Siachen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Siachen Glacier is a
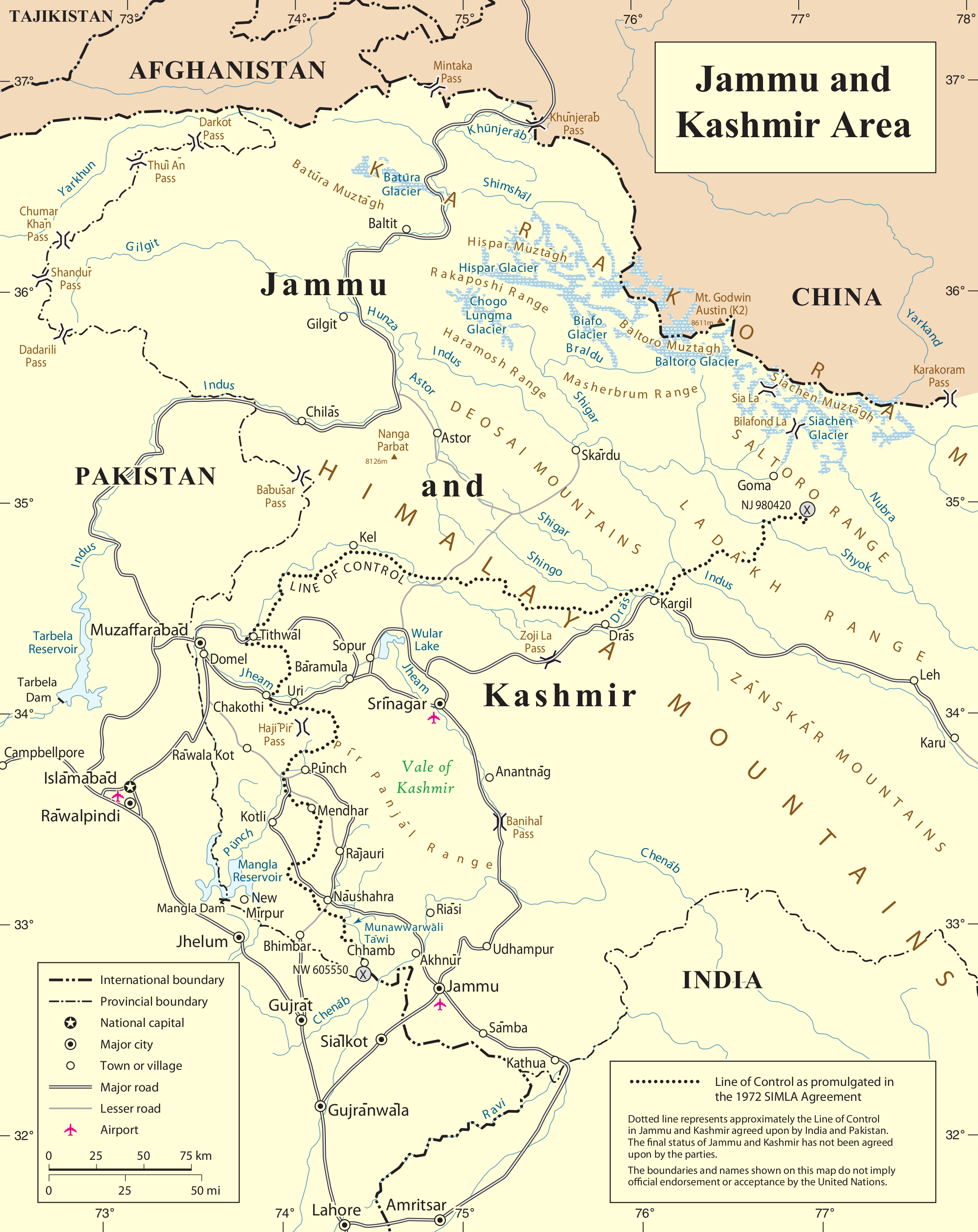 "Sia" in the Balti language refers to the
"Sia" in the Balti language refers to the
 The 1949 Karachi agreement only carefully delineated the line of separation to point
The 1949 Karachi agreement only carefully delineated the line of separation to point
 The glacier's melting waters are the main source of the Nubra River in the Indian region of
The glacier's melting waters are the main source of the Nubra River in the Indian region of
TIME Asia's cover story on Siachen Glacier (July 11, 2005)
* Kunal Verma / Rajiv Williams, ''The Long Road to Siachen: the Question Why'', Rupa & Co., New Delhi, 2010
nbsp;– ''
Siachen by Arshad H Abbasi''
Video about the Conflict in the Siachen area and its consequences
*
Nuclear rivals in Siachen talks
26 May 2005
Bharat Rakshak.
