Slot Antenna on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
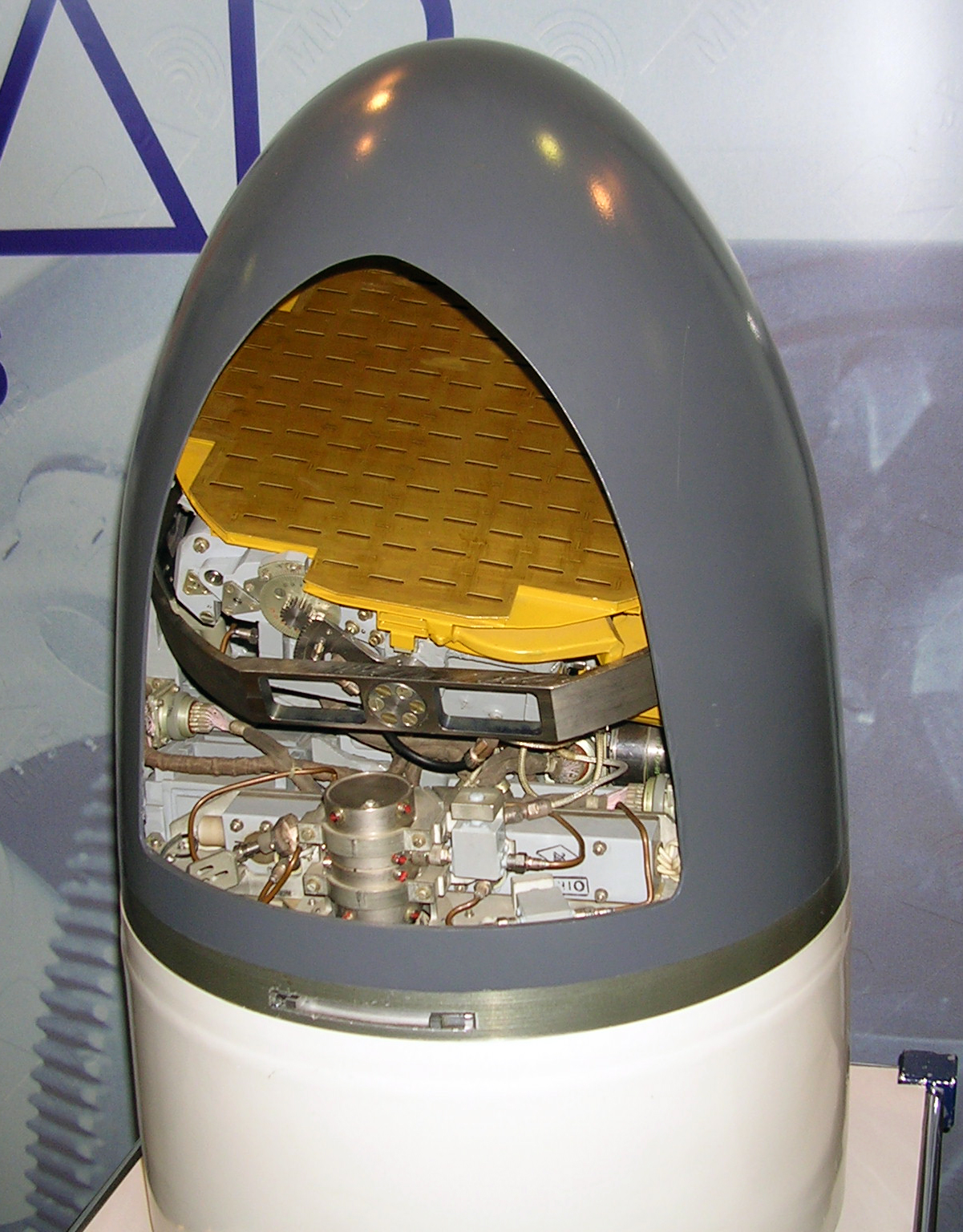 A slot antenna consists of a
A slot antenna consists of a
Slotted Waveguide Antennas
Antenna-Theory.com {{Antenna Types Radio frequency antenna types Antennas (radio) Radar Radar antennas English inventions Canadian inventions
 A slot antenna consists of a
A slot antenna consists of a metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
surface, usually a flat plate, with one or more holes or slots cut out. When the plate is driven as an antenna by an applied radio frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the u ...
current, the slot radiates electromagnetic wave
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength, ...
s in a way similar to a dipole antenna
In radio and telecommunications a dipole antenna or doublet
is one of the two simplest and most widely used antenna types, types of antenna; the other is the monopole antenna, monopole. The dipole is any one of a class of antennas producin ...
. The shape and size of the slot, as well as the driving frequency, determine the radiation pattern
In the field of antenna design the term radiation pattern (or antenna pattern or far-field pattern) refers to the ''directional'' (angular) dependence of the strength of the radio waves from the antenna or other source.Constantine A. Balanis: " ...
. Slot antennas are usually used at UHF
Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter ...
and microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
frequencies at which wavelengths are small enough that the plate and slot are conveniently small. At these frequencies, the radio waves are often conducted by a waveguide
A waveguide is a structure that guides waves by restricting the transmission of energy to one direction. Common types of waveguides include acoustic waveguides which direct sound, optical waveguides which direct light, and radio-frequency w ...
