Sima (architecture) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

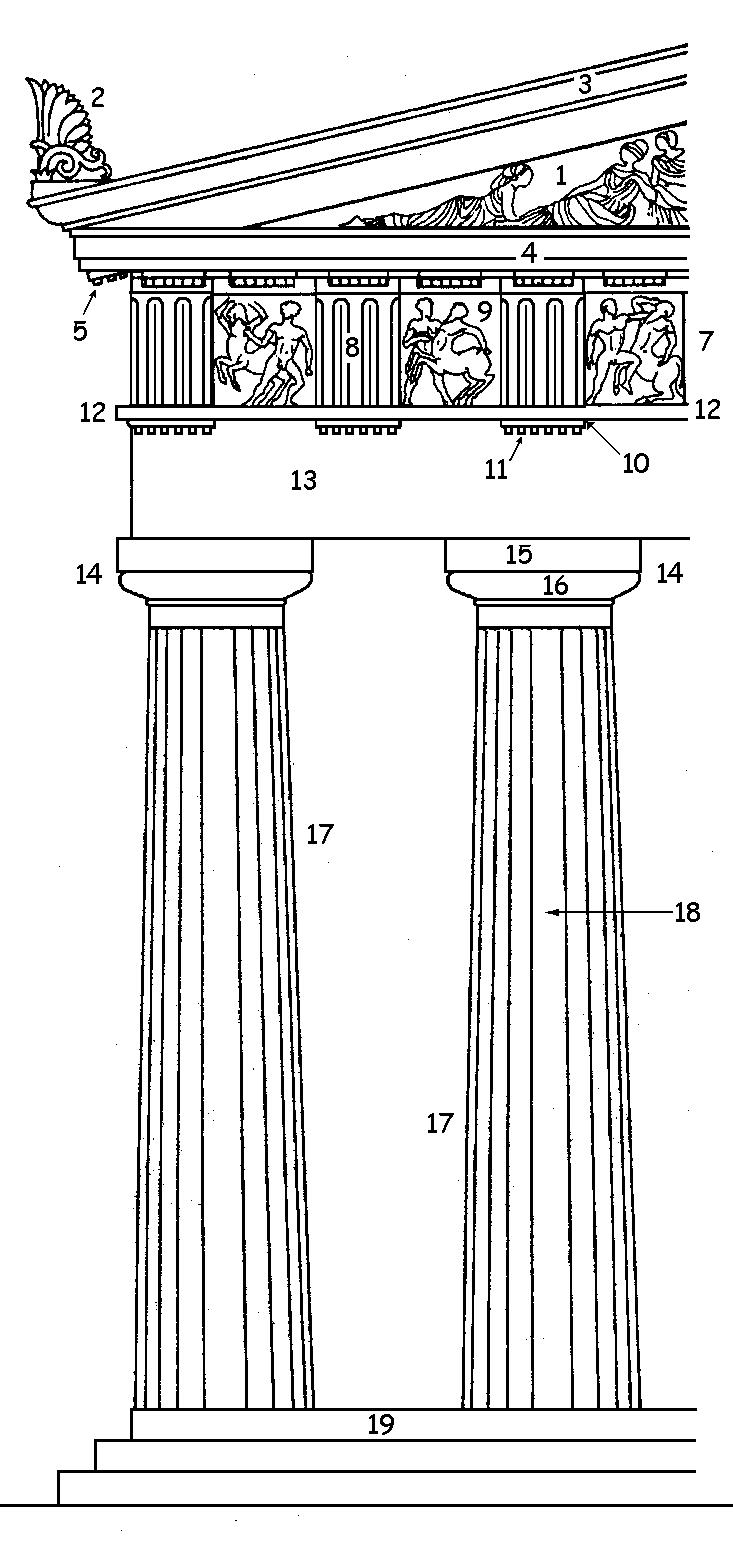 In
In
Architectural Solutions
Roofs Ancient Greek architecture {{architecturalelement-stub
classical architecture
Classical architecture typically refers to architecture consciously derived from the principles of Ancient Greek architecture, Greek and Ancient Roman architecture, Roman architecture of classical antiquity, or more specifically, from ''De archit ...
, a sima is the upturned edge of a roof
A roof (: roofs or rooves) is the top covering of a building, including all materials and constructions necessary to support it on the walls of the building or on uprights, providing protection against rain, snow, sunlight, extremes of tempera ...
which acts as a gutter. The term "sima" comes from the Greek '' simos'', meaning bent upwards.
Form
The sima runs around all four sides of abuilding
A building or edifice is an enclosed Structure#Load-bearing, structure with a roof, walls and window, windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, a ...
. It may be made of terracotta or stone. There are two basic types of sima:
* The raking sima
* The lateral sima
The raking sima is continuous and generally follows the slope of the roof. The lateral sima runs along the horizontal edges and is broken by downspouts to let out rainwater.
Decoration
Simas are normally decorated. Stone simas have continuous narratives, especially on the raking sides where they are not interrupted by spouts, similar to afrieze
In classical architecture, the frieze is the wide central section of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic order, Ionic or Corinthian order, Corinthian orders, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Patera (architecture), Paterae are also ...
. Terracotta simas have repeating patterns that are easy to reproduce with molds. In particular, raking simas were often decorated with floral motifs or other patterns.
Early simas feature tubular or half-cylindrical spouts, but by the middle of the 6th century BC these were mostly replaced with spouts in the shape of animal heads. Lion's heads were common, but ram and dog heads also existed. These animal heads may have served as religious symbolism, or as puns on the structure's geographic location.
See also
* Architectural ironmongeryReferences
External links
Architectural Solutions
Roofs Ancient Greek architecture {{architecturalelement-stub