''National Geographic'' article: Siachen Glacier Tragedy
{{Authority control Glaciers of the Karakoram Glaciers of Ladakh Subregions of Kashmir Disputed territories in Asia India–Pakistan border China–India border
glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
located in the eastern Karakoram
The Karakoram () is a mountain range in the Kashmir region spanning the border of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwestern extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Most of the Karakoram mountain range is withi ...
range of the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
, just northeast of the point NJ9842
NJ9842, also called NJ 980420 (in full: NJ 38 98000, 13 42000, yard based Indian Grid Coordinates), is the northernmost demarcated point of the India-Pakistan cease fire line in Kashmir known as the Line of Control (LoC). The India–Pakistan ...
where the Line of Control
The Line of Control (LoC) is a military control line between the Indian and Pakistanicontrolled parts of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir—a line which does not constitute a legally recognized international boundary, but ser ...
between India and Pakistan ends in northeastern Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
. At long, it is the longest glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
in the Karakoram and second-longest in the world's non-polar areas. It falls from an altitude of 5,753 m (18,875 ft) above sea level at its head at Indira Col
__NOTOC__
Indira Col West () is a mountain pass at altitude on the Indira Ridge of Siachen Muztagh in Karakoram Range. It is on the border between Indian-controlled Siachen Glacier and the Chinese-controlled Trans-Karakoram Tract (both in the d ...
on the India–China border down to 3,620 m (11,875 ft) at its terminus. The entire Siachen Glacier, with all major passes, has been under the administration of India as part of the union territory of Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory and constitutes an eastern portion of the larger Kashmir region that has been the subject of a Kashmir#Kashmir dispute, dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947 and India an ...
since 1984. Pakistan maintains a territorial claim over the Siachen Glacier and controls the region west of Saltoro Ridge, lying west of the glacier, with Pakistani posts located 1 km below more than 100 Indian posts on the ridge.
The Siachen Glacier lies immediately south of the great drainage divide
A drainage divide, water divide, ridgeline, watershed, water parting or height of land is elevated terrain that separates neighboring drainage basins. On rugged land, the divide lies along topographical ridges, and may be in the form of a single ...
that separates the Eurasian Plate from the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
in the extensively glaciated
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires d ...
portion of the Karakoram sometimes called the "Third Pole
The Third Pole, also known as the Hindu Kush-Karakoram- Himalayan system (HKKH), is a mountainous region located in the west and south of the Tibetan Plateau. Part of High-Mountain Asia, it spreads over an area of more than across nine countrie ...
". The glacier lies between the Saltoro Ridge immediately to the west and the main Karakoram range to the east. The Saltoro Ridge originates in the north from the Sia Kangri
Sia Kangri (7,422 m, 24,350 ft) is a mountain in the Baltoro Muztagh in the Karakoram. Its summit lies on the border of Pakistan and China. About a kilometer southeast of the Sia Kangri summit is the tri point where territories controlled ...
peak on the China border in the Karakoram range. The crest of the Saltoro Ridge's altitudes range from 5,450 to 7,720 m (17,880 to 25,330 feet). The major passes on this ridge are, from north to south, Sia La
Sia La is a mountain pass situated on Saltoro Ridge, in Gilgit Baltistan, Pakistan some north-northwest of map point NJ9842 which defined the end of the 1972 Line of Control between India and Pakistan as part of the Simla Agreement. Sia L ...
