Sebald Islands on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The history of the Falkland Islands () goes back at least five hundred years, with active exploration and colonisation only taking place in the 18th century. Nonetheless, the
The history of the Falkland Islands () goes back at least five hundred years, with active exploration and colonisation only taking place in the 18th century. Nonetheless, the
 When the world sea level was lower in the
When the world sea level was lower in the
 An
An  The name of the archipelago derives from
The name of the archipelago derives from
 In 1765, Captain
In 1765, Captain
 In March 1820, , a privately owned frigate that was operated as a
In March 1820, , a privately owned frigate that was operated as a
''A Voyage Towards the South Pole''
London, Longman, Rees, Orme, Brown and Green, 1827 Jewett departed from the Falkland Islands in April 1821. In total he had spent no more than six months on the island, entirely at Port Louis. In 1822, Jewett was accused of piracy by a Portuguese court, but by that time he was in Brazil.
 In 1823, the United Provinces of the River Plate granted
In 1823, the United Provinces of the River Plate granted
, Accessed 2007-07-19 On 10 June 1829, Vernet was designated as 'civil and military commandant' of the islands (no governor was ever appointed) and granted a monopoly on seal hunting rights. A protest was lodged by the British Consulate in Buenos Aires. By 1831, the colony was successful enough to be advertising for new colonists, although 's report suggests that the conditions on the islands were quite miserable.
Accessed 2007-10-02
 The Argentinian assertions of sovereignty provided the spur for Britain to send a naval task force in order to finally and permanently return to the islands.
On 3 January 1833, Captain James Onslow, of the brig-sloop , arrived at Vernet's settlement at Port Louis to request that the flag of the United Provinces of the River Plate be replaced with the British one, and for the administration to leave the islands. While Major José María Pinedo, commander of the schooner ''Sarandí'', wanted to resist, his numerical disadvantage was obvious, particularly as a large number of his crew were British mercenaries who were unwilling to fight their own countrymen. Such a situation was not unusual in the newly independent states in Latin America, where land forces were strong, but navies were frequently quite undermanned. As such he protested verbally, but departed without a fight on 5 January. Argentina claims that Vernet's colony was also expelled at this time, though sources from the time appear to dispute this, suggesting that the colonists were encouraged to remain initially under the authority of Vernet's storekeeper, William Dickson and later his deputy, Matthew Brisbane.
Initial British plans for the Islands were based upon the continuation of Vernet's settlement at Port Louis. An Argentine immigrant of Irish origin, William Dickson, was appointed as the British representative and provided with a flagpole and flag to be flown whenever ships were in harbour. In March 1833, Vernet's Deputy, Matthew Brisbane returned and presented his papers to Captain
The Argentinian assertions of sovereignty provided the spur for Britain to send a naval task force in order to finally and permanently return to the islands.
On 3 January 1833, Captain James Onslow, of the brig-sloop , arrived at Vernet's settlement at Port Louis to request that the flag of the United Provinces of the River Plate be replaced with the British one, and for the administration to leave the islands. While Major José María Pinedo, commander of the schooner ''Sarandí'', wanted to resist, his numerical disadvantage was obvious, particularly as a large number of his crew were British mercenaries who were unwilling to fight their own countrymen. Such a situation was not unusual in the newly independent states in Latin America, where land forces were strong, but navies were frequently quite undermanned. As such he protested verbally, but departed without a fight on 5 January. Argentina claims that Vernet's colony was also expelled at this time, though sources from the time appear to dispute this, suggesting that the colonists were encouraged to remain initially under the authority of Vernet's storekeeper, William Dickson and later his deputy, Matthew Brisbane.
Initial British plans for the Islands were based upon the continuation of Vernet's settlement at Port Louis. An Argentine immigrant of Irish origin, William Dickson, was appointed as the British representative and provided with a flagpole and flag to be flown whenever ships were in harbour. In March 1833, Vernet's Deputy, Matthew Brisbane returned and presented his papers to Captain
 Immediately following their
Immediately following their
 In 1833 the United Kingdom asserted authority over the Falkland Islands and
In 1833 the United Kingdom asserted authority over the Falkland Islands and  Government House opened as the offices of the Lieutenant Governor in 1847. Government House continued to develop with various additions, formally becoming the Governor's residence in 1859 when Governor Moore took residence. Government House remains the residence of the Governor.
Many of the colonists begin to move from Ansons' Harbour to Port Stanley. As the new town expanded, the population grew rapidly, reaching 200 by 1849. The population was further expanded by the arrival of 30 married
Government House opened as the offices of the Lieutenant Governor in 1847. Government House continued to develop with various additions, formally becoming the Governor's residence in 1859 when Governor Moore took residence. Government House remains the residence of the Governor.
Many of the colonists begin to move from Ansons' Harbour to Port Stanley. As the new town expanded, the population grew rapidly, reaching 200 by 1849. The population was further expanded by the arrival of 30 married
 A few years after the British had established themselves in the islands, a number of new British settlements were started. Initially many of these settlements were established in order to exploit the feral cattle on the islands. Following the introduction of the Cheviot breed of sheep to the islands in 1852, sheep farming became the dominant form of agriculture on the Islands.
A few years after the British had established themselves in the islands, a number of new British settlements were started. Initially many of these settlements were established in order to exploit the feral cattle on the islands. Following the introduction of the Cheviot breed of sheep to the islands in 1852, sheep farming became the dominant form of agriculture on the Islands.
 Lafone continued to develop his business interests and in 1849 looked to establish a joint stock company with his London creditors. The company was launched as The Royal Falkland Land, Cattle, Seal and Fishery Company in 1850 but soon thereafter was incorporated under
Lafone continued to develop his business interests and in 1849 looked to establish a joint stock company with his London creditors. The company was launched as The Royal Falkland Land, Cattle, Seal and Fishery Company in 1850 but soon thereafter was incorporated under
 In 1911 the islands had 3,275 inhabitants of whom 916 lived in Port Stanley.
A canning factory was opened in 1911 at Goose Green and was initially extremely successful. It absorbed a large proportion of surplus sheep but during the postwar slump it suffered a serious loss and closed in 1921.
Despite this setback, a mere year later, the settlement grew after it became the base for the Falkland Islands Company's sheep farm in Lafonia in 1922, with improved sheep handling and wool shed being built. In 1927, the settlement's huge sheep shearing shed was built, which is claimed to be the world's largest, with a capacity of five thousand sheep. In 1979, 100,598 sheep were shorn at Goose Green.
The mid-20th century saw a number of abortive attempts to diversify the islands' economy away from large scale sheep ranching.
In the period just after the
In 1911 the islands had 3,275 inhabitants of whom 916 lived in Port Stanley.
A canning factory was opened in 1911 at Goose Green and was initially extremely successful. It absorbed a large proportion of surplus sheep but during the postwar slump it suffered a serious loss and closed in 1921.
Despite this setback, a mere year later, the settlement grew after it became the base for the Falkland Islands Company's sheep farm in Lafonia in 1922, with improved sheep handling and wool shed being built. In 1927, the settlement's huge sheep shearing shed was built, which is claimed to be the world's largest, with a capacity of five thousand sheep. In 1979, 100,598 sheep were shorn at Goose Green.
The mid-20th century saw a number of abortive attempts to diversify the islands' economy away from large scale sheep ranching.
In the period just after the  Similarly, Ajax Bay on Falkland Sound, was developed by the Colonial Development Corporation in the 1950s, which was also responsible for developing Port Albemarle. It was mainly a refrigeration plant, and was supposed to freeze Falkland
Similarly, Ajax Bay on Falkland Sound, was developed by the Colonial Development Corporation in the 1950s, which was also responsible for developing Port Albemarle. It was mainly a refrigeration plant, and was supposed to freeze Falkland
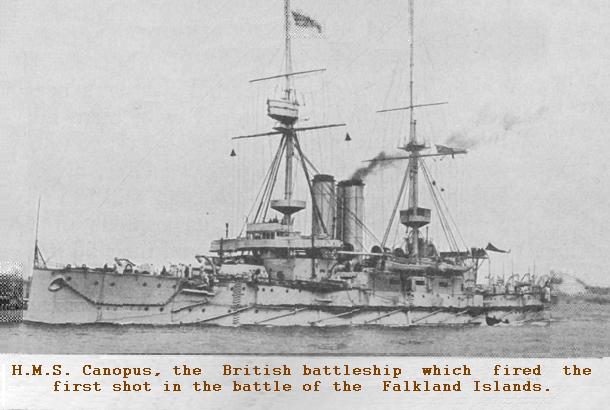
 Port Stanley became an important coaling station for the Royal Navy. This led to ships based there being involved in major naval engagements in both the First and Second World Wars.
The strategic significance of the Falkland Islands was confirmed by the second major naval engagement of the First World War.
Port Stanley became an important coaling station for the Royal Navy. This led to ships based there being involved in major naval engagements in both the First and Second World Wars.
The strategic significance of the Falkland Islands was confirmed by the second major naval engagement of the First World War.
 A more serious incident took place on 28 September 1966 when eighteen young
A more serious incident took place on 28 September 1966 when eighteen young  In November 1968, Miguel Fitzgerald was hired by the Argentine press to attempt a reprise of his 1964 landing. Accompanied by one of the 1966 hijackers, he flew to Stanley but on arrival found he could not land at the racecourse due to obstacles placed following the hijacking. The plane was forced to crash land on Eliza Cove Road, but the two occupants were unharmed. The stunt was intended to coincide with the visit of Lord Chalfont to the islands.
The latter incident proved counter-productive to the Argentine sovereignty push, as Lord Chalfont had been talking to a public meeting at the time of the plane's arrival. The islanders made it plain to Lord Chalfont that they rejected a Memorandum of Agreement negotiated between Britain and Argentina that August which stated that Britain was prepared to discuss sovereignty provided the islanders' wishes were respected. This spurred the formation of the Falkland Islands Committee by London barrister Bill Hunter-Christie and others. The Emergency Committee, as it became known, proved to be an effective lobbying organisation, constantly undermining Foreign Office initiatives on sovereignty negotiations. In December 1968, the lobbying effort managed to force the British Government to state that the islanders' wishes would be paramount.
In November 1968, Miguel Fitzgerald was hired by the Argentine press to attempt a reprise of his 1964 landing. Accompanied by one of the 1966 hijackers, he flew to Stanley but on arrival found he could not land at the racecourse due to obstacles placed following the hijacking. The plane was forced to crash land on Eliza Cove Road, but the two occupants were unharmed. The stunt was intended to coincide with the visit of Lord Chalfont to the islands.
The latter incident proved counter-productive to the Argentine sovereignty push, as Lord Chalfont had been talking to a public meeting at the time of the plane's arrival. The islanders made it plain to Lord Chalfont that they rejected a Memorandum of Agreement negotiated between Britain and Argentina that August which stated that Britain was prepared to discuss sovereignty provided the islanders' wishes were respected. This spurred the formation of the Falkland Islands Committee by London barrister Bill Hunter-Christie and others. The Emergency Committee, as it became known, proved to be an effective lobbying organisation, constantly undermining Foreign Office initiatives on sovereignty negotiations. In December 1968, the lobbying effort managed to force the British Government to state that the islanders' wishes would be paramount.
 Despite these tensions relationships between the islanders and the Argentines operating the new services in the islands were cordial. Although there was apprehension, politics were generally avoided and on a one-to-one basis there was never any real hostility.
On the international level, relations began to sour in 1975 when Argentine delegates at the London meeting of the
Despite these tensions relationships between the islanders and the Argentines operating the new services in the islands were cordial. Although there was apprehension, politics were generally avoided and on a one-to-one basis there was never any real hostility.
On the international level, relations began to sour in 1975 when Argentine delegates at the London meeting of the
 Land mines were a persistent problem for 38 years following the war. Land mine clearance was completed by November 2020.
In 1983, the UK passed the British Nationality (Falkland Islands) Act 1983, British Nationality (Falkland Islands) Act granting full British nationality law, British citizenship to the islanders. High-profile dignitaries visited to show British commitment to the islands, including Margaret Thatcher, the Charles III of the United Kingdom, Prince of Wales, and Princess Alexandra, The Honourable Lady Ogilvy, Princess Alexandra. In 1985, the Falkland Islands Dependency was split into the Falkland Islands proper and a newly separate territory of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands.
Relations between the UK and Argentina remained hostile after 1982. Although the United Nations General Assembly passed a resolution calling on the UK and Argentina to return to negotiations over the Islands' future, the UK ruled out further talks over the islands' sovereignty. The UK also maintained the arms embargo against Argentina that they initiated during the war, compelling the Argentine armed forces (a traditional UK buyer) to switch to other markets. Diplomatic relations were restored in 1989.
Relations between the English settlement in Argentina, UK and Argentina improved further in the 1990s. In 1998, Argentine President Carlos Menem visited London, where he reaffirmed Argentina claims to the Islands, but stated that only peaceful means would be used for their recovery. In 2001, UK Prime Minister Tony Blair visited Argentina, where he stated his hope that the UK and Argentina could resolve their differences. However, no talks on sovereignty took place during the visit.
Land mines were a persistent problem for 38 years following the war. Land mine clearance was completed by November 2020.
In 1983, the UK passed the British Nationality (Falkland Islands) Act 1983, British Nationality (Falkland Islands) Act granting full British nationality law, British citizenship to the islanders. High-profile dignitaries visited to show British commitment to the islands, including Margaret Thatcher, the Charles III of the United Kingdom, Prince of Wales, and Princess Alexandra, The Honourable Lady Ogilvy, Princess Alexandra. In 1985, the Falkland Islands Dependency was split into the Falkland Islands proper and a newly separate territory of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands.
