Septic tank on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A septic tank is an underground chamber made of concrete, fiberglass, or plastic through which domestic wastewater (

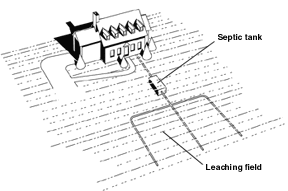 A septic tank consists of one or more concrete or plastic tanks of between 4,500 and 7,500 litres (1,000 and 2,000 gallons); one end is connected to an inlet
A septic tank consists of one or more concrete or plastic tanks of between 4,500 and 7,500 litres (1,000 and 2,000 gallons); one end is connected to an inlet
"Do pit additives work?"
Water Research Commission (WRC), University of Kwazulu-Natal, Partners in Development (PiD), South Africa It has been estimated that in the U.S. more than 1,200 septic system additives were available on the market in 2011. Very little peer-reviewed and replicated field research exists regarding the efficacy of these biological septic tank additives.S. Pradhan, Michael T. Hoover, G.H. Clark, M. Gumpertz, C. Cobb, J. Strock (2011
"Impacts of biological additives; Part 2 Septic Tank Effluent Quality and Overall Additive Efficacy"
, ''Journal of Environmental Health'', Volume 74, Number 5, p. 22–28

 While a properly maintained and located septic tank poses no higher amount of environmental problems than centralized municipal sewage treatment, certain problems could arise with a septic tank in an unsuitable location, and septic tank failures are typically more expensive to fix or replace than municipal sewer. Since septic systems require large drainfields, they are unsuitable for densely built areas.
While a properly maintained and located septic tank poses no higher amount of environmental problems than centralized municipal sewage treatment, certain problems could arise with a septic tank in an unsuitable location, and septic tank failures are typically more expensive to fix or replace than municipal sewer. Since septic systems require large drainfields, they are unsuitable for densely built areas.
 In the
In the
, 2010. Environmental Protection Agency, Ireland. Direct discharge of septic tank effluent into groundwater is prohibited in Ireland, while the indirect discharge via unsaturated subsoil into groundwater, e.g. by means of a septic drain field, or the direct discharge into surface water is permissible in accordance with a Water Pollution Act license. Registered septic tanks must be desludged by an authorized contractor at least once a year; the removed fecal sludge is disposed of, either to a managed municipal wastewater treatment facility or to agriculture provided that nutrient management regulations are met.
Septic Systems - U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
{{Authority control Sewerage infrastructure Storage tanks Sanitation
sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewerage, sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged fro ...
) flows for basic sewage treatment
Sewage treatment is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable to discharge to the surrounding environment or an intended reuse application, thereby preventing water p ...
. Settling and anaerobic digestion processes reduce solids and organics, but the treatment efficiency is only moderate (referred to as "primary treatment"). Septic tank systems are a type of simple onsite sewage facility. They can be used in areas that are not connected to a sewerage
Sewerage (or sewage system) is the infrastructure that conveys sewage or surface runoff ( stormwater, meltwater, rainwater) using sewers. It encompasses components such as receiving drains, manholes, pumping stations, storm overflows, and scr ...
system, such as rural areas. The treated liquid effluent is commonly disposed in a septic drain field, which provides further treatment. Nonetheless, groundwater pollution may occur and is a problem.
The term "septic" refers to the anaerobic bacterial environment that develops in the tank that decomposes or mineralizes the waste discharged into the tank. Septic tanks can be coupled with other onsite wastewater treatment units such as biofilter
Biofiltration is a pollution control technique using a bioreactor containing living material to capture and biologically degrade pollutants. Common uses include processing waste water, capturing harmful chemicals or silt from surface runoff, a ...
s or aerobic systems involving artificially forced aeration
Aeration (also called aerification or aeriation) is the process by which air is circulated through, mixed with or dissolved in a liquid or other substances that act as a fluid (such as soil). Aeration processes create additional surface area in t ...
.
The rate of accumulation of sludge—also called septage
Fecal sludge management (FSM) (or faecal sludge management in British English) is the storage, collection, transport, treatment and safe end use or disposal of fecal sludge. Together, the collection, transport, treatment and end use of fecal slud ...
or fecal sludge—is faster than the rate of decomposition. Therefore, the accumulated fecal sludge must be periodically removed, which is commonly done with a vacuum truck.
