SoRI-20041 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
SoRI-20041 is an "
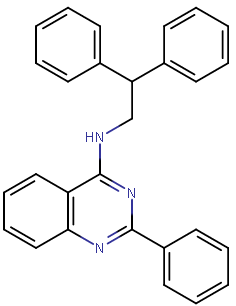 {{Dopaminergics
Neurochemistry
Quinazolines
Phenyl compounds
{{Dopaminergics
Neurochemistry
Quinazolines
Phenyl compounds
antagonist
An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the main enemy or rival of the protagonist and is often depicted as a villain.allosteric modulator
In pharmacology and biochemistry, allosteric modulators are a group of substances that bind to a receptor to change that receptor's response to stimuli. Some of them, like benzodiazepines or alcohol, function as psychoactive drugs. The site that a ...
of amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, an ...
-induced dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
release (in contrast to the related research chemicals SoRI-9804 and SoRI-20040, which are "agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an R ...
-like"). SoRI-20041 is believed to be the first example of a drug that separately modulates uptake versus release in the dopamine transporter
The dopamine transporter (DAT, also sodium-dependent dopamine transporter) is a membrane-spanning protein coded for in humans by the ''SLC6A3'' gene (also known as ''DAT1''), that pumps the neurotransmitter dopamine out of the synaptic cleft ba ...
(possibly showing how inward and outward transport represent distinct operational modes of DAT); it produces the same effects as SoRI-20040 and SoRI-9804 in uptake assays and binding assays, inhibiting the re-uptake of dopamine, but does not modulate d-amphetamine- induced DA release by inhibiting that as well, like 'agonists' of the series do.
This suggests the possibility of simultaneous action and increase of indirect-agonism through the dual action of DRA and DRI efficacy
Efficacy is the ability to perform a task to a satisfactory or expected degree. The word comes from the same roots as '' effectiveness'', and it has often been used synonymously, although in pharmacology a distinction is now often made betwee ...
existing together. This increases the inhibition of re-uptake at synaptic dopamine concentrations without interfering in the flow of release of dopamine from amphetaminergic phosphorylation at the affected transporter. This overcomes the obstacle of a compromised binding site that would be rendered unusable through the action of amphetamine. Conventional dopamine re-uptake inhibitors (such as cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
or methylphenidate
Methylphenidate, sold under the brand names Ritalin ( ) and Concerta ( ) among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It may be taken Oral adm ...
) would otherwise ineffectively target such a site on each specific transporter so affected by amphetamine, making this an example of a DRI that does not have a mutually exclusive functionality against DRA action at individual instances of DAT.
References
 {{Dopaminergics
Neurochemistry
Quinazolines
Phenyl compounds
{{Dopaminergics
Neurochemistry
Quinazolines
Phenyl compounds