Social Season on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
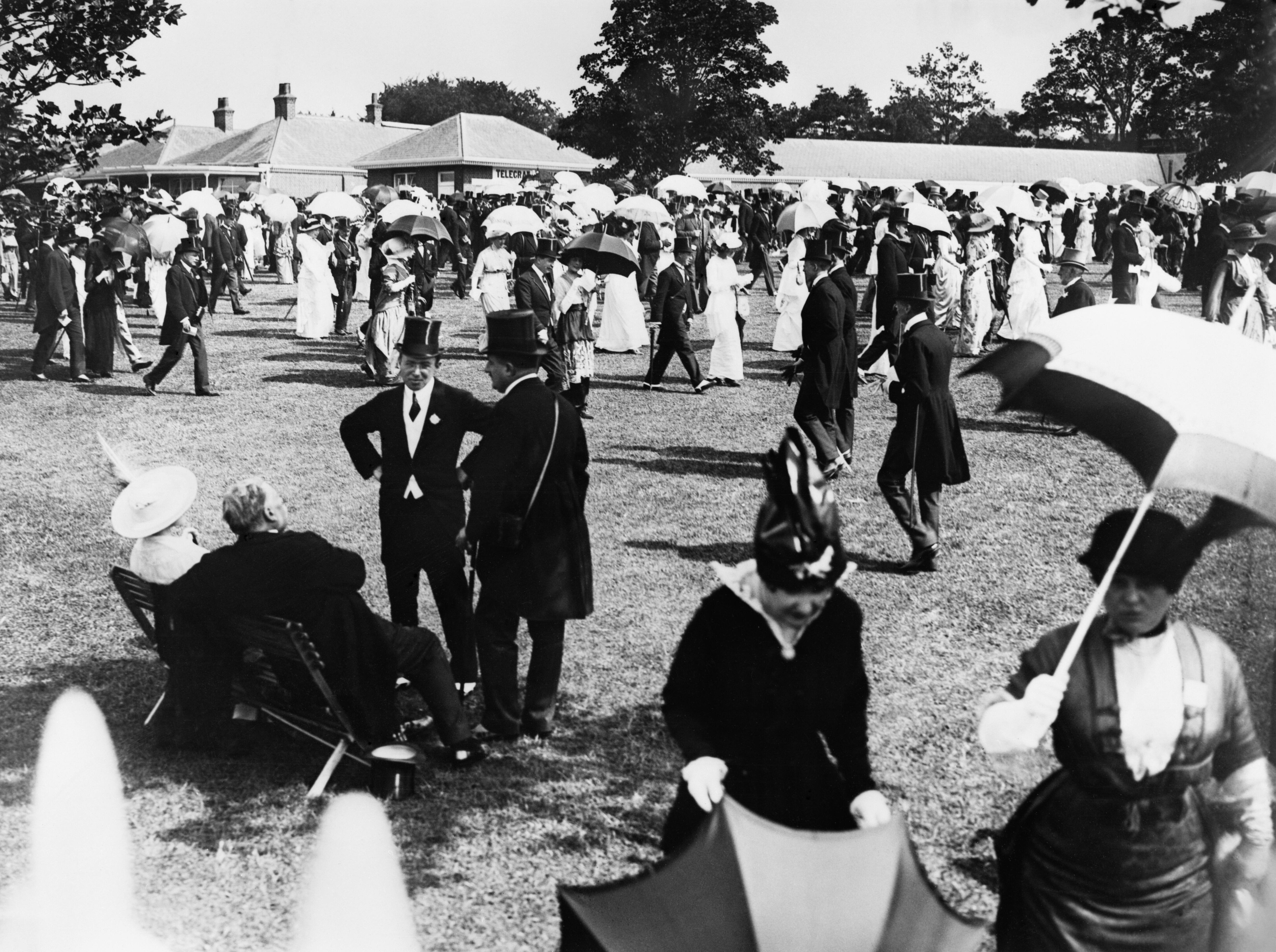 The social season, or season, refers to the traditional annual period in the spring and summer when it is customary for members of the
The social season, or season, refers to the traditional annual period in the spring and summer when it is customary for members of the



 The London social season evolved in the 17th and 18th centuries, and in its traditional form it peaked in the 19th century. In this era the British elite was dominated by families of the
The London social season evolved in the 17th and 18th centuries, and in its traditional form it peaked in the 19th century. In this era the British elite was dominated by families of the
 The social season, or season, refers to the traditional annual period in the spring and summer when it is customary for members of the
The social season, or season, refers to the traditional annual period in the spring and summer when it is customary for members of the social elite
Elitism is the notion that individuals who form an elite — a select group with desirable qualities such as intellect, wealth, power, physical attractiveness, notability, special skills, experience, lineage — are more likely to be constru ...
to hold balls, dinner parties
A party is a gathering of people who have been invited by a Hospitality, host for the purposes of socializing, conversation, recreation, or as part of a festival or other commemoration or celebration of a special occasion. A party will oft ...
and charity
Charity may refer to:
Common meanings
* Charitable organization or charity, a non-profit organization whose primary objectives are philanthropy and social well-being of persons
* Charity (practice), the practice of being benevolent, giving and sha ...
events. Until the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, it was also the appropriate time to reside in the city (generally meaning London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
in Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
and Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
in Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
) rather than in the country in order to attend such events.
In modern times in the United Kingdom, "the ondonSeason" is known to encompass various prestigious but mostly accessible events that take place during the spring and summer. The Dublin social season began to decline after the formation of the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State (6 December 192229 December 1937), also known by its Irish-language, Irish name ( , ), was a State (polity), state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-ye ...
and no longer occurs today.
The Scottish social season would follow the London one and take place in the Scottish Highlands
The Highlands (; , ) is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Scottish Lowlands, Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Scots language, Lowland Scots language replaced Scottish Gae ...
. There was a social season, or some semblance of one, in British colonies, including British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
, British Hong Kong
Hong Kong was under British Empire, British rule from 1841 to 1997, except for a Japanese occupation of Hong Kong, brief period of Japanese occupation during World War II from 1941 to 1945. It was a crown colony of the United Kingdom from 1841 ...
, British Shanghai, British Australia, British New Zealand and British Egypt
The history of Egypt under the British lasted from 1882, when it was occupied by British forces during the Anglo-Egyptian War, until 18 June 1956, when the last British forces withdrew in accordance with the Anglo-Egyptian evacuation agreem ...
. Despite being republics with no official aristocracies, the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
had social seasons in the 19th century.
Social season of London




 The London social season evolved in the 17th and 18th centuries, and in its traditional form it peaked in the 19th century. In this era the British elite was dominated by families of the
The London social season evolved in the 17th and 18th centuries, and in its traditional form it peaked in the 19th century. In this era the British elite was dominated by families of the nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally appointed by and ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. T ...
and landed gentry
The landed gentry, or the gentry (sometimes collectively known as the squirearchy), is a largely historical Irish and British social class of landowners who could live entirely from rental income, or at least had a country estate. It is t ...
, who generally regarded their country house
image:Blenheim - Blenheim Palace - 20210417125239.jpg, 300px, Blenheim Palace - Oxfordshire
An English country house is a large house or mansion in the English countryside. Such houses were often owned by individuals who also owned a Townhou ...
as their main home, but spent several months of the year in the capital to socialise and to engage in politics
Politics () is the set of activities that are associated with decision-making, making decisions in social group, groups, or other forms of power (social and political), power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of Social sta ...
