Scandinavian Mile on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
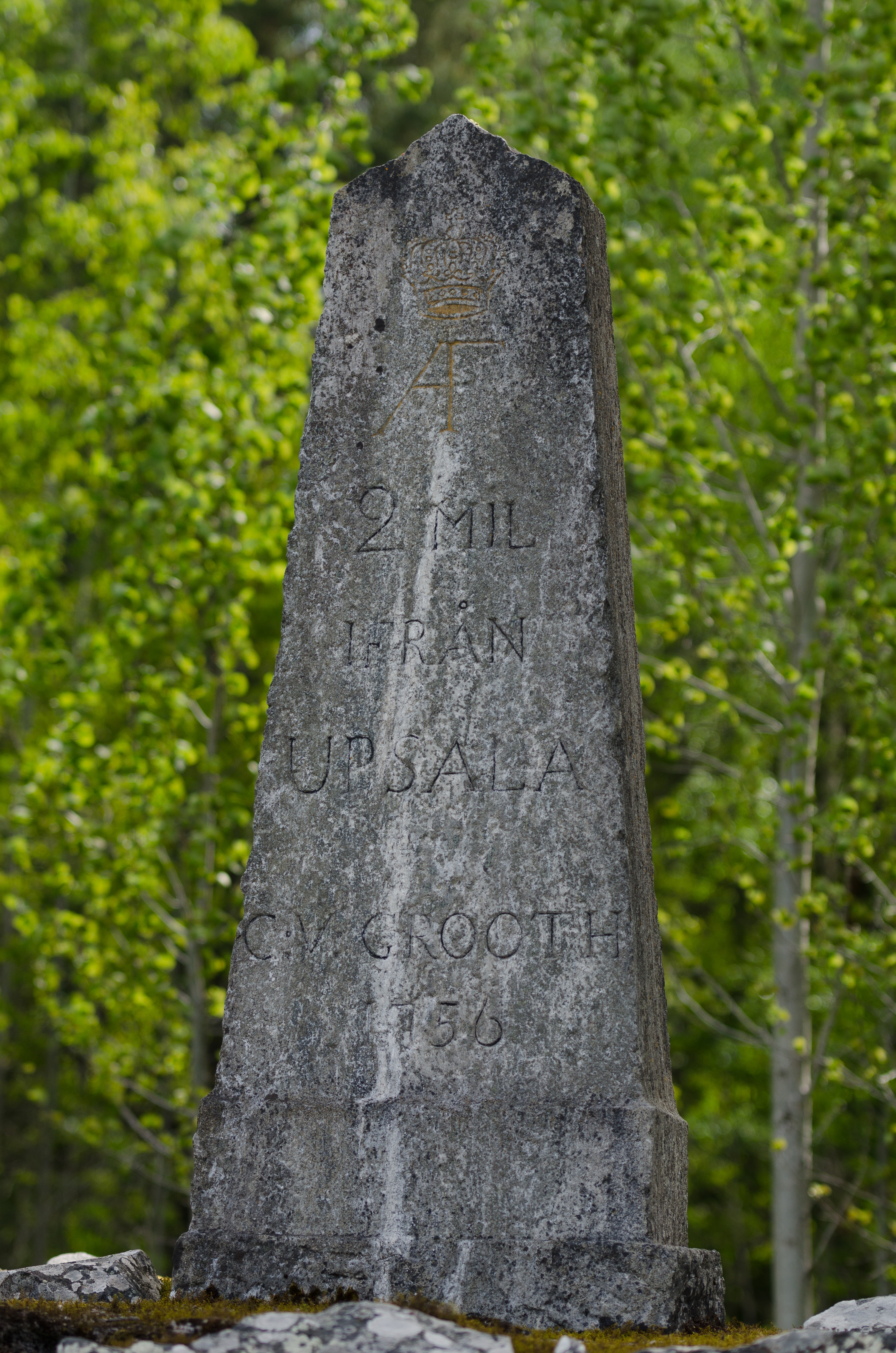 A Scandinavian mile ( Norwegian and , , ) is a unit of length common in
A Scandinavian mile ( Norwegian and , , ) is a unit of length common in
/ref> The word is derived from the same Roman source as the English mile. In Norway and Sweden, the international mile is formally called "English mile" (), although it is sometimes just referred to by the English word ''mile''. However, in situations where confusion may arise it is more common for Scandinavians to describe distances in terms of the official
 A Scandinavian mile ( Norwegian and , , ) is a unit of length common in
A Scandinavian mile ( Norwegian and , , ) is a unit of length common in Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
and Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
, to a lesser extent in Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
, but not Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
. Today, it is standardised as 1 being , but it had different values in the past.snl.no/ref> The word is derived from the same Roman source as the English mile. In Norway and Sweden, the international mile is formally called "English mile" (), although it is sometimes just referred to by the English word ''mile''. However, in situations where confusion may arise it is more common for Scandinavians to describe distances in terms of the official
SI unit
The International System of Units, internationally known by the abbreviation SI (from French ), is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of units of measurement, system of measurement. It is the only system ...
kilometre
The kilometre (SI symbol: km; or ), spelt kilometer in American English, American and Philippine English, is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one thousand metres (kilo- being the SI prefix for ). It is the ...
.
This modern definition of 10 kilometres (km) is equivalent to the obsolete myriametre, which was once used in France.
Danish mile
The Danish mile was defined as , equivalent to 4 minutes of latitude. It is no longer in use.Swedish mile
County miles
In early history, Sweden had various regional miles with their own measurements. Later on, such miles were generally defined by county (, "county miles"). Some noteworthy county miles are: * Dala mile – * Finnish mile () – around *Småland
Småland () is a historical Provinces of Sweden, province () in southern Sweden.