Description

wastewater
Wastewater (or waste water) is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of do ...
pipe and the other to a septic drain field. Generally these pipe connections are made with a T pipe, allowing liquid to enter and exit without disturbing any crust on the surface. Today, the design of the tank usually incorporates two chambers, each equipped with an access opening and cover, and separated by a dividing wall with openings located about midway between the floor and roof of the tank.
Wastewater enters the first chamber of the tank, allowing solids to settle and scum to float. The settled solids are anaerobically digested, reducing the volume of solids. The liquid component flows through the dividing wall into the second chamber, where further settlement takes place. One option for the effluent is the draining into the septic drain field, also referred to as a leach field, drain field or seepage field, depending upon locality. A percolation test
A percolation test (colloquially called a perc test) is a test to determine the water absorption rate of soil (that is, its capacity for percolation) in preparation for the building of a septic drain field (leach field) or infiltration basin. Th ...
is required prior to installation to ensure the porosity of the soil is adequate to serve as a drain field.
Septic tank effluent can also be conveyed to a secondary treatment, typically constructed wetlands. Constructed wetlands benefit from the good performance of septic tanks at removing solids, which avoids them getting clogged quickly.
Septic tank effluent can also be conveyed to a centralized treatment facility.
The remaining impurities are trapped and eliminated in the soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
, with the excess water eliminated through percolation
In physics, chemistry, and materials science, percolation () refers to the movement and filtration, filtering of fluids through porous materials. It is described by Darcy's law. Broader applications have since been developed that cover connecti ...
into the soil, through evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the Interface (chemistry), surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. A high concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evapora ...
, and by uptake through the root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
system of plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s and eventual transpiration
Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers. It is a passive process that requires no energy expense by the plant. Transpiration also cools plants, c ...
or entering groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
or surface water
Surface water is water located on top of land, forming terrestrial (surrounding by land on all sides) waterbodies, and may also be referred to as ''blue water'', opposed to the seawater and waterbodies like the ocean.
The vast majority of surfac ...
. A piping network, often laid in a stone-filled trench (see weeping tile), distributes the wastewater throughout the field with multiple drainage holes in the network. The size of the drain field is proportional to the volume of wastewater and inversely proportional to the porosity of the drainage field. The entire septic system can operate by gravity alone or, where topographic considerations require, with inclusion of a lift pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes Slurry, slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic or pneumatic energy.
Mechanical pumps serve in a wide range of application ...
.
Certain septic tank designs include siphon
A siphon (; also spelled syphon) is any of a wide variety of devices that involve the flow of liquids through tubes. In a narrower sense, the word refers particularly to a tube in an inverted "U" shape, which causes a liquid to flow upward, abo ...
s or other devices to increase the volume and velocity of outflow to the drainage field. These help to fill the drainage pipe more evenly and extend the drainage field life by preventing premature clogging or bioclogging.
An Imhoff tank is a two-stage septic system where the sludge is digested in a separate tank. This avoids mixing digested sludge with incoming sewage. Also, some septic tank designs have a second stage where the effluent from the anaerobic first stage is aerated before it drains into the seepage field.
A properly designed and normally operating septic system is odour-free. Besides periodic inspection and emptying, a septic tank should last for decades with minimal maintenance, with concrete, fibreglass, or plastic tanks lasting about 50 years.
Emptying (desludging)
Waste that is not decomposed by the anaerobic digestion must eventually be removed from the septic tank. Otherwise the septic tank fills up and wastewater containing undecomposed material discharges directly to the drainage field. Not only is this detrimental for the environment but, if the sludge overflows the septic tank into the leach field, it may clog the leach field piping or decrease the soil porosity itself, requiring expensive repairs. When a septic tank is emptied, the accumulated sludge (septage
Fecal sludge management (FSM) (or faecal sludge management in British English) is the storage, collection, transport, treatment and safe end use or disposal of fecal sludge. Together, the collection, transport, treatment and end use of fecal slud ...