. The most exclusive events were held at the townhouses
A townhouse, townhome, town house, or town home, is a type of terraced housing. A modern townhouse is often one with a small footprint on multiple floors. In a different British usage, the term originally referred to any type of city residenc ...
of leading members of the aristocracy. Exclusive public venues such as Almack's
Almack's was the name of a number of establishments and social clubs in London between the 18th and 20th centuries. Two of the social clubs would go on to fame as Brooks's and Boodle's. Almack's most famous establishment was based in assembly ...
played a secondary role. The Season coincided with the sitting of parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
; it began some time after Christmas and ran until midsummer
Midsummer is a celebration of the season of summer, taking place on or near the date of the summer solstice in the Northern Hemisphere; the longest Daytime, day of the year. The name "midsummer" mainly refers to summer solstice festivals of Eu ...
, roughly late June. Some sources say it began at Parliament's Easter session break.
The social season played a role in the political life of the country: the members of the two Houses of Parliament
The Palace of Westminster is the meeting place of the Parliament of the United Kingdom and is located in London, England. It is commonly called the Houses of Parliament after the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two legislative ch ...
were almost all participants in the season, as all Peers sitting in the House of Lords
The House of Lords is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the lower house, the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. One of the oldest ext ...
were by definition nobility, and many if not most Members of the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of ...
were gentry. But the Season also provided an opportunity for the children of marriageable age of the nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally appointed by and ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. T ...
and gentry to be launched into society. Debutante
A debutante, also spelled débutante ( ; from , ), or deb is a young woman of aristocratic or upper-class family background who has reached maturity and is presented to society at a formal "debut" ( , ; ) or possibly debutante ball. Origin ...
s were formally introduced into society by presentation to the monarch at royal court
A royal court, often called simply a court when the royal context is clear, is an extended royal household in a monarchy, including all those who regularly attend on a monarch, or another central figure. Hence, the word ''court'' may also be app ...
during the Court Drawing Rooms and Queen Charlotte's Ball
The Queen Charlotte's Ball is an annual British debutante ball. The ball was founded in 1780 by George III as a birthday celebration in honour of his wife, Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, for whom the ball is named. The Queen Charlotte's Ball ...
until the practice was abolished by Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 19268 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, her death in 2022. ...
in 1958 – reportedly at Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh
Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh (born Prince Philip of Greece and Denmark, later Philip Mountbatten; 10 June 19219 April 2021), was the husband of Queen Elizabeth II. As such, he was the consort of the British monarch from h ...
's insistence. Queen Charlotte's Ball ceased to function in 1976, but has been relaunched since, by former debutante Jennie Hallam-Peel, without the monarch's involvement, and with more limited uptake; debutantes instead curtsy
A curtsy (also spelled curtsey or incorrectly as courtsey) is a traditional gendered gesture of greeting, in which a girl or woman bends her knees while bowing her head. In Western culture it is the feminine equivalent of bowing by males, altho ...
to "Queen Charlotte's Birthday Cake".
The traditional Season went into decline after the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, when many aristocratic families gave up their London townhouses. From then on, more society events took place at public venues, making it harder to maintain social exclusivity. The opulent coming-out party held for the 17 year-old Lady Sarah Consuelo Spencer-Churchill on 7 July 1939 at Blenheim Palace
Blenheim Palace ( ) is a country house in Woodstock, Oxfordshire, England. It is the seat of the Dukes of Marlborough. Originally called Blenheim Castle, it has been known as Blenheim Palace since the 19th century. One of England's larg ...
in Oxfordshire, less than two months before World War Two
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies and the Axis powers. Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilisi ...
was declared, has been styled by some as "the last season ever". Socialite Henry (Chips) Channon noted in his diary: "I have seen much, travelled far and am accustomed to splendour, but there has never been anything like tonight".
Many events that take place far from central London
Central London is the innermost part of London, in England, spanning the City of London and several boroughs. Over time, a number of definitions have been used to define the scope of Central London for statistics, urban planning and local gove ...
(though generally within the Home Counties) came to be regarded as part of the social season, including Royal Ascot
Ascot Racecourse is a dual-purpose British racecourse, located in Ascot, Berkshire, England, about 25 miles west of London. Ascot is used for thoroughbred horse racing, and it hosts 13 of Britain's 36 annual Flat Group 1 races and three Gra ...
and the Henley Royal Regatta
Henley Royal Regatta (or Henley Regatta, its original name pre-dating Royal patronage) is a Rowing (sport), rowing event held annually on the River Thames by the town of Henley-on-Thames, England. It was established on 26 March 1839. It diffe ...
. The events that now constitute the London social season are increasingly hosted or sponsored by large companies (i.e. "corporate hospitality"). Western dress codes
Western dress codes are a set of dress codes detailing what clothes are worn for what occasion that originated in Western Europe and the United States in the 19th century. Conversely, since most cultures have intuitively applied some level equ ...
still apply to certain events in the season, especially those in which the King maintains an official role.
According to ''The Sloaney'' magazine's online guide "Sloaney Season", it starts with Cheltenham Festival
The Cheltenham Festival is a horse racing-based meeting in the National Hunt racing calendar in the United Kingdom, with race prize money second only to the Grand National. The four-day festival takes place annually in March at Cheltenham Race ...
(March), and includes the Grand National
The Grand National is a National Hunt horse race held annually at Aintree Racecourse in Aintree, Merseyside, England. First run in 1839, it ...
(April), The Boat Race
The Boat Race is an annual set of rowing races between the Cambridge University Boat Club and the Oxford University Boat Club, traditionally rowed between open-weight eights on the River Thames in London, England. It is also known as the U ...
(April), Badminton Horse Trials
The Badminton Horse Trials is a five-day event, one of only seven annual Concours Complet International (CCI) Five Star events as classified by the Fédération Équestre Internationale (FEI). It takes place in May each year in the park of ...
(May), Chelsea Flower Show
The RHS Chelsea Flower Show, formally known as the Great Spring Show,Phil Clayton, ''The Great Temple Show'' in ''The Garden'' 2008, p.452, The Royal Horticultural Society is a garden show held for five days in May by the Royal Horticultural So ...
(May), Epsom Derby
The Derby Stakes, more commonly known as the Derby and sometimes referred to as the Epsom Derby, is a Group races, Group 1 flat Horse racing, horse race in England open to three-year-old Colt (horse), colts and Filly, fillies. It is run at Ep ...
(June), Royal Ascot
Ascot Racecourse is a dual-purpose British racecourse, located in Ascot, Berkshire, England, about 25 miles west of London. Ascot is used for thoroughbred horse racing, and it hosts 13 of Britain's 36 annual Flat Group 1 races and three Gra ...