Relations between the UK and Argentina remained hostile after 1982. Although the United Nations General Assembly passed a resolution calling on the UK and Argentina to return to negotiations over the Islands' future, the UK ruled out further talks over the islands' sovereignty. The UK also maintained the arms embargo against Argentina that they initiated during the war, compelling the Argentine armed forces (a traditional UK buyer) to switch to other markets. Diplomatic relations were restored in 1989.
Relations between the English settlement in Argentina, UK and Argentina improved further in the 1990s. In 1998, Argentine President Carlos Menem visited London, where he reaffirmed Argentina claims to the Islands, but stated that only peaceful means would be used for their recovery. In 2001, UK Prime Minister Tony Blair visited Argentina, where he stated his hope that the UK and Argentina could resolve their differences. However, no talks on sovereignty took place during the visit.
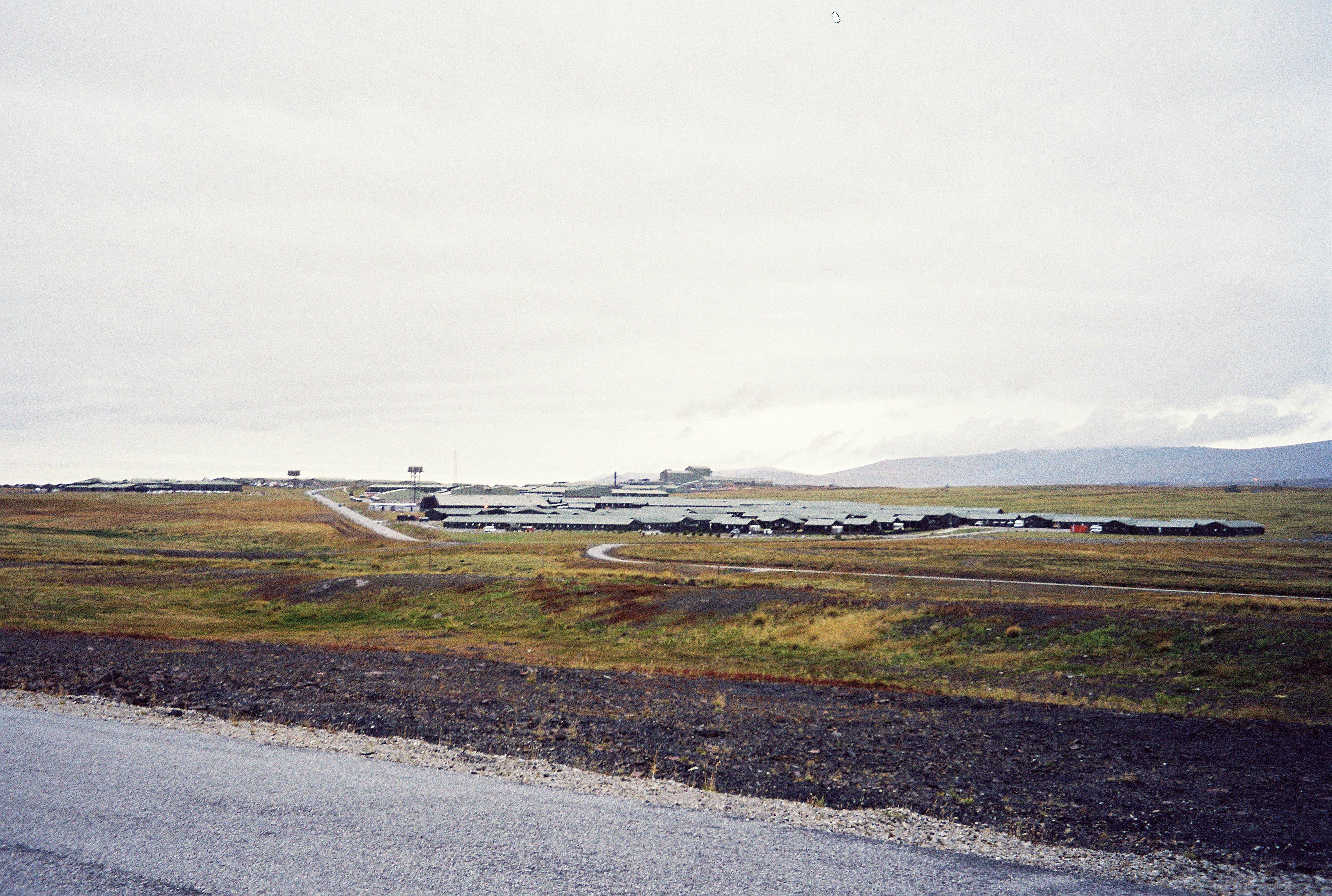 RAF Mount Pleasant, Mount Pleasant, to the west of Stanley, was chosen as the site for the new base. The airfield was opened by Prince Andrew, Duke of York, The Duke of York in 1985, and became fully operational in 1986.
Using the IATA airport code MPN, RAF Mount Pleasant also acts as the Falkland Islands' only international airport, in addition to its military role. Flights open to civilian passengers are operated twice-weekly.
These flights are currently operated by a civilian airline on behalf of the Royal Air Force, and fly to and from RAF Brize Norton in Oxfordshire, UK with a refuelling stop at RAF Ascension Island in the south-central Atlantic Ocean. Chilean airline LAN Airlines also operate weekly flights from Santiago.
RAF Mount Pleasant, Mount Pleasant, to the west of Stanley, was chosen as the site for the new base. The airfield was opened by Prince Andrew, Duke of York, The Duke of York in 1985, and became fully operational in 1986.
Using the IATA airport code MPN, RAF Mount Pleasant also acts as the Falkland Islands' only international airport, in addition to its military role. Flights open to civilian passengers are operated twice-weekly.
These flights are currently operated by a civilian airline on behalf of the Royal Air Force, and fly to and from RAF Brize Norton in Oxfordshire, UK with a refuelling stop at RAF Ascension Island in the south-central Atlantic Ocean. Chilean airline LAN Airlines also operate weekly flights from Santiago.
 Before the Falklands War, sheep-farming was the Falkland Islands' only industry. Since the late 1980s, when two species of squid popular with consumers were discovered in substantial numbers near the Falklands, fishing has become the largest part of the economy.
On 14 September 2011, Rockhopper Exploration announced plans under way for oil production to commence in 2016, through the use of Floating production storage and offloading, Floating production storage and offloading (FPSO) technology, replicating the methodology used on the Foinaven oilfield, Foinaven field off the Shetland Islands. The production site will require approximately 110 people working offshore and another 40 working onshore. The oil is expected to trade at of the Brent crude price.
Some small businesses attempted at Fox Bay have included a market garden, a salmon farm and a knitting mill with "Warrah Knitwear".
Tourism is the second-largest part of the economy. The war brought the islands newfound fame; now tourists come both to see wildlife and go on war tours. Cruise ships often visit, frequently as a tie-in to Tourism in Antarctica, Antarctica. Nonetheless, the remoteness of the archipelago, and the lack of direct flights to major cities, make the Falklands an expensive destination.
Before the Falklands War, sheep-farming was the Falkland Islands' only industry. Since the late 1980s, when two species of squid popular with consumers were discovered in substantial numbers near the Falklands, fishing has become the largest part of the economy.
On 14 September 2011, Rockhopper Exploration announced plans under way for oil production to commence in 2016, through the use of Floating production storage and offloading, Floating production storage and offloading (FPSO) technology, replicating the methodology used on the Foinaven oilfield, Foinaven field off the Shetland Islands. The production site will require approximately 110 people working offshore and another 40 working onshore. The oil is expected to trade at of the Brent crude price.
Some small businesses attempted at Fox Bay have included a market garden, a salmon farm and a knitting mill with "Warrah Knitwear".
Tourism is the second-largest part of the economy. The war brought the islands newfound fame; now tourists come both to see wildlife and go on war tours. Cruise ships often visit, frequently as a tie-in to Tourism in Antarctica, Antarctica. Nonetheless, the remoteness of the archipelago, and the lack of direct flights to major cities, make the Falklands an expensive destination.
1987 American report
by Richard D. Chenette, Lieutenant Commander, USN, laying out the history and background of the disputed claims
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20071006063014/http://www.falklands.info/history/timeline.html Timeline of Falklands Island history] {{DEFAULTSORT:History of the Falkland Islands History of the Falkland Islands, British colonization of the Americas French colonization of the Americas Spanish colonization of the Americas Falkland Islands in World War II History of South America, Falkland Islands
Falkland Islands
The Falkland Islands (; ), commonly referred to as The Falklands, is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and from Cape Dub ...
have been a matter of controversy, as they have been claimed by the French, British, Spaniards and Argentines at various points.
The islands were uninhabited when discovered by Europeans. France established a colony on the islands in 1764. In 1765, a British captain claimed the islands for Britain. In early 1770 a Spanish commander arrived from Buenos Aires with five ships and 1,400 soldiers forcing the British to leave Port Egmont. Britain and Spain almost went to war over the islands, but the British government decided that it should withdraw its presence from many overseas settlements in 1774. Spain, which had a garrison at Puerto Soledad
Puerto Soledad (''Puerto de Nuestra Señora de la Soledad'', ) was a Spanish military outpost and penal colony on the Falkland Islands, situated at an inner cove of Berkeley Sound (,Dom Pernety, Antoine-Joseph. ''Journal historique d'un voyage ...
on East Falklands, administered the garrison from Montevideo
Montevideo (, ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Uruguay, largest city of Uruguay. According to the 2023 census, the city proper has a population of 1,302,954 (about 37.2% of the country's total population) in an area of . M ...
until 1811 when it was compelled to withdraw as a result of the war against Argentine independence and the pressures of Peninsular War
The Peninsular War (1808–1814) was fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal, Spain and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French ...
. Luis Vernet attempted to establish a settlement in 1826, seeking support from both the Argentine and British Governments but most of his settlers took the opportunity to leave in 1831 following a raid by the USS ''Lexington''. An attempt made by Argentina to establish a penal colony in 1832 failed due to a mutiny. In 1833, the British returned to the Falkland Islands. Argentina invaded the islands on 2 April 1982. The British responded with an expeditionary force that forced the Argentines to surrender.
Claims of pre-Columbian discovery
 When the world sea level was lower in the
When the world sea level was lower in the Ice Age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages, and g ...
, the Falkland Islands
The Falkland Islands (; ), commonly referred to as The Falklands, is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and from Cape Dub ...
may have been joined to the mainland of South America.
While Fuegian
Fuegians are the indigenous inhabitants of Tierra del Fuego, at the southern tip of South America. The name has been credited to Captain James Weddell, who supposedly created the term in 1822.
The indigenous Fuegians belonged to several differ ...
s from Patagonia
Patagonia () is a geographical region that includes parts of Argentina and Chile at the southern end of South America. The region includes the southern section of the Andes mountain chain with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and glaciers ...
could have visited the Falklands, the islands were uninhabited when discovered by Europeans. Recent discoveries of arrowheads in Lafonia
Lafonia is a peninsula forming the southern part of East Falkland, the largest of the Falkland Islands.
Geography and geology
Shaped like the letter "E", it is joined to the northern part of the island by an isthmus that is almost wide. Wer ...
(on the southern half of East Falkland
East Falkland () is the largest island of the Falkland Islands, Falklands in the South Atlantic, having an area of or 54% of the total area of the Falklands. The island consists of two main land masses, of which the more southerly is known as L ...
) as well as the remains of a wooden canoe
A canoe is a lightweight, narrow watercraft, water vessel, typically pointed at both ends and open on top, propelled by one or more seated or kneeling paddlers facing the direction of travel and using paddles.
In British English, the term ' ...
provide evidence that the Yaghan people
The Yahgan (also called Yagán, Yaghan, Yámana, Yamana, or Tequenica) are a group of Indigenous peoples in the Southern Cone of South America. Their traditional territory includes the islands south of Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego, extending ...
of Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego (, ; Spanish for "Land of Fire", rarely also Fireland in English) is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South America, South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan.
The archipelago consists of the main is ...
may have made the journey to the islands. It is not known if these are evidence of one-way journeys, but there is no known evidence of pre-Columbian buildings or structures. However, it is not certain that the discovery predates arrival of Europeans. A Patagonian Missionary Society mission station was founded on Keppel Island
Keppel Island () is one of the Falkland Islands, lying between Saunders and Pebble islands, and near Golding Island to the north of West Falkland on Keppel Sound. It has an area of and its highest point, Mt. Keppel, is high. There is a wide ...
(off the west coast of West Falkland
West Falkland () is the second largest of the Falkland Islands in the South Atlantic. It is a hilly island, separated from East Falkland by the Falkland Sound. Its area is , 37% of the total area of the islands. Its coastline is long.
Popula ...
) in 1856. Yahgan people were at this station from 1856 to 1898 so this may be the source of the artifacts that have been found. In 2021, a paper was published on deposits of marine animal bones (primarily South American sea lion
The South American sea lion (''Otaria flavescens'', formerly ''Otaria byronia''), also called the southern sea lion and the Patagonian sea lion, is a sea lion found on the western and southeastern coasts of South America. It is the Monotypic ta ...
and Southern rockhopper penguin
The western rockhopper penguin (''Eudyptes chrysocome''), traditionally known as the southern rockhopper penguin, is a species of rockhopper penguin that is sometimes considered distinct from the northern rockhopper penguin. It occurs in subanta ...