at 5,589 m (18,336 ft), Bilafond La
Bilafond La (meaning "Pass of the Butterflies" in Balti language), also known as the Saltoro Pass, is a mountain pass situated on Saltoro Ridge, sitting immediately west of the vast Siachen Glacier, some directly north of map point NJ 98042 ...
at 5,450 m (17,880 ft), and Gyong La
Gyong La is a mountain pass situated on Saltoro Ridge southwest of the vast Siachen Glacier, some directly north of map point NJ9842 which defined the end of the 1972 Line of Control between India and Pakistan. With Pakistan controlling areas ...
at 5,689 m (18,665 ft). The average winter snowfall
Snow consists of individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water througho ...
is more than 1000 cm (35 ft) and temperatures can dip to . Including all tributary glaciers, the Siachen Glacier system covers about .
Etymology
 "Sia" in the Balti language refers to the
"Sia" in the Balti language refers to the rose
A rose is either a woody perennial plant, perennial flowering plant of the genus ''Rosa'' (), in the family Rosaceae (), or the flower it bears. There are over three hundred Rose species, species and Garden roses, tens of thousands of cultivar ...
family plant widely dispersed in the region. "Chen" refers to any object found in abundance. Thus the name Siachen refers to a land with an abundance of roses. The naming of the glacier itself, or at least its currency, is attributed to Tom Longstaff.
Dispute
Both India and Pakistan claim sovereignty over the entire Siachen region. In June 1958, firstGeological Survey of India
The Geological Survey of India (GSI) is a scientific agency of India. It was founded in 1851, as a Government of India organization under the Ministry of Mines, one of the oldest of such organisations in the world and the second oldest survey ...
expedition went to the Siachen glacier. It was the first official Indian survey of Siachen Glacier by Geological Survey of India post-1947 and that was undertaken to commemorate the International Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year (IGY; ), also referred to as the third International Polar Year, was an international scientific project that lasted from 1 July 1957 to 31 December 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War w ...
in 1958. The study included snout surveying of five glaciers namely Siachen, Mamostong, Chong Kumdan, Kichik Kumdan and Aktash Glaciers in Ladakh region. 5Q 131 05 084 was the number assigned to the Siachen glacier by the expedition. U.S.
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous ...
and Pakistani maps in the 1970s and 1980s consistently showed a dotted line from NJ9842
NJ9842, also called NJ 980420 (in full: NJ 38 98000, 13 42000, yard based Indian Grid Coordinates), is the northernmost demarcated point of the India-Pakistan cease fire line in Kashmir known as the Line of Control (LoC). The India–Pakistan ...
(the northernmost demarcated point of the India-Pakistan cease-fire line, also known as the Line of Control
The Line of Control (LoC) is a military control line between the Indian and Pakistanicontrolled parts of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir—a line which does not constitute a legally recognized international boundary, but ser ...
) to the Karakoram Pass
The Karakoram Pass () is a mountain pass between India and China in the Karakoram Range. It is the highest pass on the ancient caravan route between Leh in Ladakh and Yarkant County, Yarkand in the Tarim Basin. The name 'Karakoram' comes from ...
, which India believed to be a cartographic error and in violation of the Simla Agreement
The Simla Agreement, also spelled Shimla Agreement, was a peace treaty signed between India and Pakistan on 2 July 1972 in Shimla, the capital of Himachal Pradesh. It followed the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, which began after India interv ...
. In 1984, India launched Operation Meghdoot, a military operation that gave India control over all of the Siachen Glacier, including its tributaries. Between 1984 and 1999, frequent skirmishes took place between India and Pakistan. Indian troops under Operation Meghdoot pre-empted Pakistan's Operation Ababeel by just one day to occupy most of the dominating heights on Saltoro Ridge to the west of Siachen Glacier. However, more soldiers have died from the harsh weather conditions in the region than from combat. Pakistan lost 353 soldiers in various operations recorded between 2003 and 2010 near Siachen, including 140 Pakistanis killed in the 2012 Gayari Sector avalanche. Between January 2012 and July 2015, 33 Indian soldiers died due to adverse weather. In December 2015, Indian Union Minister of State for Defence Rao Inderjit Singh said in a written reply in the Lok Sabha
The Lok Sabha, also known as the House of the People, is the lower house of Parliament of India which is Bicameralism, bicameral, where the upper house is Rajya Sabha. Member of Parliament, Lok Sabha, Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by a ...