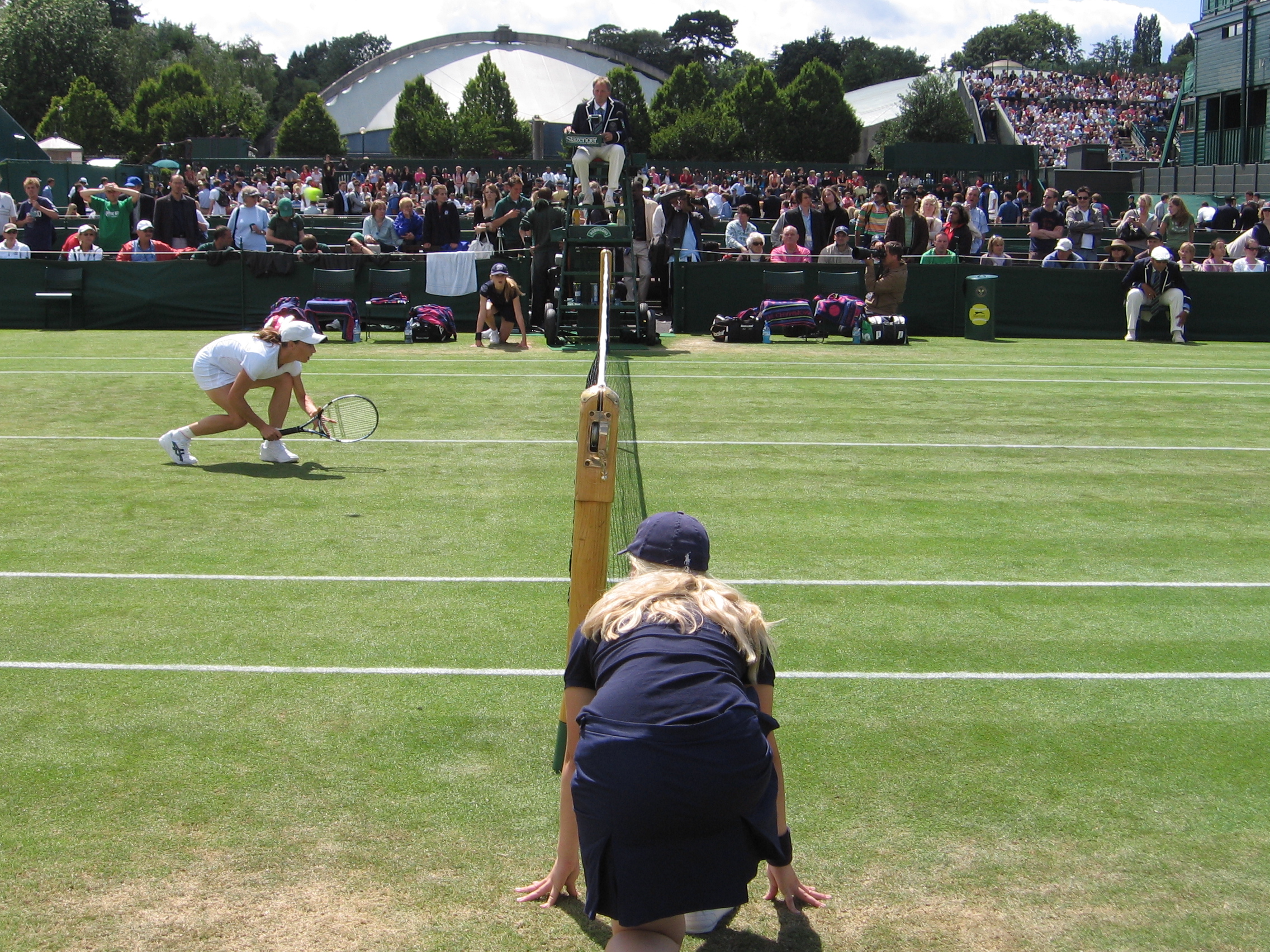
(June), Test matches at Lord's (July), Wimbledon
Wimbledon most often refers to:
* Wimbledon, London, a district of southwest London
* Wimbledon Championships, the oldest tennis tournament in the world and one of the four Grand Slam championships
Wimbledon may also refer to:
Places London
* W ...
(July), Henley Royal Regatta
Henley Royal Regatta (or Henley Regatta, its original name pre-dating Royal patronage) is a Rowing (sport), rowing event held annually on the River Thames by the town of Henley-on-Thames, England. It was established on 26 March 1839. It diffe ...
(July), Edinburgh International Festival
The Edinburgh International Festival is an annual arts festival in Edinburgh, Scotland, spread over the final three weeks in August. Notable figures from the international world of music (especially european classical music, classical music) and ...
(August) and others, ending with Goodwood Revival
The Goodwood Revival is a three-day festival held each September at Goodwood Circuit since 1998 for the types of road racing, racing cars and motorcycles that would have competed during the circuit's original period—1948–1966.
History
The ...
(September).
Arts
*Glyndebourne Opera Festival
Glyndebourne Festival Opera is an annual opera festival held at Glyndebourne, an English country house near Lewes, in East Sussex, England.
History
Under the supervision of the Christie family, the festival has been held annually since 1934, e ...
* The Proms
The BBC Proms is an eight-week summer season of daily orchestral classical music concerts and other events held annually, predominantly in the Royal Albert Hall in central London. Robert Newman founded The Proms in 1895. Since 1927, the ...
* Royal Academy Summer Exhibition
The Summer Exhibition is an open art exhibition held annually by the Royal Academy in Burlington House, Piccadilly in central London, England, during the months of June, July, and August. The exhibition includes paintings, prints, drawings, sc ...
* West End theatre
West End theatre is mainstream professional theatre staged in the large theatres in and near the West End of London.Christopher Innes"West End"in ''The Cambridge Guide to Theatre'' (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1998), pp. 1194–1195, ...
Horticulture
*Chelsea Flower Show
The RHS Chelsea Flower Show, formally known as the Great Spring Show,Phil Clayton, ''The Great Temple Show'' in ''The Garden'' 2008, p.452, The Royal Horticultural Society is a garden show held for five days in May by the Royal Horticultural So ...
Equestrianism
*Royal Ascot
Ascot Racecourse is a dual-purpose British racecourse, located in Ascot, Berkshire, England, about 25 miles west of London. Ascot is used for thoroughbred horse racing, and it hosts 13 of Britain's 36 annual Flat Group 1 races and three Gra ...
* Cheltenham Gold Cup
The Cheltenham Gold Cup is a Grade 1 National Hunt horse race run on the New Course at Cheltenham Racecourse in England, over a distance of about 3 miles 2½ furlon ...
* Badminton Horse Trials
The Badminton Horse Trials is a five-day event, one of only seven annual Concours Complet International (CCI) Five Star events as classified by the Fédération Équestre Internationale (FEI). It takes place in May each year in the park of ...
* Grand National
The Grand National is a National Hunt horse race held annually at Aintree Racecourse in Aintree, Merseyside, England. First run in 1839, it ...
* Royal Windsor Horse Show
* Epsom Derby
The Derby Stakes, more commonly known as the Derby and sometimes referred to as the Epsom Derby, is a Group races, Group 1 flat Horse racing, horse race in England open to three-year-old Colt (horse), colts and Filly, fillies. It is run at Ep ...
* Glorious Goodwood
Goodwood Racecourse is a horse-racing track five miles north of Chichester, West Sussex, in England controlled by the family of the Duke of Richmond, whose seat is nearby Goodwood House. It hosts the annual Glorious Goodwood meeting in late ...
* Cartier Queen's Cup
The Cartier Queen's Cup is a 22-goal polo tournament at the Guards Polo Club in England. Named after Queen Elizabeth II, it is held annually in May–June. According to '' Country Life'', it is the "jewel in the polo calendar" and it "encapsulates ...
The Crown
*Trooping the Colour
Trooping the Colour is a ceremonial event performed every year on Horse Guards Parade in London, United Kingdom, by regiments of Household Division, to celebrate the King's Official Birthday, official birthday of the British sovereign, though t ...
