Shipbuilder on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Shipbuilding is the
Shipbuilding is the
World's Oldest Planked Boats
, in ''
This Old Boat
, 11 December 2000.
 Austronesians traditionally made their sails from woven mats of the resilient and salt-resistant
Austronesians traditionally made their sails from woven mats of the resilient and salt-resistant

 Large multi-masted seafaring ships of Southeast Asian Austronesians first started appearing in Chinese records during the Han dynasty as the ''k'un-lun po'' or ''kunlun bo'' ("ship of the ''kunlun slave, k'un-lun'' [dark-skinned southern people]"). These ships used two types of sail of their invention, the junk sail and tanja sail. Large ships are about 50–60 metres (164–197 ft) long, had tall Freeboard (nautical), freeboard, each carrying provisions enough for a year, and could carry 200–1000 people. The Chinese recorded that these Southeast Asian ships were hired for passage to South Asia by Chinese Buddhist pilgrims and travelers, because they did not build seaworthy ships of their own until around the 8–9th century AD.
Large multi-masted seafaring ships of Southeast Asian Austronesians first started appearing in Chinese records during the Han dynasty as the ''k'un-lun po'' or ''kunlun bo'' ("ship of the ''kunlun slave, k'un-lun'' [dark-skinned southern people]"). These ships used two types of sail of their invention, the junk sail and tanja sail. Large ships are about 50–60 metres (164–197 ft) long, had tall Freeboard (nautical), freeboard, each carrying provisions enough for a year, and could carry 200–1000 people. The Chinese recorded that these Southeast Asian ships were hired for passage to South Asia by Chinese Buddhist pilgrims and travelers, because they did not build seaworthy ships of their own until around the 8–9th century AD.
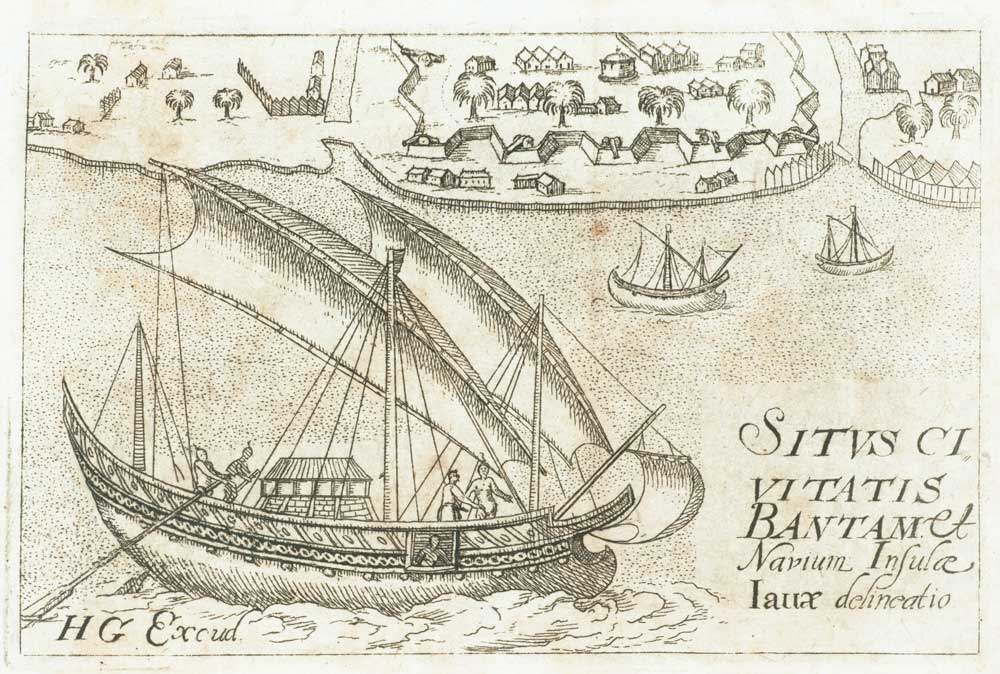 Austronesians (especially from western Island Southeast Asia) were trading in the Indian Ocean as far as Africa during this period. By around 50 to 500 AD, a group of Austronesians, believed to be from the southeastern coasts of Borneo (possibly a mixed group related to the modern Ma'anyan people, Ma'anyan, Banjar people, Banjar, and/or the Dayak people) crossed the Indian Ocean and colonized Madagascar. This resulted in the introduction of outrigger canoe technology to non-Austronesian cultures in the East African coast.
Austronesians (especially from western Island Southeast Asia) were trading in the Indian Ocean as far as Africa during this period. By around 50 to 500 AD, a group of Austronesians, believed to be from the southeastern coasts of Borneo (possibly a mixed group related to the modern Ma'anyan people, Ma'anyan, Banjar people, Banjar, and/or the Dayak people) crossed the Indian Ocean and colonized Madagascar. This resulted in the introduction of outrigger canoe technology to non-Austronesian cultures in the East African coast.
 Until recently, Viking longships were seen as marking an advance on traditional clinker (boat building), clinker-built hulls where leather thongs were used to join plank boards. This consensus has recently been challenged. Haywood has argued that earlier Frankish and Anglo-Saxon nautical practice was much more accomplished than had been thought and has described the distribution of clinker ''vs.'' carvel construction in Western Europe (see ma
Until recently, Viking longships were seen as marking an advance on traditional clinker (boat building), clinker-built hulls where leather thongs were used to join plank boards. This consensus has recently been challenged. Haywood has argued that earlier Frankish and Anglo-Saxon nautical practice was much more accomplished than had been thought and has described the distribution of clinker ''vs.'' carvel construction in Western Europe (see ma
. An insight into shipbuilding in the North Sea/Baltic areas of the early medieval period was found at Sutton Hoo, England, where a ship was buried with a chieftain. The ship was long and wide. Upward from the keel, the hull was made by overlapping nine
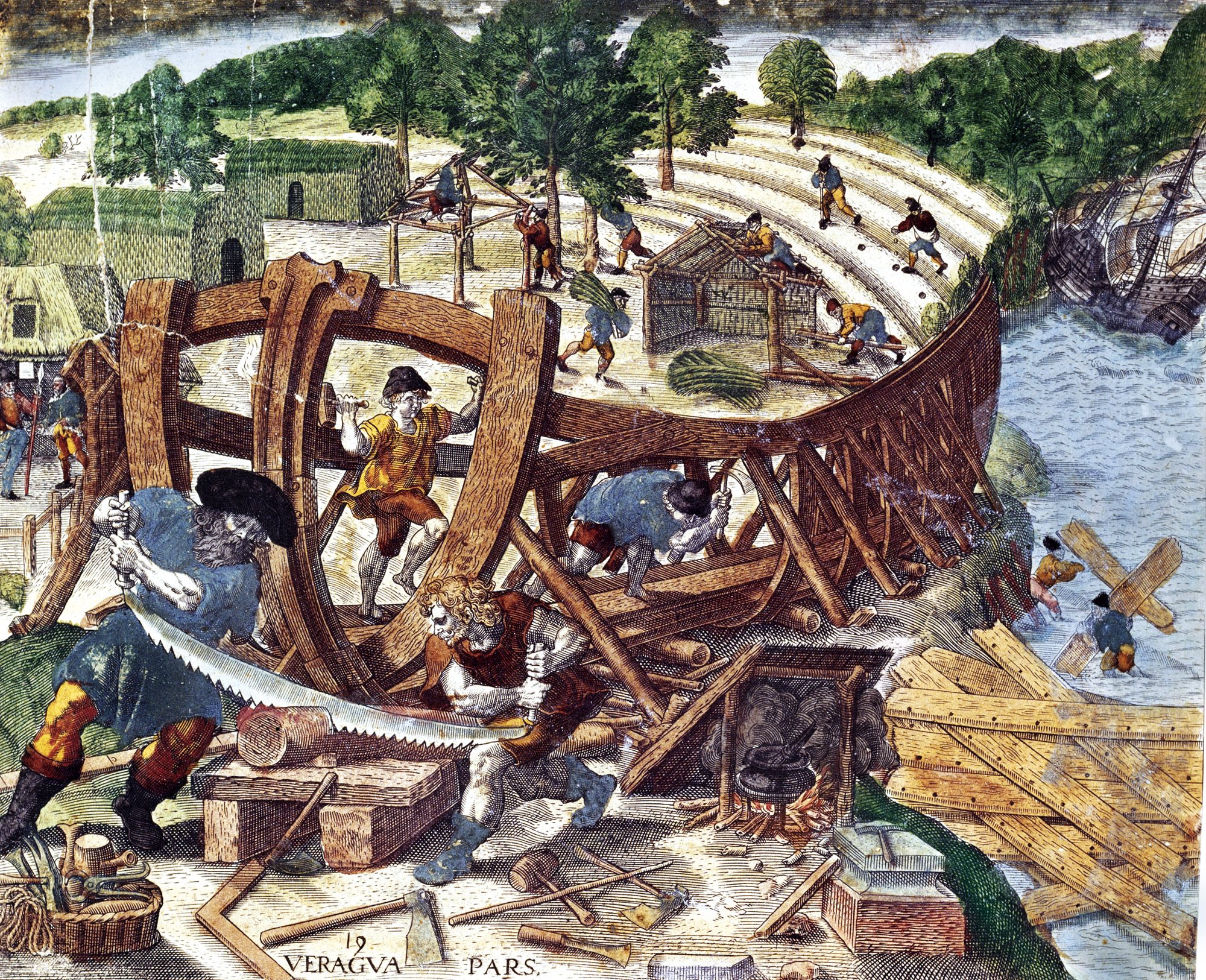
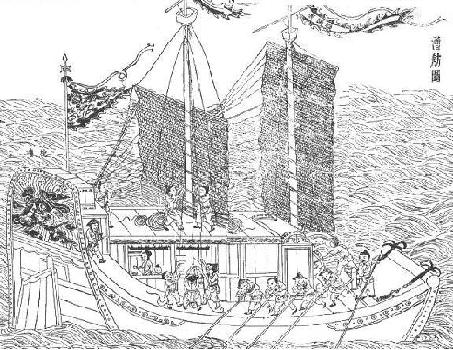 Shipbuilders in the Ming dynasty (1368~1644) were not the same as the shipbuilders in other Chinese dynasties, due to hundreds of years of accumulated experiences and rapid changes in the Ming dynasty. Shipbuilders in the Ming dynasty primarily worked for the government, under command of the Ministry of Works (imperial China), Ministry of Public Works.
