Shvetsov ASh-82 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Shvetsov ASh-82 (M-82) is a Soviet 14-cylinder, two-row, air-cooled radial
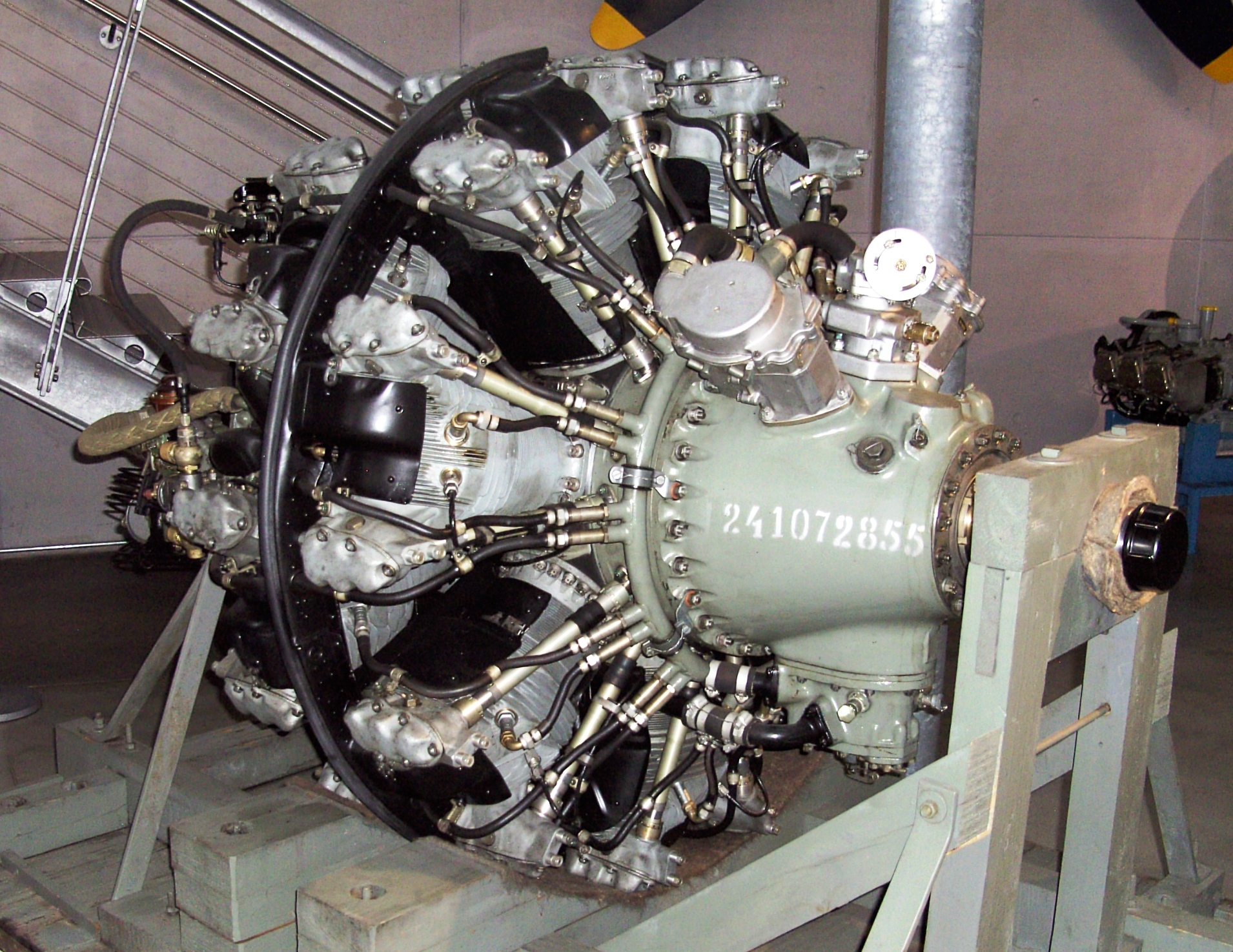 ;ASh-82T (M-82T)
:New version of the ASh-82FNV developed in the early fifties for civilian aircraft. Previous version twin superchargers were replaced with a large single-speed compressor attached to an after-cooler (the critical altitude was 2,000 m, 6,561 ft). New alloys were used and some components were upgraded, thus reducing maintenance operations. Special care was put into reducing the engine noise level and an optional exhaust double silencer was available. The engine had a new fuel injection system and improved specific fuel consumption.