) on New Island
New Island () is one of the Falkland Islands, lying north of Beaver Island (Falkland Islands), Beaver Island. It is from Stanley, Falkland Islands, Stanley and is long with an average width of . The highest point is . The northern and eastern ...
off the coast of West Falkland, at the same site where a quartzite arrowhead made of local stone had been found in 1979. The sites dated to 1275 to 1420 CE, and were interpreted as processing or midden
A midden is an old dump for domestic waste. It may consist of animal bones, human excrement, botanical material, mollusc shells, potsherds, lithics (especially debitage), and other artifacts and ecofacts associated with past human oc ...
sites where marine animals had been butchered. A charcoal spike consistent with anthropogenic causes (i.e. caused by humans) on New Island was also dated to 550 BP (1400 CE). The Yaghan people were capable seafarers, and are known to have travelled to the Diego Ramírez Islands
The Diego Ramírez Islands () are a small group of Chilean subantarctic islands located at the southernmost extreme of South America.
History
The islands were sighted on 12 February 1619 by the Spanish Garcia de Nodal expedition, and named a ...
around south of Cape Horn, and were suggested to be responsible for the creation of the mounds. Other authors have suggested that the mounds and arrowheads do not provide unambiguous evidence of pre-European presence.
The past presence of the Falkland Islands wolf
The Falkland Islands wolf (''Dusicyon australis'') was the only native land mammal of the Falkland Islands. This endemic canid became extinct in 1876, the first known canid to have become extinct in historical times.
Traditionally, it had been ...
, ''Dusicyon australis'', has often been cited as evidence of pre-European occupation of the islands, but this is contested. The animal was observed in the Falklands by Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English Natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
, but is now extinct.
The islands had no native trees when discovered but there is some ambiguous evidence of past forestation, which may be due to wood being transported by oceanic currents from Patagonia. All modern trees have been introduced by Europeans.
European discovery
 An
An archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands. An archipelago may be in an ocean, a sea, or a smaller body of water. Example archipelagos include the Aegean Islands (the o ...
in the region of the Falkland Islands appeared on Portuguese map
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on ...
s from the early 16th century. Researchers Pepper and Pascoe cite the possibility that an unknown Portuguese expedition may have sighted the islands, based on the existence of a French copy of a Portuguese map from 1516. Maps from this period show islands known as the ''Sanson'' islands in a position that could be interpreted as the Falklands.
Sightings of the islands are attributed to Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer best known for having planned and led the 1519–22 Spanish expedition to the East Indies. During this expedition, he also discovered the Strait of Magellan, allowing his fl ...
or Estêvão Gomes
Estêvão Gomes (– 1538), also known by the Spanish version of his name Esteban Gómez, was a Portuguese explorer. He sailed in the service of Castile (Spain) in the fleet of Ferdinand Magellan, but deserted the expedition when they had rea ...
of ''San Antonio'', one of the captains in the expedition, as the Falklands fit the description of those visited to gather supplies. The account given by Antonio Pigafetta
Antonio Pigafetta (; – c. 1531) was a Venetian scholar and explorer. In 1519, he joined the Spanish expedition to the Spice Islands led by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan, the world's first Magellan's circumnavigation, circumnavigation, ...
, the chronicler of Magellan's voyage, contradicts attribution to either Gomes or Magellan, since it describes the position of islands close to the Patagonia coast, with the expedition following the mainland coast and the islands visited between a latitude of 49° and 51°S and also refers to meeting "giants" (described as Sansón or Samsons in the chronicle) who are believed to be the Tehuelche Indians. Although acknowledging that Pigafetta's account casts doubt upon the claim, the Argentine historian Laurio H. Destefani asserts it probable that a ship from the Magellan expedition discovered the islands citing the difficulty in measuring longitude accurately, which means that islands described as close to the coast could be further away. Destefani dismisses attribution to Gomes since the course taken by him on his return would not have taken the ships near the Falklands.
Destefani also attributes an early visit to the Falklands by an unknown Spanish ship, although Destefani's firm conclusions are contradicted by authors who conclude the sightings refer to the Beagle Channel
Beagle Channel (; Yahgan language, Yahgan: ''Onašaga'') is a strait in the Tierra del Fuego, Tierra del Fuego Archipelago, on the extreme southern tip of South America between Chile and Argentina. The channel separates the larger main island of I ...
.
Lord Falkland
Viscount Falkland is a title in the Peerage of Scotland. The name refers to the royal burgh of Falkland in Fife.
History
The title was created in 1620 by King James VI for Sir Henry Cary, a member of the Cary family. He was born in Hertf ...
, the Treasurer of the Admiralty, who organized the first expedition to South Atlantic with the intention to explore the Islands.
When English explorer John Davis, commander of , one of the ships belonging to Thomas Cavendish
Sir Thomas Cavendish (1560 – May 1592) was an English explorer and a privateer known as "The Navigator" because he was the first who deliberately tried to emulate Sir Francis Drake and raid the Spanish towns and ships in the Pacific and ret ...
's second expedition to the New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
, separated from Cavendish off the coast of what is now southern Argentina, he decided to make for the Strait of Magellan
The Strait of Magellan (), also called the Straits of Magellan, is a navigable sea route in southern Chile separating mainland South America to the north and the Tierra del Fuego archipelago to the south. Considered the most important natura ...
in order to find Cavendish. On 9 August 1592 a severe storm battered his ship, and Davis drifted under bare masts, taking refuge "among certain Isles never before discovered". Davis did not provide the latitude of these islands, indicating they were away from the Patagonian coast (they are actually away). Navigational errors due to the longitude problem
The history of longitude describes the centuries-long effort by astronomers, cartographers and navigators to discover a means of determining the longitude (the east-west position) of any given place on Earth. The measurement of longitude is impo ...
were a common problem until the late 18th century, when accurate marine chronometers became readily available, although Destefani asserts the error here to be "unusually large".
In 1594, they may have been visited by English commander Richard Hawkins
Admiral Sir Richard Hawkins (or Hawkyns) (c. 1562 – 17 April 1622) was a 17th-century English seaman, explorer and privateer. He was the son of Admiral Sir John Hawkins.
Biography
He was from his earlier days familiar with ships and the ...
with his ship the '' Dainty'', who, combining his own name with that of Queen Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudo ...
, the "Virgin Queen", gave a group of islands the name of "Hawkins' Maidenland". However, the latitude given was off by at least 3 degrees and the description of the shore (including the sighting of bonfires) casts doubts on his discovery. Errors in the latitude measured can be attributed to a simple mistake reading a cross staff divided into minutes, meaning the latitude measured could have been 50° 48' S. The description of bonfires can also be attributed to peat fires caused by lightning, which is not uncommon in the outer islands of the Falklands in February. In 1925, Conor O'Brian analysed the voyage of Hawkins and concluded that the only land he could have sighted was Steeple Jason Island. The British historian Mary Cawkell also points out that criticism of the account of Hawkins' discovery should be tempered by the fact it was written nine years after the event; Hawkins was captured by the Spanish and spent eight years in prison.
On 24 January 1600, the Dutchman Sebald de Weert
Sebald or Sebald de Weert (May 2, 1567 – May 30 or June 1603) was a Flemish captain and vice-admiral of the Dutch East India Company (known in Dutch as ''Vereenigde Oost-Indische Compagnie'', VOC). He is most widely remembered for accurately p ...
visited the Jason Islands
The Jason Islands (Spanish language, Spanish: ''Islas Sebaldes'') are an archipelago in the Falkland Islands, lying to the far north-west of West Falkland. Three of the islands, Steeple Jason, Grand Jason and Clarke's Islet, are private nature ...
and called them the Sebald Islands (in Spanish, "Islas Sebaldinas" or "Sebaldes"). This name remained in use for the entire Falkland Islands for a long time; William Dampier
William Dampier (baptised 5 September 1651; died March 1715) was an English explorer, pirate, privateer, navigator, and naturalist who became the first Englishman to explore parts of what is today Australia, and the first person to circumnavig ...
used the name ''Sibbel de Wards'' in his reports of his visits in 1684 and 1703, while James Cook
Captain (Royal Navy), Captain James Cook (7 November 1728 – 14 February 1779) was a British Royal Navy officer, explorer, and cartographer famous for his three voyages of exploration to the Pacific and Southern Oceans, conducted between 176 ...
still referred to the Sebaldine Islands in the 1770s. The latitude that De Weert provided (50° 40') was close enough as to be considered, for the first time beyond doubt, the Falkland Islands.
English Captain John Strong, commander of ''Welfare'', sailed between the two principal islands in 1690 and called the passage "Falkland Channel" (now Falkland Sound
The Falkland Sound () is a sea strait in the Falkland Islands. Running southwest-northeast, it separates West and East Falkland.
Name
The sound was named by John Strong in 1690 for Viscount Falkland, the name only later being applied to th ...
), after Anthony Cary, 5th Viscount Falkland
Anthony Cary, 5th Viscount Falkland PC (16 February 1656 – 24 May 1694) was an English nobleman and politician.
Biography
Cary was born at Farley Castle, Somerset, the son of Henry Cary, 4th Viscount Falkland, to whose peerage he succeeded ...
(1656–1694), who as Commissioner of the Admiralty
Admiralty most often refers to:
*Admiralty, Hong Kong
* Admiralty (United Kingdom), military department in command of the Royal Navy from 1707 to 1964
*The rank of admiral
*Admiralty law
Admiralty can also refer to:
Buildings
* Admiralty, Tra ...
had financed the expedition and later became First Lord of the Admiralty
First Lord of the Admiralty, or formally the Office of the First Lord of the Admiralty, was the title of the political head of the English and later British Royal Navy. He was the government's senior adviser on all naval affairs, responsible f ...
. From this body of water the island group later took its collective name.
Early colonisation
The French explorerLouis Antoine de Bougainville
Louis-Antoine, Comte de Bougainville (; 12 November 1729 – 31 August 1811) was a French military officer and explorer. A contemporary of the British explorer James Cook, he served in the Seven Years' War and the American Revolutionary War. B ...
established a colony at Port St. Louis, on East Falkland's Berkeley Sound coast in 1764. The French name ''Îles Malouines'' was given to the islands – ''malouin'' being the adjective for the Breton
Breton most often refers to:
*anything associated with Brittany, and generally
**Breton people
**Breton language, a Southwestern Brittonic Celtic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken in Brittany
** Breton (horse), a breed
**Gale ...
port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Hamburg, Manch ...
of Saint-Malo
Saint-Malo (, , ; Gallo language, Gallo: ; ) is a historic French port in Ille-et-Vilaine, Brittany (administrative region), Brittany.
The Fortification, walled city on the English Channel coast had a long history of piracy, earning much wealth ...
. The Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
name ''Islas Malvinas'' is a translation of the French name of ''Îles Malouines''.
 In 1765, Captain
In 1765, Captain John Byron
Vice-Admiral John Byron (8 November 1723 – 1 April 1786) was a British Royal Navy officer and explorer. He earned the nickname "Foul-Weather Jack" in the press because of his frequent encounters with bad weather at sea. As a midshipman, he sa ...
, who was unaware the French had established Port Saint Louis on East Falkland, explored Saunders Island around West Falkland. After discovering a natural harbour, he named the area Port Egmont
Port Egmont (Spanish: ''Puerto de la Cruzada''; French: ''Poil de la Croisade'') was the first British settlement in the Falkland Islands, on Saunders Island off West Falkland, and is named after John Perceval, 2nd Earl of Egmont, who was First ...
and claimed the islands for Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* Great Britain, a large island comprising the countries of England, Scotland and Wales
* The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, a sovereign state in Europe comprising Great Britain and the north-eas ...
on the grounds of prior discovery. The next year Captain John MacBride
John MacBride (sometimes written John McBride; ; 7 May 1868 – 5 May 1916) was an Irish republican and military leader. He was executed by the British government for his participation in the 1916 Easter Rising in Dublin.
Early life
Jo ...
established a permanent British settlement at Port Egmont.
Under the alliance established by the Pacte de Famille
The ''Pacte de Famille'' (, Family Compact; ) is one of three separate, but similar alliances between the Bourbon kings of France and Spain. As part of the settlement of the War of the Spanish Succession that brought the House of Bourbon of Fr ...
, in 1766 France agreed to leave after the Spanish complained about French presence in territories they considered their own. Spain agreed to compensate Louis de Bougainville, the French admiral and explorer who had established the settlement on East Falkland at his own expense. In 1767, the Spanish formally assumed control of Port St. Louis and renamed it ''Puerto Soledad
Puerto Soledad (''Puerto de Nuestra Señora de la Soledad'', ) was a Spanish military outpost and penal colony on the Falkland Islands, situated at an inner cove of Berkeley Sound (,Dom Pernety, Antoine-Joseph. ''Journal historique d'un voyage ...
'' (English: Port Solitude).
In early 1770 Spanish commander, Don Juan Ignacio de Madariaga, briefly visited Port Egmont. On 10 June he returned from Argentina with five armed ships and 1400 soldiers forcing the British to leave Port Egmont. This action sparked the Falkland Crisis between 10 July 1770 to 22 January 1771 when Britain and Spain almost went to war over the islands. However, conflict was averted when the colony was re-established by Captain John Stott with the ships , HMS ''Hound'' and HMS ''Florida'' (a mail ship which had already been at the founding of the original settlement). Egmont quickly became an important port-of-call for British ships sailing around Cape Horn
Cape Horn (, ) is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island. Although not the most southerly point of South America (which is Águila Islet), Cape Horn marks the nor ...
.
With the growing economic pressures stemming from the upcoming American War of Independence
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
, the British government decided that it should withdraw its presence from many overseas settlements in 1774. On 20 May 1776 the British forces under the command of Royal Naval Lieutenant Clayton formally left Port Egmont, while leaving a plaque asserting Britain's continuing sovereignty over the islands. For the next four years, British sealers Sealer may refer either to a person or ship engaged in seal hunting, or to a sealant; associated terms include:
Seal hunting
* Sealer Hill, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica
* Sealers' Oven, bread oven of mud and stone built by sealers around 1800 ...
used Egmont as a base for their activities in the South Atlantic. This ended in 1780 when they were forced to leave by Spanish authorities who then ordered that the British colony be destroyed.
