Snakes in mythology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Snakes are a common occurrence in myths for a multitude of cultures, often associated with themes of wisdom, healing, creation, immortality, water, or the underworld.
Snakes are a common occurrence in myths for a multitude of cultures, often associated with themes of wisdom, healing, creation, immortality, water, or the underworld.
 In
In
* Hamilton A. Tyler, ''Pueblo Gods and Myths'', University of Oklahoma Press, 196
Medusa
Chinese Tradition: Nuwa makes humans
* {{usurped,
Apep Egyptian Snake God
} Snakes Legendary serpents Mythology
 Snakes are a common occurrence in myths for a multitude of cultures, often associated with themes of wisdom, healing, creation, immortality, water, or the underworld.
Snakes are a common occurrence in myths for a multitude of cultures, often associated with themes of wisdom, healing, creation, immortality, water, or the underworld.
Immortality
The West African kingdom of Dahomey regarded snakes as immortal because they appeared to be reincarnated from themselves when they sloughed their skins. Snakes were often also associated with immortality because they were observed biting their tails to form a circle and when they coiled they formed spirals. Both circles and spirals were seen as symbols ofeternity
Eternity, in common parlance, is an Infinity, infinite amount of time that never ends or the quality, condition or fact of being everlasting or eternal. Classical philosophy, however, defines eternity as what is timeless or exists outside tim ...
. This symbol has come to be known as the Ouroboros. The circle was particularly important to Dahomey
The Kingdom of Dahomey () was a West African List of kingdoms in Africa throughout history, kingdom located within present-day Benin that existed from approximately 1600 until 1904. It developed on the Abomey Plateau amongst the Fon people in ...
an myth where the snake-god Danh circled the world like a belt, corseting it and preventing it from flying apart in splinters. In Egyptian myth, the state of existence before creation was symbolized as Amduat; a many-coiled serpent from which Ra the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
and all of creation arose, returning each night and being reborn every morning. Also, in Norse mythology, the snake biting its tail (Ouroboros
The ouroboros or uroboros (; ) is an ancient symbol depicting a serpent symbolism, snake or European dragon, dragon Autocannibalism, eating its own tail. The ouroboros entered Western tradition via Egyptian mythology, ancient Egyptian iconogra ...
) symbolized the sea
A sea is a large body of salt water. There are particular seas and the sea. The sea commonly refers to the ocean, the interconnected body of seawaters that spans most of Earth. Particular seas are either marginal seas, second-order section ...
as the eternal ring which enclosed the world. In Egypt the snake has healing abilities. Hymns and offerings were made to it since it was believed that the Goddess could manifest through the snake.
"In a hymn to the goddess Mertseger, a workman on the Necropolis of Thebes relates how the goddess came to him in the form of a snake to heal his illness (Bunn1967:617).''
In Serer cosmogony and religion
Religion is a range of social system, social-cultural systems, including designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics in religion, ethics, or ...
, the serpent is the symbol of the pangool
Pangool (in Serer and Cangin) singular: Fangool (var : ''Pangol'' and ''Fangol''), are the ancient saints and ancestral spirits of the Serer people of Senegal, the Gambia and Mauritania. The Pangool play a crucial role in Serer religion and hist ...
, the saints and ancestral spirits of the Serer people
The Serer people (''Serer language, Serer proper'': Seereer or Sereer) are a West African ethnoreligious groupGastellu, Jean-Marc, ''Petit traité de matrilinarité. L'accumulation dans deux sociétés rurales d'Afrique de l'Ouest'', Cahiers ORST ...
of West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
. When a person dies, the Serer believe that their soul must make its way to ''Jaaniiw'' (a place where good souls go). Before the soul can reach Jaaniiw in order to ''reincarnate'' (''ciiɗ'' in Serer), it must transform into a black snake. During this transformation, the snake hides in a tree. For this reason, it is taboo in Serer culture to kill snakes. A great degree of respect is afforded to snakes in Serer culture, as they are the very embodiment and symbol of their saints and ancestral spirits. Like their Serer counterparts, the Dogon people
The Dogon are an ethnic group indigenous to the central plateau region of Mali, in West Africa, south of the Niger bend, near the city of Bandiagara, and in Burkina Faso. The population numbers between 400,000 and 800,000. They speak the Dogo ...
of Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
also have great reverence for the serpent. The serpent plays an active role in Dogon religion
The Dogon religion is the traditional religious or spiritual beliefs of the Dogon people of Mali. Dogons who adhere to the Dogon religion believe in one Supreme Creator called Amma (or Ama). Insoll, Timothy, ''Archaeology, Ritual, Religion'', ...
and cosmogony
Cosmogony is any model concerning the origin of the cosmos or the universe.
