scaphoid fracture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A scaphoid fracture is a break of the
 People with scaphoid fractures generally have snuffbox tenderness.
Focal tenderness is usually present in one of three places: 1) volar prominence at the distal wrist for distal pole fractures; 2) anatomic snuff box for waist or midbody fractures; 3) distal to Lister's tubercle for proximal pole fractures.
People with scaphoid fractures generally have snuffbox tenderness.
Focal tenderness is usually present in one of three places: 1) volar prominence at the distal wrist for distal pole fractures; 2) anatomic snuff box for waist or midbody fractures; 3) distal to Lister's tubercle for proximal pole fractures.
 '' Avascular necrosis'' (AVN) is one complication of scaphoid fracture. Since the scaphoid receives its arterial supply in a retrograde fashion (i.e. from distal to proximal pole), the part proximal to the fracture is usually affected.
Risk of AVN depends on the location of the fracture.
* Fractures in the proximal third have a high incidence of AVN (~30%)
* Waist fractures in the middle third is the most frequent fracture site and has moderate risk of AVN.
* Fractures in the distal third are rarely complicated by AVN.
Non union can also occur from undiagnosed or undertreated scaphoid fractures. Arterial flow to the scaphoid enters via the distal pole and travels to the proximal pole. This blood supply is tenuous, increasing the risk of nonunion, particularly with fractures at the wrist and proximal end. If not treated correctly non-union of the scaphoid fracture can lead to wrist osteoarthritis.
Symptoms may include aching in the wrist, decreased range of motion of the wrist, and pain during activities such as lifting or gripping. If x-ray results show arthritis due to an old break, the treatment plan will first focus on treating the arthritis through anti-inflammatory medications and wearing a splint when an individual feels pain in the wrist. If these treatments do not help the symptoms of arthritis, steroid injections to the wrist may help alleviate pain. Should these treatments not work, surgery may be required.
'' Avascular necrosis'' (AVN) is one complication of scaphoid fracture. Since the scaphoid receives its arterial supply in a retrograde fashion (i.e. from distal to proximal pole), the part proximal to the fracture is usually affected.
Risk of AVN depends on the location of the fracture.
* Fractures in the proximal third have a high incidence of AVN (~30%)
* Waist fractures in the middle third is the most frequent fracture site and has moderate risk of AVN.
* Fractures in the distal third are rarely complicated by AVN.
Non union can also occur from undiagnosed or undertreated scaphoid fractures. Arterial flow to the scaphoid enters via the distal pole and travels to the proximal pole. This blood supply is tenuous, increasing the risk of nonunion, particularly with fractures at the wrist and proximal end. If not treated correctly non-union of the scaphoid fracture can lead to wrist osteoarthritis.
Symptoms may include aching in the wrist, decreased range of motion of the wrist, and pain during activities such as lifting or gripping. If x-ray results show arthritis due to an old break, the treatment plan will first focus on treating the arthritis through anti-inflammatory medications and wearing a splint when an individual feels pain in the wrist. If these treatments do not help the symptoms of arthritis, steroid injections to the wrist may help alleviate pain. Should these treatments not work, surgery may be required.
 Fractures of scaphoid can occur either with direct axial compression or with hyperextension of the wrist, such as a fall on the palm on an outstretched hand. Using the Herbert classification system, there are three main types of scaphoid fractures. 10%-20% of fractures are at the proximal pole, 60%-80% are at the waist (middle), and the remainder occur at the distal pole.
Fractures of scaphoid can occur either with direct axial compression or with hyperextension of the wrist, such as a fall on the palm on an outstretched hand. Using the Herbert classification system, there are three main types of scaphoid fractures. 10%-20% of fractures are at the proximal pole, 60%-80% are at the waist (middle), and the remainder occur at the distal pole.
 Scaphoid fractures are often diagnosed using plain radiographs and multiple views are obtained as standard. However, not all fractures are apparent initially. In 1/4 of cases, the clinical examination suggests a fracture, but the X-ray does not show it, even though there is indeed a fracture. Therefore, people with tenderness over the scaphoid (those who exhibit pain to pressure in the anatomic '' snuff box'' ) are often splinted in a thumb spica for 7–10 days at which point a second set of X-rays is taken. If a minimally displaced fracture was present initially, healing will now be apparent. Even then a fracture may not be apparent. A
Scaphoid fractures are often diagnosed using plain radiographs and multiple views are obtained as standard. However, not all fractures are apparent initially. In 1/4 of cases, the clinical examination suggests a fracture, but the X-ray does not show it, even though there is indeed a fracture. Therefore, people with tenderness over the scaphoid (those who exhibit pain to pressure in the anatomic '' snuff box'' ) are often splinted in a thumb spica for 7–10 days at which point a second set of X-rays is taken. If a minimally displaced fracture was present initially, healing will now be apparent. Even then a fracture may not be apparent. A
File:ScaphoidFrac2Mark.png, A subtle scaphoid fracture
File:ScaphoidFracDedMark.png, A more obvious scaphoid fracture on a scaphoid view X ray
File:Scaphoid fracture with a radiolucent line after 12 days.jpg, Radiolucency around a 12 days old scaphoid fracture that was initially barely visible.