:A four-blade high efficiency propeller, the Typ AV-50m, was developed for the 82T version. Take-off power was 1,900 hp (1,417 kW) at 2,600 RPM, with 95 octane Avgas. Maximum continuous power was 1,630 hp (1,215 kW). At 85 octane Avgas and minor modifications, power output was rated at 1,700 hp (1,268 kW).
;ASh-82V (M-82V)
:Helicopter version of the ASh-82T developed in 1952, with axial-flow fan mounted in the fuselage's front. The engine was connected to a R-5 two-stage planetary primary gearbox with the help of a shaft (which was between the pilots seats). This engine was used in the Mi-4 and Yak-24 helicopters.
;ASh-2TK and ASh-2K (ASh-4K)
:Four-row versions of the ASh-82, developed in the late '40s. The ASh-2TK had a two-stage two-speed supercharging system with intercooler (similar to the ASh-73) that compromised the engine's long TBO. Finally the ASh-2TK was discarded and a new version was developed, the ASh-4K, with an experimental variable-speed turbocharger and after-cooler, which allowed a cruising altitude of 11,000 m (36,089 ft). The engine had 82.4 litres (5,030 cu in) and 4,000 HP (2,985 kW) at 2,600 RPM (dry). The Ash-2K (ASh-4K) version had 4,700 HP (3,507 kW) wet, with a water-methanol system.
:For political reasons, these engines were prematurely installed in Tupolev Tu-4LL testbeds at the end of 1950, when the prototypes' initial tests had barely begun. The engines had various teething and overheating problems, and required a long testing period. Most of the flaws were fixed in the mid-fifties, but the production was cancelled: in those days, the priority for the Soviet Air Force were the turboprop and jet engines.
;Dongan HS-7
:A Chinese license built copy of the ASh-82FN, and the chosen engine for powering modern 21st century reproductions of the Focke-Wulf Fw 190A.
;Dongan HS-8
:A modified version of the Dongan HS-7 which "combined the main body and supercharger of the HS-7 with the reduction gear and propeller drive of the Shvetsov ASh-82T". Built by Dongan Engine Manufacturing Company (aka Harbin Engine Factory).
;ASh-82T (M-82T)
:New version of the ASh-82FNV developed in the early fifties for civilian aircraft. Previous version twin superchargers were replaced with a large single-speed compressor attached to an after-cooler (the critical altitude was 2,000 m, 6,561 ft). New alloys were used and some components were upgraded, thus reducing maintenance operations. Special care was put into reducing the engine noise level and an optional exhaust double silencer was available. The engine had a new fuel injection system and improved specific fuel consumption.
:A four-blade high efficiency propeller, the Typ AV-50m, was developed for the 82T version. Take-off power was 1,900 hp (1,417 kW) at 2,600 RPM, with 95 octane Avgas. Maximum continuous power was 1,630 hp (1,215 kW). At 85 octane Avgas and minor modifications, power output was rated at 1,700 hp (1,268 kW).
;ASh-82V (M-82V)
:Helicopter version of the ASh-82T developed in 1952, with axial-flow fan mounted in the fuselage's front. The engine was connected to a R-5 two-stage planetary primary gearbox with the help of a shaft (which was between the pilots seats). This engine was used in the Mi-4 and Yak-24 helicopters.