During the early years of the Ming dynasty, the Ming government maintained an open policy towards sailing. Between 1405 and 1433, the government conducted seven diplomatic Ming treasure voyages to over thirty countries in Southeast Asia, India, the Middle East and Eastern Africa. The voyages were initiated by the Yongle Emperor, and led by the Admiral Zheng He. Six voyages were conducted under the Yongle Emperor's reign, the last of which returned to China in 1422. After the Yongle Emperor's death in 1424, his successor the Hongxi Emperor ordered the suspension of the voyages. The seventh and final voyage began in 1430, sent by the Xuande Emperor. Although the Hongxi and Xuande Emperors did not emphasize sailing as much as the Yongle Emperor, they were not against it. This led to a high degree of commercialization and an increase in trade. Large numbers of ships were built to meet the demand.
The Ming voyages were large in size, numbering as many as 300 ships and 28,000 men. The shipbuilders were brought from different places in China to the shipyard in Nanjing, including Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Fujian, and Huguang (now the provinces of Hubei and Hunan). One of the most famous shipyards was Long Jiang Shipyard (:zh:龙江船厂), located in Nanjing near the Treasure Shipyard where the ocean-going ships were built. The shipbuilders could build 24 models of ships of varying sizes.
Shipbuilders in the Ming dynasty (1368~1644) were not the same as the shipbuilders in other Chinese dynasties, due to hundreds of years of accumulated experiences and rapid changes in the Ming dynasty. Shipbuilders in the Ming dynasty primarily worked for the government, under command of the Ministry of Works (imperial China), Ministry of Public Works.
During the early years of the Ming dynasty, the Ming government maintained an open policy towards sailing. Between 1405 and 1433, the government conducted seven diplomatic Ming treasure voyages to over thirty countries in Southeast Asia, India, the Middle East and Eastern Africa. The voyages were initiated by the Yongle Emperor, and led by the Admiral Zheng He. Six voyages were conducted under the Yongle Emperor's reign, the last of which returned to China in 1422. After the Yongle Emperor's death in 1424, his successor the Hongxi Emperor ordered the suspension of the voyages. The seventh and final voyage began in 1430, sent by the Xuande Emperor. Although the Hongxi and Xuande Emperors did not emphasize sailing as much as the Yongle Emperor, they were not against it. This led to a high degree of commercialization and an increase in trade. Large numbers of ships were built to meet the demand.
The Ming voyages were large in size, numbering as many as 300 ships and 28,000 men. The shipbuilders were brought from different places in China to the shipyard in Nanjing, including Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Fujian, and Huguang (now the provinces of Hubei and Hunan). One of the most famous shipyards was Long Jiang Shipyard (:zh:龙江船厂), located in Nanjing near the Treasure Shipyard where the ocean-going ships were built. The shipbuilders could build 24 models of ships of varying sizes.
 Several types of ships were built for the voyages, including ''Shachuan'' (沙船), ''Fuchuan'' (福船) and ''Baochuan'' (Chinese treasure ship, treasure ship) (宝船). Zheng He's treasure ships were regarded as ''Shachuan'' types, mainly because they were made in the treasure shipyard in Nanjing. ''Shachuan'', or 'sand-ships', are ships used primarily for inland transport. However, in recent years, some researchers agree that the treasure ships were more of the ''Fuchuan'' type. It is said in vol. 176 of ''San Guo Bei Meng Hui Bian'' (三朝北盟汇编) that ships made in Fujian are the best ones. Therefore, the best shipbuilders and laborers were brought from these places to support Zheng He's expedition.
The shipyard was under the command of Ministry of Works (imperial China), Ministry of Public Works. The shipbuilders had no control over their lives. The builders, commoner's doctors, cooks and errands had lowest social status. The shipbuilders were forced to move away from their hometown to the shipyards. There were two major ways to enter the shipbuilder occupation: family tradition, or apprenticeship. If a shipbuilder entered the occupation due to family tradition, the shipbuilder learned the techniques of shipbuilding from his family and is very likely to earn a higher status in the shipyard. Additionally, the shipbuilder had access to business networking that could help to find clients. If a shipbuilder entered the occupation through an apprenticeship, the shipbuilder was likely a farmer before he was hired as a shipbuilder, or he was previously an experienced shipbuilder.
Many shipbuilders working in the shipyard were forced into the occupation. The ships built for Zheng He's voyages needed to be waterproof, solid, safe, and have ample room to carry large amounts of trading goods. Therefore, due to the highly commercialized society that was being encouraged by the expeditions, trades, and government policies, the shipbuilders needed to acquire the skills to build ships that fulfil these requirements.
Shipbuilding was not the sole industry utilising Chinese lumber at that time; the new capital was being built in Beijing from approximately 1407 onwards, which required huge amounts of high-quality wood. These two ambitious projects commissioned by Emperor Yongle would have had enormous environmental and economic effects, even if the ships were half the dimensions given in the ''History of Ming''. Considerable pressure would also have been placed on the infrastructure required to transport the trees from their point of origin to the shipyards.
Shipbuilders were usually divided into different groups and had separate jobs. Some were responsible for fixing old ships; some were responsible for making the keel and some were responsible for building the helm.
* It was the keel that determined the shape and the structure of the hull of ''Fuchuan'' Ships. The keel is the middle of the bottom of the hull, constructed by connecting three sections; stern keel, main keel and poop keel. The hull spreads in the arc towards both sides forming the keel.
* The Ship's wheel, helm was the device that controls direction when sailing. It was a critical invention in shipbuilding technique in ancient China and was only used by the Chinese for a fairly long time. With a developing recognition of its function, the shape and configuration of the helm was continually improved by shipbuilders. The shipbuilders not only needed to build the ship according to design, but needed to acquire the skills to improve the ships.
After 1477, the Ming government reversed its open maritime policies, enacting a series of isolationist policies in response to wokou, piracy. The policies, called ''Haijin'' (sea ban), lasted until the end of the Ming dynasty in 1644. During this period, Chinese navigation technology did not make any progress and even declined in some aspect.
Several types of ships were built for the voyages, including ''Shachuan'' (沙船), ''Fuchuan'' (福船) and ''Baochuan'' (Chinese treasure ship, treasure ship) (宝船). Zheng He's treasure ships were regarded as ''Shachuan'' types, mainly because they were made in the treasure shipyard in Nanjing. ''Shachuan'', or 'sand-ships', are ships used primarily for inland transport. However, in recent years, some researchers agree that the treasure ships were more of the ''Fuchuan'' type. It is said in vol. 176 of ''San Guo Bei Meng Hui Bian'' (三朝北盟汇编) that ships made in Fujian are the best ones. Therefore, the best shipbuilders and laborers were brought from these places to support Zheng He's expedition.
The shipyard was under the command of Ministry of Works (imperial China), Ministry of Public Works. The shipbuilders had no control over their lives. The builders, commoner's doctors, cooks and errands had lowest social status. The shipbuilders were forced to move away from their hometown to the shipyards. There were two major ways to enter the shipbuilder occupation: family tradition, or apprenticeship. If a shipbuilder entered the occupation due to family tradition, the shipbuilder learned the techniques of shipbuilding from his family and is very likely to earn a higher status in the shipyard. Additionally, the shipbuilder had access to business networking that could help to find clients. If a shipbuilder entered the occupation through an apprenticeship, the shipbuilder was likely a farmer before he was hired as a shipbuilder, or he was previously an experienced shipbuilder.
Many shipbuilders working in the shipyard were forced into the occupation. The ships built for Zheng He's voyages needed to be waterproof, solid, safe, and have ample room to carry large amounts of trading goods. Therefore, due to the highly commercialized society that was being encouraged by the expeditions, trades, and government policies, the shipbuilders needed to acquire the skills to build ships that fulfil these requirements.
Shipbuilding was not the sole industry utilising Chinese lumber at that time; the new capital was being built in Beijing from approximately 1407 onwards, which required huge amounts of high-quality wood. These two ambitious projects commissioned by Emperor Yongle would have had enormous environmental and economic effects, even if the ships were half the dimensions given in the ''History of Ming''. Considerable pressure would also have been placed on the infrastructure required to transport the trees from their point of origin to the shipyards.
Shipbuilders were usually divided into different groups and had separate jobs. Some were responsible for fixing old ships; some were responsible for making the keel and some were responsible for building the helm.
* It was the keel that determined the shape and the structure of the hull of ''Fuchuan'' Ships. The keel is the middle of the bottom of the hull, constructed by connecting three sections; stern keel, main keel and poop keel. The hull spreads in the arc towards both sides forming the keel.