Småland borders Blekinge, Scania, Halland, Västergötland, Östergötland and the island Öland in the Baltic Sea. The name ''Småland'' literally means "small la ...
mile – around
* Uppland
Uppland is a historical province or ' on the eastern coast of Sweden, just north of Stockholm, the capital. It borders Södermanland, Västmanland and Gästrikland. It is also bounded by lake Mälaren and the Baltic Sea.
The name literally ...
mile – = 3,600 Swedish rods = 6,000 Swedish fathoms = 18,000 Swedish ells = 36,000 Swedish feet
* Västgöta mile – around
* Ångermanland
Ångermanland ( or ) is a historical province (''landskap'') in the northern part of Sweden. It is bordered (clockwise from the north) by Swedish Lapland, Västerbotten, the Gulf of Bothnia, Medelpad and Jämtland.
The name is derived from the ...
mile – = 6,666 Swedish fathoms
Unity mile
In 1649 the Swedish government made the Uppland mile the de facto Swedish mile, or "unity mile" (), for all of Sweden, also known as "land mile" or "long mile". It could be divided into four "quarter ways" (, "firkin way"), describing a quarter of a unity mile. Old regional miles still persisted across Sweden in the 18th century and regional variations of rod, fathom, ell and foot also caused regional variation to the unity mile. This became apparent with the Swedish-Norwegian union in 1814, were the different definitions of foot in made the unity mile in Norway.Metric mile
When themetric system
The metric system is a system of measurement that standardization, standardizes a set of base units and a nomenclature for describing relatively large and small quantities via decimal-based multiplicative unit prefixes. Though the rules gover ...
was introduced, the ' was redefined to be exactly . The metric system was introduced in Norway in 1875 and Sweden in 1889, after a decision by the parliament in 1876 and a ten-year transition period from 1879.
When the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
introduced the metric system
The metric system is a system of measurement that standardization, standardizes a set of base units and a nomenclature for describing relatively large and small quantities via decimal-based multiplicative unit prefixes. Though the rules gover ...
in 1887, the Grand Duchy of Finland
The Grand Duchy of Finland was the predecessor state of modern Finland. It existed from 1809 to 1917 as an Autonomous region, autonomous state within the Russian Empire.