* Garter Service of the Order of the Garter
The Most Noble Order of the Garter is an order of chivalry founded by Edward III of England in 1348. The most senior order of knighthood in the Orders, decorations, and medals of the United Kingdom, British honours system, it is outranked in ...
* Royal Edinburgh Military Tattoo
The Royal Edinburgh Military Tattoo is an annual series of military tattoos performed by British Armed Forces, Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth and international military bands, and artistic performance teams on the Esplanade of Edinburgh Ca ...
Sport
*Boat Race
The Boat Race is an annual set of rowing races between the Cambridge University Boat Club and the Oxford University Boat Club, traditionally rowed between open-weight eights on the River Thames in London, England. It is also known as the Uni ...
* Henley Royal Regatta
Henley Royal Regatta (or Henley Regatta, its original name pre-dating Royal patronage) is a Rowing (sport), rowing event held annually on the River Thames by the town of Henley-on-Thames, England. It was established on 26 March 1839. It diffe ...
* Guards Polo Club
The Guards Polo Club is an English polo club in Windsor, Berkshire. It is closely associated with the British royal family. Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh was president of the club from its formation on 25 January 1955 until Death and funeral ...
* The Championships, Wimbledon
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The ...
* Cowes Week
Cowes Week ( ) is one of the longest-running regular regattas in the world. With 40 daily sailing races, around 500 boats, and 2500 competitors ranging from Olympic and world-class professionals to weekend sailors, it is the largest sailing ...
* Imperial Meeting
* Lord's
Lord's Cricket Ground, commonly known as Lord's, is a cricket List of Test cricket grounds, venue in St John's Wood, Westminster. Named after its founder, Thomas Lord, it is owned by Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC) and is the home of Middlesex C ...
Test cricket
Test cricket is a Forms of cricket, format of the sport of cricket, considered the game’s most prestigious and traditional form. Often referred to as the "ultimate test" of a cricketer's skill, endurance, and temperament, it is a format of i ...
match
Although several of these events are not actually held in London, such as the Hurlingham Polo Association at Guards Polo Club
The Guards Polo Club is an English polo club in Windsor, Berkshire. It is closely associated with the British royal family. Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh was president of the club from its formation on 25 January 1955 until Death and funeral ...
, the organisers of most events attempt to avoid date clashes, so it is generally possible to visit all of them in the same year.
The traditional end of the London Season is the Glorious Twelfth
The Glorious Twelfth is the twelfth day of August, signifying the start of the Driven grouse shooting, shooting season for red grouse (''Lagopus lagopus scotica'') in United Kingdom, Great Britain and Northern Ireland, with the Rock ptarmigan, p ...
of August, which marks the beginning of the shooting
Shooting is the act or process of discharging a projectile from a ranged weapon (such as a gun, bow, crossbow, slingshot, or blowpipe). Even the acts of launching flame, artillery, darts, harpoons, grenades, rockets, and guided missile ...
season. Society would retire to the country to shoot birds during the autumn and hunt foxes during the winter before coming back to London again with the spring. For some time there was also the "Harrogate
Harrogate ( ) is a spa town and civil parish in the North Yorkshire District, district and North Yorkshire, county of North Yorkshire, England. Historic counties of England, Historically in the West Riding of Yorkshire, the town is a tourist de ...
Season", where members of the upper classes would stop at Harrogate Spa to take in the waters on their way from London up to their shooting estates in the north.
Dress codes
Many events of the season have traditional expectations with regard toWestern dress codes
Western dress codes are a set of dress codes detailing what clothes are worn for what occasion that originated in Western Europe and the United States in the 19th century. Conversely, since most cultures have intuitively applied some level equ ...
.
* At Royal Ascot
Ascot Racecourse is a dual-purpose British racecourse, located in Ascot, Berkshire, England, about 25 miles west of London. Ascot is used for thoroughbred horse racing, and it hosts 13 of Britain's 36 annual Flat Group 1 races and three Gra ...
, for example, hats are compulsory in most enclosures, and to be admitted to the Royal Enclosure for the first time one must either be a guest of a member or be sponsored for membership by two members who have attended for at least six years as a member. This continues to maintain a socially exclusive character for the Royal Enclosure. Gentlemen are required to wear either black or grey morning dress
Morning dress, also known as formal day dress, is the Formal attire, formal Western dress code for day wear (disambiguation), day attire, consisting chiefly of a morning coat, waistcoat, and formal trousers for men, and an appropriate gown for ...
with waistcoat
A waistcoat ( UK and Commonwealth, or ; colloquially called a weskit) or vest ( US and Canada) is a sleeveless upper-body garment. It is usually worn over a dress shirt and necktie and below a coat as a part of most men's formal wea ...
and a top hat
A top hat (also called a high hat, or, informally, a topper) is a tall, flat-crowned hat traditionally associated with formal wear in Western dress codes, meaning white tie, morning dress, or frock coat. Traditionally made of black silk or ...
. A gentleman must remove his top hat within a restaurant, a private box, a private club or that facility's terrace, balcony or garden. Hats may also be removed within any enclosed external seating area within the Royal Enclosure Garden. Ladies must not show bare midriffs or shoulders and must wear hats. In the Queen Anne Enclosure (formerly known as the Grandstand), gentlemen are required to wear lounge suit
A suit, also called a lounge suit, business suit, dress suit, or formal suit, is a set of clothes comprising a suit jacket and trousers of identical textiles generally worn with a collared dress shirt, necktie, and dress shoes. A skirt suit ...
s with ties TIES may refer to:
* TIES, Teacher Institute for Evolutionary Science
* TIES, The Interactive Encyclopedia System
* TIES, Time Independent Escape Sequence
* Theoretical Issues in Ergonomics Science
* The International Ecotourism Society
{{disambig ...
and ladies must wear a hat.
* At Henley Royal Regatta
Henley Royal Regatta (or Henley Regatta, its original name pre-dating Royal patronage) is a Rowing (sport), rowing event held annually on the River Thames by the town of Henley-on-Thames, England. It was established on 26 March 1839. It diffe ...
, in the Stewards' Enclosure
Henley Royal Regatta (or Henley Regatta, its original name pre-dating Royal patronage) is a Rowing (sport), rowing event held annually on the River Thames by the town of Henley-on-Thames, England. It was established on 26 March 1839. It diffe ...
gentlemen must wear a lounge jacket
A suit jacket, also called a lounge jacket, dress jacket, lounge coat or suit coat, is a jacket in classic menswear that is part of a suit.
History
The jacket was originally a work jacket that came into fashion due to the French Revolution. It ...
and tie. Rowing club colours on a blazer or cap are encouraged, as is the wearing of boater
__NOTOC__
A boater (also straw boater, basher, skimmer, The English Panama, cady, katie, canotier, somer, or sennit hat) is a semi-formal summer hat for men, which was popularised in the late 19th century and early 20th century.
It is normall ...
s. A lady's skirt hem must reach below the knee and is checked before entry by the Stewards' Officers. Both ladies and gentlemen will be turned away if they fail to comply with the dress code, regardless of their prestige in rowing or elsewhere. Hats are encouraged but not required for ladies. When a student protested being denied entry to the Stewards' Enclosure for failing to meet the dress code, saying she had worn the dress "in the Royal Enclosure at Ascot and nobody said anything", a spokesman defended the dress code, saying "The intention is to maintain the atmosphere of an English Garden party of the Edwardian period
In the United Kingdom, the Edwardian era was a period in the early 20th century that spanned the reign of King Edward VII from 1901 to 1910. It is commonly extended to the start of the First World War in 1914, during the early reign of King Ge ...
by wearing a more traditional dress." Members must display their enamel badge
A badge is a device or accessory, often containing the insignia of an organization, which is presented or displayed to indicate some feat of service, a special accomplishment, a symbol of authority granted by taking an oath (e.g., police and fir ...
s at all times.