Overview
Scientific theories
In astronomy, cosmogony is the study of the origin of particular astrophysical objects or systems, and is most commonly used in ref ...
. The mythology of the Dogon's primordial ancestor Lebe, it based almost entirely on a serpent mythology. In their traditional African religious belief, they say that the Serpent Lebe guided the Dogon people from Mandé to the Bandiagara Escarpment (their current home) when they decided to migrate to flee Islamization and persecution. The Dogon believe that Lebe is the very reincarnation of the Dogon's first ancestor—who was resurrected in the form of a snake.
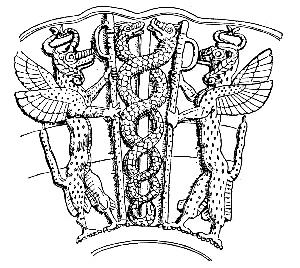
In the Sumerian culture snakes were also very important as a healing symbol. In Hammurabi’s Law Code (c. 1700 BC) the god Ninazu
Ninazu (; DNIN.A.SU">sup>DNIN.A.SU"lord healer") was a Mesopotamian god of the underworld. He was also associated with snakes and vegetation, and with time acquired the character of a warrior god. He was frequently associated with Ereshkigal, e ...
is identified as the patron of healing, and his son, Ningishzida
Ningishzida ( Sumerian: DNIN.G̃IŠ.ZID.DA, possible meaning "Lord f theGood Tree") was a Mesopotamian deity of vegetation, the underworld and sometimes war. He was commonly associated with snakes. Like Dumuzi, he was believed to spend a part ...
, is depicted with a serpent and staff symbol (Bunn 1967:618)
Creation myths
Besides the very wide known religious creation story of Adam and Eve, snakes were a common feature of manycreation myth
A creation myth or cosmogonic myth is a type of cosmogony, a symbolic narrative of how the world began and how people first came to inhabit it., "Creation myths are symbolic stories describing how the universe and its inhabitants came to be. Cre ...
s, for example many people in California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
had myths about the Rainbow Snake, which was either Mother Earth herself giving birth to all animals or a water-god whose writhing created rivers, creeks and oceans. In ancient India
Anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. The earliest known human remains in South Asia date to 30,000 years ago. Sedentism, Sedentariness began in South Asia around 7000 BCE; ...
n myth, the drought-serpent Ahi or Vritra
Vritra (, , ) is a danava in Hinduism. He serves as the personification of drought, and is an adversary of the king of the devas, Indra. As a danava, he belongs to the race of the asuras. Vritra is also known in the Vedas as Ahi ( ). He appe ...
swallowed the primordial ocean and did not release all created beings until Indra
Indra (; ) is the Hindu god of weather, considered the king of the Deva (Hinduism), Devas and Svarga in Hinduism. He is associated with the sky, lightning, weather, thunder, storms, rains, river flows, and war. volumes
Indra is the m ...
split the serpent's stomach with a thunderbolt
A thunderbolt or lightning bolt is a symbolic representation of lightning when accompanied by a loud thunderclap. In Indo-European mythology, the thunderbolt was identified with the 'Sky Father'; this association is also found in later Hel ...
. In another myth, the protector Vishnu
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation ( ...
slept on the coils of the world-serpent Shesha
Shesha (), also known by his epithets Sheshanaga () and Adishesha (), is a serpentine demigod ( naga) and king of the serpents ( Nagaraja), as well as a primordial being of creation in Hinduism. In the Puranas, Shesha is said to hold all the ...
(or " Ananta the endless";). Shesha in turn was supported on Kurma and when Kurma moved, Shesha stirred and yawned and the gaping of its jaws caused earthquakes
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they c ...
.
In Chinese mythology
Chinese mythology () is mythology that has been passed down in oral form or recorded in literature throughout the area now known as Greater China. Chinese mythology encompasses a diverse array of myths derived from regional and cultural tradit ...
, the woman-headed snake Nüwa
Nüwa, also read Nügua, is a mother goddess, culture hero, and/or member of the Three Sovereigns of Chinese mythology. She is a goddess in Chinese folk religion, Chinese Buddhism, Confucianism and Taoism. She is credited with creating humani ...
made the first humans. She made humans one at a time with clay.
