Smelter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Smelting is a process of applying heat and a chemical reducing agent to an ore to extract a desired base metal product. It is a form of extractive metallurgy that is used to obtain many metals such as
Smelting is a process of applying heat and a chemical reducing agent to an ore to extract a desired base metal product. It is a form of extractive metallurgy that is used to obtain many metals such as
 Smelting involves more than just melting the metal out of its ore. Most ores are the chemical compound of the metal and other elements, such as oxygen (as an
Smelting involves more than just melting the metal out of its ore. Most ores are the chemical compound of the metal and other elements, such as oxygen (as an
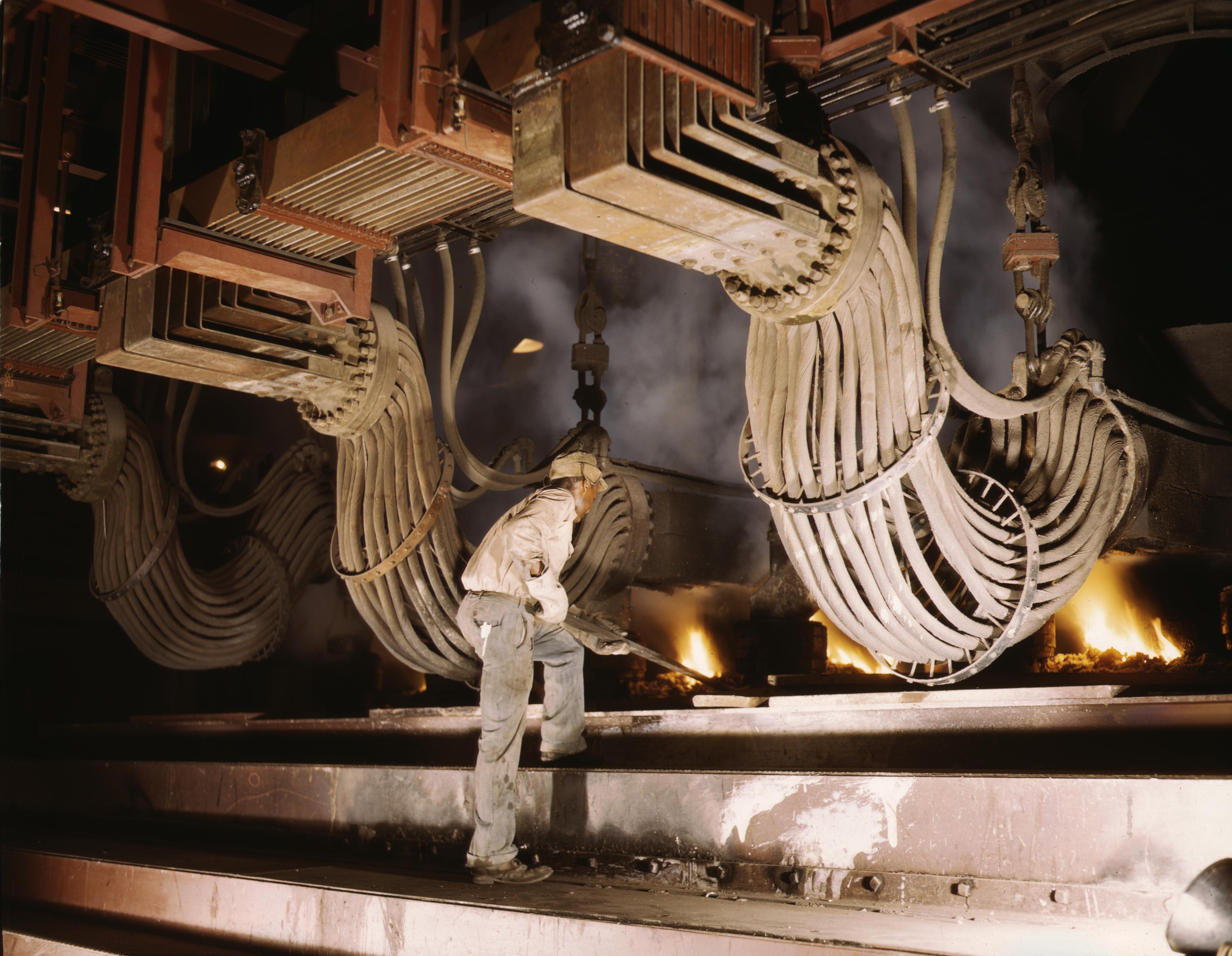
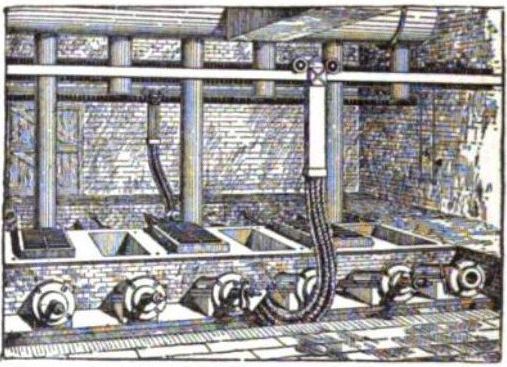 The ores of base metals are often sulfides. In recent centuries, reverberatory furnaces have been used to keep the charge being smelted separately from the fuel. Traditionally, they were used for the first step of smelting: forming two liquids, one an oxide slag containing most of the impurities, and the other a sulfide matte containing the valuable metal sulfide and some impurities. Such "reverb" furnaces are today about 40 meters long, 3 meters high, and 10 meters wide. Fuel is burned at one end to melt the dry sulfide concentrates (usually after partial roasting) which are fed through openings in the roof of the furnace. The slag floats over the heavier matte and is removed and discarded or recycled. The sulfide matte is then sent to the converter. The precise details of the process vary from one furnace to another depending on the mineralogy of the ore body.
While reverberatory furnaces produced slags containing very little copper, they were relatively energy inefficient and off-gassed a low concentration of
The ores of base metals are often sulfides. In recent centuries, reverberatory furnaces have been used to keep the charge being smelted separately from the fuel. Traditionally, they were used for the first step of smelting: forming two liquids, one an oxide slag containing most of the impurities, and the other a sulfide matte containing the valuable metal sulfide and some impurities. Such "reverb" furnaces are today about 40 meters long, 3 meters high, and 10 meters wide. Fuel is burned at one end to melt the dry sulfide concentrates (usually after partial roasting) which are fed through openings in the roof of the furnace. The slag floats over the heavier matte and is removed and discarded or recycled. The sulfide matte is then sent to the converter. The precise details of the process vary from one furnace to another depending on the mineralogy of the ore body.
While reverberatory furnaces produced slags containing very little copper, they were relatively energy inefficient and off-gassed a low concentration of
 Copper was the first metal to be smelted. How the discovery came about is debated. Campfires are about 200 °C short of the temperature needed, so some propose that the first smelting of copper may have occurred in pottery
Copper was the first metal to be smelted. How the discovery came about is debated. Campfires are about 200 °C short of the temperature needed, so some propose that the first smelting of copper may have occurred in pottery
blast furnace summary , Britannica
Puddling was also introduced in the
 Smelting is a process of applying heat and a chemical reducing agent to an ore to extract a desired base metal product. It is a form of extractive metallurgy that is used to obtain many metals such as
Smelting is a process of applying heat and a chemical reducing agent to an ore to extract a desired base metal product. It is a form of extractive metallurgy that is used to obtain many metals such as iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
, tin, lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
. Smelting uses heat and a chemical reducing agent to decompose the ore, driving off other elements as gases or slag and leaving the metal behind. The reducing agent is commonly a fossil-fuel source of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
, such as carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
from incomplete combustion of coke—or, in earlier times, of charcoal. The oxygen in the ore binds to carbon at high temperatures, as the chemical potential energy of the bonds in carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
() is lower than that of the bonds in the ore.
Sulfide ores such as those commonly used to obtain copper, zinc or lead, are roasted before smelting in order to convert the sulfides to oxides, which are more readily reduced to the metal. Roasting heats the ore in the presence of oxygen from air, oxidizing the ore and liberating the sulfur as sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is r ...
gas.
Smelting most prominently takes place in a blast furnace to produce pig iron
Pig iron, also known as crude iron, is an intermediate good used by the iron industry in the production of steel. It is developed by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. Pig iron has a high carbon content, typically 3.8–4.7%, along with si ...
, which is converted into steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
. Plants for the electrolytic reduction of aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
are referred to as aluminium smelters.
Smelters can be classified into two types depending on their business model; custom smelters and integrated smelters. A custom smelter is a smelter that treats ore on behalf of customers or buy ores. Custom smelters depend on ore concentrates from mines of mines of different ownership. Integrated smelters depend directly on a specific mining operation and tend to lie next to a mine.
Process
 Smelting involves more than just melting the metal out of its ore. Most ores are the chemical compound of the metal and other elements, such as oxygen (as an
Smelting involves more than just melting the metal out of its ore. Most ores are the chemical compound of the metal and other elements, such as oxygen (as an oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
), sulfur (as a sulfide
Sulfide (also sulphide in British English) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to large families o ...
), or carbon and oxygen together (as a carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, (), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word "carbonate" may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate group ...
). To extract the metal, workers must make these compounds undergo a chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, ...
. Smelting, therefore, consists of using suitable reducing substances that combine with those oxidizing elements to free the metal.
Roasting
In the case of sulfides and carbonates, a process called " roasting" removes the unwanted carbon or sulfur, leaving an oxide, which is more suitable for reduction to metal. Roasting is usually carried out in an oxidizing environment. A few practical examples: For sulfide ores, roasting results in replacement of sulfide, partly or completely, by oxide. For molybdenum disulfide, the main ore of Mo, roasting proceeds as follows: :Reduction
Reduction is the final, high-temperature step in smelting, in which the oxide becomes the elemental metal. A reducing environment (often provided by carbon monoxide, made by incompletecombustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion ...
in an air-starved furnace) pulls the final oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
atoms from the raw metal. The carbon source acts as a chemical reactant to remove oxygen from the ore, yielding the purified metal element as a product. The carbon source is oxidized in two stages. First, carbon (C) combusts with oxygen (O2) in the air to produce carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
(CO). Second, the carbon monoxide reacts with the ore (e.g. Fe2O3) and removes one of its oxygen atoms, releasing carbon dioxide (). After successive interactions with carbon monoxide, all of the oxygen in the ore will be removed, leaving the raw metal element (e.g. Fe). As most ores are impure, it is often necessary to use flux, such as limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
(or dolomite), to remove the accompanying rock gangue as slag. This calcination reaction emits carbon dioxide.
The required temperature varies both in absolute terms and in terms of the melting point of the base metal. Examples:
* Iron oxide
An iron oxide is a chemical compound composed of iron and oxygen. Several iron oxides are recognized. Often they are non-stoichiometric. Ferric oxyhydroxides are a related class of compounds, perhaps the best known of which is rust.
Iron ...
becomes metallic iron at roughly 1250 °C (2282 °F or 1523 K), almost 300 degrees ''below'' iron's melting point of 1538 °C (2800 °F or 1811 K).
* Mercuric oxide becomes vaporous mercury near 550 °C (1022 °F or 823 K), almost 600 degrees ''above'' mercury's melting point of -38 °C (-36.4 °F or 235 K), and also above mercury's ''boiling'' point.
