworld.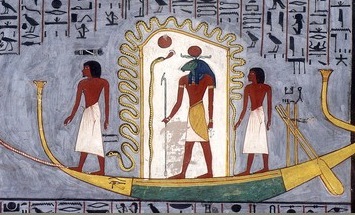 At times the horizon is described as a gate or door that leads to the Duat. There he would have to sail on the subterrestrial
At times the horizon is described as a gate or door that leads to the Duat. There he would have to sail on the subterrestrial
 In folklore, a boat of this kind is used by the sun god. Thus, as the
In folklore, a boat of this kind is used by the sun god. Thus, as the
thumb
The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the index finger. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position (where the palm is facing to the front), the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thumb ...
Solar barques were the vessels used by the sun god Ra in ancient Egyptian mythology. During the day, Ra was said to use a vessel called the Mandjet () or the Boat of Millions of Years (), and the vessel he used during the night was known as the Mesektet ().
Myth
 At times the horizon is described as a gate or door that leads to the Duat. There he would have to sail on the subterrestrial
At times the horizon is described as a gate or door that leads to the Duat. There he would have to sail on the subterrestrial Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
and cross through the twelve gates and regions,Hart 1986, pp. 68–72. with each hour of the night considered a gate overseen by twelve more protective deities. Every night enormous serpent Apophis, the god of chaos ('' isfet'') attempted to attack Ra and stop the sun-boat's journey. After defeating the snake, Ra would leave the underworld, returning emerging at dawn, lighting the day again.
He was said to travel across the sky in his falcon-headed form on the Mandjet Barque through the hours of the day, and then switch to the Mesektet Barque in his ram-headed form to descend into the underworld for the hours of the night. The progress of Ra upon the Mandjet was sometimes conceived as his daily growth, decline, death, and resurrection and it appears in the symbology of Egyptian mortuary texts.
Funerary practices and religion
 In folklore, a boat of this kind is used by the sun god. Thus, as the
In folklore, a boat of this kind is used by the sun god. Thus, as the pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''wikt:pr ꜥꜣ, pr ꜥꜣ''; Meroitic language, Meroitic: 𐦲𐦤𐦧, ; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') was the title of the monarch of ancient Egypt from the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty ( ...
was a representation of the sun god on earth, the king would use a similar boat upon his death to travel through the underworld on their journey to the afterlife.
One of the most well known examples of this is the Khufu ship, which was built and then buried at Giza
Giza (; sometimes spelled ''Gizah, Gizeh, Geeza, Jiza''; , , ' ) is the third-largest city in Egypt by area after Cairo and Alexandria; and fourth-largest city in Africa by population after Kinshasa, Lagos, and Cairo. It is the capital of ...
along with Khufu
Khufu or Cheops (died 2566 BC) was an ancient Egyptian monarch who was the second pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt, Fourth Dynasty, in the first half of the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom period (26th century BC). Khufu succeeded his ...
and the rest of the items he would take with him to the afterlife. The ship was originally displayed in the specially-built Giza Solar boat museum, but was subsequently moved to the Grand Egyptian Museum.
See also
* Ancient Egyptian royal ships *Abydos boats
The Abydos boats are the remnants of a group of ancient royal Egyptian ceremonial boats found at an archaeological site in Abydos, Egypt. Discovered in 1991, excavation of the Abydos boats began in 2000 at which time fourteen boats were identified ...
* Solar deity
* Trundholm sun chariot
References
{{authority control Ra Barques Egyptian mythology Egyptology Mythological ships