Sir Alexander Mackenzie (explorer) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sir Alexander Mackenzie ( – 12 March 1820) was a Scottish explorer and fur trader known for accomplishing the first crossing of
 On behalf of the North West Company, Mackenzie journeyed to
On behalf of the North West Company, Mackenzie journeyed to
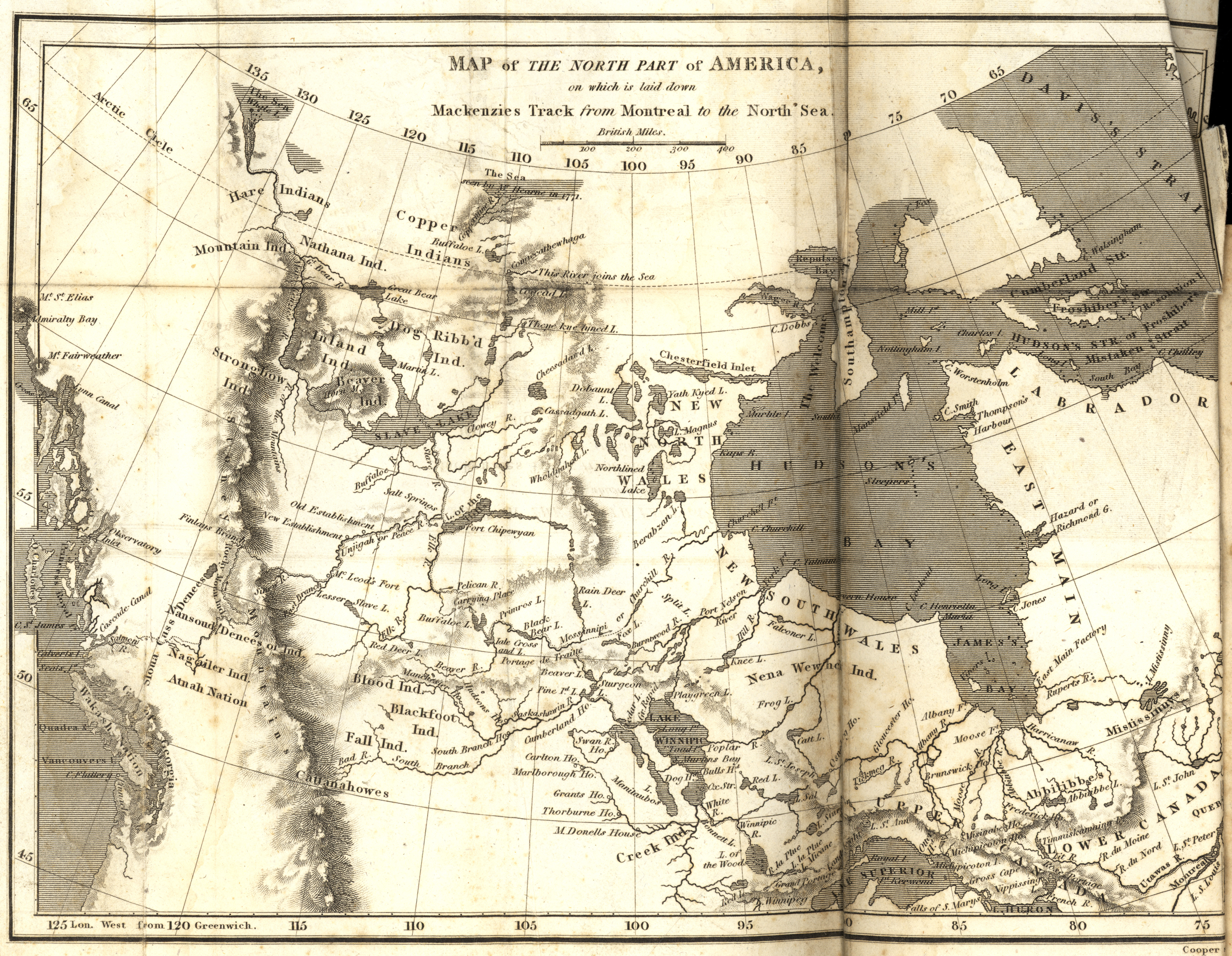
 In 1791, Mackenzie returned to
In 1791, Mackenzie returned to
(They were later reprinted.) He then presented a detailed plan of his west coast project to the British government "Preliminaries to the Establishment of a Permanent British Fishery and Trade in Furs etc. on the Continent and West Coast of North America." The British government, at the time predicting conflict with Napoleon, took no action. (Later Simon Fraser (explorer), Simon Fraser and David Thompson worked to extend the Canadian fur trade and prevent U.S. incursion in what would be Canada.) Mackenzie was
complete online transcription
*
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
north of Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
by a European in 1793. The Mackenzie River
The Mackenzie River (French: ; Slavey language, Slavey: ' èh tʃʰò literally ''big river''; Inuvialuktun: ' uːkpɑk literally ''great river'') is a river in the Canadian Canadian boreal forest, boreal forest and tundra. It forms, ...
