Single Currency on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
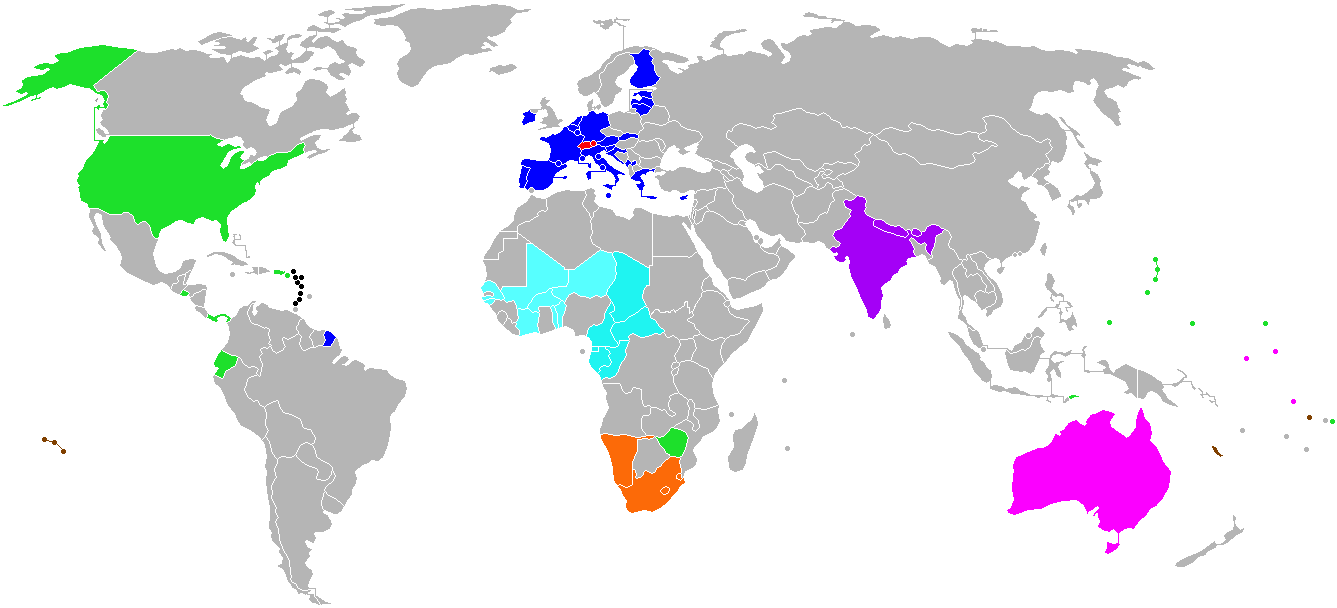 A currency union (also known as monetary union) is an intergovernmental agreement that involves two or more
A currency union (also known as monetary union) is an intergovernmental agreement that involves two or more
West Africa opts for currency unionEconomist- Antipodean currencies (Australia and New Zealand)Reasons for the collapse of the Rouble ZoneOECD Development Centre – the Rand Zone
{{Authority control Currency, Union Currency unions, International macroeconomics Proposed currencies Economic integration
states
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
sharing the same currency
A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a ''system of money'' in common use within a specific envi ...
. These states may not necessarily have any further integration (such as an economic and monetary union, which would have, in addition, a customs union
A customs union is generally defined as a type of trade bloc which is composed of a free trade area with a common external tariff.GATTArticle 24 s. 8 (a)
Customs unions are established through trade pacts where the participant countries set u ...
and a single market).
There are three types of currency unions:
* ''Informal'' – unilateral adoption of a foreign currency.
* ''Formal'' – adoption of foreign currency by virtue of bilateral or multilateral agreement with the monetary authority
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the monet ...
, sometimes supplemented by issue of local currency in currency peg regime.
* ''Formal with common policy'' – establishment by multiple countries of a common monetary policy
Monetary policy is the policy adopted by the monetary authority of a nation to affect monetary and other financial conditions to accomplish broader objectives like high employment and price stability (normally interpreted as a low and stable rat ...
and monetary authority
A central bank, reserve bank, national bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages the monetary policy of a country or monetary union. In contrast to a commercial bank, a central bank possesses a monopoly on increasing the monet ...
for their common currency.