that a total of 869 Army personnel have died on the Siachen glacier due to climatic conditions and environmental and other factors from the date that the Army launched Operation Meghdoot in 1984. In February 2016, Indian Defence Minister Manohar Parrikar
Manohar Gopalkrishna Prabhu Parrikar (13 December 1955 – 17 March 2019) was an Indian politician and a member of the Bharatiya Janata Party who was the Chief Minister of Goa for three terms. He also served as the Union Minister of Defence ...
stated that India will not vacate Siachen, as there is a trust deficit with Pakistan and also said that 915 people have died in Siachen since Operation Meghdoot in 1984. According to official records, only 220 Indian soldiers have been killed by enemy bullets since 1984 in Siachen area. Both India and Pakistan continue to deploy thousands of troops in the vicinity of Siachen and attempts to demilitarize the region have been so far unsuccessful. Prior to 1984, neither country had any military forces in this area.
Aside from the Indian and Pakistani military presence, the glacier region is unpopulated. The nearest civilian settlement is the village of Warshi, 10 miles downstream from the Indian base camp. The region is also extremely remote, with limited road connectivity. On the Indian side, roads go only as far as the military base camp at Dzingrulma (), 72 km from the head of the glacier. The Indian Army has developed various means to reach the Siachen region, including the Manali-Leh
Leh () is a city in Indian-administered Ladakh in the Kashmir#Kashmir_dispute, disputed Kashmir region. The application of the term "administered" to the various regions of Kashmir and a mention of the Kashmir dispute is supported by the WP:TE ...
- Khardung La-Siachen route. In 2012, Chief of Army Staff of the Indian Army
The Chief of the Army Staff (COAS) is a statutory office held by the professional head of the Indian Army (IA), the land forces branch of the Indian Armed Forces. Customarily held by a four-star general officer, the COAS is the senior-most ...
General Bikram Singh said that the Indian Army should stay in the region for strategic advantages, and because a "lot of blood has been shed" by Indian armed personnel for Siachen. The present ground positions, relatively stable for over a decade, mean that India maintains control over all of the Siachen Glacier and all of its tributary glaciers, as well as all the main passes and heights of the Saltoro Ridge immediately west of the glacier, including Sia La
Sia La is a mountain pass situated on Saltoro Ridge, in Gilgit Baltistan, Pakistan some north-northwest of map point NJ9842 which defined the end of the 1972 Line of Control between India and Pakistan as part of the Simla Agreement. Sia L ...
, Bilafond La
Bilafond La (meaning "Pass of the Butterflies" in Balti language), also known as the Saltoro Pass, is a mountain pass situated on Saltoro Ridge, sitting immediately west of the vast Siachen Glacier, some directly north of map point NJ 98042 ...
, Gyong La
Gyong La is a mountain pass situated on Saltoro Ridge southwest of the vast Siachen Glacier, some directly north of map point NJ9842 which defined the end of the 1972 Line of Control between India and Pakistan. With Pakistan controlling areas ...
, Yarma La (6,100m), and (5,800m). Pakistan controls the glacial valleys immediately west of the Saltoro Ridge. According to ''TIME'' magazine, India gained over in territory because of its 1980s military operations in Siachen. India has categorically stated that India will not pull its army from Siachen until the 110-km long AGPL is first authenticated, delineated and then demarcated.
 The 1949 Karachi agreement only carefully delineated the line of separation to point
The 1949 Karachi agreement only carefully delineated the line of separation to point NJ9842
NJ9842, also called NJ 980420 (in full: NJ 38 98000, 13 42000, yard based Indian Grid Coordinates), is the northernmost demarcated point of the India-Pakistan cease fire line in Kashmir known as the Line of Control (LoC). The India–Pakistan ...
