Scorpius IAU on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Scorpius is a
 Due to its location straddling the
Due to its location straddling the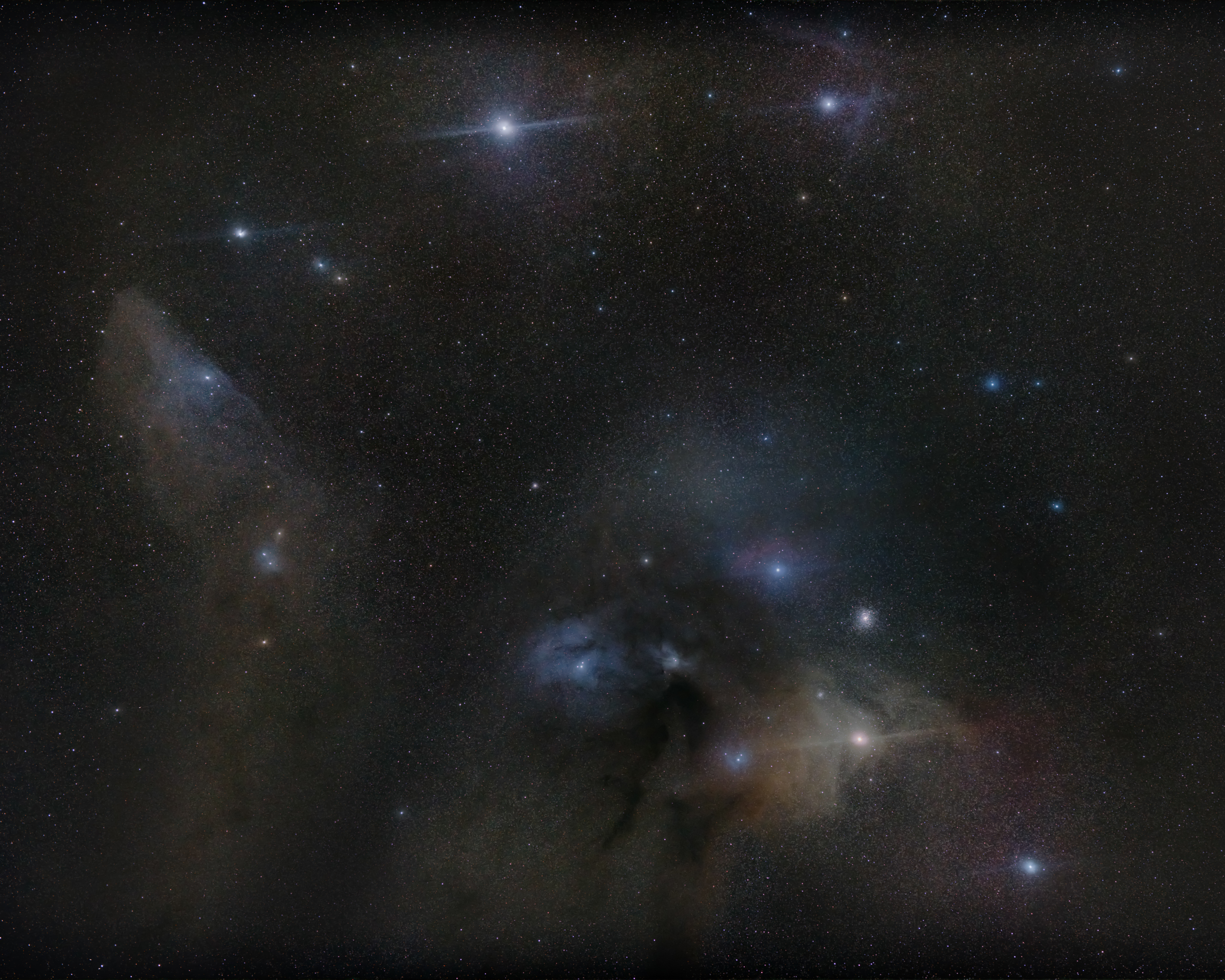 
The Deep Photographic Guide to the Constellations: Scorpius
Warburg Institute Iconographic Database (medieval and early modern images of Scorpius)
{{Sky, 16, 53, 15, -, 30, 44, 12, 10 Southern constellations Constellations listed by Ptolemy Mythological arthropods
zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north and south celestial latitude of the ecliptic – the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. Within this zodiac ...
constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The first constellati ...
located in the Southern celestial hemisphere
The southern celestial hemisphere, also called the Southern Sky, is the Southern Hemisphere, southern half of the celestial sphere; that is, it lies south of the celestial equator. This arbitrary sphere, on which seemingly fixed stars form cons ...