and Mount Sir Alexander
Mount Sir Alexander, is a , ultra-prominent mountain in the Sir Alexander Area of the Continental Ranges (sometimes referred to as the Northern Continental Ranges), Canadian Rockies located in British Columbia.
Located within Kakwa Provincial ...
are named after him.
As a leading member of the North West Company, he aspired to extend the Company's operations into western Canada and selling those furs in China. His hopes thus were intrusions on the monopoly positions of both the Hudson's Bay Company and the East India Company.
Early life
Mackenzie was born inStornoway
Stornoway (; ) is the main town, and by far the largest, of the Outer Hebrides (or Western Isles), and the capital of Lewis and Harris in Scotland.
The town's population is around 6,953, making it the third-largest island town in Scotlan ...
in Lewis
Lewis may refer to:
Names
* Lewis (given name), including a list of people with the given name
* Lewis (surname), including a list of people with the surname
Music
* Lewis (musician), Canadian singer
* " Lewis (Mistreated)", a song by Radiohe ...
. He was the third of the four children born to Kenneth 'Corc' Mackenzie (1731–1780) and his wife Isabella MacIver, from another prominent mercantile family in Stornoway. When only 14 years old, Mackenzie's father served as an ensign
Ensign most often refers to:
* Ensign (flag), a flag flown on a vessel to indicate nationality
* Ensign (rank), a navy (and former army) officer rank
Ensign or The Ensign may also refer to:
Places
* Ensign, Alberta, Alberta, Canada
* Ensign, Ka ...
to protect Stornoway during the Jacobite rising of 1745
The Jacobite rising of 1745 was an attempt by Charles Edward Stuart to regain the Monarchy of Great Britain, British throne for his father, James Francis Edward Stuart. It took place during the War of the Austrian Succession, when the bulk of t ...
. He later became a merchant and held the tack
Thermoproteati is a kingdom of archaea. Its synonym, "TACK", is an acronym for Thaumarchaeota (now Nitrososphaerota), Aigarchaeota, Crenarchaeota (now Thermoproteota), and Korarchaeota (now Thermoproteota), the first groups discovered. They ...
of Melbost
Melbost () is a traditionally Gaelic-speaking village in Point on the east coast of the Isle of Lewis, in Scotland's north-west. It is largely a crofting township and is about east of Stornoway at the head of an isthmus connecting with the E ...
; his grandfather being a younger brother of Murdoch Mackenzie, 6th Laird
Laird () is a Scottish word for minor lord (or landlord) and is a designation that applies to an owner of a large, long-established Scotland, Scottish estate. In the traditional Scottish order of precedence, a laird ranked below a Baronage of ...
of Fairburn.
Educated at the same school as Colin Mackenzie
Colonel Colin Mackenzie (1754–8 May 1821) was a Scottish army officer in the British East India Company who later became the first Surveyor General of India. He was a collector of antiquities and an orientalist and an indologist. He sur ...
, the army officer and first Surveyor General of India
The Surveyor General of India is the Head of Department of Survey of India, a department under the Ministry of Science and Technology of the Government of India. The Surveyor General is also the most senior member of the Survey of India Service, ...
, he sailed to New York City with his father to join an uncle, John Mackenzie, in 1774, after his mother died in Scotland. In 1776, during the American War of Independence
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
, his father and uncle resumed their military duties and joined the King's Royal Regiment of New York
The King's Royal Regiment of New York, also known as Johnson's Royal Regiment of New York, King's Royal Regiment, King's Royal Yorkers, and Royal Greens, were one of the first Loyalist regiments, raised on June 19, 1776, in British Canada, durin ...
as lieutenants. By 1778, for his safety as a son of loyalists, young Mackenzie was sent, or went accompanied by two aunts, to Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
. By 1779 (a year before his father's death at Carleton Island
Carleton Island is located in the St Lawrence River in upstate New York. One of the Thousand Islands, it is part of the Town of Cape Vincent, in Jefferson County.