The Spanish withdrew from the islands under pressure as a result of the Napoleonic invasion and the Argentine War of Independence
The Argentine War of Independence () was a secessionist civil war (until 1816) fought from 1810 to 1818 by Argentine patriotic forces under Manuel Belgrano, Juan José Castelli, Martín Miguel de Güemes, Martin Miguel de Guemes and José de ...
. The Spanish garrison of Puerto Soledad
Puerto Soledad (''Puerto de Nuestra Señora de la Soledad'', ) was a Spanish military outpost and penal colony on the Falkland Islands, situated at an inner cove of Berkeley Sound (,Dom Pernety, Antoine-Joseph. ''Journal historique d'un voyage ...
was removed to Montevideo
Montevideo (, ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Uruguay, largest city of Uruguay. According to the 2023 census, the city proper has a population of 1,302,954 (about 37.2% of the country's total population) in an area of . M ...
in 1811 aboard the brigantine
A brigantine is a two-masted sailing vessel with a fully square-rigged foremast and at least two sails on the main mast: a square topsail and a gaff sail mainsail (behind the mast). The main mast is the second and taller of the two masts.
Ol ...
''Gálvez'' under an order signed by Francisco Javier de Elío
Francisco is the Spanish and Portuguese form of the masculine given name ''Franciscus''.
Meaning of the name Francisco
In Spanish, people with the name Francisco are sometimes nicknamed " Paco". San Francisco de Asís was known as ''Pater Comm ...
. On departure, the Spanish also left a plaque proclaiming Spain's sovereignty over the islands as the British had done 35 years before. The total depopulation of the Falkland Islands took place.
Inter-colonial period
Following the departure of the Spanish settlers, the Falkland Islands became the domain of whalers and sealers who used the islands to shelter from the worst of the South Atlantic weather. By merit of their location, the Falkland Islands have often been the last refuge for ships damaged at sea. Most numerous among those using the islands were British and American sealers, where typically between 40 and 50 ships were engaged in exploitingfur seal
Fur seals are any of nine species of pinnipeds belonging to the subfamily Arctocephalinae in the family Otariidae. They are much more closely related to sea lions than Earless seal, true seals, and share with them external ears (Pinna (anatomy ...
s. This represents an itinerant population of up to 1,000 sailors.
''Isabella''
On 8 February 1813 ''Isabella'', a British ship of 193 tons en route fromSydney
Sydney is the capital city of the States and territories of Australia, state of New South Wales and the List of cities in Australia by population, most populous city in Australia. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Syd ...
to London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, ran aground off the coast of Speedwell Island
Speedwell Island (formerly Eagle Island; Spanish ''Isla Águila'') is one of the Falkland Islands, lying in the Falkland Sound, southwest of Lafonia, East Falkland.
The island has an area of , measuring approximately from north to south and a ...
, then known as Eagle Island. Among the ship's 54 passengers and crew, all of whom survived the wreck, was the United Irish general and exile Joseph Holt
Joseph Holt (January 6, 1807 – August 1, 1894) was an American lawyer, soldier, and politician. As a leading member of the James Buchanan#Administration and Cabinet, Buchanan administration, he succeeded in convincing Buchanan to oppose the ...
, who subsequently detailed the ordeal in his memoirs. Also aboard had been the heavily pregnant Joanna Durie, who on 21 February 1813 gave birth to Elizabeth Providence Durie.
The next day, 22 February 1813, six men set out in one of the Isabella's longboats to seek help from any nearby Spanish outposts. Braving the South Atlantic in a boat little more than long, they made landfall on the mainland at the River Plate just over a month later. The British gun brig under the command of Lieutenant William D'Aranda was sent to rescue the survivors.
On 5 April Captain Charles Barnard of the American sealer ''Nanina'' was sailing off the shore of Speedwell Island, with a discovery boat deployed looking for seals. Having seen smoke and heard gunshots the previous day, he was alert to the possibility of survivors of a ship wreck. This suspicion was heightened when the crew of the boat came aboard and informed Barnard that they had come across a new moccasin as well as the partially butchered remains of a seal. At dinner that evening, the crew observed a man approaching the ship who was shortly joined by eight to ten others. Both Barnard and the survivors from ''Isabella'' had harboured concerns the other party was Spanish and were relieved to discover their respective nationalities.
Barnard dined with the ''Isabella'' survivors that evening and finding that the British party were unaware of the War of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the Uni ...
informed the survivors that technically they were at war with each other. Nevertheless, Barnard promised to rescue the British party and set about preparations for the voyage to the River Plate. Realising that they had insufficient stores for the voyage he set about hunting wild pigs and otherwise acquiring additional food. While Barnard was gathering supplies, however, the British took the opportunity to seize ''Nanina'' and departed leaving Barnard, along with one member of his own crew and three from ''Isabella'', marooned. Shortly thereafter, ''Nancy'' arrived from the River Plate and encountered ''Nanina'', whereupon Lieutenant D'Aranda rescued the erstwhile survivors of ''Isabella'' and took ''Nanina'' itself as a prize of war
A prize of war (also called spoils of war, bounty or booty) is a piece of enemy property or land seized by a belligerent party during or after a war or battle. This term was used nearly exclusively in terms of captured ships during the 18th and 1 ...
.
Barnard and his party survived for eighteen months marooned on the islands until the British whaler
A whaler or whaling ship is a specialized vessel, designed or adapted for whaling: the catching or processing of whales.
Terminology
The term ''whaler'' is mostly historic. A handful of nations continue with industrial whaling, and one, Jap ...
s and '' Asp'' rescued them in November 1814. The British admiral in Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro, or simply Rio, is the capital of the Rio de Janeiro (state), state of Rio de Janeiro. It is the List of cities in Brazil by population, second-most-populous city in Brazil (after São Paulo) and the Largest cities in the America ...
had requested their masters to divert to the area to search for the American crew. In 1829, Barnard published an account of his survival entitled ''A Narrative of the Sufferings and Adventures of Capt Charles H. Barnard''.
Argentine colonisation attempts
 In March 1820, , a privately owned frigate that was operated as a
In March 1820, , a privately owned frigate that was operated as a privateer
A privateer is a private person or vessel which engages in commerce raiding under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign o ...
under a license issued by the United Provinces of the River Plate
United may refer to:
Places
* United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community
* United, West Virginia, an unincorporated community
Arts and entertainment Films
* ''United'' (2003 film), a Norwegian film
* ''United'' (2011 film), a BBC Two f ...
, under the command of American Colonel David Jewett, set sail looking to capture Spanish ships as prizes. He captured ''Carlota'', a Portuguese ship, which was considered an act of piracy. A storm resulted in severe damage to ''Heroína'' and sank the prize ''Carlota'', forcing Jewett to put into Puerto Soledad for repairs in October 1820.
Captain Jewett sought assistance from the British explorer James Weddell
James Weddell (24 August 1787 – 9 September 1834) was a British sailor, navigator and seal hunter who in February 1823 sailed to latitude of 74° 15′ S—a record 7.69 degrees or 532 statute miles south of the Antar ...
. Weddell reported the letter he received from Jewett as:
Sir, I have the honor of informing you that I have arrived in this port with a commission from the Supreme Government of the United Provinces of the Rio de la Plata to take possession of these islands on behalf of the country to which they belong by Natural Law. While carrying out this mission I want to do so with all the courtesy and respect all friendly nations; one of the objectives of my mission is to prevent the destruction of resources necessary for all ships passing by and forced to cast anchor here, as well as to help them to obtain the necessary supplies, with minimum expenses and inconvenience. Since your presence here is not in competition with these purposes and in the belief that a personal meeting will be fruitful for both of us, I invite you to come aboard, where you'll be welcomed to stay as long as you wish; I would also greatly appreciate your extending this invitation to any other British subject found in the vicinity; I am, respectfully yours. Signed, Jewett, Colonel of the Navy of the United Provinces of South America and commander of the frigate ''Heroína''.Many modern authors report this letter as representing the declaration issued by Jewett.Laurio H. Destéfani, ''The Malvinas, the South Georgias and the South Sandwich Islands, the conflict with Britain'', Buenos Aires, 1982 Jewett's ship received Weddell's assistance in obtaining anchorage off
Port Louis
Port Louis (, ; or , ) is the capital and most populous city of Mauritius, mainly located in the Port Louis District, with a small western part in the Black River District. Port Louis is the country's financial and political centre. It is admi ...
. Weddell reported only 30 seamen and 40 soldiers fit for duty out of a crew of 200, and how Jewett slept with pistols over his head following an attempted mutiny
Mutiny is a revolt among a group of people (typically of a military or a crew) to oppose, change, or remove superiors or their orders. The term is commonly used for insubordination by members of the military against an officer or superior, ...
earlier in the voyage. On 6 November 1820, Jewett raised the flag of the United Provinces of the River Plate (a predecessor of modern-day Argentina) and claimed possession of the islands. In the words of Weddell, "In a few days, he took formal possession of these islands for the patriot government of Buenos Ayres, read a declaration under their colours, planted on a port in ruins, and fired a salute of twenty-one guns."Weddell, James''A Voyage Towards the South Pole''
London, Longman, Rees, Orme, Brown and Green, 1827 Jewett departed from the Falkland Islands in April 1821. In total he had spent no more than six months on the island, entirely at Port Louis. In 1822, Jewett was accused of piracy by a Portuguese court, but by that time he was in Brazil.
Luis Vernet's enterprise
 In 1823, the United Provinces of the River Plate granted
In 1823, the United Provinces of the River Plate granted fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
rights to Jorge Pacheco and Luis Vernet. Travelling to the islands in 1824, the first expedition failed almost as soon as it landed, and Pacheco chose not to continue with the venture. Vernet persisted, but the second attempt, delayed until winter 1826 by a Brazilian blockade, was also unsuccessful. The expedition intended to exploit the feral
A feral (; ) animal or plant is one that lives in the wild but is descended from domesticated individuals. As with an introduced species, the introduction of feral animals or plants to non-native regions may disrupt ecosystems and has, in som ...
cattle on the islands but the boggy conditions meant the gaucho
A gaucho () or gaúcho () is a skilled horseman, reputed to be brave and unruly. The figure of the gaucho is a folk symbol of Argentina, Paraguay, Uruguay, Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil, the southern part of Bolivia, and the south of Chilean Patago ...
s could not catch cattle in their traditional way. Vernet was by now aware of conflicting British claims to the islands and sought permission from the British consulate
A consulate is the office of a consul. A type of mission, it is usually subordinate to the state's main representation in the capital of that foreign country (host state), usually an embassy (or, only between two Commonwealth countries, a ...
before departing for the islands.
In 1828, the United Provinces government granted Vernet all of East Falkland including all its resources, and exempted him from taxation if a colony could be established within three years. He took settlers, including British Captain Matthew Brisbane (who had sailed to the islands earlier with Weddell), and before leaving once again sought permission from the British Consulate in Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires, controlled by the government of the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Argentina. It is located on the southwest of the Río de la Plata. Buenos Aires is classified as an Alpha− glob ...
. The British asked for a report for the British government on the islands, and Vernet asked for British protection should they return.A brief history of the Falkland Islands Part 3 - Louis Vernet: The Great Entrepreneur, Accessed 2007-07-19 On 10 June 1829, Vernet was designated as 'civil and military commandant' of the islands (no governor was ever appointed) and granted a monopoly on seal hunting rights. A protest was lodged by the British Consulate in Buenos Aires. By 1831, the colony was successful enough to be advertising for new colonists, although 's report suggests that the conditions on the islands were quite miserable.
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English Natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
's visit in 1833 confirmed the squalid conditions in the settlement, although Captain Matthew Brisbane
Matthew Brisbane (1787 – 8 August 1833) was a Scottish mariner, sealer and notable figure in the early history of the Falkland Islands.
Early life
Little is known of Brisbane's early life. He was born in Perth, Scotland in 1787 but hi ...
(Vernet's deputy) later claimed that this was the result of the ''Lexington'' raid.Fitzroy, R., ''VOYAGES OF THE ADVENTURE AND BEAGLE. VOLUME II.''Accessed 2007-10-02
USS ''Lexington'' raid
In 1831, Vernet attempted to assert his monopoly on seal hunting rights. This led him to capture the American ships ''Harriet'', ''Superior'' and ''Breakwater''. As a reprisal, the United States consul in Buenos Aires sent CaptainSilas Duncan
Silas M. Duncan (178814 September 1834) was an officer in the United States Navy during the War of 1812.
Born in Rockaway Township, New Jersey, Duncan was appointed midshipman 15 November 1809. While third lieutenant of ''Saratoga'' during the ...
of USS ''Lexington'' to recover the confiscated property. After finding what he considered proof that at least four American fishing ships had been captured, plundered, and even outfitted for war, Duncan took seven prisoners aboard ''Lexington'' and charged them with piracy.
Also taken on board, Duncan reported, "were the whole of the (Falklands') population consisting of about forty persons, with the exception of some 'gauchos', or cowboys who were encamped in the interior." The group, principally German citizens from Buenos Aires, "appeared greatly rejoiced at the opportunity thus presented of removing with their families from a desolate region where the climate is always cold and cheerless and the soil extremely unproductive". However, about 24 people did remain on the island, mainly gauchos and several Charrúa
The Charrúa are an Indigenous people or Indigenous Nation of the Southern Cone in present-day Uruguay and the adjacent areas in Argentina ( Entre Ríos) and Brazil (Rio Grande do Sul). They were a semi-nomadic people who sustained themselves ...
Indians, who continued to trade on Vernet's account.