To conserve her energy, she dipped a rope in clay and flicked it so blobs of clay landed everywhere; each blob of clay became an individual human. The first humans of hers became high-class, but second ones became low-class.
Greek cosmological myths tell of how Ophion the snake incubated the primordial egg from which all created things were born.
The classical symbol of the Ouroboros
The ouroboros or uroboros (; ) is an ancient symbol depicting a serpent symbolism, snake or European dragon, dragon Autocannibalism, eating its own tail. The ouroboros entered Western tradition via Egyptian mythology, ancient Egyptian iconogra ...
depicts a snake in the act of eating its own tail. This symbol has many interpretations, one of which is the snake representing cyclical nature of life and death, life feeding on itself in the act of creation.
The underworld
Snakes were regularly regarded as guardians of theUnderworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underworld.
...
or messengers between the Upper and Lower worlds, because they lived in cracks and holes in the ground. The Gorgons
The Gorgons ( ; ), in Greek mythology, are three monstrous sisters, Stheno, Euryale, and Medusa, said to be the daughters of Phorcys and Ceto. They lived near their sisters the Graeae, and were able to turn anyone who looked at them to stone ...
of Greek myth were snake-women (a common hybrid) whose gaze would turn flesh into stone, the most famous of them being Medusa
In Greek mythology, Medusa (; ), also called Gorgo () or the Gorgon, was one of the three Gorgons. Medusa is generally described as a woman with living snakes in place of hair; her appearance was so hideous that anyone who looked upon her wa ...
. Nagas, "the demon cobra" and naginis were human-headed snakes whose kings and queens who lived in jewel-encrusted underground or underwater paradises and who were perpetually at war with Garuda
Garuda (; ; Vedic Sanskrit: , ) is a Hindu deity who is primarily depicted as the mount (''vahana'') of the Hindu god Vishnu. This divine creature is mentioned in the Hindu, Buddhist, and Jain faiths. Garuda is also the half-brother of the D ...
the Sun-bird. In Egyptian myth, every morning the serpent Aapep (symbolising chaos
Chaos or CHAOS may refer to:
Science, technology, and astronomy
* '' Chaos: Making a New Science'', a 1987 book by James Gleick
* Chaos (company), a Bulgarian rendering and simulation software company
* ''Chaos'' (genus), a genus of amoebae
* ...
) attacked the Sunship (symbolizing order). Aapep would try to engulf the ship and the sky was drenched red at dawn
Dawn is the time that marks the beginning of twilight before sunrise. It is recognized by the diffuse sky radiation, appearance of indirect sunlight being Rayleigh scattering, scattered in Earth's atmosphere, when the centre of the Sun's disc ha ...
and dusk
Dusk occurs at the darkest stage of twilight, or at the very end of astronomical twilight after sunset and just before nightfall.''The Random House College Dictionary'', "dusk". At predusk, during early to intermediate stages of twilight, enoug ...
with its blood as the Sun defeated it.
In Nordic myth, evil
Evil, as a concept, is usually defined as profoundly immoral behavior, and it is related to acts that cause unnecessary pain and suffering to others.
Evil is commonly seen as the opposite, or sometimes absence, of good. It can be an extreme ...
was symbolized by the serpent (actually a dragon) Nidhogg (the 'Dread Biter') who coiled around one of the three roots of Yggdrasil
Yggdrasil () is an immense and central sacred tree in Norse cosmology. Around it exists all else, including the Nine Worlds.
Yggdrasil is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'' compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and in t ...
the Tree of Life, and tried to choke or gnaw the life from it.
"Here there is an evil dragon named Nidhogg that gnaws constantly at the root, striving to destroy Yggdrasil"
In ancient Slavic paganism a deity by the name of Veles presided over the underworld. He is almost always portrayed as a serpent or dragon depending on the particular myth. The underworld was part of a mythical world tree. The roots of this tree (usually growing in water) were guarded by Veles (Volos) the serpent god.
The idea of snake-people living below the Earth was prominent in American myth. The Aztec
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the Post-Classic stage, post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central ...
underworld, Mictlan was protected by python-trees, a gigantic alligator and a snake, all of which spirits had to evade by physical ducking and weaving or cunning, before they could start the journey towards immortality. In North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
, the Brule Sioux
The Sioux or Oceti Sakowin ( ; Dakota/ Lakota: ) are groups of Native American tribes and First Nations people from the Great Plains of North America. The Sioux have two major linguistic divisions: the Dakota and Lakota peoples (translati ...
people told of three brothers transformed into rattlesnake
Rattlesnakes are venomous snakes that form the genus, genera ''Crotalus'' and ''Sistrurus'' of the subfamily Crotalinae (the pit vipers). All rattlesnakes are vipers. Rattlesnakes are predators that live in a wide array of habitats, hunting sm ...
s which permanently helped and guided their human relatives.