, where it sits near the center of the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
, between Libra
Libra generally refers to:
* Libra (constellation), a constellation
* Libra (astrology), an astrological sign based on the star constellation
Libra may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Libra'' (novel), a 1988 novel by Don DeLillo
Musi ...
to the west and Sagittarius to the east. Scorpius is an ancient constellation whose recognition predates Greek culture; it is one of the 48 constellations identified by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
in the second century.
Notable features
Stars
Scorpius contains many bright stars, includingAntares
Antares is the brightest star in the constellation of Scorpius. It has the Bayer designation α Scorpii, which is Latinisation of names, Latinised to Alpha Scorpii. Often referred to as "the heart of the scorpion", Antares is flanked by ...
(α Sco), "rival of Mars," so named because of its distinct reddish hue; β1 Sco (Graffias or Acrab), a triple star; δ Sco (Dschubba
Delta Scorpii ( Latinised from δ Scorpii, abbreviated Delta Sco, δ Sco) is a binary star (the presence of a third star in the system is being debated) in the constellation of Scorpius. The primary star is named Dschubba .
Observation
...
, "the forehead"); θ Sco (Sargas
Theta Scorpii (θ Scorpii, abbreviated Theta Sco, θ Sco) is a binary star in the southern zodiac constellation of Scorpius. The apparent visual magnitude of this star is +1.87, making it readily visible to the naked eye and one of the b ...
, of Sumerian origin); ν Sco (Jabbah); ξ Sco; π Sco (Fang); σ Sco (Alniyat); and τ Sco (Paikauhale).
Marking the tip of the scorpion's curved tail are λ Sco (Shaula
Lambda Scorpii is a triple star system and the second-brightest object in the constellation of Scorpius. It is formally named Shaula; ''Lambda Scorpii'' is its Bayer designation, which is Latinised from λ Scorpii and abbreviated Lam ...
) and υ Sco (Lesath), whose names both mean "sting." Given their proximity to one another, λ Sco and υ Sco are sometimes referred to as the Cat's Eyes.
The constellation's bright stars form a pattern like a longshoreman's hook. Most of them are massive members of the nearest OB association: Scorpius–Centaurus.
The star δ Sco, after having been a stable 2.3 magnitude
Magnitude may refer to:
Mathematics
*Euclidean vector, a quantity defined by both its magnitude and its direction
*Magnitude (mathematics), the relative size of an object
*Norm (mathematics), a term for the size or length of a vector
*Order of ...
star, flared in July 2000 to 1.9 in a matter of weeks. It has since become a variable star fluctuating between 2.0 and 1.6. This means that at its brightest it is the second brightest star in Scorpius.

U Scorpii
U Scorpii (''U Sco'') is a recurrent nova system, one of 10 known recurring novae in the Milky Way galaxy. Located near the northern edge of the constellation Scorpius it normally has a magnitude of 18, but reaches a magnitude of about 8 ...
is the fastest known nova
A nova ( novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. All observed novae involve white ...
, with a period of about 10 years.
AH Scorpii is a red supergiant
Red supergiants (RSGs) are stars with a supergiant luminosity class ( Yerkes class I) and a stellar classification K or M. They are the largest stars in the universe in terms of volume, although they are not the most massive or luminous. Betelg ...
star and one of the largest known stars, being 1,400 times larger than the Sun. It is also a luminous star, 340,000 times brighter than the Sun, although it is too faint to be seen by the naked eye, with a brightness varying from 6.5 to 9.6.
The close pair of stars ω1 Scorpii and ω² Scorpii are an optical double
In observational astronomy, a double star or visual double is a pair of stars that appear close to each other as viewed from Earth, especially with the aid of optical telescopes.
This occurs because the pair either forms a binary star (i.e. a ...
, which can be resolved by the unaided eye. One is a yellow giant, while the other is a blue B-type star in the Scorpius-Centaurus Association.
The star once designated γ Sco (despite being well within the boundaries of Libra) is today known as σ Lib. Moreover, the entire constellation of Libra
Libra generally refers to:
* Libra (constellation), a constellation
* Libra (astrology), an astrological sign based on the star constellation
Libra may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Libra'' (novel), a 1988 novel by Don DeLillo
Musi ...
was considered to be claws of Scorpius (''Chelae Scorpionis'') in Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
times, with a set of scales held aloft by Astraea
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Astraea (; ), also spelled Astrea or Astria, is a daughter of Astraeus and Eos. She is the virgin goddess of justice, innocence, purity, and precision. She is closely associated with the Greek goddess of ...
(represented by adjacent Virgo
Virgo may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Virgo (film), a 1970 Egyptian film
* Virgo (character), several Marvel Comics characters
* Virgo Asmita, a character in the manga ''Saint Seiya: The Lost Canvas''
* ''Virgo'' (album), by Virgo Four, ...
) being formed from these westernmost stars during later Greek times. The division into Libra was formalised during Ancient Greek or Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
times.
Deep-sky objects
 Due to its location straddling the
Due to its location straddling the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
, this constellation contains many deep-sky object
A deep-sky object (DSO) is any astronomical object that is not an individual star or Solar System object (such as Sun, Moon, planet, comet, etc.). The classification is used for the most part by amateur astronomers to denote visually observed fa ...
s such as the open cluster
An open cluster is a type of star cluster made of tens to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way galaxy, and ...
s Messier 6 (the Butterfly Cluster) and Messier 7
Messier 7 or M7, also designated NGC 6475 and sometimes known as the Ptolemy Cluster, is an open cluster of stars in the constellation of Scorpius. The cluster is easily detectable with the naked eye, close to the "stinger" of Scorpius. With a d ...
(the Ptolemy Cluster
Messier 7 or M7, also designated NGC 6475 and sometimes known as the Ptolemy Cluster, is an open cluster of stars in the constellation of Scorpius. The cluster is easily detectable with the naked eye, close to the "stinger" of Scorpius. With a ...
), NGC 6231 (by ζ² Sco), and the globular cluster
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars that is bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards its center. It can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of member stars, all orbiting ...
s Messier 4
Messier 4 or M4 (also known as NGC 6121 or the Spider Globular Cluster) is a globular cluster in the constellation of Scorpius. It was discovered by Philippe Loys de Chéseaux in 1745 and catalogued by Charles Messier in 1764. It was the first g ...
and Messier 80
Messier 80 (also known as M80 or NGC 6093) is a globular cluster in the constellation Scorpius. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1781, being one of his first discoveries.
This star cluster is, as to its angle from the Solar System, midwa ...
.
Messier 80
Messier 80 (also known as M80 or NGC 6093) is a globular cluster in the constellation Scorpius. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1781, being one of his first discoveries.
This star cluster is, as to its angle from the Solar System, midwa ...
(NGC 6093) is a globular cluster of magnitude 7.3, 33,000 light-years from Earth. It is a compact Shapley class II cluster; the classification indicates that it is highly concentrated and dense at its nucleus. M80 was discovered in 1781 by Charles Messier
Charles Messier (; 26 June 1730 – 12 April 1817) was a French astronomer. He published an astronomical catalogue consisting of 110 nebulae and star clusters, which came to be known as the ''Messier objects'', referred to with th ...
. It was the site of a rare discovery in 1860 when Arthur von Auwers discovered the nova T Scorpii.
NGC 6302
NGC 6302 (also known as the Bug Nebula, Butterfly Nebula, or Caldwell 69) is a bipolar planetary nebula in the constellation Scorpius. The structure in the nebula is among the most complex ever seen in planetary nebulae. The spectrum of Butte ...
, also called the Bug Nebula, is a bipolar planetary nebula. NGC 6334, also known as the Cat's Paw Nebula, is an emission nebula and star-forming region.

Mythology
InGreek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories conc ...
, several myths associated with Scorpius attribute it to Orion. According to one version, Orion boasted to the goddess Artemis
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Artemis (; ) is the goddess of the hunting, hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, transitions, nature, vegetation, childbirth, Kourotrophos, care of children, and chastity. In later tim ...
and her mother, Leto
In ancient Greek mythology and Ancient Greek religion, religion, Leto (; ) is a childhood goddess, the daughter of the Titans Coeus and Phoebe (Titaness), Phoebe, the sister of Asteria, and the mother of Apollo and Artemis.Hesiod, ''Theogony' ...
, that he would kill every animal on Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
. Artemis and Leto sent a scorpion to kill Orion. Their battle caught the attention of Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.
Zeus is the child ...
, who raised both combatants to the sky to serve as a reminder for mortals to curb their excessive pride. In another version of the myth, Artemis' twin brother, Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
, was the one who sent the scorpion to kill Orion after the hunter earned the goddess' favor by admitting she was better than him. After Zeus raised Orion and the scorpion to the sky, the former hunts every winter but flees every summer when the scorpion comes. In both versions, Artemis asked Zeus to raise Orion.
In a Greek myth without Orion, the celestial scorpion encountered Phaethon
Phaethon (; , ), also spelled Phaëthon, is the son of the Oceanids, Oceanid Clymene (mother of Phaethon), Clymene and the solar deity, sun god Helios in Greek mythology.
According to most authors, Phaethon is the son of Helios who, out of a de ...
while he was driving his father Helios
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Helios (; ; Homeric Greek: ) is the god who personification, personifies the Sun. His name is also Latinized as Helius, and he is often given the epithets Hyperion ("the one above") an ...
' Sun Chariot.Scorpio - The Legend and MythOrigins
The Babylonians called this constellation MUL.GIR.TAB - the 'Scorpion'; the signs can be literally read as 'the (creature with) a burning sting'. In some old descriptions the constellation ofLibra
Libra generally refers to:
* Libra (constellation), a constellation
* Libra (astrology), an astrological sign based on the star constellation
Libra may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Libra'' (novel), a 1988 novel by Don DeLillo
Musi ...
is treated as the Scorpion's claws. Libra was known as the Claws of the Scorpion in Babylonian (''zibānītu'' (compare Arabic ''zubānā'')) and in Greek (χηλαι).
Astrology
The Westernastrological sign
In Western astrology, astrological signs are the twelve 30-degree sectors that make up ecliptic, Earth's 360-degree orbit around the Sun. The signs enumerate from the first day of spring, known as the First Point of Aries, which is the Equinox (c ...
Scorpio differs from the astronomical constellation. Astronomically, the Sun is in Scorpius's IAU boundaries for just six days, from November 23 to November 28. Much of the difference is due to the constellation Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus () is a large constellation straddling the celestial equator. Its name comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping a snake. The serpent is represented by the constellati ...
, which is used by few astrologers. Scorpius corresponds to the Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
nakshatras Anuradha, Jyeshtha Jyeshtha may refer to:
* Jyeshtha (month), month of the Hindu calendar
* Jyestha (goddess), Hindu goddess of adversity and misfortune
* Jyeshtha (nakshatra), the 18th nakshatra (lunar mansion) in Hindu astronomy and Vedic astrology
See also
* Jye� ...
, and Mula.
Culture
*The Javanese people of Indonesia call this constellation ''Banyakangrem'' ("the brooded swan") or ''Kalapa Doyong'' ("leaning coconut tree") due to the shape similarity. *In Hawaii, Scorpius is known as the demigodMaui
Maui (; Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ) is the second largest island in the Hawaiian archipelago, at 727.2 square miles (1,883 km2). It is the List of islands of the United States by area, 17th-largest in the United States. Maui is one of ...
's Fishhook or ''Ka Makau Nui o Māui'' (meaning ''the Big Fishhook of Māui'') and the name of the fishhook was '' Manaiakalani''.
*Scorpius was divided into two asterisms which were used by Bugis
The Bugis people, also known as Buginese, are an Austronesian ethnic groupthe most numerous of the three major linguistic and ethnic groups of South Sulawesi (the others being Makassarese and Torajan), in the south-western province of Sula ...
sailors for navigation. The northern part of Scorpius ( α, β, γ or σ Lib, δ, ε, ζ, μ, σ and τ Scorpii) was called ''bintoéng lambarué'', meaning "skate stars". The southern part of Scorpius ( η, θ, ι, κ, λ and ν Scorpii) was called ''bintoéng balé mangngiwéng'', meaning "shark stars".
See also
* Scorpius (Chinese astronomy)References
* * Ian Ridpath and Wil Tirion (2007). ''Stars and Planets Guide'', Collins, London. . Princeton University Press, Princeton. .External links
The Deep Photographic Guide to the Constellations: Scorpius
Warburg Institute Iconographic Database (medieval and early modern images of Scorpius)
{{Sky, 16, 53, 15, -, 30, 44, 12, 10 Southern constellations Constellations listed by Ptolemy Mythological arthropods