* The Ship's wheel, helm was the device that controls direction when sailing. It was a critical invention in shipbuilding technique in ancient China and was only used by the Chinese for a fairly long time. With a developing recognition of its function, the shape and configuration of the helm was continually improved by shipbuilders. The shipbuilders not only needed to build the ship according to design, but needed to acquire the skills to improve the ships.
After 1477, the Ming government reversed its open maritime policies, enacting a series of isolationist policies in response to wokou, piracy. The policies, called ''Haijin'' (sea ban), lasted until the end of the Ming dynasty in 1644. During this period, Chinese navigation technology did not make any progress and even declined in some aspect.

 Initially copying wooden construction traditions with a frame over which the hull was fastened, Isambard Kingdom Brunel's of 1843 was the first radical new design, being built entirely of wrought iron. Despite her success, and the great savings in cost and space provided by the iron hull, compared to a copper-sheathed counterpart, there remained problems with fouling due to the adherence of weeds and barnacles. As a result, composite construction remained the dominant approach where fast ships were required, with wooden timbers laid over an iron frame (''Cutty Sark'' is a famous example). Later ''Great Britain''s iron hull was sheathed in wood to enable it to carry a Copper sheathing, copper-based sheathing. Brunel's represented the next great development in shipbuilding. Built-in association with John Scott Russell, it used longitudinal wikt: stringer, stringers for strength, inner and outer hulls, and Bulkhead (partition), bulkheads to form multiple watertight compartments. Steel also supplanted wrought iron when it became readily available in the latter half of the 19th century, providing great savings when compared with iron in cost and weight. Wood continued to be favored for the decks.
During World War II, the need for cargo ships was so great that construction time for Liberty ships went from initially eight months or longer, down to weeks or even days. They employed production line and prefabrication techniques such as those used in shipyards today. The total number of dry-cargo ships built in the United States in a 15-year period just before the war was a grand total of two. During the war, thousands of Liberty ships and Victory ships were built, many of them in shipyards that did not exist before the war. And, they were built by a workforce consisting largely of women and other inexperienced workers who had never seen a ship before (or even the ocean).
Initially copying wooden construction traditions with a frame over which the hull was fastened, Isambard Kingdom Brunel's of 1843 was the first radical new design, being built entirely of wrought iron. Despite her success, and the great savings in cost and space provided by the iron hull, compared to a copper-sheathed counterpart, there remained problems with fouling due to the adherence of weeds and barnacles. As a result, composite construction remained the dominant approach where fast ships were required, with wooden timbers laid over an iron frame (''Cutty Sark'' is a famous example). Later ''Great Britain''s iron hull was sheathed in wood to enable it to carry a Copper sheathing, copper-based sheathing. Brunel's represented the next great development in shipbuilding. Built-in association with John Scott Russell, it used longitudinal wikt: stringer, stringers for strength, inner and outer hulls, and Bulkhead (partition), bulkheads to form multiple watertight compartments. Steel also supplanted wrought iron when it became readily available in the latter half of the 19th century, providing great savings when compared with iron in cost and weight. Wood continued to be favored for the decks.
During World War II, the need for cargo ships was so great that construction time for Liberty ships went from initially eight months or longer, down to weeks or even days. They employed production line and prefabrication techniques such as those used in shipyards today. The total number of dry-cargo ships built in the United States in a 15-year period just before the war was a grand total of two. During the war, thousands of Liberty ships and Victory ships were built, many of them in shipyards that did not exist before the war. And, they were built by a workforce consisting largely of women and other inexperienced workers who had never seen a ship before (or even the ocean).
 After World War II, shipbuilding (which encompasses the shipyards, the marine equipment manufacturers, and many related Service industry, service and Knowledge economy, knowledge providers) grew as an important and strategic industry in a number of countries around the world. This importance stems from:
* The large number of skilled workers required directly by the shipyard, along with supporting industries such as steel mills, railroads and engine manufacturers; and
* A nation's need to manufacture and repair its own navy and vessels that support its primary Industry (economics), industries
Historically, the industry has suffered from the absence of International trade law, global rules and a tendency towards (Government, state-Subsidy, supported) over-investment due to the fact that shipyards offer a wide range of technologies, employ a significant number of workers, and generate income as the shipbuilding market is World economy, global.
Japan used shipbuilding in the 1950s and 1960s to rebuild its industrial structure; South Korea started to make shipbuilding a strategic industry in the 1970s, and China is now in the process of repeating these models with large state-supported investments in this industry. Conversely, Croatia is privatising its shipbuilding industry.
As a result, the world shipbuilding market suffers from over-capacities, depressed prices (although the industry experienced a price increase in the period 2003–2005 due to strong demand for new ships which was in excess of actual cost increases), low profit margins, trade distortions and widespread subsidisation. All efforts to address the problems in the OECD have so far failed, with the 1994 international shipbuilding agreement never entering into force and the 2003–2005 round of negotiations being paused in September 2005 after no agreement was possible. After numerous efforts to restart the negotiations these were formally terminated in December 2010. The OECD's Council Working Party on Shipbuilding (WP6) will continue its efforts to identify and progressively reduce factors that distort the shipbuilding market.
Where state Subsidy, subsidies have been removed and domestic industrial policies do not provide support in high labor cost countries, shipbuilding has gone into decline. The British shipbuilding industry is a prime example of this with its industries suffering badly from the 1960s. In the early 1970s British yards still had the capacity to build all types and sizes of merchant ships but today they have been reduced to a small number specialising in defence contracts, luxury yachts and repair work. Decline has also occurred in other European countries, although to some extent this has reduced by protective measures and industrial support policies. In the US, the Merchant Marine Act of 1920, Jones Act (which places restrictions on the ships that can be used for moving domestic cargoes) has meant that merchant shipbuilding has continued, albeit at a reduced rate, but such protection has failed to penalise shipbuilding inefficiencies. The consequence of this is that contract prices are far higher than those of any other country building oceangoing ships.
After World War II, shipbuilding (which encompasses the shipyards, the marine equipment manufacturers, and many related Service industry, service and Knowledge economy, knowledge providers) grew as an important and strategic industry in a number of countries around the world. This importance stems from:
* The large number of skilled workers required directly by the shipyard, along with supporting industries such as steel mills, railroads and engine manufacturers; and
* A nation's need to manufacture and repair its own navy and vessels that support its primary Industry (economics), industries
Historically, the industry has suffered from the absence of International trade law, global rules and a tendency towards (Government, state-Subsidy, supported) over-investment due to the fact that shipyards offer a wide range of technologies, employ a significant number of workers, and generate income as the shipbuilding market is World economy, global.
Japan used shipbuilding in the 1950s and 1960s to rebuild its industrial structure; South Korea started to make shipbuilding a strategic industry in the 1970s, and China is now in the process of repeating these models with large state-supported investments in this industry. Conversely, Croatia is privatising its shipbuilding industry.
As a result, the world shipbuilding market suffers from over-capacities, depressed prices (although the industry experienced a price increase in the period 2003–2005 due to strong demand for new ships which was in excess of actual cost increases), low profit margins, trade distortions and widespread subsidisation. All efforts to address the problems in the OECD have so far failed, with the 1994 international shipbuilding agreement never entering into force and the 2003–2005 round of negotiations being paused in September 2005 after no agreement was possible. After numerous efforts to restart the negotiations these were formally terminated in December 2010. The OECD's Council Working Party on Shipbuilding (WP6) will continue its efforts to identify and progressively reduce factors that distort the shipbuilding market.
Where state Subsidy, subsidies have been removed and domestic industrial policies do not provide support in high labor cost countries, shipbuilding has gone into decline. The British shipbuilding industry is a prime example of this with its industries suffering badly from the 1960s. In the early 1970s British yards still had the capacity to build all types and sizes of merchant ships but today they have been reduced to a small number specialising in defence contracts, luxury yachts and repair work. Decline has also occurred in other European countries, although to some extent this has reduced by protective measures and industrial support policies. In the US, the Merchant Marine Act of 1920, Jones Act (which places restrictions on the ships that can be used for moving domestic cargoes) has meant that merchant shipbuilding has continued, albeit at a reduced rate, but such protection has failed to penalise shipbuilding inefficiencies. The consequence of this is that contract prices are far higher than those of any other country building oceangoing ships.
Newsletter No. 64, December 2011, In 2022, some key shipbuilders in Europe are Fincantieri, Damen Group, Navantia, Naval Group and BAE Systems. Shipbuilding output of the United States also underwent a similar change. The US is ranked the 10th largest shipbuilder worldwide. The top companies that build large naval vessels, such as aircraft carriers and cruisers, include Huntington Ingalls, Bollinger Shipyards, Bollinger and General Dynamics. In the small to medium military vessels category, key shipbuilders include Vigor Industrial, and VT Halter Marine. As the US Navy is shifting to a new fleet architecture that is more widely distributed, unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) development is rapidly propelled to higher priority. Key strategic Program of Record includes prototyping and construction of up to 9 MUSVs, for which a sole contract was awarded to L3Harris Technologies, who partnered with Swiftships to build the MUSVs. In 2018, the US Defense Department initiated Overlord Program, and developed USV Prototypes 1 (NOMAD) and 2 (RANGER). Both of them took part in multiple fleet level exercises and demonstrations, traveled in autonomous mode, and tested numerous payloads. Nomam, formerly known as Riley Claire, is a converted offshore patrol vessel, which was built by Swiftships. The objective of the Ghost Fleet Overlord program is to convert large, commercial vessels to autonomous systems. , China builds nearly 75% of new vessels on order and has the capacity to build more ships in one month than the United States builds in a year.