Measures were taken against the settlement. The log of ''Lexington'' reports destruction of arms and a powder store, while settlers remaining later said that there was great damage to private property. Towards the end of his life, Luis Vernet authorised his sons to claim on his behalf for his losses stemming from the raid. In the case lodged against the US Government for compensation, rejected by the US Government of President Cleveland
Stephen Grover Cleveland (March 18, 1837June 24, 1908) was the 22nd and 24th president of the United States, serving from 1885 to 1889 and from 1893 to 1897. He was the first U.S. president to serve nonconsecutive terms and the first Dem ...
in 1885, Vernet stated that the settlement was destroyed.
Penal colony and mutiny
In the aftermath of the ''Lexington'' incident, Major Esteban Mestivier was commissioned by the Buenos Aires government to set up apenal colony
A penal colony or exile colony is a settlement used to exile prisoners and separate them from the general population by placing them in a remote location, often an island or distant colonial territory. Although the term can be used to refer ...
. He arrived at his destination on 15 November 1832 but his soldiers mutinied and killed him. The mutiny was suppressed by armed sailors from the French whaler ''Jean Jacques'', whilst Mestivier's widow was taken on board the British sealer ''Rapid''. ''Sarandí'' returned on 30 December 1832 and Major José María Pinedo took charge of the settlement.
British return
 The Argentinian assertions of sovereignty provided the spur for Britain to send a naval task force in order to finally and permanently return to the islands.
On 3 January 1833, Captain James Onslow, of the brig-sloop , arrived at Vernet's settlement at Port Louis to request that the flag of the United Provinces of the River Plate be replaced with the British one, and for the administration to leave the islands. While Major José María Pinedo, commander of the schooner ''Sarandí'', wanted to resist, his numerical disadvantage was obvious, particularly as a large number of his crew were British mercenaries who were unwilling to fight their own countrymen. Such a situation was not unusual in the newly independent states in Latin America, where land forces were strong, but navies were frequently quite undermanned. As such he protested verbally, but departed without a fight on 5 January. Argentina claims that Vernet's colony was also expelled at this time, though sources from the time appear to dispute this, suggesting that the colonists were encouraged to remain initially under the authority of Vernet's storekeeper, William Dickson and later his deputy, Matthew Brisbane.
Initial British plans for the Islands were based upon the continuation of Vernet's settlement at Port Louis. An Argentine immigrant of Irish origin, William Dickson, was appointed as the British representative and provided with a flagpole and flag to be flown whenever ships were in harbour. In March 1833, Vernet's Deputy, Matthew Brisbane returned and presented his papers to Captain
The Argentinian assertions of sovereignty provided the spur for Britain to send a naval task force in order to finally and permanently return to the islands.
On 3 January 1833, Captain James Onslow, of the brig-sloop , arrived at Vernet's settlement at Port Louis to request that the flag of the United Provinces of the River Plate be replaced with the British one, and for the administration to leave the islands. While Major José María Pinedo, commander of the schooner ''Sarandí'', wanted to resist, his numerical disadvantage was obvious, particularly as a large number of his crew were British mercenaries who were unwilling to fight their own countrymen. Such a situation was not unusual in the newly independent states in Latin America, where land forces were strong, but navies were frequently quite undermanned. As such he protested verbally, but departed without a fight on 5 January. Argentina claims that Vernet's colony was also expelled at this time, though sources from the time appear to dispute this, suggesting that the colonists were encouraged to remain initially under the authority of Vernet's storekeeper, William Dickson and later his deputy, Matthew Brisbane.
Initial British plans for the Islands were based upon the continuation of Vernet's settlement at Port Louis. An Argentine immigrant of Irish origin, William Dickson, was appointed as the British representative and provided with a flagpole and flag to be flown whenever ships were in harbour. In March 1833, Vernet's Deputy, Matthew Brisbane returned and presented his papers to Captain Robert FitzRoy
Vice-Admiral Robert FitzRoy (5 July 1805 – 30 April 1865) was an English officer of the Royal Navy, politician and scientist who served as the second governor of New Zealand between 1843 and 1845. He achieved lasting fame as the captain of ...
of , which coincidentally happened to be in harbour at the time. Fitzroy encouraged Brisbane to continue with Vernet's enterprise with the proviso that whilst private enterprise was encouraged, Argentine assertions of sovereignty would not be welcome.
Brisbane reasserted his authority over Vernet's settlement and recommenced the practice of paying employees in promissory notes. Due to Vernet's reduced status, the promissory notes were devalued, which meant that the employees received fewer goods at Vernet's stores for their wages. After months of freedom following the ''Lexington'' raid this accentuated dissatisfaction with the leadership of the settlement. In August 1833, under the leadership of Antonio Rivero
Antonio "El Gaucho" Rivero was a gaucho known for his leading role in the Port Louis Murders of 26 August 1833, in which five prominent members of the settlement of Port Louis on the Falkland Islands were murdered. In Argentine revisionist histor ...
, a gang of Creole and Indian gauchos ran amok in the settlement. Armed with muskets obtained from American sealers, the gang killed five members of Vernet's settlement including both Dickson and Brisbane. Shortly afterward the survivors fled Port Louis, seeking refuge on Turf Island in Berkeley Sound until rescued by the British sealer ''Hopeful'' in October 1833.
Lt Henry Smith was installed as the first British resident in January 1834. One of his first actions was to pursue and arrest Rivero's gang for the murders committed the previous August. The gang was sent for trial in London but could not be tried as the Crown Court
The Crown Court is the criminal trial court, court of first instance in England and Wales responsible for hearing all indictable offences, some Hybrid offence, either way offences and appeals of the decisions of magistrates' courts. It is ...
did not have jurisdiction over the Falkland Islands. In the British colonial system, colonies had their own, distinct governments, finances, and judicial systems. Rivero was not tried and sentenced because the British local government and local judiciary had not yet been installed in 1834; these were created later, by the 1841 British Letters Patent
Letters patent (plurale tantum, plural form for singular and plural) are a type of legal instrument in the form of a published written order issued by a monarch, President (government title), president or other head of state, generally granti ...
. Subsequently, Rivero has acquired the status of a folk hero in Argentina, where he is portrayed as leading a rebellion against British rule. Ironically it was the actions of Rivero that were responsible for the ultimate demise of Vernet's enterprise on the Falklands.
Charles Darwin revisited the Falklands in 1834; the settlements Darwin and Fitzroy both take their names from this visit.
After the arrest of Rivero, Smith set about restoring the settlement at Port Louis, repairing the damage done by the ''Lexington'' raid and renaming it 'Anson's Harbour'. Lt Lowcay succeeded Smith in April 1838, followed by Lt Robinson in September 1839 and Lt Tyssen in December 1839.
Vernet later attempted to return to the Islands but was refused permission to return. The British Crown reneged on promises and refused to recognise rights granted by Captain Onslow at the time of the reoccupation. Eventually, after travelling to London, Vernet received paltry compensation for horses shipped to Port Louis many years before. G.T. Whittington obtained a concession of from Vernet that he later exploited with the formation of the Falkland Islands Commercial Fishery and Agricultural Association. Islas del Atlántico Sur, Islas Malvinas, Historia, Ocupación Inglesa: Port Stanley, Accessed 2007-10-02
British colonisation
 Immediately following their
Immediately following their return
Return may refer to:
In business, economics, and finance
* Return on investment (ROI), the financial gain after an expense.
* Rate of return, the financial term for the profit or loss derived from an investment
* Tax return, a blank document or t ...
to the Falkland Islands and the failure of Vernet's settlement, the British maintained Port Louis as a military outpost. There was no attempt to colonise the islands following the intervention, instead there was a reliance upon the remaining rump of Vernet's settlement. Lt. Smith received little support from the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
and the islands developed largely on his initiative but he had to rely on a group of armed gauchos to enforce authority and protect British interests. Smith received advice from Vernet in this regard, and in turn continued to administer Vernet's property and provide him with regular accounts. His superiors later rebuked him for his ideas and actions in promoting the development of the small settlement in Port Louis. In frustration, Smith resigned but his successors Lt. Lowcay and Lt. Tyssen did not continue with the initiatives Smith had pursued and the settlement began to stagnate.
In 1836, East Falkland was surveyed by Admiral George Grey, and further in 1837 by Lowcay. Admiral George Grey, conducting the geographic survey in November 1836 had the following to say about their first view of East Falkland:
Pressure to develop the islands as a colony began to build as the result of a campaign mounted by British merchant G. T. Whittington. Whittington formed the Falkland Islands Commercial Fishery and Agricultural Association and (based on information indirectly obtained from Vernet) published a pamphlet entitled "The Falkland Islands". Later a petition signed by London merchants was presented to the British Government
His Majesty's Government, abbreviated to HM Government or otherwise UK Government, is the central government, central executive authority of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
demanding the convening of a public meeting to discuss the future development of the Falkland Islands. Whittington petitioned the Colonial Secretary, Lord Russell, proposing that his association be allowed to colonise the islands. In May 1840, the British Government made the decision to colonise the Falkland Islands.
Unaware of the decision by the British Government to colonise the islands, Whittington grew impatient and decided to take action of his own initiative. Obtaining two ships, he sent his brother, J. B. Whittington, on a mission to land stores and settlers at Port Louis. On arrival he presented his claim to land that his brother had bought from Vernet. Lt. Tyssen was taken aback by Whittington's arrival, indicating that he had no authority to allow this; however, he was unable to prevent the party from landing. Whittington constructed a large house for his party, and using a salting house built by Vernet established a fish-salting business. A Brief History of the Falkland Islands, Part 4 - The British Colonial Era, Accessed 2007-10-02
Establishment of Port Stanley
 In 1833 the United Kingdom asserted authority over the Falkland Islands and
In 1833 the United Kingdom asserted authority over the Falkland Islands and Richard Clement Moody
Major-General Richard Clement Moody (13 February 1813 – 31 March 1887) was a British Governor and Commander of the Royal Engineers. He was the founder and the first Lieutenant-Governor of British Columbia; and was Commanding Executive ...
, a highly esteemed Royal Engineer
The Corps of Royal Engineers, usually called the Royal Engineers (RE), and commonly known as the ''Sappers'', is the engineering arm of the British Army. It provides military engineering and other technical support to the British Armed Forces ...
, was appointed as Lieutenant Governor of the islands. This post was renamed Governor of the Falkland Islands
The governor of the Falkland Islands is the representative of the British Crown in the Falkland Islands, acting "in His Majesty's name and on His Majesty's behalf" as the islands' Viceroy in the absence of the British monarch. The role and power ...
in 1843, when he also became Commander-in-Chief of the Falkland Islands. Moody left England for Falkland on 1 October 1841 aboard the ship ''Hebe'' and
arrived in Anson's Harbour later that month. He was accompanied by twelve sappers and miners and their families; together with Whittington's colonists this brought the population of Anson's Harbour to approximately 50. When Moody arrived, the Falklands was 'almost in a state of anarchy', but he used his powers 'with great wisdom and moderation'Minutes of the Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers, Volume 90, Issue 1887, 1887, pp. 453-455, OBITUARY. MAJOR-GENERAL RICHARD CLEMENT MOODY, R.E., 1813-1887. to develop the Islands' infrastructure and, commanding detachment of sappers, erected government offices, a school and barracks, residences, ports, and a new road system.
In 1842, Moody was instructed by Lord Stanley the British Secretary of State for War and the Colonies to report on the potential of the Port William area as the site of the new capital. Moody assigned the task of surveying the area to Captain Ross, leader of the Antarctic Expedition. Captain Ross delivered his report in 1843, concluding that Port William afforded a good deep-water anchorage for naval vessels, and that the southern shores of Port Jackson was a suitable location for the proposed settlement. Moody accepted the recommendation of Ross and construction of the new settlement started in July 1843. In July 1845, at Moody's suggestion, the new capital of the islands was officially named Port Stanley
Stanley (also known as Port Stanley) is the capital city of the Falkland Islands. It is located on the island of East Falkland, on a north-facing slope in one of the wettest parts of the islands. At the 2016 census, the city had a population o ...
after Lord Stanley. Not everyone was enthused with the selection of the location of the new capital, J. B. Whittington famously remarked that "Of all the miserable bog holes, I believe that Mr Moody has selected one of the worst for the site of his town."
The structure of the Colonial Government was established in 1845 with the formation of the Legislative Council and Executive Council and work on the construction of Government House
Government House is the name of many of the official residences of governors-general, governors and lieutenant-governors in the Commonwealth and British Overseas Territories. The name is also used in some other countries.
Government Houses in th ...
commenced. The following year, the first officers appointed to the Colonial Government took their posts; by this time a number of residences, a large storage shed, carpenter's shop and blacksmith's shop had been completed and the Government Dockyard laid out. In 1845 Moody introduced tussock grass
Tussock grasses or bunch grasses are a group of grass species in the family Poaceae. They usually grow as singular plants in clumps, tufts, hummocks, or bunches, rather than forming a sod or lawn, in meadows, grasslands, and prairies. As perennia ...
into Great Britain from Falkland, for which he received the gold medal of the Royal Agricultural Society. The Coat of arms of the Falkland Islands notably includes an image of tussock grass. Moody returned to England in February 1849. Moody Brook
Moody Brook is a small watercourse that flows into Stanley Harbour on East Falkland, Falkland Islands. It is near Stanley, just to the northwest, and was formerly the location of the town barracks, which were attacked in Operation Rosario, ...
is named after him.Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Richard Clement Moody
With the establishment of the deep-water anchorage and improvements in port facilities, Stanley saw a dramatic increase in the number of visiting ships in the 1840s in part due to the California gold rush
The California gold rush (1848–1855) began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California from the rest of the U ...