, after which, the agreement states, the line of separation would continue "thence north to the glaciers". According to the Indian stance, the line of separation should continue roughly northwards along the Saltoro Range to the west of the Siachen glacier beyond NJ9842; international boundary lines that follow mountain ranges often do so by following the watershed drainage divide
A drainage divide, water divide, ridgeline, watershed, water parting or height of land is elevated terrain that separates neighboring drainage basins. On rugged land, the divide lies along topographical ridges, and may be in the form of a single ...
such as that of the Saltoro Range. The 1972 Simla Agreement
The Simla Agreement, also spelled Shimla Agreement, was a peace treaty signed between India and Pakistan on 2 July 1972 in Shimla, the capital of Himachal Pradesh. It followed the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, which began after India interv ...
made no change to the 1949 Line of Control in this northernmost sector.
Drainage
Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory and constitutes an eastern portion of the larger Kashmir region that has been the subject of a Kashmir#Kashmir dispute, dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947 and India an ...
, which drains into the Shyok River
The Shyok River (sometimes spelled Shayok) is a major tributary of the Indus River that flows through northern Ladakh in India and into Gilgit-Baltistan in Pakistan. Originating from the Central Rimo Glacier in the eastern Karakoram, it runs f ...
. The Shyok in turn joins the 3000 kilometre-long Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northw ...
which flows through Pakistan. Thus, the glacier is a major source of the Indus and feeds the largest irrigation system in the world.
Environmental issues
The glacier was uninhabited before 1984, and the presence of thousands of troops since then has introduced pollution and melting to the glacier. To support the troops, glacial ice has been cut and melted with chemicals. Dumping of non-biodegradable waste
Biodegradable waste includes any organic matter in waste which can be broken down into carbon dioxide, water, methane, compost, humus, and simple organic molecules by micro-organisms and other living things by composting, aerobic digestion, ana ...
in large quantities and the use of arms and ammunition have considerably affected the ecosystem of the region.
Glacial retreat
Preliminary findings of a survey by Pakistan Meteorological Department in 2007 revealed that the Siachen glacier has been retreating for the past 30 years and is melting at an alarming rate. The study of satellite images of the glacier showed that the glacier is retreating at a rate of about 110 metres a year and that the glacier size has decreased by almost 35 percent. In an eleven-year period, the glacier had receded nearly 800 metres, and in seventeen years about 1700 metres. It is predicted that the glaciers of the Siachen region will be reduced to about one-fifth of their 2011 size by 2035. In the twenty-nine-year period 1929–1958, well before the military occupation, the glacial retreat was recorded to be about 914 metres. One of the reasons theorized for the recent glacial retreat is chemical blasting, to construct camps and posts. In 2001 India laid oil pipelines (about 250 kilometres long) inside the glacier to supply kerosene and aviation fuel to the outposts from base camps. As of 2007, the temperature rise at Siachen was estimated at 0.2-degree Celsius annually, causing melting, avalanches, and crevasses in the glacier.Waste dumping
The waste produced by the troops stationed there is dumped in the crevasses of the glacier. Mountaineers who visited the area while on climbing expeditions witnessed large amount of garbage, empty ammunition shells,parachute
A parachute is a device designed to slow an object's descent through an atmosphere by creating Drag (physics), drag or aerodynamic Lift (force), lift. It is primarily used to safely support people exiting aircraft at height, but also serves va ...
s etc. dumped on the glacier, that neither decomposes nor can be burned because of the extreme climatic conditions. About of waste is produced and dumped in glacial crevasses daily by Indian forces. The Indian army is said to have planned a "Green Siachen, Clean Siachen" campaign to airlift the garbage from the glacier, and to use biodigestors for biodegradable waste in the absence of oxygen and freezing temperatures. Almost forty percent (40%) of the waste left at the glacier is plastic and metal, including toxins such as cobalt, cadmium and chromium that eventually affect the water of the Shyok River
The Shyok River (sometimes spelled Shayok) is a major tributary of the Indus River that flows through northern Ladakh in India and into Gilgit-Baltistan in Pakistan. Originating from the Central Rimo Glacier in the eastern Karakoram, it runs f ...
(which ultimately enters the Indus River near Skardu
Skardu (, Tibetan script: སྐར་མདོ, ) is a city located in Pakistan-administered Gilgit-Baltistan in the disputed Kashmir region. The application of the term "administered" to the various regions of Kashmir and a mention of the Kas ...
). The Indus is used for drinking and irrigation. Research is being done by scientists of The Energy and Resources Institute, to find ways to successfully dispose of the garbage generated at the glacier using scientific means. Some scientists of the Defence Research and Development Organisation
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is an agency under the Department of Defence Research and Development in the Ministry of Defence of the Government of India, charged with the military's research and development, head ...
who went on an expedition to Antarctica are also working to produce a bacterium that can thrive in extreme weather conditions and can be helpful in decomposing the biodegradable waste naturally.
Fauna and flora
Theflora
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for f ...
and fauna
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively ...
of the Siachen region are also affected by the huge military presence. The region is home to rare species including snow leopard
The snow leopard (''Panthera uncia'') is a species of large cat in the genus ''Panthera'' of the family Felidae. The species is native to the mountain ranges of Central and South Asia. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List because ...
, brown bear
The brown bear (''Ursus arctos'') is a large bear native to Eurasia and North America. Of the land carnivorans, it is rivaled in size only by its closest relative, the polar bear, which is much less variable in size and slightly bigger on av ...
and ibex
An ibex ( : ibex, ibexes or ibices) is any of several species of wild goat (genus ''Capra''), distinguished by the male's large recurved horns, which are transversely ridged in front. Ibex are found in Eurasia, North Africa and East Africa.
T ...
that are at risk because of the military presence.
Border conflict
The glacier's region is the highest battleground on Earth, where Pakistan and India have fought intermittently since April 1984. Both countries maintain a permanent military presence in the region at a height of over . Both India and Pakistan have wished to disengage from the costly military outposts. India launched Operation Meghdoot to occupy Siachen Glacier in 1984. Then, due to the Pakistani incursions during theKargil War
The Kargil War, was fought between India and Pakistan from May to July 1999 in the Kargil district of Ladakh, then part of the Indian-administered state of Jammu and Kashmir (state), Jammu and Kashmir and along the Line of Control (LoC). In In ...
in 1999, India abandoned plans to withdraw from Siachen, wary of further Pakistani incursions if they vacate the Siachen Glacier posts.
Prime Minister Manmohan Singh
Manmohan Singh (26 September 1932 – 26 December 2024) was an Indian economist, bureaucrat, academician, and statesman, who served as the prime minister of India from 2004 to 2014. He was the fourth longest-serving prime minister after Jaw ...
became the first Indian Prime Minister to visit the area, during which he called for a peaceful resolution of the problem. After that present Prime Minister Narendra Modi
Narendra Damodardas Modi (born 17 September 1950) is an Indian politician who has served as the Prime Minister of India, prime minister of India since 2014. Modi was the chief minister of Gujarat from 2001 to 2014 and is the Member of Par ...
also visited this place. President of Pakistan
The president of Pakistan () is the head of state of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. The president is the nominal head of the executive and the supreme commander of the Pakistan Armed Forces.
Asif Ali Zardari
Asif Ali Zardari (born 26 July 1955) is a Pakistani politician serving as the 14th president of Pakistan since 2024, having held the same office from 2008 to 2013. He is the president of Pakistan People's Party Parliamentarians and was the ...
also visited an area near the Siachen Glacier called Gayari Sector during 2012 with Pakistan Army Chief Gen. Ashfaq Parvez Kayani. Both of them showed their commitment to resolve the Siachen conflict as early as possible. In the previous year, the President of India
The president of India (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the head of state of the Republic of India. The president is the nominal head of the executive, the first citizen of the country, and the commander-in-chief, supreme commander of the Indian Armed ...
, Abdul Kalam
Avul Pakir Jainulabdeen Abdul Kalam ( ; 15 October 193127 July 2015) was an Indian Aerospace engineering, aerospace scientist and statesman who served as the president of India from 2002 to 2007.
Born and raised in a Muslim family in Ramesw ...
became the first head of state
A head of state is the public persona of a sovereign state.#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 "
to visit the area.
Since September 2007, India has opened up limited mountaineering and trekking expeditions to the area. The first group included cadets from Chail Military School, he head of state
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (letter), the fifth letter of the Semitic abjads
* He (pronoun), a pronoun in Modern English
* He (kana), one of the Japanese kana (へ in hiragana and ヘ in katakana)
* Ge (Cyrillic), a Cyrillic letter cal ...
being an embodiment of the State itself or representative of its international persona." The name given to the office of head of sta ...National Defence Academy
The National Defence Academy (NDA) is the joint defence service training institute of the Indian Armed Forces. Here, cadets of the Indian Army, Indian Navy, and Indian Air Force train together before they go on to their respective service a ...
, National Cadet Corps, Indian Military Academy
The Indian Military Academy (IMA) is one of the oldest military academies in India, and trains officers for the Indian Army. Located in Dehradun, Uttarakhand, it was established in 1932 following a recommendation by a military committee set up ...
, Rashtriya Indian Military College
The Rashtriya Indian Military College (abbreviated RIMC; formerly known as Prince of Wales Royal Indian Military College) () is a military school for boys situated in Doon Valley, Dehradun in India. The RIMC is a feeder institution for the Nation ...
and family members of armed forces officers. The expeditions are also meant to show to the international audience that Indian troops hold "almost all dominating heights" on the key Saltoro Ridge and to show that Pakistani troops are nowhere near the Siachen Glacier. Ignoring protests from Pakistan, India maintains that it does not need anyone's approval to send trekkers to Siachen, in what it says is essentially its own territory. In addition, the Indian Army
The Indian Army (IA) (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the Land warfare, land-based branch and largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Commander-in-Chief, Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head ...
's Army Mountaineering Institute (AMI) functions out of the region.
Peace Park proposal
The idea of declaring the Siachen region a "Peace Park" was presented by environmentalists and peace activists in part to preserve the ecosystem of the region badly affected by the military presence. In September 2003, the governments of India and Pakistan were urged by the participants of the 5th World Parks Congress held atDurban
Durban ( ; , from meaning "bay, lagoon") is the third-most populous city in South Africa, after Johannesburg and Cape Town, and the largest city in the Provinces of South Africa, province of KwaZulu-Natal.
Situated on the east coast of South ...
, to establish a peace park in the Siachen region to restore the natural biological system and protect species whose lives are at risk. Italian ecologist Giuliano Tallone said the ecological life was at serious risk, and proposed setting up a ''Siachen Peace Park'' at the conference. After a proposal of a transboundary Peace Park was floated, the International Mountaineering and Climbing Federation (UIAA) and the International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the stat ...
(IUCN) organised a conference at Geneva
Geneva ( , ; ) ; ; . is the List of cities in Switzerland, second-most populous city in Switzerland and the most populous in French-speaking Romandy. Situated in the southwest of the country, where the Rhône exits Lake Geneva, it is the ca ...
and invited Indian and Pakistani mountaineers ( Mandip Singh Soin, Harish Kapadia
Harish Kapadia (born 11 July 1945) is a Himalayan mountaineer, author and long-time editor of the '' Himalayan Journal'' from India.
He has written numerous books and articles on the Indian Himalayas. and has been invited to many countries t ...
, Nazir Sabir and Sher Khan). The region was nominated for inclusion in the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
' World Heritage List
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritag ...
as a part of the Karakoram
The Karakoram () is a mountain range in the Kashmir region spanning the border of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwestern extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Most of the Karakoram mountain range is withi ...
range, but this was deferred by the World Heritage Committee
The World Heritage Committee is a committee of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization that selects the sites to be listed as UNESCO World Heritage Sites, including the World Heritage List and the List of World Her ...
. The areas to the east and west of the Siachen region have already been declared national parks: the Karakoram Wildlife Sanctuary in India and the Central Karakoram National Park in Pakistan.
Sandia National Laboratories
Sandia National Laboratories (SNL), also known as Sandia, is one of three research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA). Headquartered in Kirtland Air Force B ...
organised conferences where military experts and environmentalists from both India and Pakistan and also from other countries were invited to present joint papers. Kent L. Biringer, a researcher at Cooperative Monitoring Center of Sandia Labs suggested setting up ''Siachen Science Center'', a high-altitude research centre where scientists and researchers from both the countries can carry out research activities related to glaciology, geology, atmospheric sciences and other related fields.