History
Originally held by the Iroquois, one of the first Europeans to take noti ...
), Mackenzie had a secured apprenticeship with Finlay, Gregory & Co., one of the most influential fur trading
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal ecosystem, boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals h ...
companies in Montreal, which was later administered by Archibald Norman McLeod
Major The Hon. Archibald Norman McLeod (17 March 1772 – after 1837) J.P., was a partner of the North West Company and a political figure in Lower Canada. In 1805, he built Fort Dunvegan. He was a member of the Beaver Club and represented Mo ...
. In 1787, the company merged with the North West Company
The North West Company was a Fur trade in Canada, Canadian fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in the regions that later became Western Canada a ...
.
Explorations
1789 Mackenzie River expedition to the Arctic Ocean
 On behalf of the North West Company, Mackenzie journeyed to
On behalf of the North West Company, Mackenzie journeyed to Lake Athabasca
Lake Athabasca ( ; French: ''lac Athabasca''; from Woods Cree: , " herethere are plants one after another") is in the north-west corner of Saskatchewan and the north-east corner of Alberta between 58° and 60° N in Canada. The lake is ...
where, in 1788, he was one of the founders of Fort Chipewyan
Fort Chipewyan , commonly referred to as Fort Chip, is an unincorporated hamlet in northern Alberta, Canada, within the Regional Municipality (RM) of Wood Buffalo.
History
Fort Chipewyan is one of the oldest European settlements in the Provi ...
. He had been sent to replace Peter Pond
Peter Pond (January 18, 1739 – 1807) was an American explorer, cartographer, merchant and soldier who was a founding member of the North West Company and the Beaver Club. Though he was born and died in Milford, Connecticut, most of his li ...
, a partner in the North West Company. From Pond, he learned that the First Nations
First nations are indigenous settlers or bands.
First Nations, first nations, or first peoples may also refer to:
Indigenous groups
*List of Indigenous peoples
*First Nations in Canada, Indigenous peoples of Canada who are neither Inuit nor Mé ...
people understood that the local rivers flowed to the north-west. Thinking that it would lead to Cook Inlet
Cook Inlet (; Sugpiaq language, Sugpiaq: ''Cungaaciq'') stretches from the Gulf of Alaska to Anchorage, Alaska, Anchorage in south-central Alaska. Cook Inlet branches into the Knik Arm and Turnagain Arm at its northern end, almost surrounding ...
in Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
, he set out by canoe on the river known to the local Dene
The Dene people () are an Indigenous group of First Nations who inhabit the northern boreal, subarctic and Arctic regions of Canada. The Dene speak Northern Athabaskan languages and it is the common Athabaskan word for "people". The term ...
First Nations people as the Dehcho (Mackenzie River), on 3 July 1789. On 14 July he reached the Arctic Ocean, rather than the Pacific. Later, in a letter to his cousin Roderick
Roderick, Rodrick or Roderic (Proto-Germanic , from , + , ) is a Germanic name, recorded from the 8th century onward.Förstemann, ''Altdeutsches Namenbuch'' (1856)740 Its Old High German forms are , , , , , ; in Gothic language ; in Old English ...
, he called the waterway "the River Disappointment," since the river did not prove to be the Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea lane between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, near the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Arctic Archipelago of Canada. The eastern route along the Arctic ...
, as he had hoped. In fact the story is probably apocryphal, as Mackenzie's own and contemporary records merely refer to it as the "Grand River." The river came to be known as the Mackenzie River
The Mackenzie River (French: ; Slavey language, Slavey: ' èh tʃʰò literally ''big river''; Inuvialuktun: ' uːkpɑk literally ''great river'') is a river in the Canadian Canadian boreal forest, boreal forest and tundra. It forms, ...
in his honour.
1792–93 Peace River expedition to the Pacific Ocean

 In 1791, Mackenzie returned to
In 1791, Mackenzie returned to Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
to study the new advance in the measurement of longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east- west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lett ...
. In the aftermath of the Nootka Crisis
The Nootka Crisis, also known as the Spanish Armament, was an international incident and political dispute between Spain and Great Britain triggered by a series of events revolving around sovereignty claims and rights of navigation and trade. It ...
with Spain, he returned to Canada in 1792, and set out to find a route to the Pacific. Accompanied by two native guides (one named Cancre), his cousin, Alexander MacKay, six Canadian voyageurs
Voyageurs (; ) were 18th- and 19th-century French and later French Canadians and others who transported furs by canoe at the peak of the North American fur trade. The emblematic meaning of the term applies to places (New France, including the ...
(Joseph Landry, Charles Ducette, François Beaulieu, Baptiste Bisson, Francois Courtois, Jacques Beauchamp), and a dog simply referred to as "our dog", Mackenzie left Fort Chipewyan
Fort Chipewyan , commonly referred to as Fort Chip, is an unincorporated hamlet in northern Alberta, Canada, within the Regional Municipality (RM) of Wood Buffalo.
History
Fort Chipewyan is one of the oldest European settlements in the Provi ...
on 10 October 1792, and travelled via the Pine River to the Peace River
The Peace River () is a river in Canada that originates in the Rocky Mountains of northern British Columbia and flows to the northeast through northern Alberta. The Peace River joins the Athabasca River in the Peace-Athabasca Delta to form the ...
. From there he travelled to a fork on the Peace River arriving 1 November where he and his cohorts built a fortification that they resided in over the winter. This later became known as Fort Fork
Fort Fork a North West Company (NWC) trading post on the Peace River, established in 1792. From 1 November 1792 to 9 May 1793, Alexander Mackenzie wintered there prior to his expedition to the Pacific Ocean. The fort was used until the NWC merged ...
.
Mackenzie left Fort Fork on 9 May 1793, following the route of the Peace River. He crossed the Great Divide and found the upper reaches of the Fraser River
The Fraser River () is the longest river within British Columbia, Canada, rising at Fraser Pass near Blackrock Mountain (Canada), Blackrock Mountain in the Rocky Mountains and flowing for , into the Strait of Georgia just south of the City of V ...
, but was warned by the local natives that the Fraser Canyon
The Fraser Canyon is a major landform of the Fraser River where it descends rapidly through narrow rock gorges in the Coast Mountains en route from the Interior Plateau of British Columbia to the Fraser Valley. Colloquially, the term "Fraser Ca ...
to the south was unnavigable and populated by belligerent tribes. He was instead directed to follow a grease trail by ascending the West Road River
The West Road River or Blackwater River or Tiyakoh is an important tributary of the Fraser River, flowing generally north-eastward from the northern slopes of the Ilgachuz Range and across the Fraser Plateau in the Chilcotin region of central Bri ...
, crossing over the Coast Mountains
The Coast Mountains () are a major mountain range in the Pacific Coast Ranges of western North America, extending from southwestern Yukon through the Alaska Panhandle and virtually all of the British Columbia Coast, Coast of British Columbia sout ...
and descending the Bella Coola River
The Bella Coola River is a major river on the Pacific slope of the Coast Mountains in southern British Columbia. The town of Bella Coola is at its mouth on North Bentinck Arm. Bella Coola Indian Reserve No. 1 is the location of the main communi ...
to the sea. He followed this advice and reached the Pacific coast on 20 July 1793, at Bella Coola, British Columbia
Bella Coola is an unincorporated community in the Bella Coola Valley of British Columbia, Canada. ''Bella Coola'' usually refers to the entire valley, encompassing the settlements of Bella Coola proper ("the townsite"), Lower Bella Coola, Ha ...
, on North Bentinck Arm
North Bentinck Arm is a short inlet about in length in the Central Coast region of British Columbia, Canada. It is an arm of Burke Channel and is linked via that waterway and Labouchere Channel to Dean Channel, which is one of the largest inlets ...
, an inlet
An inlet is a typically long and narrow indentation of a shoreline such as a small arm, cove, bay, sound, fjord, lagoon or marsh, that leads to an enclosed larger body of water such as a lake, estuary, gulf or marginal sea.
Overview
In ...
of the Pacific Ocean. Having done this, he had completed the first recorded transcontinental crossing of North America north of Mexico, 12 years before Lewis and Clark
Lewis may refer to:
Names
* Lewis (given name), including a list of people with the given name
* Lewis (surname), including a list of people with the surname
Music
* Lewis (musician), Canadian singer
* " Lewis (Mistreated)", a song by Radiohe ...
. He had unknowingly missed meeting George Vancouver
Captain (Royal Navy), Captain George Vancouver (; 22 June 1757 – 10 May 1798) was a Royal Navy officer and explorer best known for leading the Vancouver Expedition, which explored and charted North America's northwestern West Coast of the Uni ...
at Bella Coola by 48 days.
