software synthesizer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A software synthesizer or softsynth is a computer program that generates
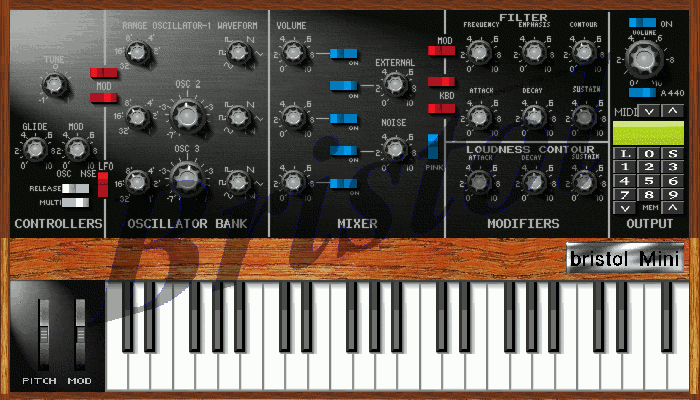 Softsynths can cover a range of synthesis methods, including subtractive synthesis (including analog modeling, a subtype),
Softsynths can cover a range of synthesis methods, including subtractive synthesis (including analog modeling, a subtype),
digital audio
Digital audio is a representation of sound recorded in, or converted into, digital signal (signal processing), digital form. In digital audio, the sound wave of the audio signal is typically encoded as numerical sampling (signal processing), ...
, usually for music. Computer software that can create sounds or music is not new, but advances in processing speed now allow softsynths to accomplish the same tasks that previously required the dedicated hardware of a conventional synthesizer
A synthesizer (also synthesiser or synth) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis a ...
. Softsynths may be readily interfaced with other music software such as music sequencer
A music sequencer (or audio sequencer or simply sequencer) is a device or application software that can record, edit, or play back music, by handling Musical note, note and performance information in several forms, typically CV/Gate, MIDI, or Open ...
s typically in the context of a digital audio workstation
A digital audio workstation (DAW ) is an electronic device or application software used for Sound recording and reproduction, recording, editing and producing audio files. DAWs come in a wide variety of configurations from a single software pr ...
. Softsynths are usually less expensive and can be more portable than dedicated hardware.
Types
 Softsynths can cover a range of synthesis methods, including subtractive synthesis (including analog modeling, a subtype),
Softsynths can cover a range of synthesis methods, including subtractive synthesis (including analog modeling, a subtype), FM synthesis
Frequency modulation synthesis (or FM synthesis) is a form of sound synthesis whereby the frequency of a waveform is changed by modulating its frequency with a modulator. The (instantaneous) frequency of an oscillator is altered in accordance wi ...
(including the similar phase distortion synthesis), physical modelling synthesis
Physical modelling synthesis refers to sound synthesis methods in which the waveform of the sound to be generated is computed using a mathematical model, a set of equations and algorithms to simulate a physical source of sound, usually a musical i ...
, additive synthesis (including the related resynthesis), and sample-based synthesis
Sample-based synthesis is a form of audio synthesis that can be contrasted to either subtractive synthesis or additive synthesis. The principal difference with sample-based synthesis is that the seed waveforms are sampled sounds or instrument ...
.
Many popular hardware synthesizers are no longer manufactured but have been emulated in software. The emulation can even extend to having graphics that model the exact placements of the original hardware controls. Some simulators can even import the original sound patches with accuracy that is nearly indistinguishable from the original synthesizer. Popular synthesizers such as the Moog Minimoog, Yamaha DX7
The Yamaha DX7 is a synthesizer manufactured by Yamaha Corporation from 1983 to 1989. It was the first successful digital synthesizer and is one of the best-selling synthesizers in history, selling more than 200,000 units.
In the early 1980s, th ...
, Korg M1, Sequential Circuits Prophet-5, Oberheim OB-X, Roland Jupiter-8, ARP 2600 and dozens of other classics have been recreated in software. Software Synth developers such as Arturia
Arturia is a French electronics company founded in 1999 and based in Grenoble, France. The company designs and manufactures audio interfaces and electronic musical instruments, including software synthesizers, drum machines, analog synthesizers, ...
offer virtual editions of analog synths like the Minimoog
The Minimoog is an analog synthesizer first manufactured by Moog Music between 1970 and 1981. Designed as a more affordable, portable version of the modular Moog synthesizer, it was the first synthesizer sold in retail stores. It was first popul ...
