Silylidene on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Silylene is a
 The α-amido centers stabilize silylenes by π-donation. The dehalogenation of diorganosilicon dihalides is a widely exploited.
The α-amido centers stabilize silylenes by π-donation. The dehalogenation of diorganosilicon dihalides is a widely exploited.
 In one study diphenylsilylene is generated by
In one study diphenylsilylene is generated by  In this reaction diphenylsilylene is extruded from the trisila ring. The silylene can be observed with UV spectroscopy at 520 nm and is short-lived with a chemical half-life of two
In this reaction diphenylsilylene is extruded from the trisila ring. The silylene can be observed with UV spectroscopy at 520 nm and is short-lived with a chemical half-life of two
chemical compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element ...
with the formula SiR2. It is the silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
analog of carbene
In organic chemistry, a carbene is a molecule containing a neutral carbon atom with a Valence (chemistry), valence of two and two unshared valence electrons. The general formula is or where the R represents substituents or hydrogen atoms.
Th ...
. Silylene rapidly when condensed.
Silylenes are formal derivatives of silylene with its hydrogens replaced by other substituents. Most examples feature amido (NR2) or alkyl/aryl groups.
Silylenes have been proposed as reactive intermediate
In chemistry, a reactive intermediate or an intermediate is a short-lived, high-energy, highly reactive molecule. When generated in a chemical reaction, it will quickly convert into a more stable molecule. Only in exceptional cases can these comp ...
s. They are carbene analog
Carbene analogs in chemistry are carbenes with the carbon atom replaced by another chemical element. Just as regular carbenes they appear in chemical reactions as reactive intermediates and with special precautions they can be stabilized and isola ...
s.
Synthesis and properties
Silylenes have been generated bythermolysis
Thermal decomposition, or thermolysis, is a chemical decomposition of a substance caused by heat. The decomposition temperature of a substance is the temperature at which the substance chemically decomposes. The reaction is usually endothermic ...
or photolysis
Photodissociation, photolysis, photodecomposition, or photofragmentation is a chemical reaction in which molecules of a chemical compound are broken down by absorption of light or photons. It is defined as the interaction of one or more photons wi ...
of polysilane
Polysilanes are organosilicon compounds with the formula (R2Si)n. They are relatives of traditional organic polymers but their backbones are composed of silicon atoms. They exhibit distinctive optical and electrical properties. They are mainly use ...
s, by silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
atom reactions (insertion
Insertion may refer to:
*Insertion (anatomy), the point of a tendon or ligament onto the skeleton or other part of the body
*Insertion (genetics), the addition of DNA into a genetic sequence
*Insertion, several meanings in medicine, see ICD-10-PCS
...
, addition
Addition (usually signified by the Plus and minus signs#Plus sign, plus symbol, +) is one of the four basic Operation (mathematics), operations of arithmetic, the other three being subtraction, multiplication, and Division (mathematics), divis ...
or abstraction), by pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process involving the Bond cleavage, separation of covalent bonds in organic matter by thermal decomposition within an Chemically inert, inert environment without oxygen. Etymology
The word ''pyrolysis'' is coined from the Gree ...
of silane
Silane (Silicane) is an inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a colorless, pyrophoric gas with a sharp, repulsive, pungent smell, somewhat similar to that of acetic acid. Silane is of practical interest as a precursor to elemental ...
s, or by reduction of 1,1-dihalosilane. It has long been assumed that the conversion of metallic Si to tetravalent silicon compounds proceeds via silylene intermediates:
:Si + Cl2 → SiCl2
:SiCl2 + Cl2 → SiCl4
Similar considerations apply to the direct process The direct process, also called the direct synthesis, Rochow process, and Müller-Rochow process is the most common technology for preparing organosilicon compounds on an industrial scale. It was first reported independently by Eugene G. Rochow and ...