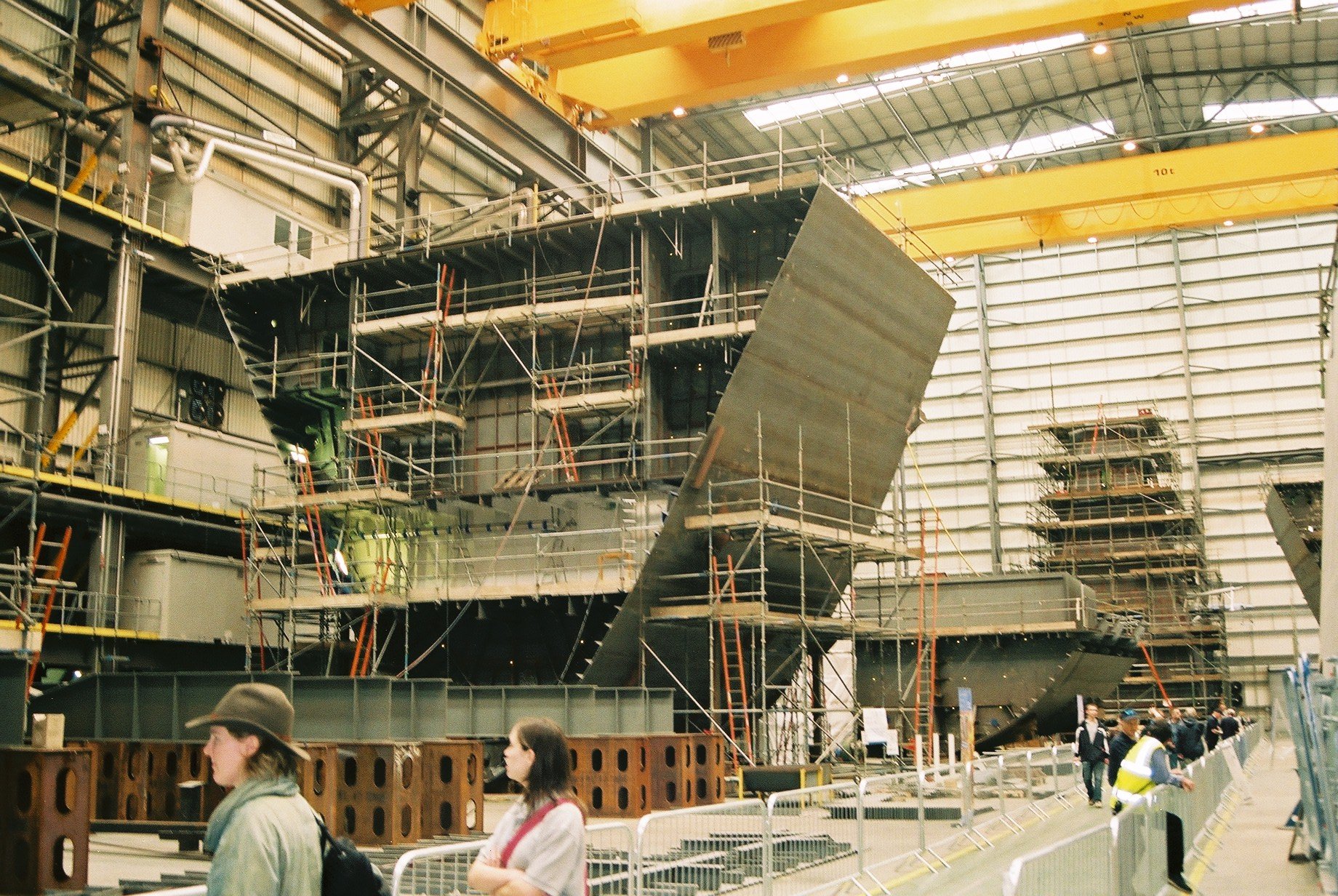 Modern shipbuilding makes considerable use of prefabrication, prefabricated modular design, modular sections. Entire multi-deck segments of the hull or Superstructure (ship), superstructure will be built elsewhere in the yard, transported to the building dock or slipway, then lifted into place. This is known as "block construction". The most modern shipyards pre-install equipment, pipes, electrical cables, and any other components within the blocks, to minimize the effort needed to assemble or install components deep within the hull once it is welded together.
Ship design work, also called naval architecture, may be conducted using a ship model basin. Previously, loftsmen at the mould lofts of
Modern shipbuilding makes considerable use of prefabrication, prefabricated modular design, modular sections. Entire multi-deck segments of the hull or Superstructure (ship), superstructure will be built elsewhere in the yard, transported to the building dock or slipway, then lifted into place. This is known as "block construction". The most modern shipyards pre-install equipment, pipes, electrical cables, and any other components within the blocks, to minimize the effort needed to assemble or install components deep within the hull once it is welded together.
Ship design work, also called naval architecture, may be conducted using a ship model basin. Previously, loftsmen at the mould lofts of
Shipbuilding Picture Dictionary
U.S. Shipbuilding
xtensive information about the U.S. shipbuilding industry, including over 500 pages of U.S. shipyard construction records
Shipbuilding News
Bataviawerf – the Historic Dutch East Indiaman Ship Yard
hipyard of the historic ships Batavia and Zeven Provincien in the Netherlands, since 1985 here have been great ships reconstructed using old construction methods.
Photos of the reconstruction of the Dutch East Indiaman Batavia
Photo web site about the reconstruction of the ''Batavia'' on the shipyard Batavia werf, a 16th-century East Indiaman in the Netherlands. The site is constantly expanding with more historic images as in 2010 the shipyard celebrates its 25th year.
Modern shipbuilding and the men engaged in it
David Pollock (London: E. & F. N. Spon, 1884). {{Authority control Shipbuilding, Shipwrights, Naval architecture
 Shipbuilding is the
Shipbuilding is the construction
Construction are processes involved in delivering buildings, infrastructure, industrial facilities, and associated activities through to the end of their life. It typically starts with planning, financing, and design that continues until the a ...
of ship
A ship is a large watercraft, vessel that travels the world's oceans and other Waterway, navigable waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research and fishing. Ships are generally disti ...
s and other floating vessels. In modern times, it normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard
A shipyard, also called a dockyard or boatyard, is a place where ships are shipbuilding, built and repaired. These can be yachts, military vessels, cruise liners or other cargo or passenger ships. Compared to shipyards, which are sometimes m ...
. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to before recorded history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world h ...
.
Until recently, with the development of complex non-maritime technologies, a ship has often represented the most advanced structure that the society building it could produce. Some key industrial advances were developed to support shipbuilding, for instance the sawing of timbers by mechanical saws propelled by windmill
A windmill is a machine operated by the force of wind acting on vanes or sails to mill grain (gristmills), pump water, generate electricity, or drive other machinery.
Windmills were used throughout the high medieval and early modern period ...
s in Dutch shipyards during the first half of the 17th century. The design process saw the early adoption of the logarithm
In mathematics, the logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, must be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of to base is , because is to the rd power: . More generally, if , the ...
(invented in 1615) to generate the curves used to produce the shape of a hull, especially when scaling up these curves accurately in the mould loft
A loft is a building's upper storey or elevated area in a room directly under the roof (American usage), or just an attic: a storage space under the roof usually accessed by a ladder (primarily British usage). A loft apartment refers to large ...
.
Shipbuilding and ship repairs, both commercial and military, are referred to as naval engineering. The construction of boat
A boat is a watercraft of a large range of types and sizes, but generally smaller than a ship, which is distinguished by its larger size or capacity, its shape, or its ability to carry boats.
Small boats are typically used on inland waterways s ...
s is a similar activity called boat building
Boat building is the design and construction of boats (instead of the larger ships) — and their on-board systems. This includes at minimum the construction of a hull, with any necessary propulsion, mechanical, navigation, safety and other ser ...
.
The dismantling of ships is called ship breaking
Ship breaking (also known as ship recycling, ship demolition, ship scrapping, ship dismantling, or ship cracking) is a type of ship disposal involving the breaking up of ships either as a source of Interchangeable parts, parts, which can be sol ...
.
The earliest evidence of maritime transport by modern humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are great apes characterized by their hairlessness, bipedalism, and high intelligen ...
is the settlement of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
between 50,000 and 60,000 years ago. This almost certainly involved raft
A raft is any flat structure for support or transportation over water. It is usually of basic design, characterized by the absence of a hull. Rafts are usually kept afloat by using any combination of buoyant materials such as wood, sealed barre ...
s, possibly equipped with some sort of sail
A sail is a tensile structure, which is made from fabric or other membrane materials, that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails may b ...
. Much of the development beyond that raft technology occurred in the "nursery" areas of the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
and in Maritime Southeast Asia
Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the Southeast Asian countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and East Timor.
The terms Island Southeast Asia and Insular Southeast Asia are sometimes given the same meaning as ...
. Favoured by warmer waters and a number of inter-visible islands, boats (and, later, ships) with water-tight hulls (unlike the "flow through" structure of a raft) could be developed. The ships of ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
were built by joining the hull planks together, edge to edge, with tenons set in mortices cut in the mating edges. A similar technique, but with the tenons being pinned in position by dowels, was used in the Mediterranean for most of classical antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the inter ...
. Both these variants are "shell first" techniques, where any reinforcing frames are inserted after assembly of the planking has defined the hull shape. Carvel construction then took over in the Mediterranean. Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other ge ...
used clinker construction, but with some flush-planked ship-building in, for instance, the bottom planking of cogs. The north-European and Mediterranean traditions merged in the late 15th century, with carvel construction being adopted in the North and the centre-line mounted rudder replacing the quarter rudder of the Mediterranean. These changes broadly coincided with improvements in sailing rigs, with the three masted ship becoming common, with square sails on the fore and main masts, and a fore and aft sail on the mizzen.
Ship-building then saw a steady improvement in design techniques and introduction of new materials. Iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
was used for more than fastenings ( nails and bolts) as structural components such as iron knees were introduced, with examples existing in the mid-18th century and from the mid-19th century onwards. This was partly led by the shortage of "compass timber", the naturally curved timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into uniform and useful sizes (dimensional lumber), including beams and planks or boards. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, window frames). ...
that meant that shapes could be cut without weaknesses caused by cuts across the grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached husk, hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and ...
of the timber. Ultimately, whole ships were made of iron and, later, steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
.
History
Pre-history
The earliest known depictions (including paintings and models) of shallow-watersailing boat
A sailboat or sailing boat is a boat propelled partly or entirely by sails and is smaller than a sailing ship. Distinctions in what constitutes a sailing boat and ship vary by region and maritime culture.
Types
Although sailboat terminology ...
s is from the 6th to 5th millennium BC of the Ubaid period
The Ubaid period (c. 5500–3700 BC) is a prehistoric period of Mesopotamia. The name derives from Tell al-'Ubaid where the earliest large excavation of Ubaid period material was conducted initially in 1919 by Henry Hall, Leonard Woolley in 19 ...
of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
. They were made from bundled reeds coated in bitumen
Bitumen ( , ) is an immensely viscosity, viscous constituent of petroleum. Depending on its exact composition, it can be a sticky, black liquid or an apparently solid mass that behaves as a liquid over very large time scales. In American Engl ...
and had bipod masts. They sailed in shallow coastal waters of the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
.
4th millennium BC
Ancient Egypt
Evidence fromAncient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
shows that the early Egyptians
Egyptians (, ; , ; ) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian identity is closely tied to Geography of Egypt, geography. The population is concentrated in the Nile Valley, a small strip of cultivable land stretchi ...
knew how to assemble planks of wood into a ship hull
A hull is the watertight body of a ship, boat, submarine, or flying boat. The hull may open at the top (such as a dinghy), or it may be fully or partially covered with a deck. Atop the deck may be a deckhouse and other superstructures, such as ...
as early as 3100 BC. Egyptian pottery as old as 4000 BC shows designs of early fluvial boats or other means for navigation. The Archaeological Institute of America
The Archaeological Institute of America (AIA) is North America, North America's oldest learned society and largest organization devoted to the world of archaeology. AIA professionals have carried out archaeological fieldwork around the world and ...
reportsWard, Cheryl.World's Oldest Planked Boats
, in ''
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
'' (Volume 54, Number 3, May/June 2009). Archaeological Institute of America
The Archaeological Institute of America (AIA) is North America, North America's oldest learned society and largest organization devoted to the world of archaeology. AIA professionals have carried out archaeological fieldwork around the world and ...
. that some of the oldest ships yet unearthed are known as the Abydos boats
The Abydos boats are the remnants of a group of ancient royal Egyptian ceremonial boats found at an archaeological site in Abydos, Egypt. Discovered in 1991, excavation of the Abydos boats began in 2000 at which time fourteen boats were identified ...
. These are a group of 14 ships discovered in Abydos that were constructed of wooden planks which were "sewn" together. Discovered by Egyptologist David O'Connor of New York University
New York University (NYU) is a private university, private research university in New York City, New York, United States. Chartered in 1831 by the New York State Legislature, NYU was founded in 1832 by Albert Gallatin as a Nondenominational ...
,Schuster, Angela M.H.This Old Boat
, 11 December 2000.
Archaeological Institute of America
The Archaeological Institute of America (AIA) is North America, North America's oldest learned society and largest organization devoted to the world of archaeology. AIA professionals have carried out archaeological fieldwork around the world and ...
. woven strap
A strap, sometimes also called strop, is an elongated flap or ribbon, usually of leather or other flexible materials.
Thin straps are used as part of clothing or baggage, or bedding such as a sleeping bag. See for example spaghetti strap, s ...
s were found to have been used to lash the planks together, and reeds or grass stuffed between the planks helped to seal the seams. Because the ships are all buried together and near a mortuary belonging to Pharaoh Khasekhemwy, originally they were all thought to have belonged to him, but one of the 14 ships dates to 3000 BC, and the associated pottery jars buried with the vessels also suggest earlier dating. The ship dating to 3000 BC was about 75 feet (23 m) long and is now thought to perhaps have belonged to an earlier pharaoh. According to professor O'Connor, the 5,000-year-old ship may have even belonged to Pharaoh Aha.
Austronesia
TheAustronesian expansion
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Southeast Asia, parts of mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesi ...
, which began with migration from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
to the island of Luzon
Luzon ( , ) is the largest and most populous List of islands in the Philippines, island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the List of islands of the Philippines, Philippine archipelago, it is the economic and political ce ...
in the Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, spread across Island Southeast Asia. Then, between 1500 BC and 1500 AD they settled uninhabited islands of the Pacific, and also sailed westward to Madagascar. This is associated with distinctive maritime technology: lashed lug construction techniques (both in outrigger canoes and in large planked sailing vessels), various types of outrigger
An outrigger is a projecting structure on a boat, with specific meaning depending on types of vessel. Outriggers may also refer to legs on a wheeled vehicle that are folded out when it needs stabilization, for example on a crane that lifts he ...
and twin-hulled canoes and a range of sailing rigs that included the crab claw sail. The origins of this technology is difficult to date, relying largely on linguistics (studying the words for parts of boats), the written comments of people from other cultures, including the observations of European explorers at the time of first contact and the later more systematic ethnographic observations of the types of craft in use. There is only a small body of archaeological evidence available. Since Island Southeast Asia contained effective maritime transport between its very large number of islands long before Austronesian seafaring, it is argued that Austronesians adopted an existing maritime technology from the existing inhabitants of this region.
Austronesian ships varied from simple canoes to large multihull
A multihull is a boat or ship with more than one Hull (watercraft), hull, whereas a vessel with a single hull is a monohull. The most common multihulls are catamarans (with two hulls), and trimarans (with three hulls). There are other types, wi ...
ships. The simplest form of all ancestral Austronesian boats had five parts. The bottom part consists of a single piece of hollowed-out log. At the sides were two planks, and two horseshoe-shaped wood pieces formed the prow
The bow () is the forward part of the hull (watercraft), hull of a ship or boat, the point that is usually most forward when the vessel is underway. The aft end of the boat is the stern.
Prow may be used as a synonym for bow or it may mean the f ...
and stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. O ...
. These were fitted tightly together edge-to-edge with dowel
The dowel is a cylindrical shape made of wood, plastic, or metal. In its original manufactured form, a dowel is long and called a ''dowel rod'', which are often cut into shorter ''dowel pins''. Dowels are commonly used as structural reinforceme ...
s inserted into holes in between, and then lashed to each other with ropes (made from rattan
Rattan, also spelled ratan (from Malay language, Malay: ''rotan''), is the name for roughly 600 species of Old World climbing palms belonging to subfamily Calamoideae. The greatest diversity of rattan palm species and genera are in the clos ...
or fiber) wrapped around protruding lugs on the planks. This characteristic and ancient Austronesian boatbuilding practice is known as the " lashed-lug" technique. They were commonly caulk
Caulk (also known as caulking and calking) is a material used to Seal (mechanical), seal Joint (building), joints or seams against leakage in various structures and piping.
The oldest form of caulk consisted of fibrous materials driven into ...
ed with pastes made from various plants as well as tapa bark and fibres which would expand when wet, further tightening joints and making the hull watertight. They formed the shell of the boat, which was then reinforced by horizontal ribs. Shipwrecks of Austronesian ships can be identified from this construction as well as the absence of metal nails. Austronesian ships traditionally had no central rudders but were instead steered using an oar on one side.
 Austronesians traditionally made their sails from woven mats of the resilient and salt-resistant
Austronesians traditionally made their sails from woven mats of the resilient and salt-resistant pandanus
''Pandanus'' is a genus of monocots with about 578 accepted species. They are palm-like, dioecious trees and shrubs native to the Old World tropics and subtropics. Common names include pandan, screw palm and screw pine. The genus is classified ...
leaves. These sails allowed Austronesians to embark on long-distance voyaging.
The ancient Champa
Champa (Cham language, Cham: ꨌꩌꨛꨩ, چمڤا; ; 占城 or 占婆) was a collection of independent Chams, Cham Polity, polities that extended across the coast of what is present-day Central Vietnam, central and southern Vietnam from ...
of Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
also uniquely developed basket-hulled boats whose hulls were composed of woven and resin
A resin is a solid or highly viscous liquid that can be converted into a polymer. Resins may be biological or synthetic in origin, but are typically harvested from plants. Resins are mixtures of organic compounds, predominantly terpenes. Commo ...
-caulk
Caulk (also known as caulking and calking) is a material used to Seal (mechanical), seal Joint (building), joints or seams against leakage in various structures and piping.
The oldest form of caulk consisted of fibrous materials driven into ...
ed bamboo, either entirely or in conjunction with plank strake
On a vessel's Hull (watercraft), hull, a strake is a longitudinal course of Plank (wood), planking or Plate (metal), plating which runs from the boat's stem (ship), stempost (at the Bow (ship), bows) to the stern, sternpost or transom (nautica ...
s. They range from small coracle
A coracle is a small, rounded, lightweight boat of the sort traditionally used in Wales, and also in parts of the west of Ireland and also particularly on the River Boyne, and in Scotland, particularly the River Spey. The word is also used for ...
s (the '' o thúng'') to large ocean-going trading ships like the '' ghe mành''.
3rd millennium BC
Ancient Egypt
Early Egyptians also knew how to assemble planks of wood with treenails to fasten them together, using pitch forcaulking
Caulk (also known as caulking and calking) is a material used to seal joints or seams against leakage in various structures and piping.
The oldest form of caulk consisted of fibrous materials driven into the wedge-shaped seams between board ...
the seams. The " Khufu ship", a 43.6-meter vessel sealed into a pit in the Giza pyramid complex
The Giza pyramid complex (also called the Giza necropolis) in Egypt is home to the Great Pyramid of Giza, Great Pyramid, the pyramid of Khafre, and the pyramid of Menkaure, along with their associated pyramid complexes and the Great Sphinx of G ...
at the foot of the Great Pyramid of Giza
The Great Pyramid of Giza is the largest Egyptian pyramid. It served as the tomb of pharaoh Khufu, who ruled during the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt, Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom. Built , over a period of about 26 years ...
in the Fourth Dynasty around 2500 BC, is a full-size surviving example which may have fulfilled the symbolic function of a solar barque
thumb
Solar barques were the vessels used by the sun god Ra in ancient Egyptian mythology. During the day, Ra was said to use a vessel called the Mandjet () or the Boat of Millions of Years (), and the vessel he used during the night was known ...
. Early Egyptians also knew how to fasten the planks of this ship together with mortise and tenon
A mortise and tenon (occasionally mortice and tenon) is a Woodworking joints, joint that connects two pieces of wood or other material. Woodworking, Woodworkers around the world have used it for thousands of years to join pieces of wood, mainly ...
joints.
Indus Valley
The oldest known tidal dock in the world was built around 2500 BC during the Harappan civilisation atLothal
Lothal () was one of the southernmost sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilization, Indus Valley civilisation, located in the Bhal region of the Indian state of Gujarat. Construction of the city is believed to have begun around 2200 BCE.
Di ...
near the present day Mangrol harbour on the Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
coast in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
. Other ports were probably at Kot Bala and Dwarka
Dwarka () is a town and municipality of Devbhumi Dwarka district in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Gujarat. It is located on the western shore of the Okhamandal Peninsula on the right bank of the Gomti river at ...
. However, it is probable that many small-scale ports, and not massive ports, were used for the Harappan maritime trade. Ships from the harbour at these ancient port cities established trade with Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
. Shipbuilding and boatmaking may have been prosperous industries in ancient India. Native labourers may have manufactured the flotilla of boats used by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
to navigate across the Hydaspes
The Jhelum River is a major river in South Asia, flowing through India and Pakistan, and is the westernmost of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It originates at Verinag and flows through the Indian-administered territory of Jammu an ...
and even the Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the dis ...
, under Nearchos.Tripathi, p. 145 The Indians also exported teak
Teak (''Tectona grandis'') is a tropical hardwood tree species in the family Lamiaceae. It is a large, deciduous tree that occurs in mixed hardwood forests. ''Tectona grandis'' has small, fragrant white flowers arranged in dense clusters (panic ...
for shipbuilding to ancient Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
. Other references to Indian timber used for shipbuilding is noted in the works of Ibn Jubayr
Ibn Jubayr (1 September 1145 – 29 November 1217; ), also written Ibn Jubair, Ibn Jobair, and Ibn Djubayr, was an Arab geographer, traveller and poet from al-Andalus. His travel chronicle describes the pilgrimage he made to Mecca from 1183 to 11 ...
.Hourani & Carswel, p. 90
2nd millennium BC

Mediterranean
The ships of Ancient Egypt'sEighteenth Dynasty
The Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XVIII, alternatively 18th Dynasty or Dynasty 18) is classified as the first dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. The Eighteenth Dynasty ...
were typically about 25 meters (80 ft) in length and had a single mast, sometimes consisting of two poles lashed together at the top making an "A" shape. They mounted a single square sail
A sail is a tensile structure, which is made from fabric or other membrane materials, that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails may b ...
on a yard
The yard (symbol: yd) is an English units, English unit of length in both the British imperial units, imperial and US United States customary units, customary systems of measurement equalling 3 foot (unit), feet or 36 inches. Sinc ...
, with an additional spar (sailing), spar along the bottom of the sail. These ships could also be oar propelled. The ocean- and sea-going ships of Ancient Egypt were constructed with cedar wood, most likely hailing from Lebanon.
The ships of Phoenicia seem to have been of a similar design.
1st millennium BC
Austronesia
Austronesians established the Austronesian maritime trade network at around 1000 to 600 BC, linking Southeast Asia with East Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and later East Africa. The route later became part of the Spice trade network and the Maritime Silk Road.China
The naval history of China stems back to the Spring and Autumn period (722 BC–481 BC) of the ancient Chinese Zhou dynasty. The Chinese built large rectangular barges known as "castle ships", which were essentially floating fortresses complete with multiple decks with guarded Defensive wall, ramparts. However, the Chinese vessels during this era were essentially fluvial (riverine). True ocean-going Chinese fleets did not appear until the 10th century Song dynasty.Mediterranean
There is considerable knowledge regarding shipbuilding and seafaring in the ancient Mediterranean.1st millennium AD
Austronesia
 Austronesians (especially from western Island Southeast Asia) were trading in the Indian Ocean as far as Africa during this period. By around 50 to 500 AD, a group of Austronesians, believed to be from the southeastern coasts of Borneo (possibly a mixed group related to the modern Ma'anyan people, Ma'anyan, Banjar people, Banjar, and/or the Dayak people) crossed the Indian Ocean and colonized Madagascar. This resulted in the introduction of outrigger canoe technology to non-Austronesian cultures in the East African coast.
Austronesians (especially from western Island Southeast Asia) were trading in the Indian Ocean as far as Africa during this period. By around 50 to 500 AD, a group of Austronesians, believed to be from the southeastern coasts of Borneo (possibly a mixed group related to the modern Ma'anyan people, Ma'anyan, Banjar people, Banjar, and/or the Dayak people) crossed the Indian Ocean and colonized Madagascar. This resulted in the introduction of outrigger canoe technology to non-Austronesian cultures in the East African coast.
China
The ancient China, Chinese also built fluvial ramming vessels as in the Greco-Roman tradition of the trireme, although oar-steered ships in China lost favor very early on since it was in the 1st century China that thestern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. O ...
-mounted rudder was first developed. This was dually met with the introduction of the Han dynasty Junk (ship), junk ship design in the same century. The Chinese were using square sails during the Han dynasty and adopted the Austronesian junk sail later in the 12th century. Iconographic remains show that Chinese ships before the 12th century used square sails, and the junk rig of Chinese ships is believed to be developed from Tanja sail, tilted sails.Needham, Joseph (1971). ''Science and Civilisation in China: Volume 4, Physics and Physical Technology, Part III: Civil Engineering and Nautics''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Southern Chinese junks were based on keeled and lashed-lug, multi-planked Austronesian ship known as ''po'' by the Chinese, from the Old Javanese ''parahu'',' Javanese ''prau'', or Malay ''perahu'' – large ship.Manguin, Pierre-Yves. 2012. "Asian ship-building traditions in the Indian Ocean at the dawn of European expansion", in: Om Prakash and D. P. Chattopadhyaya (eds), ''History of science, philosophy, and culture in Indian Civilization'', Volume III, part 7: The trading world of the Indian Ocean, 1500–1800, pp. 597–629. Delhi, Chennai, Chandigarh: Pearson. Southern Chinese junks showed characteristics of Austronesian ships that they are made using timbers of tropical origin, with keeled, V-shaped hull. This is different from northern Chinese junks, which are developed from flat-bottomed riverine boats. The northern Chinese junks were primarily built of pine or fir wood, had flat bottoms with no keel, water-tight bulkheads with no frames, transom (squared) stern and stem, and have their planks fastened with iron nails or clamps.
It was unknown when the Chinese people started adopting Southeast Asian (Austronesian) shipbuilding techniques. They may have been started as early as the 8th century, but the development was gradual and the true ocean-going Chinese junks did not appear suddenly. The word "po" survived in Chinese long after, referring to the large ocean-going junks.
Mediterranean
In September 2011, archeological investigations done at the site of Portus in Rome revealed inscriptions in ashipyard
A shipyard, also called a dockyard or boatyard, is a place where ships are shipbuilding, built and repaired. These can be yachts, military vessels, cruise liners or other cargo or passenger ships. Compared to shipyards, which are sometimes m ...
constructed during the reign of Trajan (98–117) that indicated the existence of a shipbuilders guild.
Early 2nd millennium AD
Austronesia
Roughly at this time is the last migration wave of theAustronesian expansion
The Austronesian people, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples who have settled in Taiwan, maritime Southeast Asia, parts of mainland Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesi ...