* At polo
Polo is a stick and ball game that is played on horseback as a traditional field sport. It is one of the world's oldest known team sports, having been adopted in the Western world from the game of Chovgan (), which originated in ancient ...
matches, it is usual for gentlemen to wear a blazer
A blazer is a jacket worn as part of a smart casual or business casual look.
Similar to a sport jacket, a blazer is not part of a formal suit, and the terms "sport coat" and "blazer" may be used interchangeably in daily life.
A nautical bl ...
and always white trousers. Ladies should wear flat shoes, as the tradition of "treading in the divots" (pressing back into place the clods of turf thrown up by the horses' hooves) precludes wearing heels. The famous Club House at Guards Polo Club
The Guards Polo Club is an English polo club in Windsor, Berkshire. It is closely associated with the British royal family. Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh was president of the club from its formation on 25 January 1955 until Death and funeral ...
in Windsor Great Park
Windsor Great Park is a Royal Park of to the south of the town of Windsor, Berkshire, Windsor on the border of Berkshire and Surrey in England. It is adjacent to the private Home Park, Windsor, Home Park, which is nearer the castle. The park ...
is for the use of club members only, who wear individually made gold and enamel badges. Members' guests are given special gold-embossed tags.
Scottish social season
Following the London season, most of the high society participants would travel to theScottish Highlands
The Highlands (; , ) is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Scottish Lowlands, Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Scots language, Lowland Scots language replaced Scottish Gae ...
for the Scottish season, which would last around ten weeks. There, they would rent hunting grounds from Scottish lords in genteel poverty
Genteel poverty is a state of poverty marked by one's connection or affectation towards a higher ("wiktionary:genteel, genteel") social class. Those in genteel poverty are often people, possibly Imperial, royal and noble ranks, titled, who have fa ...
to hunt. They would also host parties at country estates which involved partridge
A partridge is a medium-sized Galliformes, galliform bird in any of several genera, with a wide Indigenous (ecology), native distribution throughout parts of Europe, Asia and Africa. Several species have been introduced to the Americas. They ar ...
shooting and hunting. The climax was the Hunt Ball, a semi-private event with attendees consisting both of invitees from high society and ticket purchasers. The Scottish season was more relaxed than the London one due to the Highlands tradition of hospitality to all.
Irish social season
The Irish Social Season was a period of aristocratic entertainment and social functions that stretched from January toSt. Patrick's Day
Saint Patrick's Day, or the Feast of Saint Patrick (), is a religious and cultural holiday held on 17 March, the traditional death date of Saint Patrick (), the foremost patron saint of Ireland.
Saint Patrick's Day was made an official Chri ...
of a given year. During this period, the major and minor nobility left their country residences and lived in Georgian mansions in places like Rutland Square (now Parnell Square), Mountjoy Square
Mountjoy Square () is a garden square in Dublin, Ireland, on the Northside of the city just under a kilometre from the River Liffey. One of five Georgian squares in Dublin, it was planned and developed in the late 18th century by Luke Gardine ...
, Merrion Square
Merrion Square () is a Georgian architecture, Georgian garden square on the Southside Dublin, southside of Dublin city centre.
History
The square was laid out in 1762 to a plan by John Smyth and Jonathan Barker for the estate of Richard Fitz ...
and Fitzwilliam Square
Fitzwilliam Square () is a Georgian garden square in the south of central Dublin, Ireland. It was the last of the five Georgian squares in Dublin to be built, and is the smallest.
The middle of the square is composed of a private park, which f ...
in Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
. Those with less financial means lived in (or in some cases rented) smaller properties in streets nearby.
The focal point of the Social Season was the move of the Lord Lieutenant of Ireland
Lord Lieutenant of Ireland (), or more formally Lieutenant General and General Governor of Ireland, was the title of the chief governor of Ireland from the Williamite Wars of 1690 until the Partition of Ireland in 1922. This spanned the K ...
(the King's representative) from his 'out of season' residence, the Viceregal Lodge (now Áras an Uachtaráin, the residence of the President of Ireland
The president of Ireland () is the head of state of Republic of Ireland, Ireland and the supreme commander of the Defence Forces (Ireland), Irish Defence Forces. The presidency is a predominantly figurehead, ceremonial institution, serving as ...
) to live in state in the Viceregal Apartments in Dublin Castle
Dublin Castle () is a major Government of Ireland, Irish government complex, conference centre, and tourist attraction. It is located off Dame Street in central Dublin.
It is a former motte-and-bailey castle and was chosen for its position at ...
, where he and his wife hosted a series of levées, drawing rooms, banquets and balls in the Castle.
The period of the social season also coincided with the parliamentary sessions of the Irish House of Lords, which many of the peers in Dublin would be attending. However, the Irish Parliament was abolished with the Act of Union, which merged the Kingdoms of Great Britain and Ireland in 1801.
With the abolition of the lord lieutenancy in 1922, the emergence of a new nationalist state (the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State (6 December 192229 December 1937), also known by its Irish-language, Irish name ( , ), was a State (polity), state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-ye ...
) the same year, and the economic and social downturn that resulted from World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, the Social Season dwindled and then died. Most of the aristocratic homes in Merrion Square and Fitzwilliam Square were sold and are now used as corporate offices.
Among the Irish peers who would reside in Dublin during the 'Social Season' were
*The Duke of Leinster ''(Ireland's senior peer)''
*The Marquess of Slane
*The Duke of Ormonde
*Viscount Powerscourt
*The Earl of Fingall
*The Earl of Headfort
Other British colonies
In British territories, high society and the social season revolved around theGovernment House
Government House is the name of many of the official residences of governors-general, governors and lieutenant-governors in the Commonwealth and British Overseas Territories. The name is also used in some other countries.
Government Houses in th ...
, with an invitation to an event there often being no less exclusive than one to a court ball in London.
In British Australia and British New Zealand, there existed a high society. However, the high society's membership was very fluid and its members were way less formal in etiquette.
In British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
, the cold season, from October to April, involved the presentation of the "fishing fleet" (debutantes), peaked at Christmas and concluded with the Viceroy's Ball in April. During the hot season, which lasted until October, female members would relocate to the hills to escape the heat, leaving their men to work. Membership in high society was synonymous with membership in the exclusive local club almost every English settlement had.
In British Shanghai and British Hong Kong
Hong Kong was under British Empire, British rule from 1841 to 1997, except for a Japanese occupation of Hong Kong, brief period of Japanese occupation during World War II from 1941 to 1945. It was a crown colony of the United Kingdom from 1841 ...
, high society was less formal than India though more formal than Australia and New Zealand. In Hong Kong, high society would build houses on the Peak, which they would live in during the summer to combat the heat, although frequent mist made the situation little better. In Shanghai, the hot season was brutal while the cold season's weather was good. It was considered more luxurious and cosmopolitan than Hong Kong, and some described it as a rival to the best cities in Europe.
In British Egypt
The history of Egypt under the British lasted from 1882, when it was occupied by British forces during the Anglo-Egyptian War, until 18 June 1956, when the last British forces withdrew in accordance with the Anglo-Egyptian evacuation agreem ...
