Sharpshooter-class Torpedo Gunboat on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The ''Sharpshooter''-class torpedo gunboat was a class of torpedo gunboat built for the Royal Navy in the late 19th century. One of the class was hulked in 1904, seven were scrapped before World War I and five were converted to minesweepers. Of these minesweepers, ''Seagull'' was lost to a collision in 1918 and the rest survived the war to be broken up in the early 1920s.
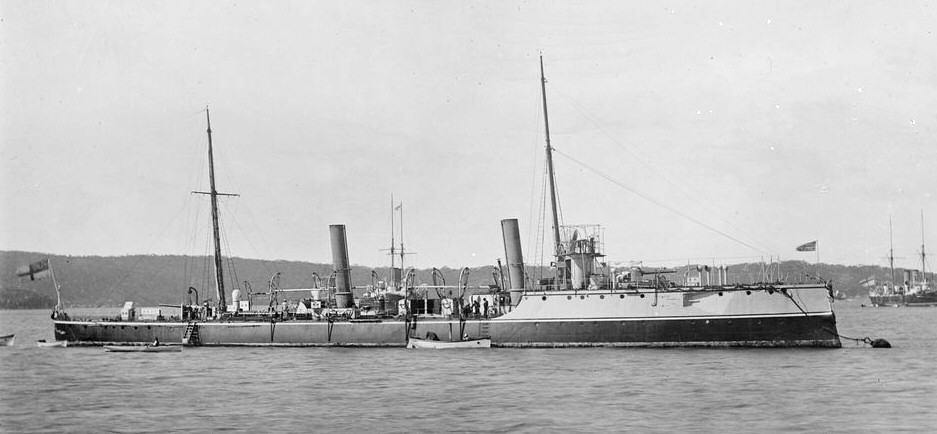
Design
The ''Sharpshooter'' class was designed by Sir William White in 1888. They had a length overall of , a beam of and a displacement of 735 tons. They were engined with two sets of Belliss and Morcom triple-expansion steam engines, two locomotive-type boilers, and twin screws. This layout produced with natural draught and with forced draught, giving them a top speed of . They carried 100 tons of coal, giving them a range of about at and were manned by 91 sailors and officers. The following ''Alarm'' class were essentially an enlarged version of the ''Sharpshooters''. From 1895 to 1898 a series of different boilers were fitted to ''Sharpshooter'', ''Sheldrake'', ''Seagull'', ''Spanker'' and ''Salamander''.Armament
At build the class was fitted with two QF /45-pounder guns and four 3-pounder guns. Five torpedo tubes were fitted, except in ''Plassey'' and ''Assaye'', which had three tubes. Three reloads were provided. Those vessels converted to minesweepers in 1909 retained their guns and had a kite winch and gallows fitted on the quarterdeck.Gray, Randal, Ed. ''Conway's All The World's Fighting Ships 1906–1921.'' Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press, 1985.Service
''Plassey'' and ''Assaye'' were built for the Bombay Marine (renamed the Royal Indian Marine in 1892). ''Whiting'' and ''Wizard'' (renamed ''Boomerang'' and ''Karakatta'' before commissioning) were assigned to the Australia Station. Seven of the class, including all the colonial service boats, were sold for breaking in 1904 - 1907, and five of the class were converted to minesweepers in 1908 - 1909. Of the five minesweepers, ''Seagull'' was lost in a collision with SS ''Corrib'' in the Clyde in 1918, and the others were sold for breaking after World War I. ''Sharpshooter'' was hulked for instructional duties in 1904 and renamed ''Northampton'', surviving until 1922 until being sold for breaking.
Ships
See also
* List of torpedo gunboats of the Royal NavyReferences
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Sharpshooter class torpedo gunboat Torpedo gunboat classes S