, when the Polynesian islands spread over vast distances across the Pacific Ocean were being colonized by the (Austronesian) Polynesians, Polynesians from Island Melanesia using double-hulled voyaging catamarans. At its furthest extent, there is a possibility that they may have reached the Americas. After the 11th century, a new type of ship called djong or Jong (ship), jong was recorded in Java and Bali. This type of ship was built using wooden dowels and treenails, unlike the ''kunlun bo'' which used vegetal fibres for lashings.
The empire of Majapahit used jong, built in northern Java, for transporting troops overseas. The jongs were transport ships which could carry 100–2000 tons of cargo and 50–1000 people, 28.99–88.56 meter in length. The exact number of jong fielded by Majapahit is unknown, but the largest number of jong deployed in an expedition is about 400 jongs, when Majapahit attacked Pasai, in 1350.Hill (June 1960). "iarchive:hikayat-raja-raja-pasai/page/2/mode/2up, Hikayat Raja-Raja Pasai". ''Journal of the Malaysian Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society''. 33: pp. 98, 157: "Then he directed them to make ready all the equipment and munitions of war needed for an attack on the land of Pasai – about four hundred of the largest junks, and also many barges (malangbang) and galleys." See also Nugroho (2011). pp. 270, 286, quoting ''Hikayat Raja-Raja Pasai'', 3: 98: "''Sa-telah itu, maka di-suroh baginda musta'idkan segala kelengkapan dan segala alat senjata peperangan akan mendatangi negeri Pasai itu, sa-kira-kira empat ratus jong yang besar-besar dan lain daripada itu banyak lagi daripada malangbang dan kelulus''." (After that, he is tasked by His Majesty to ready all the equipment and all weapons of war to come to that country of Pasai, about four hundred large jongs and other than that much more of malangbang and kelulus.)
Europe
 Until recently, Viking longships were seen as marking an advance on traditional clinker (boat building), clinker-built hulls where leather thongs were used to join plank boards. This consensus has recently been challenged. Haywood has argued that earlier Frankish and Anglo-Saxon nautical practice was much more accomplished than had been thought and has described the distribution of clinker ''vs.'' carvel construction in Western Europe (see ma
Until recently, Viking longships were seen as marking an advance on traditional clinker (boat building), clinker-built hulls where leather thongs were used to join plank boards. This consensus has recently been challenged. Haywood has argued that earlier Frankish and Anglo-Saxon nautical practice was much more accomplished than had been thought and has described the distribution of clinker ''vs.'' carvel construction in Western Europe (see ma. An insight into shipbuilding in the North Sea/Baltic areas of the early medieval period was found at Sutton Hoo, England, where a ship was buried with a chieftain. The ship was long and wide. Upward from the keel, the hull was made by overlapping nine
strake
On a vessel's Hull (watercraft), hull, a strake is a longitudinal course of Plank (wood), planking or Plate (metal), plating which runs from the boat's stem (ship), stempost (at the Bow (ship), bows) to the stern, sternpost or transom (nautica ...
s on either side with rivets fastening the oaken planks together. It could hold upwards of thirty men.
Sometime around the 12th century, northern European ships began to be built with a straight sternpost, enabling the mounting of a rudder, which was much more durable than a steering oar held over the side. Development in the Middle Ages favored "round ships", with a broad beam and heavily curved at both ends. Another important ship type was the galley, which was constructed with both sails and oars.
The first extant treatise on shipbuilding was written by Michael of Rhodes, a man who began his career as an oarsman on a Venetian galley in 1401 and worked his way up into officer positions. He wrote and illustrated a book that contains a treatise on shipbuilding, a treatise on mathematics, much material on astrology, and other materials. His treatise on shipbuilding treats three kinds of galleys and two kinds of round ships.
China
 Shipbuilders in the Ming dynasty (1368~1644) were not the same as the shipbuilders in other Chinese dynasties, due to hundreds of years of accumulated experiences and rapid changes in the Ming dynasty. Shipbuilders in the Ming dynasty primarily worked for the government, under command of the Ministry of Works (imperial China), Ministry of Public Works.
During the early years of the Ming dynasty, the Ming government maintained an open policy towards sailing. Between 1405 and 1433, the government conducted seven diplomatic Ming treasure voyages to over thirty countries in Southeast Asia, India, the Middle East and Eastern Africa. The voyages were initiated by the Yongle Emperor, and led by the Admiral Zheng He. Six voyages were conducted under the Yongle Emperor's reign, the last of which returned to China in 1422. After the Yongle Emperor's death in 1424, his successor the Hongxi Emperor ordered the suspension of the voyages. The seventh and final voyage began in 1430, sent by the Xuande Emperor. Although the Hongxi and Xuande Emperors did not emphasize sailing as much as the Yongle Emperor, they were not against it. This led to a high degree of commercialization and an increase in trade. Large numbers of ships were built to meet the demand.
The Ming voyages were large in size, numbering as many as 300 ships and 28,000 men. The shipbuilders were brought from different places in China to the shipyard in Nanjing, including Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Fujian, and Huguang (now the provinces of Hubei and Hunan). One of the most famous shipyards was Long Jiang Shipyard (:zh:龙江船厂), located in Nanjing near the Treasure Shipyard where the ocean-going ships were built. The shipbuilders could build 24 models of ships of varying sizes.
Shipbuilders in the Ming dynasty (1368~1644) were not the same as the shipbuilders in other Chinese dynasties, due to hundreds of years of accumulated experiences and rapid changes in the Ming dynasty. Shipbuilders in the Ming dynasty primarily worked for the government, under command of the Ministry of Works (imperial China), Ministry of Public Works.
During the early years of the Ming dynasty, the Ming government maintained an open policy towards sailing. Between 1405 and 1433, the government conducted seven diplomatic Ming treasure voyages to over thirty countries in Southeast Asia, India, the Middle East and Eastern Africa. The voyages were initiated by the Yongle Emperor, and led by the Admiral Zheng He. Six voyages were conducted under the Yongle Emperor's reign, the last of which returned to China in 1422. After the Yongle Emperor's death in 1424, his successor the Hongxi Emperor ordered the suspension of the voyages. The seventh and final voyage began in 1430, sent by the Xuande Emperor. Although the Hongxi and Xuande Emperors did not emphasize sailing as much as the Yongle Emperor, they were not against it. This led to a high degree of commercialization and an increase in trade. Large numbers of ships were built to meet the demand.
The Ming voyages were large in size, numbering as many as 300 ships and 28,000 men. The shipbuilders were brought from different places in China to the shipyard in Nanjing, including Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Fujian, and Huguang (now the provinces of Hubei and Hunan). One of the most famous shipyards was Long Jiang Shipyard (:zh:龙江船厂), located in Nanjing near the Treasure Shipyard where the ocean-going ships were built. The shipbuilders could build 24 models of ships of varying sizes.
Indian Ocean
In the Islamic world, shipbuilding thrived at Basra and Alexandria. The dhow, felucca, baghlah, and the sambuk became symbols of successful maritime trade around the Indian Ocean from the ports of East Africa to Southeast Asia and the ports of Sindh and Al-Hind, Hind (India) during the Abbasid period.Early modern
Bengal
Mughal Empire had a large shipbuilding industry, which was largely centred in the Bengal Subah. Economic historian Indrajit Ray estimates shipbuilding output of Bengal during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries at 223,250 tons annually, compared with 23,061 tons produced in nineteen colonies in North America from 1769 to 1771. He also assesses ship repairing as very advanced in Bengal.West Africa
Documents from 1506, for example, refer to watercraft on the Sierra Leone river carrying 120 men. Others refer to Guinea coast peoples using war canoes of varying sizes – some 70 feet in length, 7–8 feet broad, with sharp pointed ends, rowing benches on the side, and quarterdecks or forecastles build of reeds. The watercraft included miscellaneous facilities, such as cooking hearths, and storage spaces for the crew's sleeping mats. From the 17th century, some kingdoms added brass or iron cannons to their vessels. By the 18th century, however, the use of swivel cannons on war canoes accelerated. The city-state of Lagos, for instance, deployed war canoes armed with swivel cannons.Europe
With the development of the carrack, the west moved into a new era of ship construction by building the first regular oceangoing vessels. In a relatively short time, these ships grew to an unprecedented size, complexity, and cost. Shipyards became large industrial complexes, and the ships built were financed by consortia of investors. These considerations led to the documentation of design and construction practices in what had previously been a secretive trade run by master shipwrights and ultimately led to the field of naval architecture, in which professional designers and draftsmen played an increasingly important role. Even so, construction techniques changed only very gradually. The ships of the Napoleonic Wars were still built more or less to the same basic plan as those of the Spanish Armada of two centuries earlier, although there had been numerous subtle improvements in ship design and construction throughout this period. For instance, the introduction of tumblehome, adjustments to the shapes of sails and hulls, the introduction of the wheel, the introduction of hardened copper fastenings below the waterline, the introduction of copper sheathing as a deterrent to shipworm and fouling, etc.Industrial Revolution

 Initially copying wooden construction traditions with a frame over which the hull was fastened, Isambard Kingdom Brunel's of 1843 was the first radical new design, being built entirely of wrought iron. Despite her success, and the great savings in cost and space provided by the iron hull, compared to a copper-sheathed counterpart, there remained problems with fouling due to the adherence of weeds and barnacles. As a result, composite construction remained the dominant approach where fast ships were required, with wooden timbers laid over an iron frame (''Cutty Sark'' is a famous example). Later ''Great Britain''s iron hull was sheathed in wood to enable it to carry a Copper sheathing, copper-based sheathing. Brunel's represented the next great development in shipbuilding. Built-in association with John Scott Russell, it used longitudinal wikt: stringer, stringers for strength, inner and outer hulls, and Bulkhead (partition), bulkheads to form multiple watertight compartments. Steel also supplanted wrought iron when it became readily available in the latter half of the 19th century, providing great savings when compared with iron in cost and weight. Wood continued to be favored for the decks.
