Septicemic Plague on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Septicemic plague is one of the three forms of plague, and is caused by ''
 The bacteria are cosmopolitan, mainly in rodents on all continents except Australia and Antarctica. The greatest frequency of human plague infections occurs in Africa. The bacteria most commonly appear in rural areas and wherever there is poor sanitation, overcrowding, and high rodent populations in urban areas. Outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, or hunting where plague-infected animals may be found, increase the risk of contracting septicemic plague, and so do certain occupations such as veterinary or other animal-related work.
The bacteria are cosmopolitan, mainly in rodents on all continents except Australia and Antarctica. The greatest frequency of human plague infections occurs in Africa. The bacteria most commonly appear in rural areas and wherever there is poor sanitation, overcrowding, and high rodent populations in urban areas. Outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, or hunting where plague-infected animals may be found, increase the risk of contracting septicemic plague, and so do certain occupations such as veterinary or other animal-related work.
Yersinia pestis
''Yersinia pestis'' (''Y. pestis''; formerly ''Pasteurella pestis'') is a Gram-negative bacteria, gram-negative, non-motile bacteria, non-motile, coccobacillus Bacteria, bacterium without Endospore, spores. It is related to pathogens ''Yer ...
'', a gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists ...
species of bacterium
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the ...
. Septicemic plague is a systemic disease
A systemic disease is one that affects a number of Organ (anatomy), organs and Tissue (biology), tissues, or affects the Human body, body as a whole. It differs from a localized disease, which is a disease affecting only part of the body (e.g., ...
involving infection of the blood and is most commonly spread by bites from infected fleas. Septicemic plague can cause disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition in which blood clots form throughout the body, blocking Microvessel, small blood vessels. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, problems speaking, or problems ...
and is always fatal when untreated. The other varieties of the plague are bubonic plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of Plague (disease), plague caused by the Bacteria, bacterium ''Yersinia pestis''. One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and ...
and pneumonic plague
Pneumonic plague is a severe lung infection caused by the bacterium '' Yersinia pestis''. Symptoms include fever, headache, shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing. They typically start about three to seven days after exposure. It is o ...
.
Signs and symptoms
The usual symptoms are: * Abdominal pain * Bleeding under the skin due to blood clotting problems * Bleeding from mouth, nose or rectum * Gastrointestinal symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, which can be with blood, and diarrhea * Fever * Chills * Low blood pressure * Organ failure * Shock * Death of tissue (gangrene
Gangrene is a type of tissue death caused by a lack of blood supply. Symptoms may include a change in skin color to red or black, numbness, swelling, pain, skin breakdown, and coolness. The feet and hands are most commonly affected. If the ga ...
) in extremities, mostly fingers, nose, and toes
* Difficulty breathing
*Death
These symptoms are common to many human illnesses and are not considered, in and of themselves, to signify infection with any form of plague.
It is important to note that septicemic plague may be asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test).
P ...
and may cause death absent of any symptoms.
Cause
Transmission
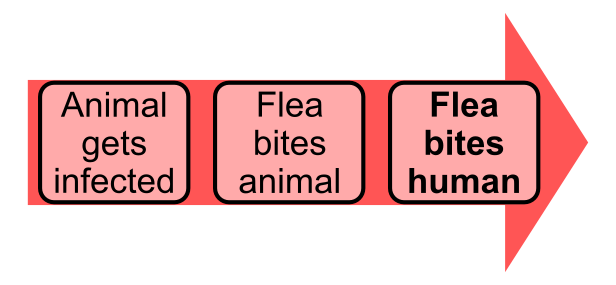
Human ''Yersinia'' infections most commonly result from the bite of an infected flea or occasionally an infected mammal. Rats specifically were a mammal that played a huge part in the spread of the disease. When rats that carried the plague died of the disease, then the fleas that were using those rodents as a food source must quickly seek a different blood stream, making things very problematic for any human nearby. After a flea consumes the blood of an infected rat, they are unable to get blood to their stomachs as masses form due to the ''Yersinia'' bacteria that is now in the flea. These masses don't allow for blood to be processed properly, leaving the flea feeling constant hunger, and this results in more bites on humans. The exposure to a flea bite from an infected flea may cause bubonic plague in humans that could develop into the septicemic plague. Cats and dogs were also susceptible to bites from infected fleas. These cats and dogs could then expose humans to the plague when the animal brings those infected fleas around people. However, like most bacterialsystemic disease
A systemic disease is one that affects a number of Organ (anatomy), organs and Tissue (biology), tissues, or affects the Human body, body as a whole. It differs from a localized disease, which is a disease affecting only part of the body (e.g., ...
s, the disease may also be transmitted through an opening in the skin or by inhaling infectious droplets of moisture from sneezes or coughs. In both cases septicemic plague need not be the result, and in particular, not the initial result, but it occasionally happens that bubonic plague for example leads to infection of the blood, and septicemic plague results. If the bacteria happen to enter the bloodstream rather than the lymph or lungs, they multiply in the blood, causing bacteremia
Bloodstream infections (BSIs) are infections of blood caused by blood-borne pathogens. The detection of microbes in the blood (most commonly accomplished by blood cultures) is always abnormal. A bloodstream infection is different from sepsis, wh ...
and severe sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs.