, the reaction of methyl chloride
Chloromethane, also called methyl chloride, Refrigerant-40, R-40 or HCC 40, is an organic compound with the chemical formula . One of the haloalkanes, it is a colorless, sweet-smelling, flammable gas. Methyl chloride is a crucial reagent in indus ...
and bulk silicon.
Early observations of silylenes involved generation of dimethylsilylene by dechlorination of dimethyldichlorosilane
Dimethyldichlorosilane is a tetrahedral organosilicon compound with the formula . At room temperature it is a colorless liquid that readily reacts with water to form both linear and cyclic Si-O chains. Dimethyldichlorosilane is made on an indust ...
:
:SiCl2(CH3)2 + 2 K → Si(CH3)2 + 2 KCl
The formation of dimethylsilylene was demonstrated by conducting the dechlorination in the presence of trimethylsilane
Trimethylsilane is the organosilicon compound with the formula (CH3)3SiH. It is a trialkylsilane. The Si-H bond is reactive. Being a gas, it is less commonly used as a reagent than the related triethylsilane, which is a liquid at room temperatur ...
: the trapped product being pentamethyldisilane:
:Si(CH3)2 + HSi(CH3)3 → (CH3)2Si(H)−Si(CH3)3
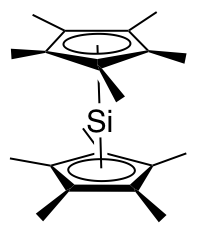
A room-temperature isolable ''N''-heterocyclic silylene is :
 The α-amido centers stabilize silylenes by π-donation. The dehalogenation of diorganosilicon dihalides is a widely exploited.
The α-amido centers stabilize silylenes by π-donation. The dehalogenation of diorganosilicon dihalides is a widely exploited.
Related reactions
 In one study diphenylsilylene is generated by
In one study diphenylsilylene is generated by flash photolysis
Flash photolysis is a pump-probe laboratory technique, in which a sample is first excited by a strong pulse of light from a pulsed laser of nanosecond, picosecond, or femtosecond pulse width or by another short-pulse light source such as a fl ...
of a trisilane:
: In this reaction diphenylsilylene is extruded from the trisila ring. The silylene can be observed with UV spectroscopy at 520 nm and is short-lived with a chemical half-life of two
In this reaction diphenylsilylene is extruded from the trisila ring. The silylene can be observed with UV spectroscopy at 520 nm and is short-lived with a chemical half-life of two microsecond
A microsecond is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one millionth (0.000001 or 10−6 or ) of a second. Its symbol is μs, sometimes simplified to us when Unicode is not available.
A microsecond is to one second, ...
s. Added methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical compound and the simplest aliphatic Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with the chemical formula (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often ab ...
acts as a chemical trap
In chemistry, a chemical trap is a chemical compound that is used to detect unstable compounds. The method relies on efficiency of bimolecular reactions with reagents to produce a more easily characterize trapped product. In some cases, the trappi ...
with a second order rate constant of which is close to diffusion control.
See also
*Carbene analogs
Carbene analogs in chemistry are carbenes with the carbon atom replaced by another chemical element. Just as regular carbenes they appear in chemical reactions as reactive intermediates and with special precautions they can be stabilized and isola ...
* ''N''-heterocyclic silylene
*Silenes
In inorganic chemistry, silenes, or disilalkenes,Philip P. Power "pi-Bonding and the Lone Pair Effect in Multiple Bonds between Heavier Main Group Elements" Chemical Reviews, 1999, 99, 3462. are silicon compounds that contain double bonds, w ...
, R2Si=SiR2
*Silylium ion
A silylium ion is a reactive organosilicon compound, silyl-containing cation with the formula . With three rather than the usual four bonds to Si, silylium ions are the silicon analogues of carbenium ions. They can be viewed as protonated silylenes ...
s, protonated silylenes
References
{{Reflist Inorganic silicon compounds Free radicals Octet-deficient functional groups