, there was a social season in Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
during the colder months, November to April. Cairo was described as "a sort of Oriental Paris or sub-tropic London — with here and there pronounced suggestions of Atlantic City, Newport, and Longacre imes
IMes is an abbreviation for an organic compound that is a common ligand in organometallic chemistry. It is an ''N''-heterocyclic carbene (NHC). The compound, a white solid, is often not isolated but instead is generated upon attachment to the me ...
Square" per Burton Holmes
Elias Burton Holmes (January 8, 1870 – July 22, 1958) was an American traveler, photographer and filmmaker credited with the invention of the " travelogue", though the term itself was apparently coined in 1898 by John Bowker. Travel stories, ...
. The main hotel was Shepherd's, and activities including visiting the pyramid
A pyramid () is a structure whose visible surfaces are triangular in broad outline and converge toward the top, making the appearance roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be of any polygon shape, such as trian ...
s, sailing in the Nile River
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the longest river i ...
, sporting events, gymkhanas, concerts, balls, and visiting the Khedive
Khedive ( ; ; ) was an honorific title of Classical Persian origin used for the sultans and grand viziers of the Ottoman Empire, but most famously for the Khedive of Egypt, viceroy of Egypt from 1805 to 1914.Adam Mestyan"Khedive" ''Encyclopaedi ...
of Egypt's court.
American social season
During theGilded Age
In History of the United States, United States history, the Gilded Age is the period from about the late 1870s to the late 1890s, which occurred between the Reconstruction era and the Progressive Era. It was named by 1920s historians after Mar ...
, the American social season was divided in two. One portion occurred in New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
during the winter, and one occurred in Newport, Rhode Island
Newport is a seaside city on Aquidneck Island in Rhode Island, United States. It is located in Narragansett Bay, approximately southeast of Providence, Rhode Island, Providence, south of Fall River, Massachusetts, south of Boston, and nort ...
during the summer.
New York season
The New York season lasted from mid-November until the start ofLent
Lent (, 'Fortieth') is the solemn Christianity, Christian religious moveable feast#Lent, observance in the liturgical year in preparation for Easter. It echoes the 40 days Jesus spent fasting in the desert and enduring Temptation of Christ, t ...
. It opened with the start of the opera season at the Academy of Music and later the Metropolitan Opera House. The boxes were zealously guarded by the elite and were typically obtained through inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, titles, debts, entitlements, privileges, rights, and obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ among societies and have changed over time. Offi ...
. Attending the opera at the grand opening and on Friday nights thereafter was the staple of the season. Caroline Astor would be treated like royalty by season participants. She would typically leave after the first act and leaving before her would be improper.
Other major events included the National Horse Show
The National Horse Show is the oldest continually held horse show in the United States. It was founded in 1883 in New York and held there until 2002, when it moved to Florida and then to Kentucky.
The National Horse Show offers competition for hu ...
in November, presentation of debutantes
A debutante, also spelled débutante ( ; from , ), or deb is a young woman of aristocratic or upper-class family background who has reached maturity and is presented to society at a formal "debut" ( , ; ) or possibly debutante ball. Original ...
at the Patriarchs' Ball in December and Mrs. Astor's annual ball in January. Throughout the winter there was an abundance of parties
A party is a gathering of people who have been invited by a host for the purposes of socializing, conversation, recreation, or as part of a festival or other commemoration or celebration of a special occasion. A party will often feature ...
, including balls, reception
Reception is a noun form of ''receiving'', or ''to receive'' something, such as art, experience, information, people, products, or vehicles. It may refer to:
Astrology
* Reception (astrology), when a planet is located in a sign ruled by another p ...
s, and dinner parties
A party is a gathering of people who have been invited by a Hospitality, host for the purposes of socializing, conversation, recreation, or as part of a festival or other commemoration or celebration of a special occasion. A party will oft ...
. The season closed with the February Charity Ball and Lent was occupied with less glamorous events and preparation for the Newport season.
Newport season
Newport was the location of the summer season due to its exclusivity. The town was initially aresort town
A resort town, resort city or resort destination is an urban area where tourism or vacationing is the primary component of the local culture and economy. A typical resort town has one or more actual resorts in the surrounding area. Sometimes ...
that attracted planters
Planters Nut & Chocolate Company is an American snack food company now owned by Hormel Foods. Planters is best known for its processed nuts and for the Mr. Peanut icon that symbolizes them. Mr. Peanut was created by grade schooler Antonio Gent ...
before the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of A ...
. However, it quickly transformed into a retreat for the New York City elite, because they acquired the land, demolished old structures and erected great mansions
A mansion is a large dwelling house. The word itself derives through Old French from the Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... from the Latin w ...
in their place. The lack of hotels and the exorbitant fees for the beach changing room kept the masses out. Because Newport was so exclusive, it was considered the place to test whether someone was accepted by the Four Hundred
400 (four hundred) is the natural number following 399 and preceding 401.
Mathematical properties
A circle is divided into 400 grads.
Integers from 401 to 499
400s
401
401 is a prime number, tetranacci number, Chen prime, prime index p ...
. Potter Palmer
Potter Palmer (May 20, 1826 – May 4, 1902) was an American businessman who was responsible for much of the development of State Street (Chicago), State Street in Chicago. Born in Albany County, New York,Bertha Palmer, who earned their new money from dry goods, initially failed this test.
The London Season by Michelle Jean Hoppe
Late Victorian/Edwardian London Season
Gilded Age New York social season
{{History of Dublin Cultural history of the United Kingdom Culture of the United Kingdom Debutantes European court festivities High society (social class) Regency London Seasons in the United Kingdom, Society Social history of the United Kingdom Social history of Ireland Culture of Ireland Seasons
Decline
In the 1890s, the society dispersed into small cliques and each clique gathered at a different location in theAmerican Northeast
The Northeastern United States (also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast) is census regions United States Census BureauLocated on the Atlantic coast of North America, the region borders Canada to its nort ...
for a lesser summer season. These events were less exclusive and the high society houses rarely rivaled the ones at Newport. During the decline, the "autumn season" emerged with participants engaging in outdoor activities such as hunting
Hunting is the Human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, and killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to obtain the animal's body for meat and useful animal products (fur/hide (sk ...
, riding, and indoor activities such as card games and amateur theater
Theatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actors to present experiences of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a stage. The performers may communi ...
. Some "winter seasons" involved winter sports, such as skiing
Skiing is the use of skis to glide on snow for basic transport, a recreational activity, or a competitive winter sport. Many types of competitive skiing events are recognized by the International Olympic Committee (IOC), and the International S ...
, tobogganing
A toboggan is a simple sled used in snowy winter recreation. It is also a traditional form of cargo transport used by the Innu, Cree and Ojibwe of North America, sometimes part of a dog train.
It is used on snow to carry one or more people ( ...
, and sledding
Sledding, sledging or sleighing is a winter sport typically carried out in a prone or seated position on a vehicle generically known as a sled (North American), a sledge (British), or a sleigh. It is the basis of three Olympic sports: luge, Skel ...
, most notably the one at the Lake Placid Club
The Lake Placid Club was a social and recreation club active from 1895 to 1980. Founded in a hotel on Mirror Lake in Lake Placid, New York, under Melvil Dewey's leadership and according to his ideals, it was instrumental in Lake Placid's develop ...