Fluxes
Fluxes are materials added to the ore during smelting to catalyze the desired reactions and to chemically bind to unwanted impurities or reaction products. Calcium carbonate or calcium oxide in the form of lime are often used for this purpose, since they react with sulfur, phosphorus, and silicon impurities to allow them to be readily separated and discarded, in the form of slag. Fluxes may also serve to control the viscosity and neutralize unwanted acids. Flux and slag can provide a secondary service after the reduction step is complete; they provide a molten cover on the purified metal, preventing contact with oxygen while still hot enough to readily oxidize. This prevents impurities from forming in the metal.Sulfide ores
 The ores of base metals are often sulfides. In recent centuries, reverberatory furnaces have been used to keep the charge being smelted separately from the fuel. Traditionally, they were used for the first step of smelting: forming two liquids, one an oxide slag containing most of the impurities, and the other a sulfide matte containing the valuable metal sulfide and some impurities. Such "reverb" furnaces are today about 40 meters long, 3 meters high, and 10 meters wide. Fuel is burned at one end to melt the dry sulfide concentrates (usually after partial roasting) which are fed through openings in the roof of the furnace. The slag floats over the heavier matte and is removed and discarded or recycled. The sulfide matte is then sent to the converter. The precise details of the process vary from one furnace to another depending on the mineralogy of the ore body.
While reverberatory furnaces produced slags containing very little copper, they were relatively energy inefficient and off-gassed a low concentration of
The ores of base metals are often sulfides. In recent centuries, reverberatory furnaces have been used to keep the charge being smelted separately from the fuel. Traditionally, they were used for the first step of smelting: forming two liquids, one an oxide slag containing most of the impurities, and the other a sulfide matte containing the valuable metal sulfide and some impurities. Such "reverb" furnaces are today about 40 meters long, 3 meters high, and 10 meters wide. Fuel is burned at one end to melt the dry sulfide concentrates (usually after partial roasting) which are fed through openings in the roof of the furnace. The slag floats over the heavier matte and is removed and discarded or recycled. The sulfide matte is then sent to the converter. The precise details of the process vary from one furnace to another depending on the mineralogy of the ore body.
While reverberatory furnaces produced slags containing very little copper, they were relatively energy inefficient and off-gassed a low concentration of sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is r ...
that was difficult to capture; a new generation of copper smelting technologies has supplanted them. More recent furnaces exploit bath smelting, top-jetting lance smelting, flash smelting, and blast furnaces. Some examples of bath smelters include the Noranda furnace, the Isasmelt furnace, the Teniente reactor, the Vunyukov smelter, and the SKS technology. Top-jetting lance smelters include the Mitsubishi smelting reactor. Flash smelters account for over 50% of the world's copper smelters. There are many more varieties of smelting processes, including the Kivset, Ausmelt, Tamano, EAF, and BF.
History
Of the seven metals known in antiquity, onlygold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
regularly occurs in nature as a native metal
A native metal is any metal that is found pure in its metallic form in nature. Metals that can be found as native element mineral, native deposits singly or in alloys include antimony, arsenic, bismuth, cadmium, chromium, cobalt, indium, iron, ma ...
. The others – copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
, silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
, tin, iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, and mercury – occur primarily as minerals, although native copper is occasionally found in commercially significant quantities. These minerals are primarily carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, (), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word "carbonate" may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate group ...
s, sulfide
Sulfide (also sulphide in British English) is an inorganic anion of sulfur with the chemical formula S2− or a compound containing one or more S2− ions. Solutions of sulfide salts are corrosive. ''Sulfide'' also refers to large families o ...
s, or oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
s of the metal, mixed with other components such as silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant f ...
and alumina. Roasting the carbonate and sulfide minerals in the air converts them to oxides. The oxides, in turn, are smelted into the metal. Carbon monoxide was (and is) the reducing agent of choice for smelting. It is easily produced during the heating process, and as a gas comes into intimate contact with the ore.
In the Old World, humans learned to smelt metals in prehistoric
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use o ...
times, more than 8000 years ago. The discovery and use of the "useful" metals – copper and bronze at first, then iron a few millennia later – had an enormous impact on human society. The impact was so pervasive that scholars traditionally divide ancient history into Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistory, prehistoric period during which Rock (geology), stone was widely used to make stone tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years and ended b ...
, Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
, and Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
.