. A boom in ship provisioning and ship-repair resulted, aided by the notoriously bad weather in the South Atlantic and around Cape Horn. Stanley and the Falkland Islands are famous as the repository of many wrecks of 19th-century ships that reached the islands only to be condemned as unseaworthy and were often employed as floating warehouses by local merchants.
At one point in the 19th century, Stanley became one of the world's busiest ports. However, the ship-repair trade began to slacken off in 1876 with the establishment of the Plimsoll line
The load line, also known as Plimsoll line, indicates the legal limit to which a ship may be loaded for specific water types and temperatures in order to safely maintain buoyancy, particularly with regard to the hazard of Wind wave, waves. The l ...
, which saw the elimination of the so-called coffin ships and unseaworthy vessels that might otherwise have ended up in Stanley for repair. With the introduction of increasingly reliable iron steamships
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships ...
in the 1890s the trade declined further and was no longer viable following the opening of the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal () is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Caribbean Sea with the Pacific Ocean. It cuts across the narrowest point of the Isthmus of Panama, and is a Channel (geography), conduit for maritime trade between th ...
in 1914. Port Stanley continued to be a busy port supporting whaling and sealing activities in the early part of the 20th century, British warships (and garrisons) in the First
First most commonly refers to:
* First, the ordinal form of the number 1
First or 1st may also refer to:
Acronyms
* Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty-Centimeters, an astronomical survey carried out by the Very Large Array
* Far Infrared a ...
and Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
and the fishing and cruise ship
Cruise ships are large passenger ships used mainly for vacationing. Unlike ocean liners, which are used for transport, cruise ships typically embark on round-trip voyages to various ports of call, where passengers may go on Tourism, tours k ...
industries in the latter half of the century.
Chelsea Pensioners
A Chelsea Pensioner, or In-Pensioner, is a resident at the Royal Hospital Chelsea, an Old soldiers' home, Old Soldiers' retirement home and nursing home for former members of the British Army located in Chelsea, London. The Royal Hospital Chelsea ...
and their families. The Royal Falkland Islands Police
The Royal Falkland Islands Police (RFIP) is the territorial police force responsible for law enforcement within the Falkland Islands.
History
The force was established on 1 November 1846 with the appointment of Francis Parry as Chief Constabl ...
were established in November 1846 with the appointment of Francis Parry as Chief Constable. The force was initially staffed by three officers – the Chief Constable, the Gaoler (responsible for prisoners), and the Night Constable (responsible for policing during the night). The Constables Ordinance 1846, which had been enacted by the colony's Legislative Council
A legislative council is the legislature, or one of the legislative chambers, of a nation, colony, or subnational division such as a province or state. It was commonly used to label unicameral or upper house legislative bodies in the Brit ...
on 27 October of that year. The Chelsea Pensioners were to form the permanent garrison and police force, taking over from the Royal Sappers and Miners Regiment which had garrisoned the early colony.
The Exchange Building opened in 1854; part of the building was later used as a church. 1854 also saw the establishment of Marmont Row, including the Eagle Inn, now known as the Upland Goose Hotel. In 1887, Jubilee Villas were built to celebrate the Golden Jubilee
A golden jubilee marks a 50th anniversary. It variously is applied to people, events, and nations.
Bangladesh
In Bangladesh, golden jubilee refers the 50th anniversary year of the separation from Pakistan and is called in Bengali language, ...
of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
. Jubilee Villas are a row of brick built houses that follow a traditional British pattern; positioned on Ross road near the waterfront, they became an iconic image during the Falklands War
The Falklands War () was a ten-week undeclared war between Argentina and the United Kingdom in 1982 over two British Overseas Territories, British dependent territories in the South Atlantic: the Falkland Islands and Falkland Islands Dependenci ...
.
Peat
Peat is an accumulation of partially Decomposition, decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, Moorland, moors, or muskegs. ''Sphagnum'' moss, also called peat moss, is one of the most ...
is common on the islands and has traditionally been exploited as a fuel. Uncontrolled exploitation of this natural resource led to peat slips in 1878 and 1886. The 1878 peat slip resulted in the destruction of several houses, whilst the 1886 peat slip resulted in the deaths of two women and the destruction of the Exchange Building.
Christ Church Cathedral was consecrated in 1892 and completed in 1903. It received its famous whalebone
Baleen is a filter-feeding system inside the mouths of baleen whales. To use baleen, the whale first opens its mouth underwater to take in water. The whale then pushes the water out, and animals such as krill are filtered by the baleen and ...
arch, constructed from the jaws of two blue whale
The blue whale (''Balaenoptera musculus'') is a marine mammal and a baleen whale. Reaching a maximum confirmed length of and weighing up to , it is the largest animal known ever to have existed. The blue whale's long and slender body can ...
s, in 1933 to commemorate the centenary
A centennial, or centenary in British English, is a 100th anniversary or otherwise relates to a century.
Notable events
Notable centennial events at a national or world-level include:
* Centennial Exhibition, 1876, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. ...
of continuous British administration. Also consecrated in 1892 was the Tabernacle United Free Church, constructed from an imported timber kit.
Development
 A few years after the British had established themselves in the islands, a number of new British settlements were started. Initially many of these settlements were established in order to exploit the feral cattle on the islands. Following the introduction of the Cheviot breed of sheep to the islands in 1852, sheep farming became the dominant form of agriculture on the Islands.
A few years after the British had established themselves in the islands, a number of new British settlements were started. Initially many of these settlements were established in order to exploit the feral cattle on the islands. Following the introduction of the Cheviot breed of sheep to the islands in 1852, sheep farming became the dominant form of agriculture on the Islands.
Salvador Settlement
Salvador, also called Salvador Settlement Corral, is a small harbour and Human settlement, settlement on East Falkland, in the Falkland Islands, It is on the north east coast, on the south shore of Port Salvador. It is one of a handful of Spanish ...
was one of the earliest, being started in the 1830s, by a Gibraltarian
Gibraltarians (Spanish: ''gibraltareños'', colloquially: '' llanitos'') are an ethnic group native to Gibraltar, a British overseas territory located near the southernmost tip of the Iberian Peninsula at the entrance to the Mediterranean Sea ...
immigrant (hence its other name of "Gibraltar Settlement"), and it is still run by his descendants, the Pitalugas.
Cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are calle ...
were concentrated in the southern part of East Falkland, an area that became known as Lafonia. Lafone was an absentee landlord and never actually set foot on the islands. His activities were not monitored by the British and rather than introducing more British settlers as he promised, he brought large numbers of Spanish and Indian gauchos to hunt cattle. In 1846, they established Hope Place on the south shores of Brenton Loch. Vernet furnished Samuel Fisher Lafone, a British merchant operating from Montevideo, with details of the Falkland Islands including a map. Sensing that the exploitation of feral cattle on the islands would be a lucrative venture, in 1846 he negotiated a contract with the British Government that gave him exclusive rights to this resource. Until 1846 Moody had allotted feral cattle to new settlers and the new agreement not only prevented this but made Stanley dependent upon Lafone for supplies of beef
Beef is the culinary name for meat from cattle (''Bos taurus''). Beef can be prepared in various ways; Cut of beef, cuts are often used for steak, which can be cooked to varying degrees of doneness, while trimmings are often Ground beef, grou ...
. In 1849 a sod wall (the Boca wall) was built across the isthmus at Darwin to control the movement of cattle.
royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but ...
as The Falkland Islands Company Limited. Lafone became a director and his brother-in-law J.P. Dale the company's first manager in the islands. By 1852, the feral cattle had been hunted virtually to extinction by gauchos and the company switched to sheep farming with the introduction of the Cheviot breed of sheep. Hope Place proved to be an unsuitable location and the operation moved to Darwin. In 1860, the Lafone Beef contract was terminated but the Falkland Islands Company was given a grant to Lafonia. Ownership of the remaining cattle outside of Lafonia reverted to the Crown and hunting cattle without permission was banned.
In the second half of the 19th century, Darwin, Goose Green
Goose Green, also known simply as Goose, is a hamlet in Lafonia on East Falkland in the Falkland Islands. It lies on Choiseul Sound, on the east side of the island's central isthmus, south-southwest of Darwin. With a population of about 4 ...
, Fox Bay and Port Howard
Port Howard (, ) is the largest settlement on West Falkland (unless Fox Bay is taken as one settlement, instead of two). It is in the east of the island, on an inlet of Falkland Sound. It is on the lower slopes of Mount Maria (part of the Hor ...
were established. Port Howard was founded by James Lovegrove Waldron, and his brother in 1866; the Waldron brothers later left for Patagonia, but left the farm under local management.Wigglesworth, Angela. (1992) ''Falkland People''. Pub. Peter Owen.
Darwin was initially the haunt of gauchos and cattle farmers, but sheep farming came to dominate the area, and Scottish shepherds were brought in. A few years later, the first large tallow works in the islands (though not the first) was set up by the FIC in 1874. It handled 15,891 sheep in 1880.
From the 1880s, until 1972, Darwin and Fox Bay had their own separate medical officers. Nowadays, most medical care is based in Stanley.
Exploitation of maritime resources
The Falkland Islands were used as a base for whaling ships hunting thesouthern right whale
The southern right whale (''Eubalaena australis'') is a baleen whale, one of three species classified as right whales belonging to the genus ''Eubalaena''. Southern right whales inhabit oceans south of the Equator, between the latitudes of 20� ...
and sperm whale
The sperm whale or cachalot (''Physeter macrocephalus'') is the largest of the toothed whales and the largest toothed predator. It is the only living member of the Genus (biology), genus ''Physeter'' and one of three extant species in the s ...
from the 1770s until British authority was established over the islands and surrounding seas. Whaling was briefly revived with the establishment of a whaling station on New Island
New Island () is one of the Falkland Islands, lying north of Beaver Island (Falkland Islands), Beaver Island. It is from Stanley, Falkland Islands, Stanley and is long with an average width of . The highest point is . The northern and eastern ...
from 1909 to 1917 until whaling operations moved to South Georgia
South Georgia is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic Ocean that is part of the British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands. It lies around east of the Falkland Islands. ...
.
Fur seals had long been exploited for their pelts but numbers entered a drastic decline in the early 19th century. As a result, seal hunting died off, although continuing at a low level. In order to conserve stocks, a ban on the hunting of fur seals during summers months was enacted in 1881, but it was not until 1921 that hunting was banned entirely.
Elephant seal
Elephant seals or sea elephants are very large, oceangoing earless seals in the genus ''Mirounga''. Both species, the northern elephant seal (''M. angustirostris'') and the southern elephant seal (''M. leonina''), were hunted to the brink of ...
s were exploited for oil but like the fur seals their numbers declined drastically in the mid-1850s. Sealers instead turned their attention to the South American sea lion
The South American sea lion (''Otaria flavescens'', formerly ''Otaria byronia''), also called the southern sea lion and the Patagonian sea lion, is a sea lion found on the western and southeastern coasts of South America. It is the Monotypic ta ...
resulting in a dramatic decline in their numbers that made sealing uneconomic. Attempts to revive the trade, including a sealing station at Port Albemarle, were unsuccessful.
Even penguins were exploited for oil. Rockhopper and gentoo penguin
Penguins are a group of aquatic flightless birds from the family Spheniscidae () of the order Sphenisciformes (). They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere. Only one species, the Galápagos penguin, is equatorial, with a sm ...
s were rendered down in trypots from 1860 until the 1880s.
Twentieth century
Establishment of communications
Although the first telephone lines were installed by the Falkland Islands Company in the 1880s, the Falkland Islands Government was slow to embrace telephony. It was not until 1897 that a telephone line was installed between Cape Pembroke lighthouse and thepolice station
A police station is a facility operated by police or a similar law enforcement agency that serves to accommodate police officers and other law enforcement personnel. The role served by a police station varies by agency, type, and jurisdiction, ...
. The islands isolation was broken in 1911 when Guglielmo Marconi
Guglielmo Giovanni Maria Marconi, 1st Marquess of Marconi ( ; ; 25 April 1874 – 20 July 1937) was an Italian electrical engineer, inventor, and politician known for his creation of a practical radio wave-based Wireless telegraphy, wireless tel ...
installed a wireless telegraphy
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas pi ...
station that enabled telegrams to be sent to mainland Uruguay. Cable & Wireless, The Falkland Islands, Our History
A line was laid between Darwin and Stanley, with the ship ''Consort'' landing poles on the coast. Construction commenced in 1906 and was finished in 1907 (a length of nearly ). The line was initially only for business but the public could make calls occasionally. Lines continued to be laid to most of the major settlements in the islands, with the Falkland Islands police responsible for their maintenance until 1927. Communications among the settlements relied on the telephone network until radio telephones were introduced in the 1950s, although the telephone network continued until 1982. Telecommunications improved dramatically after the Falklands War, when an earth station was installed to allow direct dialling for the first time. In 1997, an Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the Global network, global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a internetworking, network of networks ...
service was launched and by 2002 nearly 90% of Falkland homes had Internet access.
Economic development
 In 1911 the islands had 3,275 inhabitants of whom 916 lived in Port Stanley.
A canning factory was opened in 1911 at Goose Green and was initially extremely successful. It absorbed a large proportion of surplus sheep but during the postwar slump it suffered a serious loss and closed in 1921.
Despite this setback, a mere year later, the settlement grew after it became the base for the Falkland Islands Company's sheep farm in Lafonia in 1922, with improved sheep handling and wool shed being built. In 1927, the settlement's huge sheep shearing shed was built, which is claimed to be the world's largest, with a capacity of five thousand sheep. In 1979, 100,598 sheep were shorn at Goose Green.
The mid-20th century saw a number of abortive attempts to diversify the islands' economy away from large scale sheep ranching.
In the period just after the
In 1911 the islands had 3,275 inhabitants of whom 916 lived in Port Stanley.