Originating in the 16th century as a titular grand duchy held by the Monarc ...
decided to redefine the old Finnish mile ''peninkulma'' (, ), which was based on the Swedish mile, to also be . In Finland, however, it has been much less in use than in Sweden and Norway.
Usage
The ' is currently not used on road signs, and kilometre is the standard for most formal written distances. However, it is very common incolloquial speech
Colloquialism (also called ''colloquial language'', ''colloquial speech'', ''everyday language'', or ''general parlance'') is the linguistic style used for casual and informal communication. It is the most common form of speech in conversation amo ...
, including 5 km, which is referred to in Swedish as "half a '" (). The ' has however not lost all formal uses. Various tax deductions, for example regarding distance travelled for business purposes, are measured in ' by the Swedish Tax Agency
The Swedish Tax Agency () is a government agencies in Sweden, government agency in Sweden responsible for national tax collection and administering the Population registration in Sweden, population registration.
The agency was formed on 1 January ...
(). It is also used in the most common unit for measuring vehicle fuel consumption – "litres per '" – and in Sweden in second-hand car advertisements, where odometer
An odometer or odograph is an instrument used for measuring the distance traveled by a vehicle, such as a bicycle or car. The device may be electronic, mechanical, or a combination of the two (electromechanical). The noun derives from ancient Gr ...
readings are often quoted in ' though the car itself records kilometres.
Metric farsang
InIran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
and Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, an indigenous unit of measurement, equivalent to the Scandinavian mile, is used, known as ''farsang''. Originally a Persian unit of measurement, equivalent to the European league, known as '' parasang'' (4.8 or 5.6 km). It was redefined in Iran as 10 kilometres on 31 May 1926.
The older Iranian farsang survives regionally as farsakh-song. In Turkey there is a "light farsang" defined as , similar to the Scandinavian forest mile.
Other Scandinavian miles
Beyond the normal mile, there was also a "forest mile" () that was half as long as the normal ', i.e. a bit over , and equal to an even older unit of measurement, the ('rest', 'pause'), so named since it was seen as the distance a man would normally be able to walk between rests, corresponding to the league in other countries. There was also a "fell mile" (, seefell
A fell (from Old Norse ''fell'', ''fjall'', "mountain"Falk and Torp (2006:161).) is a high and barren landscape feature, such as a mountain or Moorland, moor-covered hill. The term is most often employed in Fennoscandia, Iceland, the Isle of M ...
) which was almost double the normal mile, i.e. just under .
In literature
Naomi Mitchison
Naomi Mary Margaret Mitchison, Baroness Mitchison (; 1 November 1897 – 11 January 1999) was a List of Scottish novelists, Scottish novelist and poet. Often called a doyenne of Scottish literature, she wrote more than 90 books of historical an ...
, in her autobiographic book ''You May Well Ask'', relates an experience during a walking tour in Sweden: "Over in Gotland
Gotland (; ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a Provinces of Sweden, province/Counties of Sweden, county (Swedish län), Municipalities of Sweden, municipality, a ...
I walked again, further than I would have if I had realized that the milestones were in old Swedish miles, so that my disappointing three-mile walk along the cold sea edge under the strange ancient fortifications was really fifteen English miles".Naomi Mitchison
Naomi Mary Margaret Mitchison, Baroness Mitchison (; 1 November 1897 – 11 January 1999) was a List of Scottish novelists, Scottish novelist and poet. Often called a doyenne of Scottish literature, she wrote more than 90 books of historical an ...
, You may well ask", London, 1979, Part I, Chap 7.
See also
* Danish units of measurementReferences
{{reflist Units of length Science and technology in Norway Science and technology in Sweden Decimalisation 1889 introductions