The theory of the optimal currency area addresses the question of how to determine what geographical regions should share a currency in order to maximize economic efficiency.
Advantages and disadvantages
Implementing a new currency in a country is always a controversial topic because it has both many advantages and disadvantages. New currency has different impacts on businesses and individuals, which creates more points of view on the usefulness of currency unions. As a consequence, governmental institutions often struggle when they try to implement a new currency, for example by entering a currency union.Advantages
*A currency union helps its members strengthen their competitiveness on a global scale and eliminate the exchange rate risk. *Transactions among member states can be processed faster and their costs decrease since fees to banks are lower. *Prices are more transparent and so are easier to compare, which enables fair competition. *The probability of a monetary crisis is lower. The more countries there are in the currency union, the more they are resistant to crisis.Disadvantages
*The member states lose their sovereignty in monetary policy decisions. There is usually an institution (such as a central bank) that takes care of the monetary policymaking in the whole currency union. *The risk of asymmetric "shocks" may occur. The criteria set by the currency union are never perfect, so a group of countries might be substantially worse off while the others are booming. *Implementing a new currency causes high financial costs. Businesses and also single persons have to adapt to the new currency in their country, which includes costs for the businesses to prepare their management, employees, and they also need to inform their clients and process plenty of new data. *Unlimited capital movement may cause moving most resources to the more productive regions at the expense of the less productive regions. The more productive regions tend to attract more capital in goods and services, which might avoid the less productive regions.Convergence and divergence
Convergence in terms ofmacroeconomics
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that deals with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. This includes regional, national, and global economies. Macroeconomists study topics such as output (econ ...
means that countries have a similar economic behaviour (similar inflation rates and economic growth
In economics, economic growth is an increase in the quantity and quality of the economic goods and Service (economics), services that a society Production (economics), produces. It can be measured as the increase in the inflation-adjusted Outp ...
).
It is easier to form a currency union for countries with more convergence as these countries have the same or at least very similar goals. The European Monetary Union (EMU) is a contemporary model for forming currency unions. Membership in the EMU requires that countries follow a strictly defined set of criteria (the member states are required to have a specific rate of inflation, government deficit, government debt
A country's gross government debt (also called public debt or sovereign debt) is the financial liabilities of the government sector. Changes in government debt over time reflect primarily borrowing due to past government deficits. A deficit occu ...
, long-term interest rates
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, ...
and exchange rate
In finance, an exchange rate is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency. Currencies are most commonly national currencies, but may be sub-national as in the case of Hong Kong or supra-national as in the case of ...
). Many other unions have adopted the view that convergence is necessary, so they now follow similar rules to aim the same direction.
Divergence is the exact opposite of convergence. Countries with different goals are very difficult to integrate in a single currency union. Their economic behaviour is completely different, which may lead to disagreements. Divergence is therefore not optimal for forming a currency union.
History
The first currency unions were established in the 19th century. The GermanZollverein
The (), or German Customs Union, was a coalition of States of the German Confederation, German states formed to manage tariffs and economic policies within their territories. Organized by the 1833 treaties, it formally started on 1 January 1 ...
came into existence in 1834, and by 1866, it included most of the German states. The fragmented states of the German Confederation agreed on common policies to increase trade and political unity.
The Latin Monetary Union
The Monetary Convention of 23 December 1865 was a unified system of coinage that provided a degree of monetary integration among several European countries, initially Belgium, France, Italy and Switzerland, at a time when the circulation of bank ...
, comprising France, Belgium, Italy, Switzerland, and Greece, existed between 1865 and 1927, with coinage made of gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
and silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
. Coins of each country were legal tender and freely interchangeable across the area. The union's success made other states join informally.
The Scandinavian Monetary Union, comprising Sweden, Denmark, and Norway, existed between 1873 and 1905 and used a currency based on gold. The system was dissolved by Sweden in 1924.
A currency union among the British colonies and protectorates in Southeast Asia, namely the Federation of Malaya, North Borneo, Sarawak, Singapore and Brunei was established in 1952. The Malaya and British Borneo dollar, the common currency for circulation was issued by the Board of Commissioners of Currency, Malaya and British Borneo from 1953 until 1967. Following the cessation of the common currency arrangement, Malaysia (the combination of Federation of Malaya, North Borneo, Sarawak), Singapore and Brunei began issuing their own currencies. Contemporarily, a currency reunion of these countries might still be feasible based on the findings of economic convergence.
List of currency unions
Existing
Note: Every customs and monetary union and economic and monetary union also has a currency union. is theoretically in a currency union with four blocs as the South African rand,Botswana pula
The Pula (also known as the Botswana dollar) is the currency of Botswana. It has the ISO 4217 code ''BWP'' and is subdivided into 100 ''thebe''. ''Pula'' literally means "rain" in Setswana, because rain is very scarce in Botswana—home to much o ...
, British pound and US dollar freely circulate. The US Dollar was, until 2016, official tender.
Additionally, the autonomous and dependent territories, such as some of the EU member state special territories, are sometimes treated as separate customs territory
A customs territory is a territory with uniform customs regulations and there are no internal customs or similar taxes within the territory. Customs territories may fall into several types:
* A sovereign state, including a federation
* A trade bloc ...
from their mainland state or have varying arrangements of formal or de facto customs union
A customs union is generally defined as a type of trade bloc which is composed of a free trade area with a common external tariff.GATTArticle 24 s. 8 (a)
Customs unions are established through trade pacts where the participant countries set u ...
, common market and currency union (or combinations thereof) with the mainland and in regards to third countries through the trade pacts signed by the mainland state.
Currency union in Europe
The European currency union is a part of theEconomic and Monetary Union of the European Union
The economic and monetary union (EMU) of the European Union is a group of policies aimed at converging the economies of member states of the European Union at three stages.
There are three stages of the EMU, each of which consists of progressi ...
(EMU). EMU was formed during the second half of the 20th century after historic agreements, such as Treaty of Paris (1951)
The Treaty of Paris (formally the Treaty establishing the European Coal and Steel Community) was signed on 18 April 1951 between France, Italy, West Germany, Belgium, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands, establishing the European Coal and Steel C ...
, Maastricht Treaty
The Treaty on European Union, commonly known as the Maastricht Treaty, is the foundation treaty of the European Union (EU). Concluded in 1992 between the then-twelve Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Communities, ...
(1992). In 2002, the euro
The euro (currency symbol, symbol: euro sign, €; ISO 4217, currency code: EUR) is the official currency of 20 of the Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union. This group of states is officially known as the ...
, a single European currency, was adopted by 12 member states. Currently, the Eurozone
The euro area, commonly called the eurozone (EZ), is a Monetary union, currency union of 20 Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (Euro sign, €) as their primary currency ...
has 20 member states. The other members of the European Union are required to adopt the euro as their currency (except for Denmark, which has been given the right to opt out), but there has not been a specific date set. The main independent institution responsible for stability of the euro is the European Central Bank
The European Central Bank (ECB) is the central component of the Eurosystem and the European System of Central Banks (ESCB) as well as one of seven institutions of the European Union. It is one of the world's Big Four (banking)#International ...
(ECB). The Eurosystem
The Eurosystem is the monetary authority of the eurozone, the collective of European Union member states that have adopted the euro as their sole official currency. The European Central Bank (ECB) has, under Article 16 of its Statute,
groups together the ECB and the national central banks (NCBs) of the Member States whose currency is the euro. The European System of Central Banks
The European System of Central Banks (ESCB) is an institution that comprises the European Central Bank (ECB) and the national central banks (NCBs) of all 27 member states of the European Union (EU). Its objective is to ensure price stability ...
(ESCB) is made up of the ECB and the national central banks of all Member States of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
(EU), regardless of whether or not they have adopted the euro. The Governing Board consists of the Executive Committee of the ECB and the governors of individual national banks, and determines the monetary policy, as well as short-term monetary objectives, key interest rates and the extent of monetary reserves.
Planned
Disbanded
* betweenBahrain
Bahrain, officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, is an island country in West Asia. Situated on the Persian Gulf, it comprises a small archipelago of 50 natural islands and an additional 33 artificial islands, centered on Bahrain Island, which mak ...
and Abu Dhabi
Abu Dhabi is the capital city of the United Arab Emirates. The city is the seat of the Abu Dhabi Central Capital District, the capital city of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, and the UAE's List of cities in the United Arab Emirates, second-most popu ...
using the Bahraini dinar
* between Bahrain
Bahrain, officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, is an island country in West Asia. Situated on the Persian Gulf, it comprises a small archipelago of 50 natural islands and an additional 33 artificial islands, centered on Bahrain Island, which mak ...
, Kuwait
Kuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is a country in West Asia and the geopolitical region known as the Middle East. It is situated in the northern edge of the Arabian Peninsula at the head of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Kuwait ...
, Oman
Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline ...
, Qatar
Qatar, officially the State of Qatar, is a country in West Asia. It occupies the Geography of Qatar, Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it shares Qatar–Saudi Arabia border, its sole land b ...
and the Trucial States
The Trucial States, also known as the Trucial Coast, the Trucial Sheikhdoms, or Trucial Oman, was a group of tribal confederations to the south of the Persian Gulf (southeastern Arabia) whose leaders had signed protective treaties, or truce ...
, using the Gulf rupee from 1959 until 1966
* between Aden
Aden () is a port city located in Yemen in the southern part of the Arabian peninsula, on the north coast of the Gulf of Aden, positioned near the eastern approach to the Red Sea. It is situated approximately 170 km (110 mi) east of ...
, , Bahrain
Bahrain, officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, is an island country in West Asia. Situated on the Persian Gulf, it comprises a small archipelago of 50 natural islands and an additional 33 artificial islands, centered on Bahrain Island, which mak ...
, Kenya
Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country located in East Africa. With an estimated population of more than 52.4 million as of mid-2024, Kenya is the 27th-most-populous country in the world and the 7th most populous in Africa. ...
, Kuwait
Kuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is a country in West Asia and the geopolitical region known as the Middle East. It is situated in the northern edge of the Arabian Peninsula at the head of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Kuwait ...
, Oman
Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline ...
, Qatar
Qatar, officially the State of Qatar, is a country in West Asia. It occupies the Geography of Qatar, Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it shares Qatar–Saudi Arabia border, its sole land b ...
, British Somaliland
British Somaliland, officially the Somaliland Protectorate (), was a protectorate of the United Kingdom in modern Somaliland. It was bordered by Italian Somalia, French Somali Coast and Ethiopian Empire, Abyssinia (Italian Ethiopia from 1936 ...
, the Trucial States
The Trucial States, also known as the Trucial Coast, the Trucial Sheikhdoms, or Trucial Oman, was a group of tribal confederations to the south of the Persian Gulf (southeastern Arabia) whose leaders had signed protective treaties, or truce ...
, Uganda
Uganda, officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the ...
, Zanzibar
Zanzibar is a Tanzanian archipelago off the coast of East Africa. It is located in the Indian Ocean, and consists of many small Island, islands and two large ones: Unguja (the main island, referred to informally as Zanzibar) and Pemba Island. ...
and British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
(later independent India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
) using the Indian rupee
The Indian rupee (symbol: ₹; code: INR) is the official currency of India. The rupee is subdivided into 100 '' paise'' (Hindi plural; singular: ''paisa''). The issuance of the currency is controlled by the Reserve Bank of India. The Reserve ...
until 1974
* between Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
and the Grand-Duchy of Luxemburg ( Belgium-Luxembourg Economic Union) using the Belgian/Luxembourgish franc from 1921 to the Euro
* between British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
and the Straits Settlements
The Straits Settlements () were a group of British territories located in Southeast Asia. Originally established in 1826 as part of the territories controlled by the British East India Company, the Straits Settlements came under control of the ...
(1837–1867) using the Indian rupee
The Indian rupee (symbol: ₹; code: INR) is the official currency of India. The rupee is subdivided into 100 '' paise'' (Hindi plural; singular: ''paisa''). The issuance of the currency is controlled by the Reserve Bank of India. The Reserve ...
* between Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the south ...
and Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
(briefly from January 1, 1993 to February 8, 1993) using the Czechoslovak koruna
* between Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
and Eritrea
Eritrea, officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa, with its capital and largest city being Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia in the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, south, Sudan in the west, and Dj ...
using the Ethiopian birr
* between France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, Monaco
Monaco, officially the Principality of Monaco, is a Sovereign state, sovereign city-state and European microstates, microstate on the French Riviera a few kilometres west of the Regions of Italy, Italian region of Liguria, in Western Europe, ...
, and Andorra
Andorra, officially the Principality of Andorra, is a Sovereignty, sovereign landlocked country on the Iberian Peninsula, in the eastern Pyrenees in Southwestern Europe, Andorra–France border, bordered by France to the north and Spain to A ...
using the French franc
The franc (; , ; currency sign, sign: F or Fr), also commonly distinguished as the (FF), was a currency of France. Between 1360 and 1641, it was the name of coins worth 1 livre tournois and it remained in common parlance as a term for this amoun ...
*between Austria-Hungary and Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (, ; ; ), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein ( ), is a Landlocked country#Doubly landlocked, doubly landlocked Swiss Standard German, German-speaking microstate in the Central European Alps, between Austria in the east ...
using the Austro-Hungarian krone
* between the Eastern Caribbean
The Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS; French: ''Organisation des États de la Caraïbe orientale'', OECO) is an inter-governmental organisation dedicated to economic harmonisation and integration, protection of human and legal ...
, Jamaica
Jamaica is an island country in the Caribbean Sea and the West Indies. At , it is the third-largest island—after Cuba and Hispaniola—of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean. Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, west of Hispaniola (the is ...
, Barbados
Barbados, officially the Republic of Barbados, is an island country in the Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies and the easternmost island of the Caribbean region. It lies on the boundary of the South American ...
, Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago, officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean, comprising the main islands of Trinidad and Tobago, along with several List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, smaller i ...
and British Guiana
British Guiana was a British colony, part of the mainland British West Indies. It was located on the northern coast of South America. Since 1966 it has been known as the independent nation of Guyana.
The first known Europeans to encounter Guia ...
using the British West Indies dollar
The British West Indies dollar (BWI$) was the currency of British Guiana and the Eastern Caribbean territories of the British West Indies from 1949 to 1965, when it was largely replaced by the East Caribbean dollar, and was one of the currencies u ...
* between the Eastern Caribbean
The Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS; French: ''Organisation des États de la Caraïbe orientale'', OECO) is an inter-governmental organisation dedicated to economic harmonisation and integration, protection of human and legal ...
, Barbados
Barbados, officially the Republic of Barbados, is an island country in the Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies and the easternmost island of the Caribbean region. It lies on the boundary of the South American ...
, Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago, officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean, comprising the main islands of Trinidad and Tobago, along with several List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, smaller i ...
and British Guiana
British Guiana was a British colony, part of the mainland British West Indies. It was located on the northern coast of South America. Since 1966 it has been known as the independent nation of Guyana.
The first known Europeans to encounter Guia ...
using the Eastern Caribbean dollar
The Eastern Caribbean dollar (currency symbol, symbol: EC$; ISO 4217, code: XCD) is the currency of all seven full members and one associate member of the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS). The successor to the British West Indies d ...
* between Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, Vatican City
Vatican City, officially the Vatican City State (; ), is a Landlocked country, landlocked sovereign state and city-state; it is enclaved within Rome, the capital city of Italy and Bishop of Rome, seat of the Catholic Church. It became inde ...
, and San Marino
San Marino, officially the Republic of San Marino, is a landlocked country in Southern Europe, completely surrounded by Italy. Located on the northeastern slopes of the Apennine Mountains, it is the larger of two European microstates, microsta ...
using the Italian lira
The lira ( , ; : lire, , ) was the currency of Italy between 1861 and 2002. It was introduced by the Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy in 1807 at par with the French franc, and was subsequently adopted by the different s ...
* between Jamaica
Jamaica is an island country in the Caribbean Sea and the West Indies. At , it is the third-largest island—after Cuba and Hispaniola—of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean. Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, west of Hispaniola (the is ...
and the Cayman Islands
The Cayman Islands () is a self-governing British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory, and the largest by population. The territory comprises the three islands of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, which are located so ...
using the Jamaican pound and later Jamaican dollar
* between Kenya
Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country located in East Africa. With an estimated population of more than 52.4 million as of mid-2024, Kenya is the 27th-most-populous country in the world and the 7th most populous in Africa. ...
, Uganda
Uganda, officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the ...
, and Zanzibar
Zanzibar is a Tanzanian archipelago off the coast of East Africa. It is located in the Indian Ocean, and consists of many small Island, islands and two large ones: Unguja (the main island, referred to informally as Zanzibar) and Pemba Island. ...
using the East African rupee
* between Kenya
Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country located in East Africa. With an estimated population of more than 52.4 million as of mid-2024, Kenya is the 27th-most-populous country in the world and the 7th most populous in Africa. ...
, Uganda
Uganda, officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the ...
, and Zanzibar
Zanzibar is a Tanzanian archipelago off the coast of East Africa. It is located in the Indian Ocean, and consists of many small Island, islands and two large ones: Unguja (the main island, referred to informally as Zanzibar) and Pemba Island. ...
(and later ) using the East African florin
* between Kenya
Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country located in East Africa. With an estimated population of more than 52.4 million as of mid-2024, Kenya is the 27th-most-populous country in the world and the 7th most populous in Africa. ...
, and Zanzibar
Zanzibar is a Tanzanian archipelago off the coast of East Africa. It is located in the Indian Ocean, and consists of many small Island, islands and two large ones: Unguja (the main island, referred to informally as Zanzibar) and Pemba Island. ...
(later merged as Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t ...
), Uganda
Uganda, officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the ...
, South Arabia
South Arabia (), or Greater Yemen, is a historical region that consists of the southern region of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia, mainly centered in what is now the Republic of Yemen, yet it has also historically included Najran, Jazan, ...
, British Somaliland
British Somaliland, officially the Somaliland Protectorate (), was a protectorate of the United Kingdom in modern Somaliland. It was bordered by Italian Somalia, French Somali Coast and Ethiopian Empire, Abyssinia (Italian Ethiopia from 1936 ...
and Italian Somaliland
Italian Somaliland (; ; ) was a protectorate and later colony of the Kingdom of Italy in present-day Somalia, which was ruled in the 19th century by the Sultanate of Hobyo and the Majeerteen Sultanate in the north, and by the Hiraab Imamate and ...
using the East African shilling
The East African shilling was the Pound sterling, sterling unit of account in British Empire, British-controlled areas of East Africa from 1921 until 1969. It was issued by the East African Currency Board. It is also the proposed name for a com ...
* Latin Monetary Union
The Monetary Convention of 23 December 1865 was a unified system of coinage that provided a degree of monetary integration among several European countries, initially Belgium, France, Italy and Switzerland, at a time when the circulation of bank ...
(1865–1927), initially between France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
and Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
, and later involving Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
, Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
, and other countries.
* between Liberia
Liberia, officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to Guinea–Liberia border, its north, Ivory Coast to Ivory Coast–Lib ...
and the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
using the United States dollar
The United States dollar (Currency symbol, symbol: Dollar sign, $; ISO 4217, currency code: USD) is the official currency of the United States and International use of the U.S. dollar, several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introdu ...
* between Mauritius
Mauritius, officially the Republic of Mauritius, is an island country in the Indian Ocean, about off the southeastern coast of East Africa, east of Madagascar. It includes the main island (also called Mauritius), as well as Rodrigues, Ag ...
and Seychelles
Seychelles (, ; ), officially the Republic of Seychelles (; Seychellois Creole: ), is an island country and archipelagic state consisting of 155 islands (as per the Constitution) in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city, Victoria, ...
using the Mauritian rupee
The Mauritian rupee (Currency symbol, sign: Re (singular) and Rs (plural); ISO 4217, ISO code: MUR; ) is the currency of Mauritius. One rupee is subdivided into 100 cents. Several other currencies are also called rupee.
Coins
In 1877, coins for ...
* between Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
, the Gambia
The Gambia, officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. Geographically, The Gambia is the List of African countries by area, smallest country in continental Africa; it is surrounded by Senegal on all sides except for ...
, Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone, officially the Republic of Sierra Leone, is a country on the southwest coast of West Africa. It is bordered to the southeast by Liberia and by Guinea to the north. Sierra Leone's land area is . It has a tropical climate and envi ...
, the Gold Coast and Liberia
Liberia, officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the West African coast. It is bordered by Sierra Leone to Liberia–Sierra Leone border, its northwest, Guinea to Guinea–Liberia border, its north, Ivory Coast to Ivory Coast–Lib ...
using the British West African pound
The pound was the currency of British West Africa, a group of British colonies, protectorates and mandate territories. It was equal to one pound sterling and was similarly subdivided into 20 shillings, each of 12 pence. It was issued from 1912 ...
* between Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
and the North German states (1838–1857) using the North German thaler
The North German thaler was a currency used by several states of Northern Germany from 1690 to 1873, first under the Holy Roman Empire, then by the German Confederation. Originally equal to the Reichsthaler specie or silver coin from 1566 until t ...
* between Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
and the former Soviet republics (1991–1993) using the Soviet ruble
The ruble or rouble (; rus, рубль, r=rubl', p=rublʲ) was the currency of the Soviet Union. It was introduced in 1922 and replaced the Russian ruble#Imperial ruble (1704-1922), Imperial Russian ruble. One ruble was divided into 100 kopecks ...
* between Qatar
Qatar, officially the State of Qatar, is a country in West Asia. It occupies the Geography of Qatar, Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it shares Qatar–Saudi Arabia border, its sole land b ...
and all the emirates of the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE), or simply the Emirates, is a country in West Asia, in the Middle East, at the eastern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is a Federal monarchy, federal elective monarchy made up of Emirates of the United Arab E ...
, except Abu Dhabi
Abu Dhabi is the capital city of the United Arab Emirates. The city is the seat of the Abu Dhabi Central Capital District, the capital city of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, and the UAE's List of cities in the United Arab Emirates, second-most popu ...
using the Qatari and Dubai riyal
* between Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
and Qatar
Qatar, officially the State of Qatar, is a country in West Asia. It occupies the Geography of Qatar, Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it shares Qatar–Saudi Arabia border, its sole land b ...
using the Saudi riyal
* between Western Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa and known until 1997 as Western Samoa, is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania, in the South Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu), two smaller, inhabit ...
and New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
using the New Zealand pound
* Scandinavian Monetary Union (1870s until 1924), between Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
and Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
* between the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands, also known simply as the Solomons,John Prados, ''Islands of Destiny'', Dutton Caliber, 2012, p,20 and passim is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 1000 smaller islands in Melanesia, part of Oceania, t ...
, Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n ...
and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
using the Australian dollar
The Australian dollar (currency sign, sign: $; ISO 4217, code: AUD; also abbreviated A$ or sometimes AU$ to distinguish it from other dollar, dollar-denominated currencies; and also referred to as the dollar or Aussie dollar) is the official ...
*between Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, Papua, New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is ...
, Nauru
Nauru, officially the Republic of Nauru, formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country and microstate in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies within the Micronesia subregion of Oceania, with its nearest neighbour being Banaba (part of ...
, the Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands, also known simply as the Solomons,John Prados, ''Islands of Destiny'', Dutton Caliber, 2012, p,20 and passim is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 1000 smaller islands in Melanesia, part of Oceania, t ...
, and the Gilbert and Ellice Islands
The Gilbert and Ellice Islands (GEIC as a colony) in the Pacific Ocean was part of the British Empire from 1892 to 1976. It was a British protectorate, protectorate from 1892 to 12 January 1916, and then a crown colony, colony until 1 January 1 ...
using the Australian pound
The pound (sign: £, £A for distinction) was the currency of Australia from 1910 until 14 February 1966, when it was replaced by the Australian dollar. Like other £sd currencies, it was subdivided into 20 shillings (denoted by the symbol s o ...
* between Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
, Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in southern Germany. In earlier times it was considered to be on both sides of the Upper Rhine, but since the Napoleonic Wars, it has been considered only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Ba ...
, Württemberg
Württemberg ( ; ) is a historical German territory roughly corresponding to the cultural and linguistic region of Swabia. The main town of the region is Stuttgart.
Together with Baden and Province of Hohenzollern, Hohenzollern, two other histo ...
, Frankfurt
Frankfurt am Main () is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Hesse. Its 773,068 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the List of cities in Germany by population, fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located in the forela ...
, and Hohenzollern using the South German guilder
* between Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
and Andorra
Andorra, officially the Principality of Andorra, is a Sovereignty, sovereign landlocked country on the Iberian Peninsula, in the eastern Pyrenees in Southwestern Europe, Andorra–France border, bordered by France to the north and Spain to A ...
using the Spanish peseta
* between Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago, officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean, comprising the main islands of Trinidad and Tobago, along with several List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, smaller i ...
and Grenada
Grenada is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean Sea. The southernmost of the Windward Islands, Grenada is directly south of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and about north of Trinidad and Tobago, Trinidad and the So ...
using the Trinidad and Tobago dollar
The Trinidad and Tobago dollar ( currency code TTD) is the currency of Trinidad and Tobago. It is normally abbreviated with the dollar sign $, or alternatively TT$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies. It is subdivided int ...
* between Brunei
Brunei, officially Brunei Darussalam, is a country in Southeast Asia, situated on the northern coast of the island of Borneo. Apart from its coastline on the South China Sea, it is completely surrounded by the Malaysian state of Sarawak, with ...
, Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
, and Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
(1953–1967) using the Malaya and British Borneo dollar
The Malaya and British Borneo dollar (; ) was the currency of Federation of Malaya, Malaya, Colony of Singapore, Singapore, Crown Colony of Sarawak, Sarawak, Crown Colony of North Borneo, North Borneo, Brunei and the Riau archipelago from 1953 ...
* between Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
, Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
, Guangzhouwan
The Leased Territory of Guangzhouwan, officially the and historically known in English as Kwangchowan or Kwangchow Wan, was a coastal territory of Zhanjiang, China leased to France and administered by French Indochina. The capital of the t ...
, Annam, Tonkin
Tonkin, also spelled Tongkin, Tonquin or Tongking, is an exonym referring to the northern region of Vietnam. During the 17th and 18th centuries, this term referred to the domain '' Đàng Ngoài'' under Trịnh lords' control, including both the ...
, and Cochinchina
Cochinchina or Cochin-China (, ; ; ; ; ) is a historical exonym and endonym, exonym for part of Vietnam, depending on the contexts, usually for Southern Vietnam. Sometimes it referred to the whole of Vietnam, but it was commonly used to refer t ...
(later Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
) between 1885 and 1952 using the French Indochinese piastre
* between , South West Africa
South West Africa was a territory under Union of South Africa, South African administration from 1915 to 1990. Renamed ''Namibia'' by the United Nations in 1968, Independence of Namibia, it became independent under this name on 21 March 1990. ...
, and Bechuanaland (later independent Botswana
Botswana, officially the Republic of Botswana, is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory part of the Kalahari Desert. It is bordered by South Africa to the sou ...
) using the South African rand
* between Egypt, Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, and Mandatory Palestine (until 1926) using the Egyptian pound
* between West Germany and East Germany between 1 July 1990 and 3 October 1990, as part of a temporary, so-called "Monetary, Economic and Social Union" prior to German reunification.
* between what ultimately became the Republic of Ireland and the United Kingdom, between 1928 and 1979. The Irish Pound was held at exactly the same value as Sterling for this period, although it was not accepted for payments in the UK.
* Yen Bloc (between 1905 and 1945), between the Empire of Japan, the Korean Empire, Manchukuo, Mengjiang, the Wang Jingwei regime, and Japanese-occupied Southeast Asia prior to and during World War II.
Never materialized
* proposed Pan-American monetary union – abandoned in the form proposed by Argentina * proposed monetary union between the United Kingdom andNorway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
using the pound sterling during the late 1940s and early 1950s
* proposed gold-backed, pan-African monetary union put forward by Muammar Gaddafi prior to his death
See also
* List of circulating fixed exchange rate currencies, List of pegged currencies * North American Currency Union (Amero)Not currently on any political agenda, based mostly off conspiracy theories.References
Further reading
* Nicola Acocella, Acocella, N. and Di Bartolomeo, G. and Tirelli, P. [2007], ‘''Monetary conservatism and fiscal coordination in a monetary union''’, in: ‘''Economics Letters''’, 94(1): 56–63. *External links
West Africa opts for currency union
{{Authority control Currency, Union Currency unions, International macroeconomics Proposed currencies Economic integration