During World War II, the need for cargo ships was so great that construction time for Liberty ships went from initially eight months or longer, down to weeks or even days. They employed production line and prefabrication techniques such as those used in shipyards today. The total number of dry-cargo ships built in the United States in a 15-year period just before the war was a grand total of two. During the war, thousands of Liberty ships and Victory ships were built, many of them in shipyards that did not exist before the war. And, they were built by a workforce consisting largely of women and other inexperienced workers who had never seen a ship before (or even the ocean).
Initially copying wooden construction traditions with a frame over which the hull was fastened, Isambard Kingdom Brunel's of 1843 was the first radical new design, being built entirely of wrought iron. Despite her success, and the great savings in cost and space provided by the iron hull, compared to a copper-sheathed counterpart, there remained problems with fouling due to the adherence of weeds and barnacles. As a result, composite construction remained the dominant approach where fast ships were required, with wooden timbers laid over an iron frame (''Cutty Sark'' is a famous example). Later ''Great Britain''s iron hull was sheathed in wood to enable it to carry a Copper sheathing, copper-based sheathing. Brunel's represented the next great development in shipbuilding. Built-in association with John Scott Russell, it used longitudinal wikt: stringer, stringers for strength, inner and outer hulls, and Bulkhead (partition), bulkheads to form multiple watertight compartments. Steel also supplanted wrought iron when it became readily available in the latter half of the 19th century, providing great savings when compared with iron in cost and weight. Wood continued to be favored for the decks.
During World War II, the need for cargo ships was so great that construction time for Liberty ships went from initially eight months or longer, down to weeks or even days. They employed production line and prefabrication techniques such as those used in shipyards today. The total number of dry-cargo ships built in the United States in a 15-year period just before the war was a grand total of two. During the war, thousands of Liberty ships and Victory ships were built, many of them in shipyards that did not exist before the war. And, they were built by a workforce consisting largely of women and other inexperienced workers who had never seen a ship before (or even the ocean).
Worldwide shipbuilding industry
Present day shipbuilding
Beyond the 2000s, the three East Asian manufacturing powerhouses, People's Republic of China, China, South Korea and Japan, have dominated world shipbuilding by completed gross tonnage. China State Shipbuilding Corporation, China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation, Hyundai Heavy Industries, Samsung Heavy Industries, Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering and Imabari Shipbuilding supply most of the global market for large container ship, container, bulk carrier, tanker (ship), tanker and roll-on/roll-off, Ro-ro ships. During the early 2020s, Chinese shipbuilders saw an increase in orders as operators demand green technology, greener fleets. , China’s shipbuilding output, newly received orders and orders-on-hand accounted for 50%, 67%, and 55% of the global market share, respectively, with double-digital growth of all three indexes compared to the previous year. According to a September 2023 report by the Alliance for American Manufacturing (based on a leaked presentation slide from an earlier United States Navy, USN briefing, verified by the Office of Naval Intelligence), China's shipbuilding capacity is 232 times greater than the United States, with a manufacturing capacity of roughly 23,250,000 million tons compared to less than 100,000 tons by U.S. shipyards. When referring to the ship type, then China, South Korea and Japan are the producing countries of the carrier ships as mentioned above. While Italy, France, Finland, Germany, United Kingdom and other European countries are the makers of cruise ships (the most), icebreakers, crane vessel and so on. The market share of European ship builders began to decline in the 1960s as they lost work to Japan in the same way Japan most recently lost their work to South Korea and China. Over the four years from 2007, the total number of employees in the European shipbuilding industry declined from 150,000 to 115,000.Zagreb Institute of Public FinanceNewsletter No. 64, December 2011, In 2022, some key shipbuilders in Europe are Fincantieri, Damen Group, Navantia, Naval Group and BAE Systems. Shipbuilding output of the United States also underwent a similar change. The US is ranked the 10th largest shipbuilder worldwide. The top companies that build large naval vessels, such as aircraft carriers and cruisers, include Huntington Ingalls, Bollinger Shipyards, Bollinger and General Dynamics. In the small to medium military vessels category, key shipbuilders include Vigor Industrial, and VT Halter Marine. As the US Navy is shifting to a new fleet architecture that is more widely distributed, unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) development is rapidly propelled to higher priority. Key strategic Program of Record includes prototyping and construction of up to 9 MUSVs, for which a sole contract was awarded to L3Harris Technologies, who partnered with Swiftships to build the MUSVs. In 2018, the US Defense Department initiated Overlord Program, and developed USV Prototypes 1 (NOMAD) and 2 (RANGER). Both of them took part in multiple fleet level exercises and demonstrations, traveled in autonomous mode, and tested numerous payloads. Nomam, formerly known as Riley Claire, is a converted offshore patrol vessel, which was built by Swiftships. The objective of the Ghost Fleet Overlord program is to convert large, commercial vessels to autonomous systems. , China builds nearly 75% of new vessels on order and has the capacity to build more ships in one month than the United States builds in a year.
Modern shipbuilding manufacturing techniques
 Modern shipbuilding makes considerable use of prefabrication, prefabricated modular design, modular sections. Entire multi-deck segments of the hull or Superstructure (ship), superstructure will be built elsewhere in the yard, transported to the building dock or slipway, then lifted into place. This is known as "block construction". The most modern shipyards pre-install equipment, pipes, electrical cables, and any other components within the blocks, to minimize the effort needed to assemble or install components deep within the hull once it is welded together.
Ship design work, also called naval architecture, may be conducted using a ship model basin. Previously, loftsmen at the mould lofts of
Modern shipbuilding makes considerable use of prefabrication, prefabricated modular design, modular sections. Entire multi-deck segments of the hull or Superstructure (ship), superstructure will be built elsewhere in the yard, transported to the building dock or slipway, then lifted into place. This is known as "block construction". The most modern shipyards pre-install equipment, pipes, electrical cables, and any other components within the blocks, to minimize the effort needed to assemble or install components deep within the hull once it is welded together.
Ship design work, also called naval architecture, may be conducted using a ship model basin. Previously, loftsmen at the mould lofts of shipyard
A shipyard, also called a dockyard or boatyard, is a place where ships are shipbuilding, built and repaired. These can be yachts, military vessels, cruise liners or other cargo or passenger ships. Compared to shipyards, which are sometimes m ...
s were responsible for taking the dimensions, and details from drawings and plans and translating this information into templates, battens, ordinates, cutting sketches, profiles, margins and other data. However, since the early 1970s computer-aided design became normal for the shipbuilding design and lofting process.
Modern ships, since roughly 1940, have been produced almost exclusively of welding, welded steel. Early welded steel ships used steels with inadequate fracture toughness, which resulted in some ships suffering catastrophic brittle fracture structural cracks (see problems of the Liberty ship). Since roughly 1950, specialized steels such as ABS Steels with good properties for ship construction have been used. Although it is commonly accepted that modern steel has eliminated brittle fracture in ships, some controversy still exists. Brittle fracture of modern vessels continues to occur from time to time because grade A and grade B steel of unknown toughness or fracture appearance transition temperature (FATT) in ships' side shells can be less than adequate for all ambient conditions.
As modern shipbuilding panels on a panel line become lighter and thinner, the laser hybrid welding technique is utilized. The laser hybrid blend focuses a higher energy beam on the material to be joined, allowing it to keyhole with a much higher depth to width ratio than comparative traditional welding techniques. Typically a MIG process trails the keyhole providing filler material for the weld joint. This allows for very high penetration without excessive heat input from decreased weld metal deposited leading to less distortion and welding at higher travel speeds.
Ship repair industry
All ships need repair work at some point in their working lives. A part of these jobs must be carried out under the supervision of the classification society. A lot of maintenance is carried out while at sea or in port by ship's crew. However, a large number of repair and maintenance works can only be carried out while the ship is out of commercial operation, in a ship repair yard. Prior to undergoing repairs, a tanker must dock at a deballasting station for completing the tank cleaning operations and pumping ashore its slops (dirty cleaning water and hydrocarbon residues).See also
* Ancient shipbuilding techniques * Boat building * List of shipbuilders and shipyards * List of the largest shipbuilding companies * List of Russian marine engineers * Ships of ancient Rome * *References
Notes
* *External links
Shipbuilding Picture Dictionary
U.S. Shipbuilding
xtensive information about the U.S. shipbuilding industry, including over 500 pages of U.S. shipyard construction records
Shipbuilding News
Bataviawerf – the Historic Dutch East Indiaman Ship Yard
hipyard of the historic ships Batavia and Zeven Provincien in the Netherlands, since 1985 here have been great ships reconstructed using old construction methods.
Photos of the reconstruction of the Dutch East Indiaman Batavia
Photo web site about the reconstruction of the ''Batavia'' on the shipyard Batavia werf, a 16th-century East Indiaman in the Netherlands. The site is constantly expanding with more historic images as in 2010 the shipyard celebrates its 25th year.
Modern shipbuilding and the men engaged in it
David Pollock (London: E. & F. N. Spon, 1884). {{Authority control Shipbuilding, Shipwrights, Naval architecture