. Others involved escaping the snow to Palm Beach and Daytona Beach
Daytona Beach is a coastal resort city in Volusia County, Florida, United States. Located on the East Coast of the United States, its population was 72,647 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Deltona–Daytona Beach–Ormond Beach metropo ...
.
By the turn of the 20th century, members of the Four Hundred de-emphasized their native "social seasons" and typically mingled with European elites in Europe for the summer in European seasons, such as the London and Paris seasons.
Washington season
There was a social season inWashington, DC
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and Federal district of the United States, federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from ...
in the late 18th century and 19th century. The Congressional Season began in December, or earlier if Congress began its session earlier, and ended in June when prominent members would take their summer vacations. The Official or Fashionable Season began on New Year's Day
In the Gregorian calendar, New Year's Day is the first day of the calendar year, January 1, 1 January. Most solar calendars, such as the Gregorian and Julian calendars, begin the year regularly at or near the December solstice, northern winter ...
with general receptions at the Executive Mansion and by the Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filin ...
ministers and ended at the beginning of Lent. The Congressional Season is when entertainments and amusements peaked.
There were two types of receptions. Afternoon receptions were open to any reputable person dressed for the occasion while evening receptions typically required an invitation. Due to the transient nature of the city stemming from most of its elite being elected and appointed officials, many new money figures were able to establish themselves into high society there, such as Mary Leiter
Mary Victoria Curzon, Baroness Curzon of Kedleston, (née Leiter; 27 May 1870 – 18 July 1906), was an American heiress who married George Curzon, the future Viceroy of India.
In America
Mary Victoria Leiter was born in Chicago, the eldest ...
and Evalyn Walsh McLean
Evalyn McLean ( Walsh; August 1, 1886 – April 26, 1947) was an American mining heiress and socialite, famous for reputedly being an owner of the Hope Diamond (which was bought in 1911 for US$180,000 from Pierre Cartier), as well as another f ...
.
French social season
The high society of France in the 19th century was called ''le gratin'' (upper crust) and consisted of those with old money, especially througharistocratic
Aristocracy (; ) is a form of government that places power in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocrats.
Across Europe, the aristocracy exercised immense economic, political, and social influence. In Western Christian co ...
lineage and new money, consisting of wealthy industrialists, well-bred members of the Bourse and a few titled Jewish families, such as the Rothschilds
The Rothschild family ( , ) is a wealthy Ashkenazi Jews, Ashkenazi Jewish noble banking family originally from Frankfurt. The family's documented history starts in 16th-century Frankfurt; its name is derived from the family house, Rothschild, ...
. The little season lasted from December to Easter
Easter, also called Pascha ( Aramaic: פַּסְחָא , ''paskha''; Greek: πάσχα, ''páskha'') or Resurrection Sunday, is a Christian festival and cultural holiday commemorating the resurrection of Jesus from the dead, described in t ...
and consisted of ''bal blancs'' (debutante balls), dinners, musical concerts, horse races, and the opera.
The ''Grande Saison'' (Grand Season), that lasted from mid-April to June, would open with the ''Concourse Hippiques'', a horse show held in the ''Palais d’Industrie'' on the Champs-Élysées
The Avenue des Champs-Élysées (, ; ) is an Avenue (landscape), avenue in the 8th arrondissement of Paris, France, long and wide, running between the Place de la Concorde in the east and the Place Charles de Gaulle in the west, where the Arc ...
. At the beginning of May, the Paris Salon would open, where patrons would check out artists' sculptures, paintings and decorative art. The Grand Season would conclude with the French Grand Prix
The French Grand Prix (), formerly known as the Grand Prix de l'ACF (Automobile Club de France), is an auto race held as part of the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile's annual Formula One World Championship. It is one of the oldest ...
, which had a large attendance. Fashion was paramount throughout the season, with ladies and mannequins displaying the latest fashions. After the Grand Prix, French high society would close their Paris homes and locate to the country for the summer and fall.
In popular culture
* A London season features inJane Austen
Jane Austen ( ; 16 December 1775 – 18 July 1817) was an English novelist known primarily for #List of works, her six novels, which implicitly interpret, critique, and comment on the English landed gentry at the end of the 18th century ...
's ''Sense and Sensibility
''Sense and Sensibility'' ( working title; ''Elinor and Marianne'') is the first novel by the English author Jane Austen, published in 1811. It was published anonymously: ''By A Lady'' appears on the title page where the author's name might h ...
'' and is often a key plot device in Regency romance
Regency romances are a subgenre of romance novels set during the period of the British Regency (1811–1820) or early 19th century. Rather than simply being versions of contemporary romance stories transported to a historical setting, Regency r ...
novels.
* The 1927 novel '' Lucia in London'' by E. F. Benson
Edward Frederic Benson (24 July 1867 – 29 February 1940) was an English novelist, biographer, memoirist, historian and short story writer.
Early life
E. F. Benson was born at Wellington College (Berkshire), Wellington College in Berkshire, ...
is set during the London season in the 1920s.
* The 1938 novel ''Death in a White Tie
Death is the end of life; the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain a living organism. Death eventually and inevitably occurs in all organisms. The remains of a former organism normally begin to decompose shor ...
'' by Ngaio Marsh
Dame Edith Ngaio Marsh ( ; 23 April 1895 – 18 February 1982) was a New Zealand mystery writer, writer.
As a crime writer during the "Golden Age of Detective Fiction", Marsh is known as one of the Detective fiction#Golden Age detective novel ...
is set during the London season.
* Eliza Doolittle
Eliza Doolittle is a fictional character and the protagonist in George Bernard Shaw's play '' Pygmalion'' (1913) and its 1956 musical adaptation, ''My Fair Lady''.
Eliza (from Lisson Grove, London) is a Cockney flower seller, who comes to Prof ...
's first public tryout and debut into high society in ''My Fair Lady
''My Fair Lady'' is a musical theatre, musical with a book and lyrics by Alan Jay Lerner and music by Frederick Loewe. The story, based on George Bernard Shaw's 1913 play ''Pygmalion (play), Pygmalion'' and on the Pygmalion (1938 film), 1938 film ...
'', the musical film version of George Bernard Shaw
George Bernard Shaw (26 July 1856 – 2 November 1950), known at his insistence as Bernard Shaw, was an Irish playwright, critic, polemicist and political activist. His influence on Western theatre, culture and politics extended from the 188 ...
's play Pygmalion, uses the idea of Ascot Racecourse
Ascot Racecourse is a dual-purpose British racecourse, located in Ascot, Berkshire, England, about 25 miles west of London. Ascot is used for thoroughbred horse racing, and it hosts 13 of Britain's 36 annual Flat Group 1 races and three Grade ...
as a setting.
* The novel ''The Leopard
''The Leopard'' ( ) is a novel by Italian writer Giuseppe Tomasi di Lampedusa, which chronicles the changes in Sicilian life and society during the ''Risorgimento''. Published posthumously in 1958 by Feltrinelli, after two rejections by the ...
'' by Giuseppe Tomasi di Lampedusa
Giuseppe Tomasi, 11th Prince of Lampedusa, 12th Duke of Palma, GE (23 December 1896 – 23 July 1957), known as Giuseppe Tomasi di Lampedusa (), was a Sicilian writer, nobleman, and Prince of Lampedusa. He is most famous for his only novel, '' ...