He had wanted to continue westward out of a desire to reach the open ocean, but was stopped by the hostility of the Heiltsuk people
The Heiltsuk , sometimes historically referred to as ''Bella Bella'', or ''Híɫzaqv'' are an Indigenous people of the Central Coast region in British Columbia, centred on the island community of Bella Bella. The government of the Heiltsuk pe ...
. Hemmed in by Heiltsuk war canoes, he wrote a message on a rock near the water's edge of Dean Channel
Dean Channel is the upper end of one of the longest inlets of the British Columbia Coast, from its head at the mouth of the Kimsquit River. The Dean River, one of the main rivers of the Coast Mountains, enters Dean Channel about below the hea ...
, using a reddish paint made of vermilion and bear grease, and turned back east. The painting read: "“Alexander Mackenzie, from Canada, by land, the twenty-second of July, one thousand seven hundred and ninety-three”" (at the time Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
was a name for the former French territory in what is now southern Quebec and Ontario). The words, partly abbreviated, were later inscribed permanently by (Captain) R.P. Bishop and his surveyors in 1923. The site is now Sir Alexander Mackenzie Provincial Park and is designated First Crossing of North America National Historic Site. In 2016, Mackenzie was named a National Historic Person
Persons of National Historic Significance (National Historic People) () are people designated by the Canadian government as being nationally significant in the history of the country. Designations are made by the Minister of the Environment on the ...
.
He returned the way he had come, arriving at Fort Chipewyan on Aug. 24. He spent the winter there working in the fur trade. The next year he returned to Montreal. Soon after, he travelled to the U.S. and to London. He returned to Montreal and became one of the leading partners of the North West Company. In 1799 he left the Company and travelled to London to lobby on behalf of the Canadian fur trade. In 1800 he returned to Canada and aided in the formation of the New North West Company (also known as the XY Company).
In his journal Mackenzie recorded the Carrier language
The Dakelh () or Carrier language is a Northern Athabaskan language. It is named after the Dakelh people, a First Nations people of the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada, for whom Carrier has been a common English name derived from F ...
for the first time.
Later life and family
In 1801 he returned to London and that year the journals of his exploratory journeys were publishe(They were later reprinted.) He then presented a detailed plan of his west coast project to the British government "Preliminaries to the Establishment of a Permanent British Fishery and Trade in Furs etc. on the Continent and West Coast of North America." The British government, at the time predicting conflict with Napoleon, took no action. (Later Simon Fraser (explorer), Simon Fraser and David Thompson worked to extend the Canadian fur trade and prevent U.S. incursion in what would be Canada.) Mackenzie was
knighted
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of a knighthood by a head of state (including the pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church, or the country, especially in a military capacity.
The concept of a knighthood ...
in 1802.
He returned to Canada, where as Sir Mackenzie, he was lionized. He was elected to the Legislature of Lower Canada. He served as member for Huntingdon County
Huntingdon is a market town in the Huntingdonshire district of Cambridgeshire, England. The town was given its town charter by King John in 1205. It was the county town of the historic county of Huntingdonshire. Oliver Cromwell was born there ...
from 1804 to 1808.
In 1812 Mackenzie, then aged 48, returned to Scotland, where he married 14-year-old Geddes Mackenzie, twin heiress of Avoch
Avoch harbour
Avoch ( ; from the – meaning mouth of the stream) is a harbour-village located on the south-east coast of the Black Isle, on the Moray Firth.
History Origins
Ormond Castle or ''Avoch Castle'' was a stronghold built on the s ...
. They had two sons and a daughter. Her grandfather, Captain John Mackenzie of Castle Leod (great-grandson of George Mackenzie, 2nd Earl of Seaforth
George Mackenzie, 2nd Earl of Seaforth (died 1651) was a Highland clan chief and Scottish nobleman, who played an equivocating role in Scotland in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms.
Origins
Mackenzie was the son of Kenneth Mackenzie, 1st Lord Mack ...
), purchased the estate of Avoch with money left to him by his first cousin and brother-in-law, Admiral George Geddes Mackenzie. Lady Mackenzie's father was a first cousin of the father of George Simpson, Governor of the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), originally the Governor and Company of Adventurers of England Trading Into Hudson’s Bay, is a Canadian holding company of department stores, and the oldest corporation in North America. It was the owner of the ...
. The Mackenzies lived alternately in Avoch and London.
He died in 1820 of Bright's disease
Bright's disease is a historical classification of kidney diseases that are described in modern medicine as acute or chronic nephritis. It was characterized by swelling and the presence of albumin in the urine. It was frequently accompanied ...
, at about the age of 56 (his date of birth is unknown). He is buried at Avoch on the Black Isle
The Black Isle (, ) is a peninsula within Ross and Cromarty, in the Scottish Highlands. It includes the towns of Cromarty and Fortrose, and the villages of Culbokie, Resolis, Jemimaville, Rosemarkie, Avoch, Munlochy, Tore, and North Kesso ...
.
Legacy
TheMackenzie River
The Mackenzie River (French: ; Slavey language, Slavey: ' èh tʃʰò literally ''big river''; Inuvialuktun: ' uːkpɑk literally ''great river'') is a river in the Canadian Canadian boreal forest, boreal forest and tundra. It forms, ...
and Mount Sir Alexander
Mount Sir Alexander, is a , ultra-prominent mountain in the Sir Alexander Area of the Continental Ranges (sometimes referred to as the Northern Continental Ranges), Canadian Rockies located in British Columbia.
Located within Kakwa Provincial ...
are named for him, as is Mackenzie Bay
MacKenzie Bay is a relatively small embayment of the western extremity of the Amery Ice Shelf, Antarctica, about northeast of Foley Promontory. On 10 February 1931 the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) sigh ...
, and the municipality of Mackenzie, British Columbia
Mackenzie is a district municipality within the Fraser-Fort George Regional District in central British Columbia, Canada. The community is located at the south end of Williston Lake. The townsite, established by Alexandra Forest Industries (acq ...
.
There are a number of schools in Canada named after him, such as Sir Alexander Mackenzie Senior Public School
The Toronto District School Board (TDSB), formerly known as English-language Public District School Board No. 12 prior to 1999, is the English-language public-secular school board for Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The minority public-secular franco ...
in Toronto, Sir Alexander Mackenzie Elementary School in Vancouver, and Sir Alexander Mackenzie Elementary School in St. Albert. Also Sir Alexander Mackenzie School in the Bella Coola Valley, BC.
He is referenced in the 1981 folk
Folk or Folks may refer to:
Sociology
*Nation
*People
* Folklore
** Folk art
** Folk dance
** Folk hero
** Folk horror
** Folk music
*** Folk metal
*** Folk punk
*** Folk rock
** Folk religion
* Folk taxonomy
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Fo ...
song "Northwest Passage" by Stan Rogers
Stanley Allison Rogers (November 29, 1949 – June 2, 1983) was a Canadian folk musician and songwriter who sang traditional-sounding songs frequently inspired by Canadian history and the working people's daily lives, especially from the fishin ...
.
The Alexander Mackenzie rose (Explorer Series), developed in 1985 by Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada
Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada (AAFC; sometimes Ag-Canada; )''Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada'' is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of Agriculture and Agri-Food (). is the Structure of the Can ...
, was named in his honour.
Between 1989 and 1993, the Mackenzie Bicentennial Sea-to-Sea Expeditions of Lakehead University
Lakehead University is a public research university with campuses in Thunder Bay and Orillia, Ontario, Canada. Lakehead University, shortened to 'Lakehead U', is non-denominational and provincially supported. It has undergraduate programs, gradua ...
attempted a segmented re-enactment of the journey between Montreal and Bella Coola, British Columbia
Bella Coola is an unincorporated community in the Bella Coola Valley of British Columbia, Canada. ''Bella Coola'' usually refers to the entire valley, encompassing the settlements of Bella Coola proper ("the townsite"), Lower Bella Coola, Ha ...
, but was unable to complete the final overland Grease Trail when its First Nation owners refused permission.
The legend of Mackenzie is a running theme in Boundary Waters (2025) by Tristan Hughes.Hughes, Tristan (2025). ''Boundary Waters''. Parthian Books. ISBN 9781914595844.
References
Bibliography
* * * Wade, Mark S. (1927). "Mackenzie of Canada". William Blackwood & Sons Ltd., Edinburgh & London 1927complete online transcription
*
External links
* * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Mackenzie, Alexander 18th-century British explorers 1760s births 1820 deaths Burials in Highland (council area) Deaths from nephritis Explorers of Canada British explorers of the Arctic Knights Bachelor Scottish knights Members of the Legislative Assembly of Lower Canada North West Company North West Company people People from Stornoway Persons of National Historic Significance (Canada) Scottish explorers of North America