The Pomo
The Pomo are a Indigenous peoples of California, Native American people of California. Historical Pomo territory in Northern California was large, bordered by the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast to the west, extending inland to ...
people told of a woman who married a rattlesnake-prince and gave birth to four snake-children who freely moved between the two worlds of their parents. The Hopi
The Hopi are Native Americans who primarily live in northeastern Arizona. The majority are enrolled in the Hopi Tribe of Arizona and live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona; however, some Hopi people are enrolled in the Colorado ...
people told of a young man who ventured into the underworld and married a snake-princess.
Snakes have been associated with Hecate
Hecate ( ; ) is a goddess in ancient Greek religion and mythology, most often shown holding a pair of torches, a key, or snakes, or accompanied by dogs, and in later periods depicted as three-formed or triple-bodied. She is variously associat ...
, the Greek goddess of magic and the lower world.
Water
Snakes were also commonly associated with water especially myths about the primordial ocean being formed of a huge coiled snake as in Ahi/Vritra
Vritra (, , ) is a danava in Hinduism. He serves as the personification of drought, and is an adversary of the king of the devas, Indra. As a danava, he belongs to the race of the asuras. Vritra is also known in the Vedas as Ahi ( ). He appe ...
in early Indian myth and Jormungand in Nordic myth. Sea monsters lived in every ocean from the seven-headed crocodile-serpent Leviathan
Leviathan ( ; ; ) is a sea serpent demon noted in theology and mythology. It is referenced in several books of the Hebrew Bible, including Psalms, the Book of Job, the Book of Isaiah, and the pseudepigraphical Book of Enoch. Leviathan is of ...
of Hebrew myth to the sea-god Koloowisi of the Zuni people
The Zuni (; formerly spelled ''Zuñi'') are Native American Pueblo peoples native to the Zuni River valley. The Zuni people today are federally recognized as the Zuni Tribe of the Zuni Reservation, New Mexico, and most live in the Pueblo o ...
of North America and the Greek monster Scylla
In Greek mythology, Scylla ( ; , ) is a legendary, man-eating monster that lives on one side of a narrow channel of water, opposite her counterpart, the sea-swallowing monster Charybdis. The two sides of the strait are within an arrow's range o ...
with six snake-necks. In some cultures, eels (which spend their early lives in freshwater before returning to the sea as adults) were regarded as magical creatures.
Rivers and lakes often had snake-gods or snake-guardians including Untekhi the fearsome water-spirit of the Missouri River
The Missouri River is a river in the Central United States, Central and Mountain states, Mountain West regions of the United States. The nation's longest, it rises in the eastern Centennial Mountains of the Bitterroot Range of the Rocky Moun ...
. Until recently, some northern European communities held well dressing ceremonies to appease the snake-spirits which lived in village wells and told legends of saints defeating malevolent lake-snakes e.g. Saint George
Saint George (;Geʽez: ጊዮርጊስ, , ka, გიორგი, , , died 23 April 303), also George of Lydda, was an early Christian martyr who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to holy tradition, he was a soldier in the ...
killing a maiden-devouring serpent or Saint Columba
Columba () or Colmcille (7 December 521 – 9 June 597 AD) was an Gaelic Ireland, Irish abbot and missionary evangelist credited with spreading Christianity in what is today Scotland at the start of the Hiberno-Scottish mission. He founded the ...
lecturing the Loch Ness Monster
The Loch Ness Monster (), known affectionately as Nessie, is a mythical creature in Scottish folklore that is said to inhabit Loch Ness in the Scottish Highlands. It is often described as large, long-necked, and with one or more humps protrud ...
which then stopped eating humans and became shy of human visitors.
Carved stones depicting a seven-headed cobra
COBRA or Cobra, often stylized as CoBrA, was a European avant-garde art group active from 1948 to 1951. The name was coined in 1948 by Christian Dotremont from the initials of the members' home countries' capital cities: Copenhagen (Co), Brussels ...
are commonly found near the sluices of the ancient irrigation tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engine; ...
s in Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
; these are believed to have been placed as guardians of the water.
Wisdom
Snakes were associated with wisdom in many mythologies, perhaps due to the appearance of pondering their actions as they prepare to strike, which was copied by medicine men in the build-up toprophecy
In religion, mythology, and fiction, a prophecy is a message that has been communicated to a person (typically called a ''prophet'') by a supernatural entity. Prophecies are a feature of many cultures and belief systems and usually contain di ...
in parts of West Africa. Usually the wisdom of snakes was regarded as ancient and beneficial towards humans but sometimes it could be directed against humans. In East Asia
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
snake-dragons watched over good harvests, rain, fertility and the cycle of the seasons, whilst in ancient Greece and India, snakes were considered to be lucky and snake-amulets were used as talismans against evil.
The Biblical story of the fall of man
The fall of man, the fall of Adam, or simply the Fall, is a term used in Christianity to describe the transition of the first man and woman from a state of innocent obedience to God in Christianity, God to a state of guilty disobedience.
*
*
*
* ...
(also found in the Islamic Qu'ran) tells of how Adam and Eve were deceived into disobeying God by a snake (identified as Satan
Satan, also known as the Devil, is a devilish entity in Abrahamic religions who seduces humans into sin (or falsehood). In Judaism, Satan is seen as an agent subservient to God, typically regarded as a metaphor for the '' yetzer hara'', or ' ...
by both Paul
Paul may refer to:
People
* Paul (given name), a given name, including a list of people
* Paul (surname), a list of people
* Paul the Apostle, an apostle who wrote many of the books of the New Testament
* Ray Hildebrand, half of the singing duo ...
and John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second E ...
in II Corinthians and Revelation, respectively). In the story, the snake convinces Eve to eat fruit from the Tree of Knowledge of Good and Evil, which she then convinces Adam to do as well. As a result, God banishes Adam and Eve from the garden and curses the snake.
In the state of Kerala, India, snake shrines occupy most households. Snakes were called upon by the creator of Kerala, Parasurama, to make the saline land fertile. The Mannarasala Shri Nagaraja Temple
A Nagaraja ( ', ) is a king of the various races of the nāga, the divine or semi-divine, half-human, half-serpent beings that reside in the netherworld ( Patala), and can occasionally take human form.
Rituals devoted to these supernatural being ...
is one of the main centers of worship. The presiding deity here is Nagaraja
A Nagaraja ( ', ) is a king of the various races of the nāga, the divine or semi-divine, half-human, half-serpent beings that reside in the netherworld ( Patala), and can occasionally take human form.
Rituals devoted to these supernatural being ...
- a five-headed snake god born to human parents as a blessing for their caretaking of snakes during a fire. It is believed that Nagaraja left his earthly life and took Samadhi
Statue of a meditating Rishikesh.html" ;"title="Shiva, Rishikesh">Shiva, Rishikesh
''Samādhi'' (Pali and ), in Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism, is a state of meditative consciousness. In many Indian religious traditions, the cultivati ...
but still resides in a chamber of the temple.
Hebrew scripture discusses the wisdom of the snake, Jesus encourages his disciples, telling them "I am sending you out like sheep into the midst of wolves; so be as wise as serpents..." (Matt 10:16). In these scriptures, snakes are characterized as cunning and noxious but wise nonetheless.
Healing
Healing and snakes were associated in ancient Greek myth withAsclepius
Asclepius (; ''Asklēpiós'' ; ) is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Religion in ancient Greece, Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis (lover of Apollo), Coronis, or Arsinoe (Greek myth), Ars ...
, whose snake-familiars would crawl across the bodies of sick people asleep at night in his shrines and lick them back to health.
In northern Europe and West Asia, snakes were associated with healing whilst in parts of South Asia, snakes are regarded as possessing aphrodisiac
An aphrodisiac is a substance that increases libido, sexual desire, sexual attraction, sexual pleasure, or sexual behavior. These substances range from a variety of plants, spices, and foods to synthetic chemicals. Natural aphrodisiacs, such as ...
qualities. Greek myth held that people could acquire second hearing and second sight if their ears or eyes were licked by a snake.
The Hopi people
The Hopi are Native Americans who primarily live in northeastern Arizona. The majority are enrolled in the Hopi Tribe of Arizona and live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona; however, some Hopi people are enrolled in the Colorado ...
of North America viewed snakes as symbols of healing, transformation, and fertility. Snakes in Mexican folk culture tell about the fear of the snake to the pregnant women where the snake attacks the umbilical cord.