This initial stage of sepsis is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and s ...
. In septicemic plague, bacterial endotoxin
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), now more commonly known as endotoxin, is a collective term for components of the outermost membrane of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria, such as '' E. coli'' and ''Salmonella'' with a common structural archit ...
s cause disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), where tiny blood clots form throughout the body, commonly resulting in localised ischemic
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems ...
necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who i ...
, tissue death from lack of circulation and perfusion
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ (anatomy), organ or a tissue (biology), tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion may also refer t ...
.
DIC results in depletion of the body's clotting resources, so that it can no longer control bleeding. Consequently, the unclotted blood bleeds into the skin and other organs, leading to a red or black patchy rash and to hematemesis
Hematemesis is the vomiting of blood. It can be confused with hemoptysis (coughing up blood) or epistaxis (nosebleed), which are more common. The source is generally the upper gastrointestinal tract, typically above the suspensory muscle of du ...
(vomiting blood) or hemoptysis
Hemoptysis or haemoptysis is the discharge of blood or blood-stained sputum, mucus through the mouth coming from the bronchi, larynx, vertebrate trachea, trachea, or lungs. It does not necessarily involve coughing. In other words, it is the airw ...
(coughing up blood). The rash may cause bumps on the skin that look somewhat like insect bites, usually red, sometimes white in the centre.
Septicemic plague is caused by horizontal and direct transmission. Horizontal transmission is the transmitting of a disease from one individual to another regardless of blood relation. Direct transmission occurs from close physical contact with individuals, through common air usage, or from direct bite from a flea or an infected rodent. Most common rodents may carry the bacteria and so may Leporidae
Leporidae () is the family of rabbits and hares, containing over 70 species of extant mammals in all. The family name comes from "Lepus", hare in Latin. Together with the pikas, the Leporidae constitute the mammalian order Lagomorpha. Leporidae ...
such as rabbits.
 The bacteria are cosmopolitan, mainly in rodents on all continents except Australia and Antarctica. The greatest frequency of human plague infections occurs in Africa. The bacteria most commonly appear in rural areas and wherever there is poor sanitation, overcrowding, and high rodent populations in urban areas. Outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, or hunting where plague-infected animals may be found, increase the risk of contracting septicemic plague, and so do certain occupations such as veterinary or other animal-related work.
The bacteria are cosmopolitan, mainly in rodents on all continents except Australia and Antarctica. The greatest frequency of human plague infections occurs in Africa. The bacteria most commonly appear in rural areas and wherever there is poor sanitation, overcrowding, and high rodent populations in urban areas. Outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, or hunting where plague-infected animals may be found, increase the risk of contracting septicemic plague, and so do certain occupations such as veterinary or other animal-related work.
Diagnosis
A doctor or veterinarian will perform a physical exam which includes asking about the medical history and possible sources of exposure. The following possible test could include: * Blood samples (detecting antibodies) * Culture samples of body fluids (check for the bacteria ''Yersinia pestis'') * Kidney and liver testing * Checking lymphatic system for signs of infection * Examining body fluids for abnormal signs * Checking for swelling * Checking for signs of dehydration * Checking for fever * Checking for lung infectionPrevention
The following steps and precautions should be used to avoid infection of the septicemic plague: * Caregivers of infected patients should wear masks, gloves, goggles and gowns * Take antibiotics if close contact with the infected patient has occurred * Use insecticides throughout the house * Avoid contact with dead rodents or sick cats * Set traps if mice or rats are present around the house * Do not allow family pets to roam in areas where plague is common * Flea control and treatment for animals (especially rodents)Treatment
Starting antibiotics early is the first step in treating septicemic plague in humans. One of the following antibiotics may be used: *Streptomycin
Streptomycin is an antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium complex, ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex, endocarditis, brucellosis, Burkholderia infection, ''Burkholderia'' i ...
* Gentamicin
Gentamicin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections. This may include bone infections, endocarditis, pelvic inflammatory disease, meningitis, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis amo ...
* Tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis. It is available in oral an ...
or Doxycycline
Doxycycline is a Broad-spectrum antibiotic, broad-spectrum antibiotic of the Tetracycline antibiotics, tetracycline class used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat pneumonia, bacterial p ...
* Chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by intravenous, injection into a vein, it is used to treat meningitis, pl ...
* Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes bone and joint infections, intra-abdominal infections, certain types of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin ...
Lymph nodes may require draining and the patient will need close monitoring.
In animals, antibiotics such as tetracycline or doxycycline can be used. Intravenous drip may be used to assist in dehydration scenarios. Flea treatment can also be used. In some cases, euthanasia may be the best option for treatment and to prevent further spreading.
Prognosis
Untreated septicemic plague is almost always fatal. Early treatment with antibiotics reduces the mortality rate to between 4 and 15 per cent. Death is almost inevitable if treatment is delayed more than about 24 hours, and some people may even die on the same day theypresent
The present is the period of time that is occurring now. The present is contrasted with the past, the period of time that has already occurred; and the future, the period of time that has yet to occur.
It is sometimes represented as a hyperplan ...
with the disease.
Epidemiology
In 2015, Taylor Gaes, a 16-year-old in Larimer County in northern Colorado, contracted septicemic plague and subsequently died after being bitten by a flea that had bitten a rodent on his family's rural property. Only three people in Colorado had contracted the bacteria in the previous thirty years.History
The septicemic plague was the least common of the three plague varieties that occurred during theBlack Death
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the list of epidemics, most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. ...
from 1348 to 1350 (the other two being bubonic plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of Plague (disease), plague caused by the Bacteria, bacterium ''Yersinia pestis''. One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and ...
and pneumonic plague
Pneumonic plague is a severe lung infection caused by the bacterium '' Yersinia pestis''. Symptoms include fever, headache, shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing. They typically start about three to seven days after exposure. It is o ...
). Like the others, septicemic plague spread from East Asia
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
through trade routes on the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
and down to the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
.
Major port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Hamburg, Manch ...
cities and trade centres such as Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
and Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
were hit the hardest. The massive loss of the working population in Europe following the Black Death, resulting in the increased economic bargaining power of the serf
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery. It developed du ...
labour force, was a major precipitating factor for the Peasants' Revolt
The Peasants' Revolt, also named Wat Tyler's Rebellion or the Great Rising, was a major uprising across large parts of England in 1381. The revolt had various causes, including the socio-economic and political tensions generated by the Black ...
of 1381.
Other animals
Septicemic plague is azoonosis
A zoonosis (; plural zoonoses) or zoonotic disease is an infectious disease of humans caused by a pathogen (an infectious agent, such as a virus, bacterium, parasite, fungi, or prion) that can jump from a non-human vertebrate to a human. When ...
, a disease that generally is acquired by humans from animals, such as rodents and carnivores. Goats, sheep and camels also may carry the bacteria. Cats rarely develop clinical signs but can be infected and exhibit symptoms such as vomiting or diarrhea. Areas west of the Great Plains of North America are one region where plague-infected animals commonly occur. Plague-infested animals are found in many other countries as well, especially in developing countries where health controls are not effective.
Animals that commonly carry plague bacteria are large rodents and Leporidae
Leporidae () is the family of rabbits and hares, containing over 70 species of extant mammals in all. The family name comes from "Lepus", hare in Latin. Together with the pikas, the Leporidae constitute the mammalian order Lagomorpha. Leporidae ...
, but carnivore
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they ar ...
s sometimes also become infected by their prey. Prey animals are not immune to the disease, and outbreaks of various strains of plague, such as sylvatic plague, have on occasion devastated populations of black-tailed prairie dog
The black-tailed prairie dog (''Cynomys ludovicianus'') is a rodent of the family Sciuridae (the squirrels) found in the Great Plains of North America from about the United States–Canada border to the United States–Mexico border. Unlike some ...
s and black-footed ferret
The black-footed ferret (''Mustela nigripes''), also known as the American polecatHeptner, V. G. (Vladimir Georgievich); Nasimovich, A. A; Bannikov, Andrei Grigorovich; Hoffmann, Robert S. (2001)''Mammals of the Soviet Union''Volume: v. 2, pt. 1 ...
s.
Plague has been active in black-tailed prairie dog populations since the 1960s. In the United States outbreaks only occur in the western States and they are devastating, with mortality rates near 100% because the animals have no immunity to the plague. Survivors are the ones that happened not to become infected and colonies that recover from a plague outbreak remain at risk.
Because black-footed ferrets prey on black-tailed prairie dogs, wild ferret populations also fall victim to sylvatic plague. An outbreak can kill nearly 100% of ferrets in a population, and surviving ferrets commonly face starvation because prairie dogs are their main prey. Spray-and-vaccinate campaigns have aimed at preventing the spread of the plague among these animals.
Similar septicemic problems occur in many countries across the world, especially in developing countries where spending on health systems is very low and health controls are not effective.
References
{{Portal bar, Medicine Insect-borne diseases Plague (disease) Zoonotic bacterial diseases de:Pest#Pestsepsis