;ASh-2TK and ASh-2K (ASh-4K)
:Four-row versions of the ASh-82, developed in the late '40s. The ASh-2TK had a two-stage two-speed supercharging system with intercooler (similar to the ASh-73) that compromised the engine's long TBO. Finally the ASh-2TK was discarded and a new version was developed, the ASh-4K, with an experimental variable-speed turbocharger and after-cooler, which allowed a cruising altitude of 11,000 m (36,089 ft). The engine had 82.4 litres (5,030 cu in) and 4,000 HP (2,985 kW) at 2,600 RPM (dry). The Ash-2K (ASh-4K) version had 4,700 HP (3,507 kW) wet, with a water-methanol system.
:For political reasons, these engines were prematurely installed in Tupolev Tu-4LL testbeds at the end of 1950, when the prototypes' initial tests had barely begun. The engines had various teething and overheating problems, and required a long testing period. Most of the flaws were fixed in the mid-fifties, but the production was cancelled: in those days, the priority for the Soviet Air Force were the turboprop and jet engines.
;Dongan HS-7
:A Chinese license built copy of the ASh-82FN, and the chosen engine for powering modern 21st century reproductions of the Focke-Wulf Fw 190A.
;Dongan HS-8
:A modified version of the Dongan HS-7 which "combined the main body and supercharger of the HS-7 with the reduction gear and propeller drive of the Shvetsov ASh-82T". Built by Dongan Engine Manufacturing Company (aka Harbin Engine Factory).
 * Amtorg KM-2 (Improved PBY Catalina, built under Consolidated license)
* Douglas TS-82
* Gudkov Gu-82 (Prototype)
*
* Amtorg KM-2 (Improved PBY Catalina, built under Consolidated license)
* Douglas TS-82
* Gudkov Gu-82 (Prototype)
*
aircraft engine
An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Aircraft using power components are referred to as powered flight. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbin ...
developed from the Shvetsov M-62, which in turn was the result of development of the M-25, a licensed version of the Wright R-1820 Cyclone
The Wright R-1820 Cyclone 9 is an American radial engine developed by Curtiss-Wright, widely used on aircraft in the 1930s through 1950s. It was produced under license in France as the Hispano-Suiza 9V or Hispano-Wright 9V, and in the Soviet Uni ...
.
Design and development
Arkadiy Shvetsov re-engineered the Wright Cyclone design, through the OKB-19 design bureau he headed, for Russian aviation engine manufacturing practices and metric dimensions and fasteners, reducing thestroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
, dimensions and weight. This allowed the engine to be used in light aircraft, where an American-design Twin Cyclone, of some 930 kg (2,045 lb) weight in "dry" condition could not be installed.
The engine entered production in 1940 and saw service in a number of Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
aircraft. It powered the Tupolev Tu-2 and Pe-8 bombers and the inline engine-powered LaGG-3 was adapted for the ASh-82 producing the famous Lavochkin La-5
The Lavochkin La-5 (Лавочкин Ла-5) was a Soviet Union, Soviet fighter aircraft of World War II. It was a development and refinement of the Lavochkin-Gorbunov-Goudkov LaGG-3, LaGG-3, replacing the earlier model's Inline engine (aeronaut ...
fighter and its development, Lavochkin La-7, additionally the Lavochkin La-9 with its Lavochkin La-11 escort variant and Ilyushin Il-14 airliner were created around the engine. Over 70,000 ASh-82s were built. They were built in the 1950s to 1960s era under licence, both in Czechoslovakia (as the M-82) by the Walter (Motorlet) factory in Prague-Jinonice and in the German Democratic Republic by the VEB Industriewerke Karl-Marx-Stadt.