, the ARP 2600, as well as the Yamaha CS-80. GForce produces a Minimoog (with sounds designed by Rick Wakeman) and a version of the ARP Odyssey. There is also a variety of popular software synthesizers that are exclusively software. Synths like Serum 2 and its predecessor Serum (both created by Steve Duda under Xfer Records), Pigments by Arturia
Arturia is a French electronics company founded in 1999 and based in Grenoble, France. The company designs and manufactures audio interfaces and electronic musical instruments, including software synthesizers, drum machines, analog synthesizers, ...
, Vital developed by Vital Audio, and even Alchemy, originally developed by Camel Audio, which is famously associated with Logic Pro after its acquisition by Apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
.
Some softsynths are sample-based, and frequently have more capability than hardware units, since computers have fewer restrictions on memory than dedicated hardware synthesizers. Sample libraries may be many gigabytes in size. Some are specifically designed to mimic real-world instruments such as pianos. Sample libraries' formats include '' .wav'', '' .sf'' or .sf2.
Softsynths suffer their own issues compared to traditional hardware. Softsynths tend to have more latency than hardware; they can also suffer from crashes and data loss. This is why oftentimes a composer or virtual conductor will want a "draft mode" for initial score editing and then use the "production mode" to generate high-quality sound as one gets closer to the final version. The draft mode allows for quicker turn-around, perhaps in real time, but will not have the full quality of the production mode. The draft render is roughly analogous to a wire-frame or "big polygon" animation when creating 3D animation or CGI. Both are based on the trade-off between quality and turn-around time for reviewing drafts and changes.
Software instrument
A software instrument can be a synthesized version of a real instrument (like the sounds of aviolin
The violin, sometimes referred to as a fiddle, is a wooden chordophone, and is the smallest, and thus highest-pitched instrument (soprano) in regular use in the violin family. Smaller violin-type instruments exist, including the violino picc ...
or drums), or a unique instrument, generated by computer software. Software instruments have been made popular by the convergence of synthesizers and computers, as well as sequencing software like GarageBand
GarageBand is a software application by Apple Inc., Apple for macOS, iPadOS, and iOS devices that allows users to create music or Podcast, podcasts. It is a lighter, amateur-oriented offshoot of Logic Pro. GarageBand was originally released for ...
, Logic Pro, and Ableton Live. Also of note is software like Csound and Nyquist, which can be used to program software instruments.
History
In 1986, Aegis released Sonix for the Commodore Amiga. Alongside a graphical score editor, Sonix featured a 4-voice software synthesizer. It featured MIDI input, a recognizable user interface, waveform drawing, an envelope, LFO, and non-resonant filter - calculating the synthesized result in real-time and sending it out, polyphonically, to the Amiga's 4 PCM-based channels. In 1996, Steinberg, a German software company, released the VST standard. In 1997, Seer Systems released the first commercial software synthesizer, named Reality, which combined previously used forms of synthesis such as PCM, wavetable, FM, additive and physical modeling. This helped integrate software synthesizers into DAW software, streamlining usage. As computers became more powerful, software synthesizers did as well. This led to developments in new forms of synthesis such as granular synthesis. Other software synthesizers focused on recreating or imitating other instruments. For example, some software synthesizers focused on physical modeling in order to imitate instruments like organs and electric pianos.See also
* :Software synthesizers * :Music software plugin architectures *Digital audio editor
Audio editing software is any software or computer program which allows editing and generating audio data. Audio editing software can be implemented completely or partly as a library, as a computer application, as a web application, or as a ...
* Modular synthesizer
Modular synthesizers are synthesizers composed of separate modules for different functions. The modules can be connected together by the user to create a patch. The outputs from the modules may include audio signals, analog control voltages, ...
* Music sequencer
A music sequencer (or audio sequencer or simply sequencer) is a device or application software that can record, edit, or play back music, by handling Musical note, note and performance information in several forms, typically CV/Gate, MIDI, or Open ...
* Sound module
* Synthesizer
A synthesizer (also synthesiser or synth) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis a ...
* '' SynthFont''
* TiMidity++
* Video game music
Video game music (VGM) is the soundtrack that accompanies video games. Early video game music was once limited to sounds of early sound chips, such as programmable sound generators (PSG) or FM synthesis chips. These limitations have led to t ...
* List of music software
This is a list of software for creating, performing, learning, analyzing, researching, broadcasting and editing music. This article only includes software, not services.
For streaming services such as iHeartRadio, Pandora (service), Pandora, Prime ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Software Synthesizer Music software * MIDI