AAFP: Diagnosis and Management of Scaphoid Fractures
Wheeless: Scaphoid fracture
{{Authority control Bone fractures Injuries of wrist and hand Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
scaphoid bone
The scaphoid bone is one of the carpal bones of the wrist. It is situated between the hand and forearm on the thumb side of the wrist (also called the lateral or radial side). It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. The scaphoid b ...
in the wrist
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal ...
. Symptoms generally includes pain at the base of the thumb which is worse with use of the hand. The anatomic snuffbox is generally tender and swelling may occur. Complications may include nonunion of the fracture, avascular necrosis of the proximal part of the bone, and arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of ...
.
Scaphoid fractures are most commonly caused by a fall on an outstretched hand. Diagnosis is generally based on a combination of clinical examination and medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to revea ...
. Some fractures may not be visible on plain X-rays
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
. In such cases the affected area may be immobilised in a splint or cast and reviewed with repeat X-rays in two weeks, or alternatively an MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
or bone scan
A bone scan or bone scintigraphy is a nuclear medicine imaging technique used to help diagnose and assess different bone diseases. These include cancer of the bone or metastasis, location of bone inflammation and fractures (that may not be vis ...
may be performed.
The fracture may be preventable by using wrist guards during certain activities. In those in whom the fracture remains well aligned a cast
Cast may refer to:
Music
* Cast (band), an English alternative rock band
* Cast (Mexican band), a progressive Mexican rock band
* The Cast, a Scottish musical duo: Mairi Campbell and Dave Francis
* ''Cast'', a 2012 album by Trespassers William ...
is generally sufficient. If the fracture is displaced then surgery is generally recommended. Healing may take up to six months.
It is the most commonly fractured carpal bone. Males are affected more often than females.
Signs and symptoms
 People with scaphoid fractures generally have snuffbox tenderness.
Focal tenderness is usually present in one of three places: 1) volar prominence at the distal wrist for distal pole fractures; 2) anatomic snuff box for waist or midbody fractures; 3) distal to Lister's tubercle for proximal pole fractures.
People with scaphoid fractures generally have snuffbox tenderness.
Focal tenderness is usually present in one of three places: 1) volar prominence at the distal wrist for distal pole fractures; 2) anatomic snuff box for waist or midbody fractures; 3) distal to Lister's tubercle for proximal pole fractures.
Complications

 '' Avascular necrosis'' (AVN) is one complication of scaphoid fracture. Since the scaphoid receives its arterial supply in a retrograde fashion (i.e. from distal to proximal pole), the part proximal to the fracture is usually affected.
Risk of AVN depends on the location of the fracture.
* Fractures in the proximal third have a high incidence of AVN (~30%)
* Waist fractures in the middle third is the most frequent fracture site and has moderate risk of AVN.
* Fractures in the distal third are rarely complicated by AVN.
Non union can also occur from undiagnosed or undertreated scaphoid fractures. Arterial flow to the scaphoid enters via the distal pole and travels to the proximal pole. This blood supply is tenuous, increasing the risk of nonunion, particularly with fractures at the wrist and proximal end. If not treated correctly non-union of the scaphoid fracture can lead to wrist osteoarthritis.
Symptoms may include aching in the wrist, decreased range of motion of the wrist, and pain during activities such as lifting or gripping. If x-ray results show arthritis due to an old break, the treatment plan will first focus on treating the arthritis through anti-inflammatory medications and wearing a splint when an individual feels pain in the wrist. If these treatments do not help the symptoms of arthritis, steroid injections to the wrist may help alleviate pain. Should these treatments not work, surgery may be required.
'' Avascular necrosis'' (AVN) is one complication of scaphoid fracture. Since the scaphoid receives its arterial supply in a retrograde fashion (i.e. from distal to proximal pole), the part proximal to the fracture is usually affected.
Risk of AVN depends on the location of the fracture.
* Fractures in the proximal third have a high incidence of AVN (~30%)
* Waist fractures in the middle third is the most frequent fracture site and has moderate risk of AVN.
* Fractures in the distal third are rarely complicated by AVN.
Non union can also occur from undiagnosed or undertreated scaphoid fractures. Arterial flow to the scaphoid enters via the distal pole and travels to the proximal pole. This blood supply is tenuous, increasing the risk of nonunion, particularly with fractures at the wrist and proximal end. If not treated correctly non-union of the scaphoid fracture can lead to wrist osteoarthritis.