, and the 1963 film of the same name by Luchino Visconti
Luchino Visconti di Modrone, Count of Lonate Pozzolo (; 2 November 1906 – 17 March 1976) was an Italian filmmaker, theatre and opera director, and screenwriter. He was one of the fathers of Italian neorealism, cinematic neorealism, but later ...
, portray the Palermitan season during the Risorgimento
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the annexation of various states of the Italian peninsula and its outlying isles to the Kingdom of ...
.
* The events of Julian Fellowes
Julian Alexander Kitchener-Fellowes, Baron Fellowes of West Stafford (born 17 August 1949), known professionally as Julian Fellowes, is an English actor, novelist, writer, producer, film director, and Conservative peer. He has received nume ...
's novel ''Past Imperfect'' take place during the 1968 season in London.
* In the 2003 film '' What a Girl Wants'', Lord Henry Dashwood invites his new-found daughter Daphne to attend the London Season.
* The 2009 young-adult novel ''The Season'' by Sarah MacLean
Sarah MacLean (born December 23, 1978) is a ''New York Times'' bestselling American author of young adult novels and romance novels. Her first adult romance novel, ''Nine Rules to Break When Romancing a Rake'' debuted on the New York Times Best ...
portrays a young woman entering her first London Season.
* Vincente Minnelli
Vincente Minnelli (; born Lester Anthony Minnelli; February 28, 1903 – July 25, 1986) was an American Theatre director, stage director and film director. From a career spanning over half a century, he is best known for his sophisticated innovat ...
's '' The Reluctant Debutante''
* In the British period drama ''Downton Abbey
''Downton Abbey'' is a British historical drama television series set in the early 20th century, created and co-written by Julian Fellowes. It first aired in the United Kingdom on ITV (TV network), ITV on 26 September 2010 and in the United St ...
'' the outspoken youngest daughter of the fictional Earl of Grantham
Earl of Grantham is a title in the Peerage of England created on 24 December 1698, along with the titles Viscount Boston, of Boston in the County of Lincoln, and Baron Alford, of Alford in the County of Lincoln, for Henry de Nassau d'Auverquer ...
, Lady Sybil, is presented as a debutante at court in London during her first season. The family are also portrayed to move to London for the duration of the season, returning to their country seat at the end of it. The show's 2013 Christmas Special (set in the summer of 1923) focuses on cousin Lady Rose McClare's debutante ball
A debutante, also spelled débutante ( ; from , ), or deb is a young woman of aristocratic or upper-class family background who has reached maturity and is presented to society at a formal "debut" ( , ; ) or possibly debutante ball. Original ...
and presentation at court.
* Oscar Wilde
Oscar Fingal O'Fflahertie Wills Wilde (16 October 185430 November 1900) was an Irish author, poet, and playwright. After writing in different literary styles throughout the 1880s, he became one of the most popular and influential playwright ...
's novel ''The Picture of Dorian Gray
''The Picture of Dorian Gray'' is an 1890 philosophical fiction and Gothic fiction, Gothic horror fiction, horror novel by Irish writer Oscar Wilde. A shorter novella-length version was published in the July 1890 issue of the American period ...
''; and his plays ''Lady Windermere's Fan
''Lady Windermere's Fan, A Play About a Good Woman'' is a four-act comedy by Oscar Wilde, first performed on Saturday, 20 February 1892, at the St James's Theatre in London.
The story concerns Lady Windermere, who suspects that her husband is ...
'', ''An Ideal Husband
''An Ideal Husband'' is a four-act play by Oscar Wilde that revolves around blackmail and political corruption, and touches on the themes of public and private honour. It was first produced at the Haymarket Theatre, London in 1895 and ran for ...
'' and ''The Importance of Being Earnest
''The Importance of Being Earnest, a Trivial Comedy for Serious People'' is a play by Oscar Wilde, the last of his four drawing-room plays, following ''Lady Windermere's Fan'' (1892), ''A Woman of No Importance'' (1893) and ''An Ideal Husban ...
''.
* In Michel Faber's ''The Crimson Petal and the White
''The Crimson Petal and the White'' is a 2002 novel by Michel Faber set in Victorian era, Victorian England.
The title is from an 1847 poem by Alfred, Lord Tennyson entitled "Now Sleeps the Crimson Petal", the opening line of which is "Now slee ...
'', the Season is part of the plot.
* The ''Malory-Anderson Family Saga'' series of historical romance novels by Johanna Lindsey
Johanna Helen Lindsey (née Howard, March 10, 1952 – October 27, 2019) was an American writer of historical romance novels. All of her books reached the ''New York Times'' bestseller list, many reaching No. 1.
Personal life
Johanna He ...
is set primarily in London, the first one opening in 1817. Throughout the series, one Season or another and the balls thrown during them, are mentioned in dialogue and are sometimes central to the plot lines themselves.
* Honoré de Balzac
Honoré de Balzac ( , more commonly ; ; born Honoré Balzac; 20 May 1799 – 18 August 1850) was a French novelist and playwright. The novel sequence ''La Comédie humaine'', which presents a panorama of post-Napoleonic French life, is ...
's novel ''The Muse of the Department'' contains a description of the London Season:
London is the capital of shops and of speculation, the government is made there. The aristocracy inscribes itself there only during sixty days, it there takes its orders, it inspects the government kitchen, it passes in review its daughters to marry, and equipages to sell, it says good-day and goes away promptly ; - it is so little amusing that it supports itself only for the few days called the season.* Most of the Regency Romance novels by
Georgette Heyer
Georgette Heyer (; 16 August 1902 – 4 July 1974) was an English novelist and short-story writer, in both the Regency romance and detective fiction genres. Her writing career began in 1921, when she turned a story conceived for her ail ...
feature the London Season.
* The Royal Ascot racecourse was used as a filming location in the James Bond
The ''James Bond'' franchise focuses on James Bond (literary character), the titular character, a fictional Secret Intelligence Service, British Secret Service agent created in 1953 by writer Ian Fleming, who featured him in twelve novels ...
film ''A View to a Kill
''A View to a Kill'' is a 1985 spy film, the fourteenth in the ''James Bond'' series produced by Eon Productions, and the seventh and final appearance of Roger Moore as the fictional MI6 agent James Bond. Although the title is adapted from ...
'' (1985), in which Bond was beginning his mission to defeat the villainous Max Zorin
Maximillian Zorin is a fictional character and the main antagonist in the 1985 James Bond film '' A View to a Kill''. He is portrayed by Christopher Walken.
Biography
In the 1985 film '' A View to a Kill'', Maximillian Zorin ( Christopher Walken) ...
, whose horse was racing there.
* The events depicted in the Netflix period drama
A historical drama (also period drama, period piece or just period) is a dramatic work set in the past, usually used in the context of film and television, which presents history, historical events and characters with varying degrees of fiction s ...
series ''Bridgerton'' take place during the London Season. Julia Quinn's Bridgerton (novel series), Bridgerton novels, on which the Netflix series is based, also primarily take place in London during the Season.
* The London Season is an important part of the board game ''John Company (board game), John Company''.
* The London Season is the setting of the second arc in the manga and anime series "Black Butler".
Notes
Further reading
*External links
The London Season by Michelle Jean Hoppe
Late Victorian/Edwardian London Season
Gilded Age New York social season
{{History of Dublin Cultural history of the United Kingdom Culture of the United Kingdom Debutantes European court festivities High society (social class) Regency London Seasons in the United Kingdom, Society Social history of the United Kingdom Social history of Ireland Culture of Ireland Seasons