A canning factory was opened in 1911 at Goose Green and was initially extremely successful. It absorbed a large proportion of surplus sheep but during the postwar slump it suffered a serious loss and closed in 1921.
Despite this setback, a mere year later, the settlement grew after it became the base for the Falkland Islands Company's sheep farm in Lafonia in 1922, with improved sheep handling and wool shed being built. In 1927, the settlement's huge sheep shearing shed was built, which is claimed to be the world's largest, with a capacity of five thousand sheep. In 1979, 100,598 sheep were shorn at Goose Green.
The mid-20th century saw a number of abortive attempts to diversify the islands' economy away from large scale sheep ranching.
In the period just after the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, Port Albemarle, in the south west of West Falkland, was enlarged by the Colonial Development Company and included its own power station, jetty, Nissen hut
A Nissen hut is a prefabricated steel structure originally for military use, especially as barracks, made from a 210° portion of a cylindrical skin of corrugated iron. It was designed during the First World War by the Canadian-American-British e ...
s etc.; this was an attempt to revive the old sealing industry which had flourished during the 19th century. However, the project proved to be nonviable, not least because seal numbers had declined massively.
 Similarly, Ajax Bay on Falkland Sound, was developed by the Colonial Development Corporation in the 1950s, which was also responsible for developing Port Albemarle. It was mainly a refrigeration plant, and was supposed to freeze Falkland
Similarly, Ajax Bay on Falkland Sound, was developed by the Colonial Development Corporation in the 1950s, which was also responsible for developing Port Albemarle. It was mainly a refrigeration plant, and was supposed to freeze Falkland mutton
Lamb and mutton, collectively sheep meat (or sheepmeat) is one of the most common meats around the world, taken from the domestic sheep, ''Ovis aries'', and generally divided into lamb, from sheep in their first year, hogget, from sheep in thei ...
, but this was found to be economically nonviable, despite the huge expense incurred. Many of the pre-fabricated houses here were moved to Stanley. The site later became a British field hospital during the landings of Operation Sutton
Operation Sutton was the code name for the British landings on the shores of San Carlos Water, at Ajax Bay and Port San Carlos, near San Carlos on East Falkland.
Landings
During the night, 3 Commando Brigade along with attached units of ...
.
The seas around the Falkland Islands were not well policed prior to the Falklands War, and many foreign boats fished off the islands, despite protests that potential revenue was being lost. Fishing licences were only later to be introduced.
Education
In 1956, J. L. Waldron Ltd built a school at Port Howard, possibly inspired by the "gift" of the FIC at Darwin, a few years earlier.Strange, Ian, ''The Falkland Islands'', 1983 Up until the 1970s, Goose Green was the site of a boarding school, run by the state. "Camp" children boarded here, and there were 40 spaces. The boarding school was later transferred to Stanley, although the recent emphasis has been on locally based education. The school itself became an Argentine HQ, and was burnt down. A new (day) school has been built for local children.First World War

 Port Stanley became an important coaling station for the Royal Navy. This led to ships based there being involved in major naval engagements in both the First and Second World Wars.
The strategic significance of the Falkland Islands was confirmed by the second major naval engagement of the First World War.
Port Stanley became an important coaling station for the Royal Navy. This led to ships based there being involved in major naval engagements in both the First and Second World Wars.
The strategic significance of the Falkland Islands was confirmed by the second major naval engagement of the First World War. Admiral
Admiral is one of the highest ranks in many navies. In the Commonwealth nations and the United States, a "full" admiral is equivalent to a "full" general in the army or the air force. Admiral is ranked above vice admiral and below admiral of ...
Graf Maximilian von Spee's East Asia Squadron
The German East Asia Squadron () was an Imperial German Navy cruiser squadron which operated mainly in the Pacific Ocean between the mid-1890s until 1914, when it was destroyed at the Battle of the Falkland Islands. It was based at Germany's Ji ...
called at the islands on its trip from the Pacific Ocean back to Germany, intending to destroy the Royal Navy radio relay station and coaling depot there. Unknown to von Spee, a British squadron, including two battlecruiser
The battlecruiser (also written as battle cruiser or battle-cruiser) was a type of capital ship of the first half of the 20th century. These were similar in displacement, armament and cost to battleships, but differed in form and balance of att ...
s considerably more powerful than his forces, had been sent to hunt down his squadron and happened to be in the harbour coaling. In the one-sided battle which followed, most of von Spee's squadron was sunk. Canopus Hill
Canopus Hill is located on the island of East Falkland near Stanley, the capital city of the Falkland Islands. It is named after , which fired the first shots in the Battle of the Falkland Islands during World War I
World War I or th ...
, south of Stanley, is named after , which had fired the first shot in the battle.
Second World War
TheFalkland Islands Defence Force
The Falkland Islands Defence Force (FIDF) is the locally maintained volunteer defence unit in the Falkland Islands, a British Overseas Territory. The FIDF works alongside the military units supplied by the United Kingdom to ensure the security ...
was called out to man gun positions and signalling posts around Stanley as soon as word was received of Britain's declaration of war on 3 September 1939. Mounted patrols were carried out in the Camp, and coast-watching stations were created around the islands to guard against the approach of enemy ships and the landing of enemy forces. The Falkland Islanders experienced much the same kind of war-time privations and restrictions as the British population, including black-outs, travel restrictions, and rationing.
In December 1939, in the immediate aftermath of the Battle of the River Plate, heavy cruiser , which had been self-refitting in the Falkland Islands at the time of the battle, steamed to join and at the mouth of the River Plate, trapping the . Convinced by British propaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded l ...
and false intelligence that a major naval task force awaited his ship and short of ammunition, Captain Langsdorf of ''Admiral Graf Spee'' chose instead to scuttle the ship rather than face the Royal Navy.
Operation Tabarin, an expedition to the Antarctic, was mounted from the islands during the war. The purpose of the expedition was to assert Britain's claims on the continent, as well as gather scientific data. Operation Tabarin was later replaced by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey, which was later renamed the British Antarctic Survey
The British Antarctic Survey (BAS) is the United Kingdom's national polar research institute. It has a dual purpose, to conduct polar science, enabling better understanding of list of global issues, global issues, and to provide an active prese ...
.
In 1942, in response to the Japanese entry into the war, additional forces were sent to the islands to strengthen their defence against invasion. The largest component of these additional forces was a battalion of the West Yorkshire Regiment
The West Yorkshire Regiment (Prince of Wales's Own) (14th Foot) was an infantry regiment of the British Army. In 1958 it amalgamated with the East Yorkshire Regiment (15th Foot) to form the Prince of Wales's Own Regiment of Yorkshire which was ...
. In 1944, as a result of the reduced threat of invasion from Japan, the West Yorks were replaced by a smaller contingent of the Royal Scots
The Royal Scots (The Royal Regiment), once known as the Royal Regiment of Foot, was the oldest and most senior infantry regiment line infantry, of the line of the British Army, having been raised in 1633 during the reign of Charles I of England ...
.
Over the whole war more than 150 Falkland Islanders out of a population of only 2,300 volunteered for the British armed forces - 6.5% of the entire population - 24 of whom did not return. In July 1944, all volunteers were given the right to be identified by a "Falkland Islands" shoulder-flash. In addition to these contributions to the British war-effort, the Falkland Islands also donated five Supermarine Spitfire
The Supermarine Spitfire is a British single-seat fighter aircraft that was used by the Royal Air Force and other Allies of World War II, Allied countries before, during, and after World War II. It was the only British fighter produced conti ...
s to the British Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
.
Argentine incursions
With the exception of an attempt by PresidentJuan Perón
Juan Domingo Perón (, , ; 8 October 1895 – 1 July 1974) was an Argentine military officer and Statesman (politician), statesman who served as the History of Argentina (1946-1955), 29th president of Argentina from 1946 to Revolución Libertad ...
to buy the Falkland Islands in 1953 which was rejected as inconceivable by the British government, the immediate post-war period was fairly uneventful. However, a series of incidents in the 1960s marked the intensification of Argentine sovereignty claims.
The first of these took place in 1964, when a light plane piloted by Miguel Fitzgerald touched down on the racecourse at Stanley. Leaping from the aircraft, he handed a letter claiming sovereignty to a bemused islander before flying off again. The stunt was timed to coincide with Argentine diplomatic efforts at the UN Decolonisation Committee.
 A more serious incident took place on 28 September 1966 when eighteen young
A more serious incident took place on 28 September 1966 when eighteen young Peronists
Peronism, also known as justicialism, is an Argentine ideology and movement based on the ideas, doctrine and legacy of Juan Perón (1895–1974). It has been an influential movement in 20th- and 21st-century Argentine politics. Since 1946, Pe ...
staged a symbolic invasion of the Islands by hijacking
Hijacking may refer to:
Common usage
Computing and technology
* Bluejacking, the unsolicited transmission of data via Bluetooth
* Brandjacking, the unauthorized use of a company's brand
* Browser hijacking
* Clickjacking (including ''likej ...
an Aerolíneas Argentinas
Aerolíneas Argentinas, formally ''Aerolíneas Argentinas S.A.'', is the state-owned flag carrier of Argentina and the country's largest airline. The airline was created in 1949, from the merger of Aeroposta Argentina (AA), Aviación del Lito ...
airliner and landing it in Stanley; the group called this action Operativo Cóndor. There, they raised seven Argentine flags and took four islanders hostage. The planning had been done during a trip to the islands that one of the leaders had made as a tourist.
The airliner left at from Buenos Aires, bound for Río Gallegos
Rio or Río is the Portuguese and Spanish word for "river". The word also exists in Italian, but is largely obsolete and used in a poetical or literary context to mean "stream".
Rio, RIO or Río may also refer to:
Places United States
* Rio, Fl ...
with 48 passengers on board, including Argentine Rear Admiral José María Guzmán, who was on his way to Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego (, ; Spanish for "Land of Fire", rarely also Fireland in English) is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South America, South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan.
The archipelago consists of the main is ...
, an Argentine territory of which he was governor. Two armed men entered the flight deck and ordered the pilot to change course toward the Falklands. The pilot attempted to land at the racecourse but the plane hit telegraph poles, and the undercarriage sank into the mud. Islanders, assuming that the plane was in trouble, rushed to assist but found themselves taken hostage by the hijackers (included in the group of four was a young police sergeant, Terry Peck, who became a local hero in the Falklands War). Les Gleadell, acting Governor of the Falkland Islands, ordered that the DC-4 be surrounded. He received three of the invaders, who announced that they had as much right as anyone to be there and in reply were firmly told that they should disarm and give up. The result of this meeting was an agreement that seven men, including Peck and Captain Ian Martin, commanding a four-man Royal Marines detachment, should be exchanged for the hostages aboard the aircraft. The 26 passengers were then allowed to disembark and sent to lodge with local families, as the island had no hotel. On being taken past the governor's residence, Guzmán laughingly commented: ''"Mi casa"'' ("my house").
After a bitterly cold night in the aircraft, which contained only brandy, wine, orange juice and a few biscuits, the kidnappers surrendered. They were kept locked up in an annex to St Mary's Church for a week until they were put aboard an Argentine ship, the ''Bahía Buen Suceso,'' which had lingered outside the harbor awaiting conclusion of the affair. The men were tried in Argentina on crimes that included illegal deprivation of freedom, possession of weapons of war, illegal association, piracy, and robbery in the open. The leaders were sentenced to three years in prison and the others to nine months.
On October of the same year a group of Argentine naval special forces conducted covert landings from the submarine ARA ''Santiago del Estero''. The 12-man team, which landed some from Stanley, was led by Juan José Lombardo who later, as Chief of Naval Operations, planned the 1982 invasion of the Falkland Islands
Argentine forces invaded the Falkland Islands on 2 April 1982 in a military operation code-named Operation Rosario (). The invasion served as a catalyst for the subsequent Falklands War. The Argentines mounted amphibious landings and the invas ...
.
 In November 1968, Miguel Fitzgerald was hired by the Argentine press to attempt a reprise of his 1964 landing. Accompanied by one of the 1966 hijackers, he flew to Stanley but on arrival found he could not land at the racecourse due to obstacles placed following the hijacking. The plane was forced to crash land on Eliza Cove Road, but the two occupants were unharmed. The stunt was intended to coincide with the visit of Lord Chalfont to the islands.
The latter incident proved counter-productive to the Argentine sovereignty push, as Lord Chalfont had been talking to a public meeting at the time of the plane's arrival. The islanders made it plain to Lord Chalfont that they rejected a Memorandum of Agreement negotiated between Britain and Argentina that August which stated that Britain was prepared to discuss sovereignty provided the islanders' wishes were respected. This spurred the formation of the Falkland Islands Committee by London barrister Bill Hunter-Christie and others. The Emergency Committee, as it became known, proved to be an effective lobbying organisation, constantly undermining Foreign Office initiatives on sovereignty negotiations. In December 1968, the lobbying effort managed to force the British Government to state that the islanders' wishes would be paramount.
In November 1968, Miguel Fitzgerald was hired by the Argentine press to attempt a reprise of his 1964 landing. Accompanied by one of the 1966 hijackers, he flew to Stanley but on arrival found he could not land at the racecourse due to obstacles placed following the hijacking. The plane was forced to crash land on Eliza Cove Road, but the two occupants were unharmed. The stunt was intended to coincide with the visit of Lord Chalfont to the islands.
The latter incident proved counter-productive to the Argentine sovereignty push, as Lord Chalfont had been talking to a public meeting at the time of the plane's arrival. The islanders made it plain to Lord Chalfont that they rejected a Memorandum of Agreement negotiated between Britain and Argentina that August which stated that Britain was prepared to discuss sovereignty provided the islanders' wishes were respected. This spurred the formation of the Falkland Islands Committee by London barrister Bill Hunter-Christie and others. The Emergency Committee, as it became known, proved to be an effective lobbying organisation, constantly undermining Foreign Office initiatives on sovereignty negotiations. In December 1968, the lobbying effort managed to force the British Government to state that the islanders' wishes would be paramount.