, also known as fecal sludge) is pumped out of the tank by a vacuum truck. How often the septic tank must be emptied depends on the volume of the tank relative to the input of solids, the amount of indigestible solids, and the ambient temperature (because anaerobic digestion occurs more efficiently at higher temperatures), as well as usage, system characteristics and the requirements of the relevant authority.
Some health authorities require tanks to be emptied at prescribed intervals, while others leave it up to the decision of an inspector. Some systems require pumping every few years or sooner, while others may be able to go 10–20 years between pumpings. An older system with an undersize tank that is being used by a large family will require much more frequent pumping than a new system used by only a few people. Anaerobic decomposition is rapidly restarted when the tank is refilled.
An empty tank may be damaged by hydrostatic pressure causing the tank to partially "float" out of the ground, especially in flood situations or very wet ground conditions.
Another option is "scheduled desludging" of septic tanks which has been initiated in several Asian countries including the Philippines, Malaysia, Vietnam, Indonesia, and India. In this process, every property is covered along a defined route and the property occupiers are informed in advance about desludging that will take place.
Maintenance
The maintenance of a septic system is often the responsibility of the resident or property owner. Some forms of abuse or neglect include the following:User's actions
* Excessive disposal of cooking oils and grease can cause the inlet drains to block. Oils and grease are often difficult to degrade and can cause odor problems and difficulties with the periodic emptying. * Flushing non-biodegradable waste items down the toilet such as cigarette butts, cotton buds/swabs or menstrual hygiene products andcondom
A condom is a sheath-shaped Barrier contraception, barrier device used during sexual intercourse to reduce the probability of pregnancy or a Sexually transmitted disease, sexually transmitted infection (STI). There are both external condo ...
s can cause a septic tank to clog and fill rapidly, so these materials should not be disposed of in that manner. The same applies when the toilet is connected to a sewer rather than a septic tank.
* Using the toilet for disposal of food waste
The causes of food going uneaten are numerous and occur throughout the food system, during food production, production, food processing, processing, Food distribution, distribution, Grocery store, retail and food service sales, and Social clas ...
can cause a rapid overload of the system with solids and contribute to failure.
* Certain chemicals may damage the components of a septic tank or kill the bacteria needed in the septic tank for the system to operate properly, such as pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s, herbicide
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weed killers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page f ...
s, materials with high concentrations of bleach or caustic soda (lye), or any other inorganic materials such as paints or solvents.
* Using water softeners – the brine discharge from water softeners may harm the bacteria responsible for breaking down the wastewater. Usually, however, the brine is sufficiently diluted with other wastewater that it does not adversely affect the septic system.
Other factors
* Roots from trees and shrubbery protruding above the tank or drainfield may clog and/or rupture them. Trees that are directly within the vicinity of a concrete septic tank have the potential to penetrate the tank as the system ages and the concrete begins to develop cracks and small leaks. Tree roots can cause serious flow problems due to plugging and blockage of drain pipes, and the trees themselves tend to expand extremely vigorously due to the ready supply of nutrients from the septic system. * Playgrounds and storage buildings may cause damage to a tank and the drainage field. In addition, covering the drainage field with an impermeable surface, such as a driveway or parking area, will seriously affect its efficiency and possibly damage the tank and absorption system. * Excessive water entering the system may overload it and cause it to fail. * Very high rainfall, rapid snowmelt, andflood
A flood is an overflow of water (list of non-water floods, or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant con ...
ing from rivers or the sea can all prevent a drain field from operating, and can cause flow to back up, interfering with the normal operation of the tank. High winter water table
The water table is the upper surface of the phreatic zone or zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with groundwater, which may be fresh, saline, or brackish, depending on the loc ...
s can also result in groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
flowing back into the septic tank.
* Over time, biofilm
A biofilm is a Syntrophy, syntrophic Microbial consortium, community of microorganisms in which cell (biology), cells cell adhesion, stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy ext ...
s develop on the pipes of the drainage field, which can lead to blockage. Such a failure can be referred to as "biomat failure".
Septic tank additives
Septic tank additives have been promoted by some manufacturers with the aim to improve the effluent quality from septic tanks, reduce sludge build-up and to reduce odors. These additives—which are commonly based on " effective microorganisms"—are usually costly in the longer term and fail to live up to expectations.Foxon, K., Still, D. (2012)"Do pit additives work?"