, and the antenna consists of slots in the waveguide; this is called a slotted waveguide antenna. Multiple slots act as a directive array antenna and can emit a narrow fan-shaped beam of microwaves. They are used in standard laboratory microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300&n ...
sources used for research, UHF television transmitting antennas, antennas on missiles and aircraft, sector antennas for cellular base station
A cell site, cell phone tower, cell base tower, or cellular base station is a cellular frequencies, cellular-enabled mobile device site where antenna (electronics), antennas and electronic communications equipment are placed (typically on a Rad ...
s, and particularly marine radar
Marine radars are X band or S band radars on ships, used to detect other ships and land hazards, to provide bearing and distance for collision avoidance and navigation at sea. They are electronic navigation instruments that use a rotating a ...
antennas. A slot antenna's main advantages are its size, design simplicity, and convenient adaptation to mass production using either waveguide or PC board technology.
Structure
As shown by H. G. Booker in 1946, fromBabinet's principle
In physics, Babinet's principle states that the diffraction pattern from an opaque body is identical to that from an aperture (a hole in a screen) of the same size and shape except for the overall forward beam intensity. It was formulated in the ...
in optics a slot in a metal plate or waveguide has the same radiation pattern
In the field of antenna design the term radiation pattern (or antenna pattern or far-field pattern) refers to the ''directional'' (angular) dependence of the strength of the radio waves from the antenna or other source.Constantine A. Balanis: " ...
as a driven rod antenna whose rod is the same shape as the slot, with the exception that the electric field
An electric field (sometimes called E-field) is a field (physics), physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles such as electrons. In classical electromagnetism, the electric field of a single charge (or group of charges) descri ...
and magnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
directions are interchanged; the antenna is a magnetic dipole instead of an electric dipole; the magnetic field is parallel to the long axis of the slot and the electric field is perpendicular. Thus the radiation pattern of a slot can be calculated by the same well-known equations used for rod element antennas like the dipole
In physics, a dipole () is an electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs in two ways:
* An electric dipole moment, electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative electric charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple ...
. The waves are linearly polarized perpendicular to the slot axis. Slots up to a wavelength long have a single main lobe with maximum radiation perpendicular to the surface.
Antennas consisting of multiple parallel slots in a waveguide are widely used array antennas. They have a radiation pattern similar to a corresponding linear array of dipole antennas, with the exception that the slot can only radiate into the space on one side of the waveguide surface, 180° of the surrounding space. There are two widely used types:
; Longitudinal slotted waveguide antenna: The slots' axis is parallel to the axis of the waveguide. This has a radiation pattern similar to a collinear dipole antenna, and is usually mounted vertically. The radiation pattern is almost omnidirectional in the horizontal plane perpendicular to the antenna over the 180° azimuth in front of the slot, but narrow in the vertical plane, with the vertical gain increasing approximately 3 dB with each doubling of the number of slots. The radiation is horizontally polarized. It is used for vertical omnidirectional transmitting antennas for UHF television stations. For broadcasting, a cylindrical or semicircular waveguide is sometimes used with several columns of slots cut in different sides to give an omnidirectional 360° radiation pattern.
; Transverse slotted waveguide antenna: The slots are almost perpendicular to the axis of the waveguide but skewed at a small angle, with alternate slots skewed at opposite angles. This radiates a dipole pattern in the plane perpendicular to the antenna, and a very sharp beam in the plane of the antenna. Its largest use is for microwave marine radar
Marine radars are X band or S band radars on ships, used to detect other ships and land hazards, to provide bearing and distance for collision avoidance and navigation at sea. They are electronic navigation instruments that use a rotating a ...
antennas. The antenna is mounted horizontally on a mechanical drive that rotates the antenna about a vertical axis, scanning the antenna's vertical fan-shaped beam 360° around the water surface surrounding the ship out to the horizon with each revolution. The wide vertical spread of the beam ensures that even in bad weather when the ship and the antenna axis is being rocked over a wide angle by waves the radar beam will not miss the surface.
History
The slot antenna was invented in 1938 by Alan Blumlein, while working for EMI. He invented it in order to produce a practical type of antenna for VHF television broadcasting that would have horizontal polarization, an omnidirectional horizontal radiation pattern and a narrow vertical radiation pattern. Prior to its use in surface search radar, such systems used a parabolic segment reflector, or " cheese antenna". The slotted waveguide antenna was the result of collaborative radar research carried on byMcGill University
McGill University (French: Université McGill) is an English-language public research university in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. Founded in 1821 by royal charter,Frost, Stanley Brice. ''McGill University, Vol. I. For the Advancement of Learning, ...
and the National Research Council of Canada during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. The co-inventors, W.H. Watson and E.W. Guptill of McGill, were granted a United States patent for the device, described as a "directive antenna for microwaves", in 1951.
Other uses
In a related application, so-called ''leaky waveguides'' are also used in the determination of railcar positions in certain rapid transit applications. They are used primarily to determine the precise position of the train when it is being brought to a halt at a station, so that the doorway positions will align correctly with queuing points on the platform or with a second set of safety doors should such be provided.See also
*Microwave Radiometer (Juno)
Microwave Radiometer (MWR) is an instrument on the Juno (spacecraft), ''Juno'' orbiter sent to planet Jupiter. MWR is a multi-wavelength microwave radiometer for making observations of Jupiter's deep atmosphere. MWR can observe radiation fro ...
(has a slot array antenna)
* RIMFAX (radar for Mars rover has slot antenna design)
References
External links
*Slotted Waveguide Antennas
Antenna-Theory.com {{Antenna Types Radio frequency antenna types Antennas (radio) Radar Radar antennas English inventions Canadian inventions