Growing links with Argentina
Partly as the result of diplomatic pressure, economic and political links with Argentina increased in the 1960s and 1970s. These became severed after the end of the Falklands War, but before the war they were not entirely negative, and some islanders sent their children to boarding schools in Argentina. Realising that any talks on the sovereignty issue would be derailed if it did not meet with the islanders' wishes, the British and Argentine Governments enacted a series of measures designed to encourage dependence on Argentina. In 1971, following secret talks between the two Governments (and without consulting the islanders), the communications agreement was signed. The thrust of the agreement was the establishment of direct air and sea links between the islands and Argentina, together with agreements on postal and telephony services. Following the agreement the subsidised shipping link with Montevideo ended, a passenger and cargo ship service to the mainland (that would ameliorate any dependence on Argentina) was promised by the British but never provided. ''Líneas Aéreas del Estado'' (LADE), the airline operated by the Argentine Air Force (''Fuerza Aérea Argentina'' or FAA), began an air link to the islands. Initially this service operatedamphibious aircraft
An amphibious aircraft, or amphibian, is an aircraft that can Takeoff, take off and Landing, land on both solid ground and water. These aircraft are typically Fixed-wing aircraft, fixed-wing, though Amphibious helicopter, amphibious helicopte ...
between Comodoro Rivadavia
Comodoro Rivadavia (), often shortened to Comodoro ( ), is a city in the Patagonian Provinces of Argentina, province of Chubut Province, Chubut in southern Argentina, located on the San Jorge Gulf, an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean, at the foot of th ...
and Stanley using Grumman HU-16 Albatross
The Grumman HU-16 Albatross is a large, twin-radial engined amphibious flying boat that was used by the United States Air Force (USAF), the U.S. Navy (USN), the U.S. Coast Guard (USCG), and the Royal Canadian Air Force primarily as a search and ...
aircraft. The inauguration of the service was commemorated by a series of stamps issued by both the Argentine and Falkland Island postal services. In 1972, a temporary airstrip was constructed by Argentina near Stanley. Britain constructed a small permanent airstrip in 1976 suitable only for short haul flights.
As part of the agreement, islanders had to travel via Argentina and were forced to carry Argentine Identity Cards issued in Buenos Aires. The ''Tarjeta Provisoria'' or "white card" as they were known were hated by the islanders, who felt they were a '' de facto'' Argentine passport
A passport is an official travel document issued by a government that certifies a person's identity and nationality for international travel. A passport allows its bearer to enter and temporarily reside in a foreign country, access local aid ...
, since only islanders were required to use them and not other temporary residents of the islands. Tensions were raised further with the agreement that male Falkland Islanders
Falkland Islanders, also called FalklandersChater, Tony. ''The Falklands''. St. Albans: The Penna Press, 1996. p. 137. and nicknamed Kelpers, are the people of the British Overseas Territory of the Falkland Islands.
Identity
The Islande ...
would not have to undertake conscription into the Argentine Army
The Argentine Army () is the Army, land force branch of the Armed Forces of the Argentine Republic and the senior military service of Argentina. Under the Argentine Constitution, the president of Argentina is the commander-in-chief of the Armed For ...
, since this carried the implication that Falkland Islanders were Argentine citizens.
LADE set up an office in Stanley and mail was routed through Argentina. Medical treatments unavailable in the islands were provided in Argentina and scholarships were made available for study in Buenos Aires, Córdoba and other Argentine cities. Spanish language teachers were provided by Argentina. Foreign Office
Foreign may refer to:
Government
* Foreign policy, how a country interacts with other countries
* Ministry of Foreign Affairs, in many countries
** Foreign Office, a department of the UK government
** Foreign office and foreign minister
* United ...
officials in Stanley were instructed to do everything possible to foster good relations between the Falkland Islands and Argentina.
The islands became more dependent upon Argentina, when the British and Argentine governments agreed that the islands would be supplied with petrol, diesel and oil by YPF
YPF S.A. (, formerly ; English: "Fiscal Oilfields") is a vertically integrated, majority state-owned Argentine energy company, engaged in oil and gas exploration and production, and the transportation, refining, and marketing of gas and pe ...
, the Argentine national oil and gas company.
International Parliamentary Union
The Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU; , UIP) is an international organization of national parliaments. Its primary purpose is to promote democratic governance, accountability, and cooperation among its members; other initiatives include advancing g ...
condemned Britain's "act of international piracy" in establishing a colony in the Falkland Islands. Diplomatic relations between Britain and Argentina were broken but resumed in 1976.
In October 1975, the British Government tasked Lord Shackleton
Edward Arthur Alexander Shackleton, Baron Shackleton (15 July 1911 – 22 September 1994) was a British geographer, Royal Air Force officer and Labour Party politician.
Early life and career
Born in Wandsworth, London, Shackleton was the young ...
(son of the Antarctic explorer Sir Ernest Shackleton
Sir Ernest Henry Shackleton (15 February 1874 – 5 January 1922) was an Anglo-Irish Antarctic explorer who led three British expeditions to the Antarctic. He was one of the principal figures of the period known as the Heroic Age of Antarc ...
) with an economic survey of the Falkland Islands. The Argentine Government reacted furiously and refused permission for Lord Shackleton to travel via Argentina. Later the ship transporting Shackleton to the islands, , was fired upon by the Argentine destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, maneuverable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy, or carrier battle group and defend them against a wide range of general threats. They were conceived i ...
ARA ''Almirante Storni''.
In 1976, after a military junta
A military junta () is a system of government led by a committee of military leaders. The term ''Junta (governing body), junta'' means "meeting" or "committee" and originated in the Junta (Peninsular War), national and local junta organized by t ...
took control of the country, Argentina covertly established a military base on Southern Thule. It was discovered by the British Antarctic Survey ship in 1977. The British protested but restricted their response to a diplomatic protest. Backing up the diplomatic efforts, the British Prime Minister Jim Callaghan sent a naval task force consisting of surface ships and a nuclear submarine
A nuclear submarine is a submarine powered by a nuclear reactor, but not necessarily nuclear-armed.
Nuclear submarines have considerable performance advantages over "conventional" (typically diesel-electric) submarines. Nuclear propulsion ...
. Nevertheless, Argentine aircraft and warships harassed ships fishing in Falkland waters.
Lord Shackleton's report was delivered in 1977 and documented the economic stagnation in the islands. It nevertheless concluded that the islands made a net contribution to the British economy and had economic potential for development. Recommendations included oil exploration, exploitation of the fisheries, extension of the Stanley runway, the creation of a development agency, the expansion of the road network, expansion of the facilities at Stanley harbour and the breakdown of absentee landlord owned farms into family units. The report was largely ignored at the time, as it was felt that acting upon it would sour relations with Argentina. A reprise of the report by Lord Shackleton in 1982 following the Falklands War became the blueprint for subsequent economic development of the islands.
Falklands War
Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
invaded the islands on 2 April 1982, using special forces, which landed at Mullet Creek
Mullet Creek is a small river in East Falkland. It is not a major watercourse, but is best known for its part in the Falklands War On April 2, 1982, Argentinian marines led by Guillermo Sanchez-Sabarots, landed his squadron of special forces at ...
and advanced on Government House in Stanley, with a secondary force coming in from Yorke Bay. They encountered little opposition, there being only a small force of fifty-seven British marines and eleven sailors, in addition to the Falkland Islands Defence Force (who were later sent to Fox Bay). There was only one Argentine fatality. The event garnered international attention at a level which the islands had never experienced before, and made them a household name in the UK.
For a brief period, the Falkland Islands found themselves under Argentine control. This included Spanish-language signage, and attempts to make the islanders drive on the right
Drive or The Drive may refer to:
Motoring
* Driving, the act of controlling a vehicle
* Road trip, a journey on roads
Roadways
Roadways called "drives" may include:
* Driveway, a private road for local access to structures, abbreviated "drive"
* ...
(although few roads in the Falklands at the time actually had two lanes). In many parts of the Camp
Camp may refer to:
Areas of confinement, imprisonment, or for execution
* Concentration camp, an internment camp for political prisoners or politically targeted demographics, such as members of national or minority ethnic groups
* Extermination ...
, such as Goose Green and Pebble Island
Pebble Island is one of the Falkland Islands, situated north of West Falkland. It is possibly named after the peculiarly spherical pebbles found at its western tip.
Description
The island, the fifth largest in the Falklands archipelago, stretch ...
, the islanders found themselves under house arrest
House arrest (also called home confinement, or nowadays electronic monitoring) is a legal measure where a person is required to remain at their residence under supervision, typically as an alternative to imprisonment. The person is confined b ...
.
The British responded with an expeditionary force that landed seven weeks later and, after fierce fighting, forced the Argentine garrison to surrender on 14 June 1982. The war proved to be an anomaly in a number of different respects, not least that it proved that small arms still had a role to play. It also had major consequences for the military junta, which was toppled soon afterwards.
Margaret Thatcher's general political legacy remains controversial and divisive within the UK and within the context of the Falklands her government's withdrawal of HMS ''Endurance'' is a stated contributing factor to the causes of the conflict because it gave the wrong signals about the UK attitude towards maintaining its possession. However, within the Falklands, she is considered a heroine because of the determination of her response to the Argentine invasion. The islanders celebrate Margaret Thatcher Day on 10 January; and Thatcher Drive in Stanley is named after her.
Post-war
Following the war, Britain focused on improving its facilities on the islands. It increased its military presence significantly, building a large base at RAF Mount Pleasant and its port at Mare Harbour. It also invested heavily in improving facilities in Stanley and transport and infrastructure around the islands, tarmacking the Stanley–Mount Pleasant road and many roads within Stanley. The population has risen due to the growth of Stanley, but has declined in ''Camp'' (the countryside). Since November 2008, a regular ferry service has linked East and West Falkland, carrying cars, passengers and cargo serviced by MV ''Concordia Bay'', a twin-screw shallow draught landing craft. A major change to the governance of the Falkland Islands was introduced by the 1985 constitution. The Falkland Islands Government (FIG) became a parliamentary representative dependency, whose members are democratically elected; while the governor, as head of government and representative of the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, monarch, is purely a figurehead without Executive (government), executive powers. Effectively, the Falkland Islands are self-governing, with the exception of foreign policy. (The FIG represents itself at the United Nations Special Committee on Decolonisation, as the British Government no longer attends.) Links with Argentina were severed in the post-war period, and laws introduced forbidding Argentine citizens from buying land. An alternative trading partner was found in Chile, with links developing over the years, including flights to Punta Arenas, Chile, Punta Arenas (in the far south of Patagonian Chile, near Tierra del Fuego). In recent years, Argentines have been allowed to visit the islands again, often to visit the military cemeteries where their friends and loved ones are buried.Increased British military presence and new bases
After the war, the British still faced potential future aggression, so an aircraft carrier was kept on station guarding the islands with its Squadron (aviation), squadron of Sea Harriers, while the local airfield was prepared for jet aircraft. took guard duty first, whilst went north to change a gearbox. ''Invincible'' then returned to relieve ''Hermes'', which urgently needed to have its boilers cleaned. ''Invincible'' remained until was rushed south (being commissioned during the journey). Once the Port Stanley runway was ready for jets, several RAF F-4 Phantoms were stationed there, relieving ''Illustrious.'' The islands lacked barracks for a permanent garrison, so the Ministry of defence chartered two former car ferries as barracks ships: from the Union Company of New Zealand and from Sealink in Britain. ''Rangatira'' arrived in Port Stanley on 11 July 1982 and stayed until 26 September 1983. Later, the British government decided to construct a new RAF base as the centrepiece of plans to strengthen the island defences and deter any further attempts to take the Falklands by force. This was a massive undertaking – including construction of the world's longest corridor, linking the barracks, messes, recreation and welfare areas of the base. The base is occasionally referred to by residents as "the Death Star" because of its vast size and sometimes confusing layout.Attempts at diversifying the economy
Conservation
In line with increasing global interest in Environmentalism, environmental issues, some nature reserves have been established around the islands, although there are no national parks. In 1990, the Clifton family who owned Sea Lion Island sold it to the Falkland Island Development Company. They had planted 60,000 stands of tussac grass, considered important because on the main islands much tussac has been depredated by grazing. A similar trend may be seen on Bleaker Island, where the farm "went organic" in 1999. Also in the 1990s, Steeple Jason Island and Grand Jason Island were bought by New York City, New York philanthropist Michael Steinhardt, who later donated them to the Bronx Zoo-based Wildlife Conservation Society. He also gave them US dollar, US$425,000 to build a conservation station named after himself and his wife Judy.See also
* History of South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands * Origins of Falkland Islanders *Puerto Soledad
Puerto Soledad (''Puerto de Nuestra Señora de la Soledad'', ) was a Spanish military outpost and penal colony on the Falkland Islands, situated at an inner cove of Berkeley Sound (,Dom Pernety, Antoine-Joseph. ''Journal historique d'un voyage ...
* Sovereignty of the Falkland Islands
* ''The Falkland Islands Journal''
* Timeline of the history of the Falkland Islands
References
External links
1987 American report
by Richard D. Chenette, Lieutenant Commander, USN, laying out the history and background of the disputed claims
*[https://web.archive.org/web/20071006063014/http://www.falklands.info/history/timeline.html Timeline of Falklands Island history] {{DEFAULTSORT:History of the Falkland Islands History of the Falkland Islands, British colonization of the Americas French colonization of the Americas Spanish colonization of the Americas Falkland Islands in World War II History of South America, Falkland Islands