Water Research Commission (WRC), University of Kwazulu-Natal, Partners in Development (PiD), South Africa It has been estimated that in the U.S. more than 1,200 septic system additives were available on the market in 2011. Very little peer-reviewed and replicated field research exists regarding the efficacy of these biological septic tank additives.S. Pradhan, Michael T. Hoover, G.H. Clark, M. Gumpertz, C. Cobb, J. Strock (2011
"Impacts of biological additives; Part 2 Septic Tank Effluent Quality and Overall Additive Efficacy"
, ''Journal of Environmental Health'', Volume 74, Number 5, p. 22–28
Environmental concerns

 While a properly maintained and located septic tank poses no higher amount of environmental problems than centralized municipal sewage treatment, certain problems could arise with a septic tank in an unsuitable location, and septic tank failures are typically more expensive to fix or replace than municipal sewer. Since septic systems require large drainfields, they are unsuitable for densely built areas.
While a properly maintained and located septic tank poses no higher amount of environmental problems than centralized municipal sewage treatment, certain problems could arise with a septic tank in an unsuitable location, and septic tank failures are typically more expensive to fix or replace than municipal sewer. Since septic systems require large drainfields, they are unsuitable for densely built areas.
Odor, gas emissions and carbon footprint
Some constituents of wastewater, especially sulfates, under the anaerobic conditions of septic tanks, are reduced tohydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist ...
, a pungent and toxic gas. Nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . salt (chemistry), Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are solubility, soluble in wa ...
s and organic nitrogen compounds can be reduced to ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
. Because of the anaerobic conditions, fermentation
Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and organic end products. Organic molecules, such as glucose or other sugars, are catabolized and reduce ...
and methanogenesis processes take place, which may generate carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
and/or methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
. Both carbon dioxide and methane are greenhouse gases, with methane having a global warming potential about 25 times larger than carbon dioxide. This makes septic tanks potential greenhouse gas emitters. The same methane can be burnt to produce energy for local usage.
Nutrients in the effluent
Septic tanks by themselves are ineffective at removingnitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
compounds that have potential to cause algal blooms in waterways into which affected water from a septic system finds its way. This can be remedied by using a nitrogen-reducing technology, such as hybrid constructed wetlands, or by simply ensuring that the leach field is properly sited to prevent direct entry of effluent into bodies of water.
The fermentation processes cause the contents of a septic tank to be anaerobic with a low redox
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is t ...
potential, which keeps phosphates in a soluble and, thus, mobilized form. Phosphates discharged from a septic tank into the environment can trigger prolific plant growth including algal blooms, which can also include blooms of potentially toxic cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteri ...
.
The soil's capacity to retain phosphorus is usually large enough to handle the load through a normal residential septic tank. An exception occurs when septic drain fields are located in sandy or coarser soils on property adjacent to a water body. Because of limited particle surface area, these soils can become saturated with phosphates. Phosphates will progress beyond the treatment area, posing a threat of eutrophication
Eutrophication is a general term describing a process in which nutrients accumulate in a body of water, resulting in an increased growth of organisms that may deplete the oxygen in the water; ie. the process of too many plants growing on the s ...
to surface waters.
Pathogens
Diseases extremely dangerous to human contact such as E. coli and other coliform bacteria are often reported following failures of septic tanks. A properly functioning septic system, on the other hand, provides significant reduction of pathogens compared to direct discharge due to settling (in the tank) and soil absorption (in the drain field). Log reductions of 4–8 for coliform bacteria, 0–2 for viruses are achieved in the effluent. Parasitic worm eggs are also removed. Additional filters may be added to improve removal performance although they will need to be replaced periodically.Groundwater pollution
In areas with high population density, groundwater pollution beyond acceptable limits may occur. Some small towns experience the costs of building very expensive centralized wastewater treatment systems because of this problem, due to the high cost of extended collection systems. To reduce residential development that might increase the demand to construct an expensive centralized sewerage system, building moratoriums and limitations on the subdivision of property are often imposed. Ensuring existing septic tanks are functioning properly can also be helpful for a limited time, but becomes less effective as a primary remediation strategy as population density increases.Surface water pollution
In areas adjacent to water bodies with fish orshellfish
Shellfish, in colloquial and fisheries usage, are exoskeleton-bearing Aquatic animal, aquatic invertebrates used as Human food, food, including various species of Mollusca, molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish ...
intended for human consumption, improperly maintained and failing septic systems contribute to pollution levels that can force harvest restrictions and/or commercial or recreational harvest closures.