Variants
;ASh-82-111 (M-82-111) :First mass-produced ASh-82, with carburettors and one two-speed supercharger. Engine had lubrication and carburettor problems in harsh winter conditions. ;ASh-82-112 (M-82-112) :Improved M-82-111 with longer Time between overhaul (TBO) and better reliability. Redesigned carburettors, oil pumps, gear, turbocharger and reinforced pushrods. ;ASh-82F (M-82F) :Identical to ASh-82 except for longer Time between overhaul and improved cooling and lubrication system. ;ASh-82FNV (M-82FNV) :Improved M-82F with direct fuel injection, power output increased to 1,380 kW (1,850 hp) compared to the 1,268 kW (1,700 hp) of the M-82 and M-82F. ;ASh-82FN (M-82FN) :Series production M-82FNV, used by Pe-8 long-range bombers and Lavochkin La-5FN and La-7 fighters. ;ASh-21 (M-21) :Single-row 7-cylinder version of ASh-82 for Yakovlev Yak-11 trainer, entered production in 1946, used also to power e.g. the Mil Mi-1 helicopter.Applications
Ilyushin Il-2
The Ilyushin Il-2 ( Russian: Илью́шин Ил-2) is a ground-attack plane that was produced by the Soviet Union in large numbers during the Second World War. The word ''shturmovík'' (Cyrillic: штурмовик), the generic Russian term ...
(prototype)
* Ilyushin Il-12
* Ilyushin Il-14
* Kocherigin OPB-5 (prototype)
* Lisunov Li-2
The Lisunov Li-2 (NATO reporting name: Cab), originally designated PS-84, was a license-built Soviet-version of the Douglas DC-3. It was produced by Factory #84 in Khimki, Moscow-Khimki and, after the factory's evacuation in 1941, at the Tash ...
* Lavochkin La-5
The Lavochkin La-5 (Лавочкин Ла-5) was a Soviet Union, Soviet fighter aircraft of World War II. It was a development and refinement of the Lavochkin-Gorbunov-Goudkov LaGG-3, LaGG-3, replacing the earlier model's Inline engine (aeronaut ...
* Lavochkin La-7
* Lavochkin La-9
* Lavochkin La-11
* MiG-5
* MiG-9
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-9 (, USAF/DoD reporting names, USAF/DoD designation: Type 1, NATO reporting name: Fargo) was the first turbojet fighter aircraft, fighter developed by Mikoyan, Mikoyan-Gurevich in the years immediately after World War I ...
I-210 (1941 Prototype)
* Mikoyan-Gurevich I-211 prototype
* Mil Mi-4
* Petlyakov Pe-2
The Petlyakov Pe-2 ( — nickname «Пешка» (Pawn); NATO reporting name: Buck) was a Soviet Union, Soviet twin-engine dive bomber used during World War II. One of the outstanding tactical attack aircraft of the war,Ethell 1996, p. 152. it ...
* Petlyakov Pe-8
The Petlyakov Pe-8 () was a Soviet heavy bomber designed before World War II, and the only four-engine bomber the USSR built during the war. Produced in limited numbers, it was used to bomb Berlin in August 1941. It was also used for so-called " ...
* Polikarpov I-185
The Polikarpov I-185 was a Soviet fighter aircraft designed in 1940. It was flown with three engines but all of them were either insufficiently developed for service use or their full production was reserved for other fighters already in producti ...
(Prototype)
* Sukhoi Su-2
* Sukhoi Su-4
* Sukhoi Su-7
The Sukhoi Su-7 ( NATO designation name: Fitter-A) is a swept wing, supersonic fighter aircraft developed by the Soviet Union in 1955. Originally, it was designed as a tactical, low-level dogfighter, but was not successful in this role. On the ...
* Sukhoi Su-12
* Tupolev Tu-2
* Yakovlev Yak-24
* Yakovlev Yak-3
The Yakovlev Yak-3 (Russian language, Russian: Яковлев Як-3) is a single-engine, single-seat World War II Soviet Union, Soviet fighter aircraft, fighter. Robust and easy to maintain, it was much liked by both pilots and ground crew.Glan ...
(Yak-3U variant)
Specifications (ASh-82T)
See also
References
Notes
{{Shvetsov aeroengines Aircraft air-cooled radial piston engines Shvetsov aircraft engines 1940s aircraft piston engines