Snake gods
The anthropomorphic basis of many myth-systems meant snake-gods were rarely depicted solely as snakes. Exceptions to this were theFiji
Fiji, officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about ...
an creator-god Ndengei, the dozen creator-gods of the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands, also known simply as the Solomons,John Prados, ''Islands of Destiny'', Dutton Caliber, 2012, p,20 and passim is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 1000 smaller islands in Melanesia, part of Oceania, t ...
(each with different responsibilities), the Aztec Mother Goddess Coatlicue, and the Voodoo snake-spirits Damballa, Simbi and Petro. Snake-gods were more often portrayed as hybrids or shape-shifters; for example, North American snake-spirits could change between human and serpentine forms whilst keeping the characteristics of both. Likewise, the Korean snake goddess Eobshin was portrayed as a black snake that had human ears.
The Mayan sky-goddess was associated with snakes. However, in her case, the snakes leaned into her ears and whispered the secrets of the universe (i.e. the secrets of herself). In Indian myth, Shiva
Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions w ...
had a cobra coiled on his head and another at rest on his shoulder, ready to strike his enemies. Egyptian myth has had several snake-gods, from the 'coiled one' Mehen who assisted Ra in fighting Aapep every day to the two-headed Nehebkau who guarded the underworld. In Korean mythology, the goddess Eobshin was the snake goddess of wealth, as snakes ate rats and mice that gnawed on the crops.
The Horned Serpent appears in the mythologies of many Native Americans. Details vary among tribes, with many of the stories associating the mystical figure with water, rain, lightning and thunder. Horned Serpents were major components of the Southeastern Ceremonial Complex of North American prehistory.
Ancient Mesopotamia
 In
In ancient Mesopotamia
The Civilization of Mesopotamia ranges from the earliest human occupation in the Paleolithic period up to Late antiquity. This history is pieced together from evidence retrieved from archaeological excavations and, after the introduction of writ ...
, Nirah
Nirah was a Mesopotamian god who served as the messenger (''šipru'') of Ištaran, the god of Der. He was depicted in the form of a snake.
Name and character
The name Nirah means "little snake" in Sumerian. It could be written with the log ...
, the messenger god of Ištaran, was represented as a serpent on ''kudurru
A kudurru was a type of stone document used as a boundary stone and as a record of land grants to vassals by the Kassites and later dynasties in ancient Babylonia between the 16th and 7th centuries BC. The original kudurru would typically be stor ...
s'', or boundary stones. Representations of two intertwined serpents are common in Sumerian art
The art of Mesopotamia has survived in the record from early hunter-gatherer societies (8th millennium BC) on to the Bronze Age cultures of the Sumerian, Akkadian, Babylonian and Assyrian empires. These empires were later replaced in the Iron Ag ...
and Neo-Sumerian artwork and still appear sporadically on cylinder seal
A cylinder seal is a small round cylinder, typically about one inch (2 to 3 cm) in width, engraved with written characters or figurative scenes or both, used in ancient times to roll an impression onto a two-dimensional surface, generally ...
s and amulets until as late as the thirteenth century BC. The horned viper ('' Cerastes cerastes'') appears in Kassite and Neo-Assyrian kudurrus and is invoked in Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
n texts as a magical protective entity. A dragon-like creature with horns, the body and neck of a snake, the forelegs of a lion, and the hind-legs of a bird appears in Mesopotamian art from the Akkadian Period until the Hellenistic Period
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
(323 BC–31 BC). This creature, known in Akkadian as the ''mušḫuššu
The ''mušḫuššu'' (; formerly also read as or ) or mushkhushshu () is a creature from ancient Mesopotamian mythology. A mythological hybrid, it is a scaly animal with hind legs resembling the talons of an eagle, lion-like forelimbs, a long ...
'', meaning "furious serpent", was used as a symbol for particular deities and also as a general protective emblem. It seems to have originally been the attendant of the Underworld god Ninazu
Ninazu (; DNIN.A.SU">sup>DNIN.A.SU"lord healer") was a Mesopotamian god of the underworld. He was also associated with snakes and vegetation, and with time acquired the character of a warrior god. He was frequently associated with Ereshkigal, e ...
, but later became the attendant to the Hurrian
The Hurrians (; ; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri) were a people who inhabited the Ancient Near East during the Bronze Age. They spoke the Hurro-Urartian language, Hurrian language, and lived throughout northern Syria (region) ...
storm-god Tishpak, as well as, later, Ninazu's son Ningishzida
Ningishzida ( Sumerian: DNIN.G̃IŠ.ZID.DA, possible meaning "Lord f theGood Tree") was a Mesopotamian deity of vegetation, the underworld and sometimes war. He was commonly associated with snakes. Like Dumuzi, he was believed to spend a part ...
, the Babylonian national god
A national god or tribal god is a guardian deity whose special concern is supposed to be the safety and well-being of an 'ethnic group' (''nation''). This is contrasted with other guardian figures such as family gods responsible for the well-be ...
Marduk
Marduk (; cuneiform: Dingir, ᵈAMAR.UTU; Sumerian language, Sumerian: "calf of the sun; solar calf"; ) is a god from ancient Mesopotamia and patron deity of Babylon who eventually rose to prominence in the 1st millennium BC. In B ...
, the scribal god Nabu
Nabu (, ) is the Babylonian patron god of literacy, scribes, wisdom, and the rational arts. He is associated with the classical planet Mercury in Babylonian astronomy.
Etymology and meaning
The Akkadian means 'announcer' or 'authorised pe ...
, and the Assyrian national god Ashur.
Quetzalcoatl
The Aztec spirit of intelligence and the wind, Quetzalcoatl ("Plumed Serpent"). Although not entirely a snake, the plumed serpent, Quetzalcoatl, in Mesoamerican cultures, particularly Mayan andAztec
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the Post-Classic stage, post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central ...
, held a multitude of roles as a deity. He was viewed as a twin entity which embodied that of god and man and equally man and serpent, yet was closely associated with fertility. In ancient Aztec mythology
Aztec mythology is the body or collection of myths of the Aztec civilization of Central Mexico. The Aztecs were a culture living in central Mexico and much of their mythology is similar to that of other Mesoamerican cultures. According to legend ...
, Quetzalcoatl was the son of the fertility earth goddess, Cihuacoatl, and cloud serpent and hunting god, Mixcoatl
Mixcoatl (, from mixtli "cloud" and cōātl "serpent"), or Camaxtle or Camaxtli, was the god of the hunt and identified with the Milky Way, the stars, and the heavens in several Mesoamerican cultures. He was the patron deity of the Otomi peopl ...
. His roles took the form of everything from bringer of morning winds and bright daylight for healthy crops, to a sea god capable of bringing on great floods. As shown in the images there are images of the sky serpent with its tail in its mouth, it is believed to be a reverence to the sun, for which Quetzalcoatl was also closely linked.
Rituals
TheHopi
The Hopi are Native Americans who primarily live in northeastern Arizona. The majority are enrolled in the Hopi Tribe of Arizona and live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona; however, some Hopi people are enrolled in the Colorado ...
people of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
performed an annual snake dance to celebrate the union of Snake Youth (a Sky spirit) and Snake Girl (an Underworld spirit), and to renew fertility
Fertility in colloquial terms refers the ability to have offspring. In demographic contexts, fertility refers to the actual production of offspring, rather than the physical capability to reproduce, which is termed fecundity. The fertility rate ...
of Nature
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physic ...
. During the dance, live snakes were handled and at the end of the dance the snakes were released into the fields to guarantee good crops. "The snake dance is a prayer to the spirits of the clouds, the thunder and lightning, that the rain may fall on the growing crops.." In the northwestern Indian city, Banaras, a festival called Naga Pancami is celebrated during the rainy season of Sravana (July/August) to pay homage to the supernatural snakes or deities. Thousands of people gather around snake pools called Naga kuan that are said to lead to Nagaloka, the lavish underwater world of these snake deities or Nagas. Worshippers bathe in and jump from the ledges into the pools as a way to honor them and ensure that they provide things like fertility of the land and its people, and protection from the poisons (wrath) of its bite. In this region, females are more numbered as the worshippers of Nagas, which most closely resemble religious ritual.
See also
* Aapep - an ancient Egyptian deity who embodied chaos and appears in art as a giant serpent * Ahi orVritra
Vritra (, , ) is a danava in Hinduism. He serves as the personification of drought, and is an adversary of the king of the devas, Indra. As a danava, he belongs to the race of the asuras. Vritra is also known in the Vedas as Ahi ( ). He appe ...
- a serpent or dragon in Hinduism, the personification of drought
* Atum
Atum (, Egyptian: ''jtm(w)'' or ''tm(w)'', ''reconstructed'' ; Coptic ''Atoum''), sometimes rendered as Atem, Temu, or Tem, is the primordial God in Egyptian mythology from whom all else arose. He created himself and is the father of Shu and ...
- an ancient Egyptian deity of creation, sometimes depicted as a serpent
* Bobbi-Bobbi - to the Binbinga people of northern Australia, a huge supernatural snake who lived in the heavens in the Dreamtime
* Echidna
Echidnas (), sometimes known as spiny anteaters, are quill-covered monotremes (egg-laying mammals) belonging to the Family (biology), family Tachyglossidae , living in Australia and New Guinea. The four Extant taxon, extant species of echidnas ...
- in Greek mythology, a half-woman and half-snake monster
* Eobshin - the goddess of the storage and wealth in Korean mythology, believed to be a black snake with ears
* Glycon— an ancient snake god, having a large and influential cult within the Roman Empire in the 2nd century; the contemporary satirist Lucian proclaimed the god a hoax, supposedly represented by a hand puppet
* Illuyankas - a serpentine dragon in Hittite mythology
* Leviathan
Leviathan ( ; ; ) is a sea serpent demon noted in theology and mythology. It is referenced in several books of the Hebrew Bible, including Psalms, the Book of Job, the Book of Isaiah, and the pseudepigraphical Book of Enoch. Leviathan is of ...
- a monstrous Biblical sea serpent
* Jörmungandr
In Norse mythology, Jörmungandr (, see Etymology), also known as the Midgard Serpent or World Serpent (, "worm of Midgard"), is an unfathomably large and monstrous sea serpent or worm who dwells in the world sea, encircling the Earth ( Midga ...
- a sea serpent in Norse mythology
* Meretseger
Meretseger (also known as Mersegrit' or Mertseger) was a Theban cobra-goddess in ancient Egyptian religion, in charge with guarding and protecting the vast Theban Necropolis — on the west bank of the Nile, in front of Thebes — and especiall ...
- an ancient Egyptian cobra-goddess
* Nehustan - a Biblical bronze serpent which God told Moses
In Abrahamic religions, Moses was the Hebrews, Hebrew prophet who led the Israelites out of slavery in the The Exodus, Exodus from ancient Egypt, Egypt. He is considered the most important Prophets in Judaism, prophet in Judaism and Samaritani ...
to erect, but was later destroyed when it became an idol
* Rod of Asclepius
In Greek mythology, the Rod of Asclepius (⚕; , , , sometimes also spelled Asklepios), also known as the Staff of Aesculapius and as the asklepian, is a serpent-entwined rod wielded by the Greek god Asclepius, a deity associated with healing ...
- a serpent-entwined rod wielded by the Greek god Asclepius, a deity associated with healing and medicine
* Serpents in the Bible
Serpents () are referred to in both the Hebrew Bible and the New Testament. The Serpent (symbolism), symbol of a serpent or snake played important roles in the religious traditions and cultural life of ancient Greece, Ancient Egypt, Egypt, Mesopot ...
* Serpent (symbolism)
The serpent, or snake, is one of the oldest and most widespread mythological symbols. The word is derived from Latin ''serpens'', a crawling animal or snake. Snakes have been associated with some of the oldest rituals known to humankindRobbins, L ...
* Snakes in Chinese mythology
Snakes (also known as serpents) are an important motif in Chinese mythology. There are various myths, legends, and folk tales about snakes. Chinese mythology refers to these and other myths found in the historical geographic area(s) of China. Thes ...
* Tefnut - an ancient Egyptian deity of moisture, sometimes depicted as a lion-headed serpent
* Sheshnag - an ancient hindu god, supposedly he keeps earth on his head
* Medusa
In Greek mythology, Medusa (; ), also called Gorgo () or the Gorgon, was one of the three Gorgons. Medusa is generally described as a woman with living snakes in place of hair; her appearance was so hideous that anyone who looked upon her wa ...
- a woman cursed by Athena to become a snake woman, and people who sees her eyes will petrify
* Quetzalcoatl - (pron. Quet-zal-co-at) or 'Plumed Serpent' was one of the most important gods in ancient Mesoamerica. A mix of bird and rattlesnake, his name is a combination of the Nahuatl words quetzal (the emerald plumed bird) and coatl (serpent). Quetzalcóatl was the god of winds and rain, and the creator of the world and humanity.
References
* John Bathurst Deane, ''Worship of the Serpent: Traced Throughout the World'* Hamilton A. Tyler, ''Pueblo Gods and Myths'', University of Oklahoma Press, 196
External links
Medusa
Chinese Tradition: Nuwa makes humans
* {{usurped,
Apep Egyptian Snake God
} Snakes Legendary serpents Mythology