Symptoms may include aching in the wrist, decreased range of motion of the wrist, and pain during activities such as lifting or gripping. If x-ray results show arthritis due to an old break, the treatment plan will first focus on treating the arthritis through anti-inflammatory medications and wearing a splint when an individual feels pain in the wrist. If these treatments do not help the symptoms of arthritis, steroid injections to the wrist may help alleviate pain. Should these treatments not work, surgery may be required.
Mechanism
 Fractures of scaphoid can occur either with direct axial compression or with hyperextension of the wrist, such as a fall on the palm on an outstretched hand. Using the Herbert classification system, there are three main types of scaphoid fractures. 10%-20% of fractures are at the proximal pole, 60%-80% are at the waist (middle), and the remainder occur at the distal pole.
Fractures of scaphoid can occur either with direct axial compression or with hyperextension of the wrist, such as a fall on the palm on an outstretched hand. Using the Herbert classification system, there are three main types of scaphoid fractures. 10%-20% of fractures are at the proximal pole, 60%-80% are at the waist (middle), and the remainder occur at the distal pole.
Diagnosis
 Scaphoid fractures are often diagnosed using plain radiographs and multiple views are obtained as standard. However, not all fractures are apparent initially. In 1/4 of cases, the clinical examination suggests a fracture, but the X-ray does not show it, even though there is indeed a fracture. Therefore, people with tenderness over the scaphoid (those who exhibit pain to pressure in the anatomic '' snuff box'' ) are often splinted in a thumb spica for 7–10 days at which point a second set of X-rays is taken. If a minimally displaced fracture was present initially, healing will now be apparent. Even then a fracture may not be apparent. A
Scaphoid fractures are often diagnosed using plain radiographs and multiple views are obtained as standard. However, not all fractures are apparent initially. In 1/4 of cases, the clinical examination suggests a fracture, but the X-ray does not show it, even though there is indeed a fracture. Therefore, people with tenderness over the scaphoid (those who exhibit pain to pressure in the anatomic '' snuff box'' ) are often splinted in a thumb spica for 7–10 days at which point a second set of X-rays is taken. If a minimally displaced fracture was present initially, healing will now be apparent. Even then a fracture may not be apparent. A CT Scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
can then be used to evaluate the scaphoid with greater resolution. The use of MRI, if available, is preferred over CT and can give one an immediate diagnosis. Bone scintigraphy is also an effective method for diagnosis fracture which do not appear on Xray.Treatment
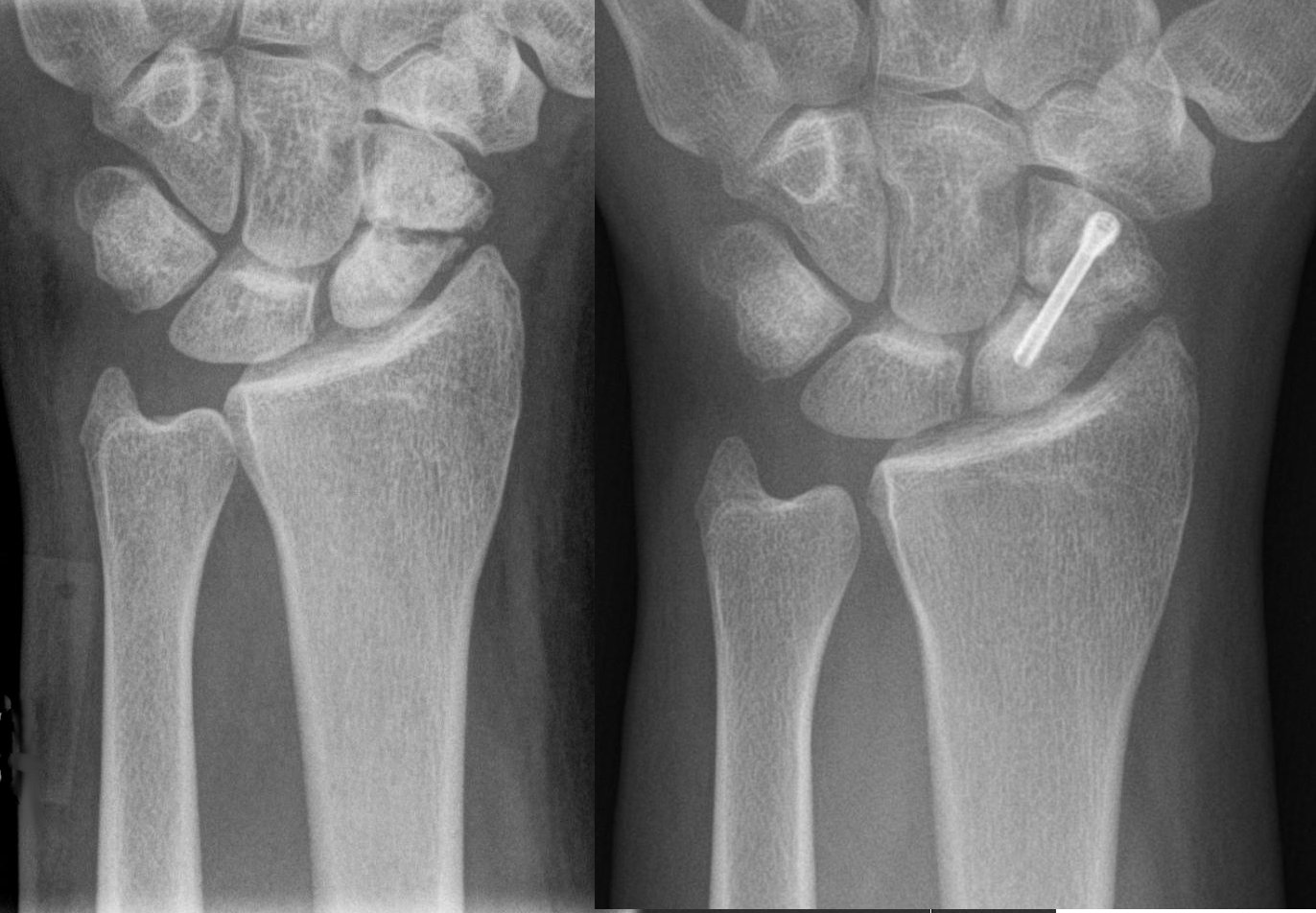