Use
 In the
In the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, the 2008 American Housing Survey indicated that about 20 percent of all households rely on septic tanks, and that the overwhelming majority of systems are located in rural
In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry are typically desc ...
(50%) and suburb
A suburb (more broadly suburban area) is an area within a metropolitan area. They are oftentimes where most of a metropolitan areas jobs are located with some being predominantly residential. They can either be denser or less densely populated ...
an (47%) areas. Indianapolis
Indianapolis ( ), colloquially known as Indy, is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Indiana, most populous city of the U.S. state of Indiana and the county seat of Marion County, Indiana, Marion ...
is one example of a large city where many of the city's neighborhoods still rely on separate septic systems. In Europe, septic systems are generally limited to rural areas.
Regulations
European Union
In theEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
the EN 12566 standard provides the general requirements for packaged and site assembled treatment plants used for domestic wastewater treatment.
Part 1 ( EN 12566-1) is for septic tanks that are prefabricated or factory manufactured and made of polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging (plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including bott ...
, glass reinforced polyester, polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer Propene, propylene.
Polypropylene belongs to the group of polyolefin ...
, PVC-U, steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
or concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of aggregate bound together with a fluid cement that cures to a solid over time. It is the second-most-used substance (after water), the most–widely used building material, and the most-manufactur ...
. Part 4 ( EN 12566-4) regulates septic tanks that are assembled on site from prefabricated kits, generally of concrete construction. Certified septic tanks of both types must pass a standardized hydraulic test to assess their ability to retain suspended solids within the system. Additionally, their structural adequacy in relevant ground conditions is assessed in terms of water-tightness, treatment efficiency, and structural behaviour.
France
InFrance
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, about 4 million households (or 20% of the population) are using on-site wastewater disposal systems (''l’assainissement non collectif''), including septic tanks (''fosse septique''). The legal framework for regulating the construction and maintenance of septic systems was introduced in 1992 and updated in 2009 and 2012 with the intent to establish the technical requirements applicable to individual sewerage systems. Septic tanks in France are subject to inspection by SPANC (''Service Public d’Assainissement Non Collectif''), a professional body appointed by the respective local authorities to enforce wastewater collection laws, at least once in four years. Following the introduction of EN 12566, the discharge of effluent directly into ditches or watercourses is prohibited, unless the effluent meets prescribed standards.
Ireland
According to the Census of Ireland 2011, 27.5% of Irish households (i.e. about 440,000 households), with the majority in rural areas, use an individual septic tank. Following aEuropean Court of Justice
The European Court of Justice (ECJ), officially the Court of Justice (), is the supreme court of the European Union in matters of European Union law. As a part of the Court of Justice of the European Union, it is tasked with interpreting ...
judgment made against Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
in 2009 that deemed the country non-compliant with the Waste Framework Directive in relation to domestic wastewaters disposed of in the countryside, the Water Services (Amendment) Act 2012 was passed in order to regulate wastewater discharges from domestic sources that are not connected to the public sewer network and to provide arrangements for registration and inspection of existing individual domestic wastewater treatment systems.
Additionally, a code of practice has been developed by the Environmental Protection Agency to regulate the planning and construction of new septic tanks, secondary treatment systems, septic drain fields and filter systems.Code of Practice: Wastewater Treatment Systems for Single Houses, 2010. Environmental Protection Agency, Ireland. Direct discharge of septic tank effluent into groundwater is prohibited in Ireland, while the indirect discharge via unsaturated subsoil into groundwater, e.g. by means of a septic drain field, or the direct discharge into surface water is permissible in accordance with a Water Pollution Act license. Registered septic tanks must be desludged by an authorized contractor at least once a year; the removed fecal sludge is disposed of, either to a managed municipal wastewater treatment facility or to agriculture provided that nutrient management regulations are met.
United Kingdom
Since 2015, only certain property owners inEngland
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
and Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
with septic tanks or small packaged sewage treatment systems need to register their systems, and either apply for a permit or qualify for an exemption with the Environment Agency
The Environment Agency (EA) is a non-departmental public body, established in 1996 and sponsored by the United Kingdom government's Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, with responsibilities relating to the protection and enha ...
. Permits need to be granted to systems that discharge more than a certain volume of effluent in a given time or that discharge effluent directly into sensitive areas (e.g., some groundwater protection zones). In general, permits are not granted for new septic tanks that discharge directly into surface waters. A septic tank discharging into a watercourse must be replaced or upgraded by 1 January 2020 to a Sewage Treatment Plant (also called an Onsite sewage facility), or sooner if the property is sold before this date, or if the Environment Agency (EA) finds that it is causing pollution.
In Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ; ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, part of the United Kingdom in the north-east of the island of Ireland. It has been #Descriptions, variously described as a country, province or region. Northern Ireland shares Repub ...
, the Department of the Environment must give permission for all wastewater discharges where it is proposed that the discharge will go to a waterway or soil infiltration system. The discharge consent will outline conditions relating to the quality and quantity of the discharge in order to ensure the receiving waterway or the underground aquifer can absorb the discharge.
The Water Environment Regulations 2011 regulate the registration of septic tank systems in Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
. Proof of registration is required when new properties are being developed or existing properties change ownership.
Australia
In Australia, septic tank design and installation requirements are regulated by State Governments, through Departments of Health and Environmental Protection Agencies. Regulation may include Codes of Practice and Legislation. Regulatory requirements for the design and installation of septic tanks commonly references Australian Standards (1547 and 1546). Capacity requirements for septic tanks may be outlined within Codes of Practice, and can vary between states. Mainly because of water leaching from the effluent drains of a lot of closely spaced septic systems, many council districts (e.g.Sunshine Coast, Queensland
The Sunshine Coast is a peri-urbanisation, peri-urban region in South East Queensland, Australia. In 1967, it was defined as "the area contained in the ormerShires of Shire of Landsborough, Landsborough, Shire of Maroochy, Maroochy and Shire ...
) have banned septic systems, and require them to be replaced with much more expensive small-scale sewage treatment
Sewage treatment is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable to discharge to the surrounding environment or an intended reuse application, thereby preventing water p ...
systems that actively pump air into the tank, producing an aerobic environment. Septic systems have to be replaced as part of any new building applications, regardless of how well the old system performed.
United States
According to the US Environmental Protection Agency, in the United States it is the home owners' responsibility to maintain their septic systems. Anyone who ignores this requirement will eventually experience costly repairs when solids escape the tank and clog the clarified liquid effluent disposal system. In Washington, for example, a "shellfish protection district" or "clean water district" is a geographic service area designated by a county to protect water quality and tideland resources. The district provides a mechanism to generate local funds for water quality services to control non-point sources of pollution, such as septic system maintenance. The district also serves as an educational resource, calling attention to the pollution sources that threaten shellfish growing waters.Slang usage
The term "septic tank", or more usually "septic", is used in some parts of Britain as a slang term to refer to Americans, from Cockneyrhyming slang
Rhyming slang is a form of slang word construction in the English language. It is especially prevalent among Cockneys in England, and was first used in the early 19th century in the East End of London; hence its alternative name, Cockney rhymin ...
septic tank equalling yank. This is sometimes further shortened to "seppo" by Australians .
See also
*Cesspit
Cesspit, cesspool and soak pit in some contexts are terms with various meanings: they are used to describe either an underground holding tank (sealed at the bottom) or a Dry well, soak pit (not sealed at the bottom). A cesspit can be used for ...
* Fecal sludge management
* Grease trap
* Sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
* Off-the-grid
Off-the-grid or off-grid is a characteristic of buildings and a lifestyle designed in an independent manner without reliance on one or more public utilities. The term "off-the-grid" traditionally refers to not being connected to the electrical ...
References
External links
Septic Systems - U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
{{Authority control Sewerage infrastructure Storage tanks Sanitation