In the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
, pre-Inca
The Inca Empire, officially known as the Realm of the Four Parts (, ), was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The History of the Incas, Inca ...
civilizations of the central Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range ...
in Peru had mastered the smelting of copper and silver at least six centuries before the first Europeans arrived in the 16th century, while never mastering the smelting of metals such as iron for use with weapon craft.
Copper and bronze
 Copper was the first metal to be smelted. How the discovery came about is debated. Campfires are about 200 °C short of the temperature needed, so some propose that the first smelting of copper may have occurred in pottery
Copper was the first metal to be smelted. How the discovery came about is debated. Campfires are about 200 °C short of the temperature needed, so some propose that the first smelting of copper may have occurred in pottery kiln
A kiln is a thermally insulated chamber, a type of oven, that produces temperatures sufficient to complete some process, such as hardening, drying, or Chemical Changes, chemical changes. Kilns have been used for millennia to turn objects m ...
s. (The development of copper smelting in the Andes, which is believed to have occurred independently of the Old World, may have occurred in the same way.)
The earliest current evidence of copper smelting, dating from between 5500 BC and 5000 BC, has been found in Pločnik and Belovode, Serbia. A mace head found in Turkey and dated to 5000 BC, once thought to be the oldest evidence, now appears to be hammered, native copper.
Combining copper with tin or arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
in the right proportions produces bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
, an alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
that is significantly harder than copper. The first copper/arsenic bronzes date from 4200 BC from Asia Minor. The Inca bronze alloys were also of this type. Arsenic is often an impurity in copper ores, so the discovery could have been made by accident. Eventually, arsenic-bearing minerals were intentionally added during smelting.
Copper–tin bronzes, harder and more durable, were developed around 3500 BC, also in Asia Minor.
How smiths learned to produce copper/tin bronzes is unknown. The first such bronzes may have been a lucky accident from tin-contaminated copper ores. However, by 2000 BC, people were mining tin on purpose to produce bronze—which is remarkable as tin is a semi-rare metal, and even a rich cassiterite ore only has 5% tin.
The discovery of copper and bronze manufacture had a significant impact on the history of the Old World. Metals were hard enough to make weapons that were heavier, stronger, and more resistant to impact damage than wood, bone, or stone equivalents. For several millennia, bronze was the material of choice for weapons such as sword
A sword is an edged and bladed weapons, edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter ...
s, dagger
A dagger is a fighting knife with a very sharp point and usually one or two sharp edges, typically designed or capable of being used as a cutting or stabbing, thrusting weapon.State v. Martin, 633 S.W.2d 80 (Mo. 1982): This is the dictionary or ...
s, battle axes, and spear and arrow
An arrow is a fin-stabilized projectile launched by a bow. A typical arrow usually consists of a long, stiff, straight shaft with a weighty (and usually sharp and pointed) arrowhead attached to the front end, multiple fin-like stabilizers c ...
points, as well as protective gear such as shields, helmets, greaves (metal shin guards), and other body armor. Bronze also supplanted stone, wood, and organic materials in tools and household utensils—such as chisels, saws, adzes, nails, blade shears, knives, sewing needle
A sewing needle, used for hand-sewing, is a long slender tool with a pointed tip at one end and a hole (or ''eye'') to hold the sewing thread. The earliest needles were made of bone or wood; modern needles are manufactured from high carbon steel ...
s and pins, jugs, cooking pots and cauldrons, mirrors, and horse harness
A horse harness is a device that connects a horse to a horse-drawn vehicle or another type of load to pull. There are two main designs of horse harness: (1) the Breastplate (tack)#Harness, breast collar or breaststrap, and (2) the Horse collar, ...
es. Tin and copper also contributed to the establishment of trade networks that spanned large areas of Europe and Asia and had a major effect on the distribution of wealth among individuals and nations.
Tin and lead
The earliest known cast lead beads were thought to be in the Çatalhöyük site inAnatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
(Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
), and dated from about 6500 BC. However, recent research has discovered that this was not lead, but rather cerussite and galena, minerals rich in, but distinct from, lead.
Since the discovery happened several millennia before the invention of writing, there is no written record of how it was made. However, tin and lead can be smelted by placing the ores in a wood fire, leaving the possibility that the discovery may have occurred by accident. Recent scholarship however has called this find into question.
Lead is a common metal, but its discovery had relatively little impact in the ancient world. It is too soft to use for structural elements or weapons, though its high density relative to other metals makes it ideal for sling projectiles. However, since it was easy to cast and shape, workers in the classical world of Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically r ...
and Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Em ...
used it extensively to pipe and store water. They also used it as a mortar in stone buildings.
Tin was much less common than lead, is only marginally harder, and had even less impact by itself.
Early iron smelting
The earliest evidence for iron-making is a small number of iron fragments with the appropriate amounts of carbon admixture found in the Proto-Hittite layers at Kaman-Kalehöyük and dated to 2200–2000 BC. Souckova-Siegolová (2001) shows that iron implements were made in Central Anatolia in very limited quantities around 1800 BC and were in general use by elites, though not by commoners, during the New Hittite Empire (~1400–1200 BC). Archaeologists have found indications of iron working inAncient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
, somewhere between the Third Intermediate Period and 23rd Dynasty (ca. 1100–750 BC). Significantly though, they have found no evidence of iron ore smelting in any (pre-modern) period. In addition, very early instances of carbon steel were in production around 2000 years ago (around the first-century.) in northwest Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t ...
, based on complex preheating principles. These discoveries are significant for the history of metallurgy.
Most early processes in Europe and Africa involved smelting iron ore in a bloomery
A bloomery is a type of metallurgical furnace once used widely for smelting iron from its iron oxides, oxides. The bloomery was the earliest form of smelter capable of smelting iron. Bloomeries produce a porous mass of iron and slag called ...
, where the temperature is kept low enough so that the iron does not melt. This produces a spongy mass of iron called a bloom, which then must be consolidated with a hammer to produce wrought iron. Some of the earliest evidence to date for the bloomery smelting of iron is found at Tell Hammeh, Jordan, radiocarbon-dated to .
Later iron smelting
From the medieval period, an indirect process began to replace the direct reduction in bloomeries. This used a blast furnace to makepig iron
Pig iron, also known as crude iron, is an intermediate good used by the iron industry in the production of steel. It is developed by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. Pig iron has a high carbon content, typically 3.8–4.7%, along with si ...
, which then had to undergo a further process to make forgeable bar iron. Processes for the second stage include fining in a finery forge. In the 13th century during the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history between and ; it was preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended according to historiographical convention ...
the blast furnace was introduced by China who had been using it since as early as 200 b.c during the Qin dynasty
The Qin dynasty ( ) was the first Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China. It is named for its progenitor state of Qin, a fief of the confederal Zhou dynasty (256 BC). Beginning in 230 BC, the Qin under King Ying Zheng enga ...
blast furnace summary , Britannica
Puddling was also introduced in the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
.
Both processes are now obsolete, and wrought iron is now rarely made. Instead, mild steel is produced from a Bessemer converter or by other means including smelting reduction processes such as the Corex Process.
Environmental and occupational health impacts
Smelting has serious effects on the environment, producing wastewater and slag and releasing such toxic metals ascopper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, silver, iron, cobalt, and selenium
Selenium is a chemical element; it has symbol (chemistry), symbol Se and atomic number 34. It has various physical appearances, including a brick-red powder, a vitreous black solid, and a grey metallic-looking form. It seldom occurs in this elem ...
into the atmosphere. Smelters also release gaseous sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is r ...
, contributing to acid rain
Acid rain is rain or any other form of Precipitation (meteorology), precipitation that is unusually acidic, meaning that it has elevated levels of hydrogen ions (low pH). Most water, including drinking water, has a neutral pH that exists b ...
, which acidifies soil and water.
The smelter in Flin Flon, Canada was one of the largest point sources of mercury in North America in the 20th century. Even after smelter releases were drastically reduced, landscape re-emission continued to be a major regional source of mercury. Lakes will likely receive mercury contamination from the smelter for decades, from both re-emissions returning as rainwater and leaching of metals from the soil.
Air pollution
Air pollutants generated by aluminium smelters include carbonyl sulfide, hydrogen fluoride,polycyclic compound
In the field of organic chemistry, a polycyclic compound is an organic compound featuring several closed ring (chemistry), rings of atoms, primarily carbon. These ring substructures include cycloalkanes, aromaticity, aromatics, and other ring ...
s, lead, nickel, manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
, polychlorinated biphenyls, and mercury. Copper smelter emissions include arsenic, beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, hard, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with ...
, cadmium, chromium, lead, manganese, and nickel. Lead smelters typically emit arsenic, antimony, cadmium and various lead compounds.
Wastewater
Wastewater pollutants discharged by iron and steel mills includes gasification products such asbenzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hyd ...
, naphthalene
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white Crystal, crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 Parts-per notation ...
, anthracene, cyanide, ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
, phenol
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire.
The molecule consists of a phenyl group () ...
s and cresols, together with a range of more complex organic compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-co ...
s known collectively as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH). Treatment technologies include recycling of wastewater; settling basins, clarifier
Clarifiers are settling tanks built with mechanical means for continuous removal of solids being deposited by Sedimentation (water treatment), sedimentation. A clarifier is generally used to remove solid particulates or suspended solids from li ...
s and filtration systems for solids removal; oil skimmers and filtration; chemical precipitation and filtration for dissolved metals; carbon adsorption and biological oxidation for organic pollutants; and evaporation.
Pollutants generated by other types of smelters varies with the base metal ore. For example, aluminum smelters typically generate fluoride
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic, Monatomic ion, monatomic Ion#Anions and cations, anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose ...
, benzo(a)pyrene, antimony and nickel, as well as aluminum. Copper smelters typically discharge cadmium, lead, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
, arsenic and nickel, in addition to copper. Lead smelters may discharge antimony, asbestos, cadmium, copper and zinc, in addition to lead.
Health impacts
Labourers working in the smelting industry have reported respiratory illnesses inhibiting their ability to perform the physical tasks demanded by their jobs.Regulations
In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency has published pollution control regulations for smelters. * Air pollution standards under the Clean Air Act * Water pollution standards ( effluent guidelines) under the Clean Water Act.See also
*Cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
* Ellingham diagram, useful in predicting the conditions under which an ore reduces to its metal
* Copper extraction techniques
* Clinker
* Cupellation
* Lead smelting
* Metallurgy
* Metallurgy in pre-Columbian America
* Pyrometallurgy
* Wrought iron
* Zinc smelting
References
Bibliography
*Pleiner, R. (2000) ''Iron in Archaeology. The European Bloomery Smelters'', Praha, Archeologický Ústav Av Cr. *Veldhuijzen, H.A. (2005) Technical Ceramics in Early Iron Smelting. The Role of Ceramics in the Early First Millennium Bc Iron Production at Tell Hammeh (Az-Zarqa), Jordan. In: Prudêncio, I.Dias, I. and Waerenborgh, J.C. (Eds.) ''Understanding People through Their Pottery; Proceedings of the 7th European Meeting on Ancient Ceramics (Emac '03)''. Lisboa, Instituto Português de Arqueologia (IPA). *Veldhuijzen, H.A. and Rehren, Th. (2006) Iron Smelting Slag Formation at Tell Hammeh (Az-Zarqa), Jordan. In: Pérez-Arantegui, J. (Ed.) ''Proceedings of the 34th International Symposium on Archaeometry, Zaragoza, 3–7 May 2004''. Zaragoza, Institución «Fernando el Católico» (C.S.I.C.) Excma. Diputación de Zaragoza.External links
{{Authority control Firing techniques Metallurgical processes de:Verhüttung