In popular culture
In the 2018 Hollywood movie '' Mission: Impossible – Fallout'', a rogue agent plants nuclear bombs at the base of the Siachen Glacier. The scene was actually filmed in Preikestolen,Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
, due to the Indian government denying permission to film in Kashmir.
See also
*Batura Glacier
Batura Glacier (), long, is one of the largest and longest glaciers outside of the polar regions.Tajikistan's Fedchenko Glacier is long, Siachen Glacier is long, Biafo Glacier long, and Baltoro Glacier long. The Bruggen or Pio XI Glacier ...
* Colonel Narendra Kumar
* NJ9842
NJ9842, also called NJ 980420 (in full: NJ 38 98000, 13 42000, yard based Indian Grid Coordinates), is the northernmost demarcated point of the India-Pakistan cease fire line in Kashmir known as the Line of Control (LoC). The India–Pakistan ...
* Indira Col
__NOTOC__
Indira Col West () is a mountain pass at altitude on the Indira Ridge of Siachen Muztagh in Karakoram Range. It is on the border between Indian-controlled Siachen Glacier and the Chinese-controlled Trans-Karakoram Tract (both in the d ...
* Robert D. Hodgson
* Baltoro Glacier
The Baltoro Glacier (; ) is a glacier located in the Shigar District of the Gilgit-Baltistan region in Pakistan. It stretches for in length. It is one of the longest glaciers outside the polar regions. It is home to some of the world’s high ...
* Saltoro Kangri
Saltoro Kangri, previously known as Peak 36, stands as the highest peak within the Saltoro Mountains subrange, which is part of the larger Karakoram range. This subrange is also referred to as the Saltoro Range and is situated within the Karakor ...
* Sia La
Sia La is a mountain pass situated on Saltoro Ridge, in Gilgit Baltistan, Pakistan some north-northwest of map point NJ9842 which defined the end of the 1972 Line of Control between India and Pakistan as part of the Simla Agreement. Sia L ...
* Bilafond La
Bilafond La (meaning "Pass of the Butterflies" in Balti language), also known as the Saltoro Pass, is a mountain pass situated on Saltoro Ridge, sitting immediately west of the vast Siachen Glacier, some directly north of map point NJ 98042 ...
* Gyong La
Gyong La is a mountain pass situated on Saltoro Ridge southwest of the vast Siachen Glacier, some directly north of map point NJ9842 which defined the end of the 1972 Line of Control between India and Pakistan. With Pakistan controlling areas ...
* Actual Ground Position Line
* 2016 Siachen Glacier avalanche
* Siachen Muztagh
__NOTOC__
The Siachen Muztagh is a remote subrange of the eastern Karakoram Range. Close to 60% is in area controlled by China, 40% in area controlled by India. Pakistan claims the Indian-controlled portion as part of the Siachen Conflict. India ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* Myra MacDonald (2008) ''Heights of Madness: One Woman's Journey in Pursuit of a Secret War'', Rupa, New Delhi . The first full account of the Siachen war to be told from the Indian and Pakistani sides. * V. R. Raghavan, ''Siachen: Conflict Without End'', Viking, New Delhi, 2002TIME Asia's cover story on Siachen Glacier (July 11, 2005)
* Kunal Verma / Rajiv Williams, ''The Long Road to Siachen: the Question Why'', Rupa & Co., New Delhi, 2010
nbsp;– ''
The Washington Times
''The Washington Times'' is an American Conservatism, conservative daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It covers general interest topics with an emphasis on Politics of the United States, national politics. Its broadsheet daily edit ...
''
Siachen by Arshad H Abbasi''
External links
Video about the Conflict in the Siachen area and its consequences
*
BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broad ...
reportNuclear rivals in Siachen talks
26 May 2005
Bharat Rakshak.
''National Geographic'' article: Siachen Glacier Tragedy
{{Authority control Glaciers of the Karakoram Glaciers of Ladakh Subregions of Kashmir Disputed territories in Asia India–Pakistan border China–India border