Treatment of scaphoid fractures is guided by the location in the bone of the fracture (proximal, waist, distal), displacement (or instability) of the fracture, and patient tolerance for cast immobilization. For non and minimally displaced fractures (up to 2mm) of the scaphoid waist, cast immobilisation (with surgical fixation for non-united fractures at 6 to 12 weeks) is as effective as immediate surgery fixation and results in less complications." The choice of short arm, short arm thumb spica or long arm cast is debated in the medical literature and no clear consensus or proof of the benefit of one type of casting or another has been shown; although it is generally accepted to use a short arm or short arm thumb spica for non displaced fractures. Fractures that are more proximal take longer to heal. It is expected the distal third will heal in 6 to 8 weeks, the middle third will take 8–12 weeks, and the proximal third will take 12–24 weeks. The scaphoid receives its blood supply primarily from lateral and distal branches of the radial artery. Blood flows from the top/distal end of the bone in a retrograde fashion down to the proximal pole; if this blood flow is disrupted by a fracture, the bone may not heal. Surgery is necessary at this point to mechanically mend the bone together. Percutaneous screw fixation is recommended over an open surgical approach when it is possible to achieve acceptable bone alignment closed as minimal incisions can preserves the palmar ligament complex and local vasculature, and help avoid soft tissue complications. This surgery includes screwing the scaphoid bone back together at the most perpendicular angle possible to promote quicker and stronger healing of the bone. Internal fixation can be done dorsally with a percutaneous incision and arthroscopic assistance or via a minimal open dorsal approach, or via a volar approach in which case slight excavation of the edge of the trapezium bone may be necessary to reach the scaphoid as 80% of this bone is covered with articular cartilage, which makes it difficult to gain access to the scaphoid.Prognosis
A non-union (pseudarthrosis
Nonunion is permanent failure of healing following a broken bone unless intervention (such as surgery) is performed. A fracture with nonunion generally forms a structural resemblance to a fibrous joint, and is therefore often called a "false j ...
) can occur in 2 to 5% of cases.
In the aftermath, 90% of non-operated individuals return to sports, with 88% reaching their previous level. Among those who underwent surgery, the rate of returning to sports is 98%, and 96% return to their previous level. The average time observed for resuming sports is 14 weeks for non-operated individuals and 7 weeks for those who had surgery.
Epidemiology
Fractures of the scaphoid are common in young males. They are less common in children and older adults because the distal radius is weaker contributor to the wrist and more likely to fracture in these age groups. Scaphoid fractures account for 50%-80% of carpal injuries.Terminology
These are also called navicular fractures (the scaphoid also being called the carpal navicular), although this can be confused with thenavicular bone
The navicular bone is a small bone found in the feet of most mammals.
Human anatomy
The navicular bone in humans is one of the tarsus (skeleton), tarsal bones, found in the foot. Its name derives from the human bone's resemblance to a small ...
in the foot.
References
External links
AAFP: Diagnosis and Management of Scaphoid Fractures
Wheeless: Scaphoid fracture
{{Authority control Bone fractures Injuries of wrist and hand Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate