Saud (other) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The House of Saud ( ) is the ruling
 ''House of Saud'' is a translation of ''ʾĀl Saud'', an Arabic dynastic name formed by adding the word '' ʾĀl'' (meaning "family of" or "House of", not to be confused with ''Al'' meaning "the") to the personal name of an ancestor. In the case of the Al Saud, the ancestor is Saud ibn Muhammad ibn Muqrin, the father of the dynasty's 18th century founder Muhammad bin Saud (Muhammad, son of Saud).
The surname "Al Saud" is carried by any descendant of Muhammad bin Saud or his three brothers Farhan, Thunayyan, and Mishari. Al Saud's other family branches like Saud Al Kabir, the Al Jiluwi, the Al Thunayan, the Al Mishari and the Al Farhan are called
''House of Saud'' is a translation of ''ʾĀl Saud'', an Arabic dynastic name formed by adding the word '' ʾĀl'' (meaning "family of" or "House of", not to be confused with ''Al'' meaning "the") to the personal name of an ancestor. In the case of the Al Saud, the ancestor is Saud ibn Muhammad ibn Muqrin, the father of the dynasty's 18th century founder Muhammad bin Saud (Muhammad, son of Saud).
The surname "Al Saud" is carried by any descendant of Muhammad bin Saud or his three brothers Farhan, Thunayyan, and Mishari. Al Saud's other family branches like Saud Al Kabir, the Al Jiluwi, the Al Thunayan, the Al Mishari and the Al Farhan are called
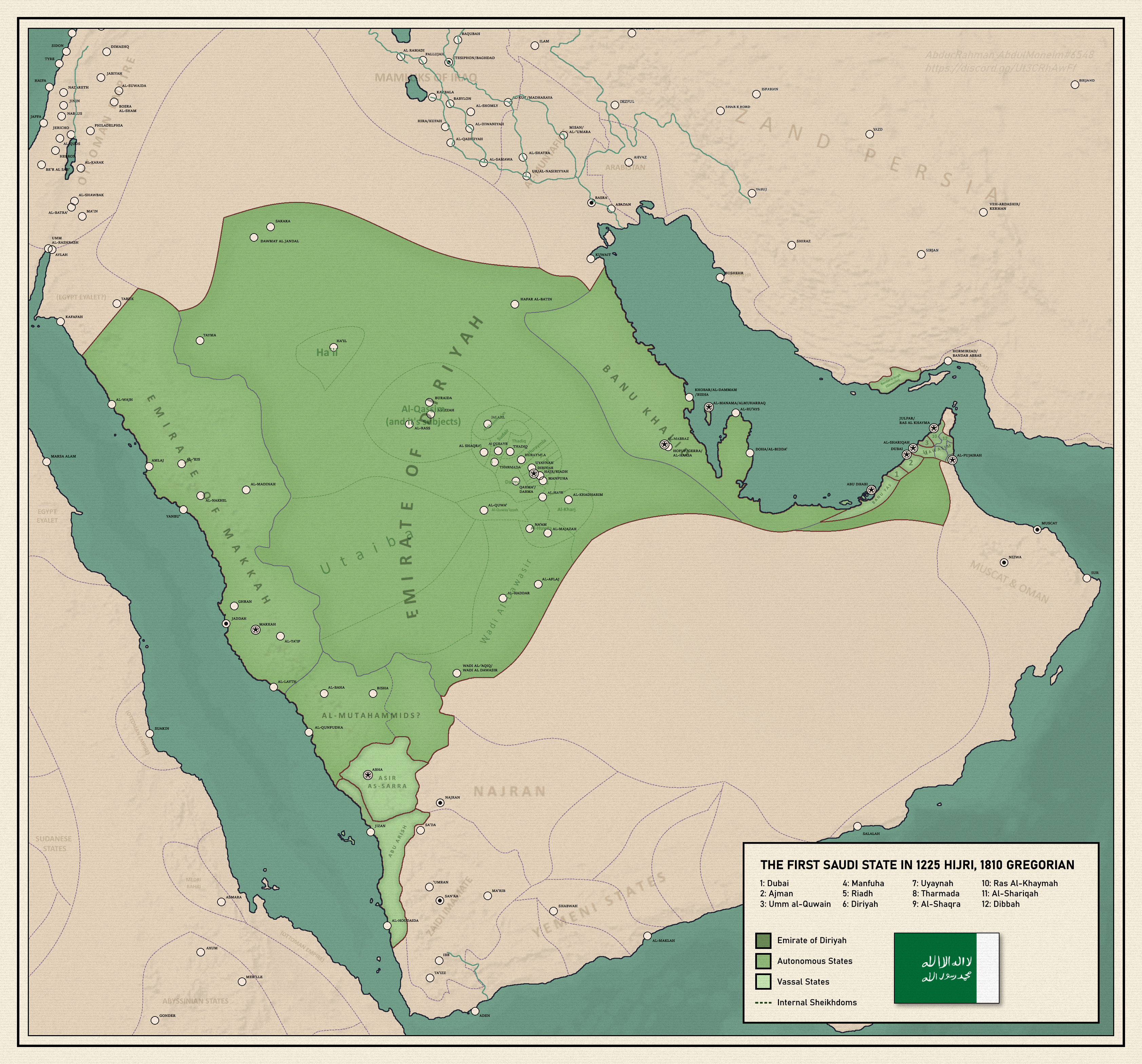 The First Saudi State was founded in 1727. This period was marked by conquest of neighboring areas and by religious zeal. At its height, the First Saudi State included most of the territory of modern-day
The First Saudi State was founded in 1727. This period was marked by conquest of neighboring areas and by religious zeal. At its height, the First Saudi State included most of the territory of modern-day
 In June 2015, ''
In June 2015, ''
 Due to its
Due to its
ImageSize = width:900 height:auto barincrement:20
PlotArea = top:10 bottom:50 right:130 left:20
AlignBars = late
DateFormat = yyyy
Period = from:1720 till:2025
TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal
ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:10 start:1720
Colors =
id:Imam value:green legend: Imam
Legend = columns:4 left:150 top:24 columnwidth:100
TextData =
pos:(20,27) textcolor:black fontsize:M
text:"Title:"
BarData =
barset:PM
PlotData=
align:left fontsize:S shift:(3,-4) anchor:from width:15
barset:PM
from: 1720 till: 1725 color:Imam text:" Saud I" fontsize:10
from: 1744 till: 1765 color:Imam text:" Muhammad I" fontsize:10
from: 1765 till: 1803 color:Imam text:" Abdulaziz I" fontsize:10
from: 1803 till: 1814 color:Imam text:" Saud II" fontsize:10
from: 1814 till: 1818 color:Imam text:" Abdullah I" fontsize:10
from: 1823 till: 1834 color:Imam text:" Turki" fontsize:10
from: 1834 till: 1834 color:Imam text:" Mishari" fontsize:10
from: 1834 till: 1838 color:Imam text:"
 * The Royal Flag consists of a green flag, with an
* The Royal Flag consists of a green flag, with an
royal family
A royal family is the immediate family of monarchs and sometimes their extended family.
The term imperial family appropriately describes the family of an emperor or empress, and the term papal family describes the family of a pope, while th ...
of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
. It is composed of the descendants of Muhammad bin Saud
Muhammad bin Saud Al Muqrin Al Saud (; 1687–1765), also known as Ibn Saud, was the emir of Diriyah and is considered the founder of the First Saudi State and the House of Saud, Saud dynasty, named after his father, Saud bin Muhammad Al Muqrin. ...
, founder of the Emirate of Diriyah
The first Saudi state (), officially the Emirate of Diriyah (), was established in 1744, when the emir of a Najdi town called Diriyah, Muhammad I, and the religious leader Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab signed a pact to found a socio-religious ...
, known as the First Saudi State
The first Saudi state (), officially the Emirate of Diriyah (), was established in 1744, when the emir of a Najdi town called Diriyah, Muhammad I, and the religious leader Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab signed a pact to found a socio-religious r ...
, (1727–1818), and his brothers, though the ruling faction of the family is primarily led by the descendants of Ibn Saud
Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman Al Saud (; 15 January 1875Ibn Saud's birth year has been a source of debate. It is generally accepted as 1876, although a few sources give it as 1880. According to British author Robert Lacey's book ''The Kingdom'', ...
, the modern founder of Saudi Arabia. It forms a subtribe of the larger prominent ancient Banu Hanifa
Banu Hanifa () is an ancient Arab tribe inhabiting the area of al-Yamama in the central region of modern-day Saudi Arabia. The tribe belongs to the great Rabi'ah branch of North Arabian tribes, which also included Abdul Qays, Taghlib, al-N ...
tribe of Arabia, from which well known 7th century Arabian theologist Maslama ibn Ḥabīb originates. The most influential position of the royal family is the King of Saudi Arabia
The king of Saudi Arabia, officially the king of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (; ''Malik al-Mamlakat al-ʿArabiyat as-Suʿūdiyya''), is head of state and of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, who holds absolute power. He is the head of the Saudi ...
, an absolute monarch. The family in total is estimated to comprise 15,000 members; however, the majority of power, influence and wealth is possessed by a group of about 2,000 of them. Some estimates of the royal family's wealth measure their net worth at $1.4 trillion. This figure includes the market capitalization of Saudi Aramco
Saudi Aramco ( ') or Aramco (formerly Arabian-American Oil Company), officially the Saudi Arabian Oil Company, is a majority state-owned petroleum and natural gas company that is the national oil company of Saudi Arabia. , it is the fourth- l ...
, the state oil and gas company, and its vast assets in fossil fuel reserves, making them the wealthiest family in the world and the wealthiest in recorded history.
The House of Saud has had four phases: the Sheikhdom of Diriyah
The Sheikhdom of Dir'iyah (), was a polity in central Arabia from 1446 to 1744 and the predecessor to the first Saudi state. Its capital was At-Turaif District, and it was based around the banks of Wadi Hanifa. It was ruled by the Muani'a dynasty ...
(1446–1744); the Emirate of Diriyah
The first Saudi state (), officially the Emirate of Diriyah (), was established in 1744, when the emir of a Najdi town called Diriyah, Muhammad I, and the religious leader Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab signed a pact to found a socio-religious ...
(1727–1818), marked by the expansion of Salafism
The Salafi movement or Salafism () is a Islamic fundamentalism, fundamentalist Islamic revival, revival movement within Sunni Islam, originating in the late 19th century and influential in the Islamic world to this day. The name "''Salafiyya''" ...
; the Emirate of Nejd
The second Saudi state (), officially known as the Emirate of Najd, was a state that existed between 1824 and 1891 in the Najd region of what is now Saudi Arabia. Saudi rule was restored to central (Najd) and Eastern Arabia after the first Sau ...
(1824–1891), marked with continuous infighting; and the current state (1902–present), which evolved into the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in 1932 and now wields considerable influence in the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
. The family has had conflicts with the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, the Sharif of Mecca
The Sharif of Mecca () was the title of the leader of the Sharifate of Mecca, traditional steward of the Holiest sites in Islam, Islamic holy cities of Mecca and Medina. The term ''sharif'' is Arabic for "noble", "highborn", and is used to desc ...
, the Al Rashid family of Ha'il and their vassal houses in Najd
Najd is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes most of the central region of Saudi Arabia. It is roughly bounded by the Hejaz region to the west, the Nafud desert in Al-Jawf Province, al-Jawf to the north, ...
along with numerous Islamist groups both inside and outside Saudi Arabia and Shia minority in Saudi Arabia.
The succession to the Saudi Arabian throne was designed to pass from one son of the first king, Ibn Saud, to another. The monarchy was hereditary
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic inform ...
by agnatic seniority
Agnatic seniority is a patrilineality, patrilineal principle of inheritance where the order of succession to the throne prefers the monarch's younger brother over the monarch's own sons. A monarch's children (the next generation) succeed only ...
until 2006, when a royal decree
A decree is a legal proclamation, usually issued by a head of state, judge, royal figure, or other relevant authorities, according to certain procedures. These procedures are usually defined by the constitution, Legislative laws, or customary l ...
provided that future Saudi kings are to be elected by a committee of Saudi princes. King Salman
Salman bin Abdulaziz Al Saud (; born 31 December 1935) has been King of Saudi Arabia since 2015, and was Prime Minister of Saudi Arabia from 2015 to 2022. He is the 25th son of King Abdulaziz, the founder of Saudi Arabia. He assumed the thro ...
, who reigns currently, first replaced the next crown prince, his brother Muqrin, with his nephew Muhammad bin Nayef. In 2017, Muhammad bin Nayef was replaced by Mohammed bin Salman
Mohammed bin Salman Al Saud (; born 31 August 1985), also known as MBS or MbS, is the ''de facto'' ruler of the Saudi Arabia, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, formally serving as Crown Prince of Saudi Arabia, Crown Prince and Prime Minister of Sa ...
, King Salman's son, as the crown prince after an approval by the Allegiance Council with 31 out of 34 votes. The king-appointed cabinet includes more members of the royal family.
Title
cadet branches
A cadet branch consists of the male-line descendants of a monarch's or patriarch's younger sons ( cadets). In the ruling dynasties and noble families of much of Europe and Asia, the family's major assets (realm, titles, fiefs, property and inco ...
. Members of the cadet branches hold high and influential positions in government though they are not in the line of succession to the Saudi throne. Many cadet members intermarry within the Al Saud to re-establish their lineage and continue to wield influence in the government.
All male members of the royal family have the title of Emir
Emir (; ' (), also Romanization of Arabic, transliterated as amir, is a word of Arabic language, Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocratic, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person po ...
(Prince
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The ...
). However, the sons and patrilineal
Patrilineality, also known as the male line, the spear side or agnatic kinship, is a common kinship system in which an individual's family membership derives from and is recorded through their father's lineage. It generally involves the inheritanc ...
grandsons of Kings are referred to by the style
Style, or styles may refer to:
Film and television
* ''Style'' (2001 film), a Hindi film starring Sharman Joshi, Riya Sen, Sahil Khan and Shilpi Mudgal
* ''Style'' (2002 film), a Tamil drama film
* ''Style'' (2004 film), a Burmese film
* '' ...
"His Royal Highness
Royal Highness is a style (manner of address), style used to address or refer to some members of royal families, usually princes or princesses. Kings and their female Queen consort, consorts, as well as queens regnant, are usually styled ''Maje ...
" (HRH), differing from patrilineal great-grandsons and members of cadet branches who are called "His Highness
Highness (abbreviation HH, oral address Your Highness) is a formal style (manner of address), style used to address (in grammatical person, second person) or refer to (in grammatical person, third person) certain members of a reigning or formerly ...
" (HH), while the reigning king uses the additional title of Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques
His Majesty the Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques (abbreviated as CTHM; ), or Protector of the Two Holy Cities, is a Royal and noble styles, royal style that has been used officially by the King of Saudi Arabia, monarchs of Saudi Arabia since 19 ...
.
History
Origins and early history
The earliest recorded ancestor of the Al Saud was Mani' ibn Rabiah Al-Muraydi, who settled inDiriyah
Diriyah (; formerly romanization of Arabic, romanized as Dereyeh and Dariyya) is a towns in Saudi Arabia, town and governorate in Saudi Arabia. Located on the northwestern outskirts of the Saudi capital, Riyadh, Diriyah was the original home of t ...
in 1446–1447 with his clan, the Mrudah. The Mrudah are believed to be descended from the Banu Hanifa
Banu Hanifa () is an ancient Arab tribe inhabiting the area of al-Yamama in the central region of modern-day Saudi Arabia. The tribe belongs to the great Rabi'ah branch of North Arabian tribes, which also included Abdul Qays, Taghlib, al-N ...
branch of the larger Rabi'ah tribal confederation. The Banu Hanifa played an important role in shaping the Middle East and Arabia from the 6th century.
Mani' was invited to Diriyah by a relative named Ibn Dir, who was the ruler of a group of villages and estates that make up modern-day Riyadh
Riyadh is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyadh Province and the centre of the Riyadh Governorate. Located on the eastern bank of Wadi Hanifa, the current form of the metropolis largely emerged in th ...
. Mani's clan had been on a sojourn in east Arabia, near Al-Qatif
Qatif Governorate ( ''Al-Qaṭīf'') is a list of governorates of Saudi Arabia, governorate and urban area located in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia, Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. It extends from Ras Tanura and Jubail in the north to Damma ...
, from an unknown point in time. Ibn Dir handed Mani two estates, called al-Mulaybeed and Ghusayba. Mani and his family settled and renamed the region Al Diriyah after their benefactor Ibn Dir.
The Mrudah became rulers of Al Diriyah, which prospered along the banks of Wadi Hanifa
Wadi Hanifa (), historically known as Wadi al-Arad, is a ''wadi'' (seasonal river) in the Najd region, Riyadh Province, in central Saudi Arabia. The valley runs for a length of from northwest to southeast, cutting through the city of Riyadh, ...
and became an important Najdi settlement. As the clan grew larger, power struggles ensued, with one branch leaving for nearby Dhruma, while another branch (the "Al Watban") left for the town of az-Zubayr in southern Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
. The Al Muqrin became the ruling family among the Mrudah in Diriyah.
The name of the clan comes from Sheikh Saud ibn Muhammad ibn Muqrin, who died in 1725.
Emirate of Diriyah
 The First Saudi State was founded in 1727. This period was marked by conquest of neighboring areas and by religious zeal. At its height, the First Saudi State included most of the territory of modern-day
The First Saudi State was founded in 1727. This period was marked by conquest of neighboring areas and by religious zeal. At its height, the First Saudi State included most of the territory of modern-day Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
, and raids by Al Saud's allies and followers reached into Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
, Oman
Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline ...
, Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, and Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
. Islamic scholars, particularly Muhammad ibn Abdul Wahhab and his descendants, are believed to have played a significant role in Saudi rule during this period. The Saudis and their allies referred to themselves during this period as the ''Muwahhidun'' or ''Ahl al-Tawhid'' ("the monotheists"). Later they were referred to as the Wahhabis
Wahhabism is an exonym for a Salafi revivalist movement within Sunni Islam named after the 18th-century Hanbali scholar Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab. It was initially established in the central Arabian region of Najd and later spread to other ...
, a particularly strict, puritanical Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
ic sect, named for its founder.
Leadership of Al Saud during the time of their first state passed from father to son without incident. The first imam, Muhammad bin Saud, was succeeded by his eldest son, Abdulaziz
Abdulaziz (; ; 8 February 18304 June 1876) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 25 June 1861 to 30 May 1876, when he was overthrown in a government coup. He was a son of Sultan Mahmud II and succeeded his brother Abdulmejid I in 1861.
Ab ...
in 1765. In 1802, Abdulaziz's forces led 10,000 Wahhabi soldiers in an attack on the Shi'ite
Shia Islam is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib () as both his political successor (caliph) and as the spiritual leader of the Muslim community (imam). However, his right is understood to ...
holy city of Karbala
Karbala is a major city in central Iraq. It is the capital of Karbala Governorate. With an estimated population of 691,100 people in 2024, Karbala is the second largest city in central Iraq, after Baghdad. The city is located about southwest ...
, in what is now southern Iraq and where Hussein ibn Ali
Husayn ibn Ali (; 11 January 626 – 10 October 680 CE) was a social, political and religious leader in early medieval Arabia. The grandson of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and an Alid (the son of Ali ibn Abi Talib and Muhammad's daughter ...
, the grandson of Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
is buried. The Wahhabi soldiers killed more than 2,000 people, including women and children. They plundered the city, demolishing the massive golden dome above Hussein's tomb and loaded hundreds of camels with weapons, jewelry, coins and other valuable goods.
The attack on Karbala convinced the Ottomans and the Egyptians that the Saudis were a threat to regional peace. Abdulaziz was killed in 1803 by an assassin, believed by some to have been a Shi'ite seeking revenge over the sacking of Karbala the year before. Abdul-Aziz was in turn succeeded by his son, Saud, under whose rule the Saudi state reached its greatest extent. By the time Saud died in 1814, his son and successor Abdullah bin Saud had to contend with an Ottoman-Egyptian invasion in the Wahhabi war seeking to retake lost Ottoman Empire territory. The mainly Egyptian force succeeded in defeating Abdullah's forces, taking over the then-Saudi capital of Diriyyah in 1818. Abdullah was taken prisoner and was soon beheaded by the Ottomans in Constantinople, putting an end to the First Saudi State. The Egyptians sent many members of the Al Saud clan and other members of the local nobility as prisoners to Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
and Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
, and razed the Saudi capital of Diriyyah.
Emirate of Nejd
A few years after the fall ofDiriyah
Diriyah (; formerly romanization of Arabic, romanized as Dereyeh and Dariyya) is a towns in Saudi Arabia, town and governorate in Saudi Arabia. Located on the northwestern outskirts of the Saudi capital, Riyadh, Diriyah was the original home of t ...
in 1818, the Saudis were able to re-establish their authority in Najd, establishing the Emirate of Nejd, commonly known as the Second Saudi State, with its capital in Riyadh.
Compared to the First Saudi State, the second Saudi period was marked by less territorial expansion (it never reconquered the Hijaz
Hejaz is a historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes the majority of the western region of Saudi Arabia, covering the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif and Al-Bahah. It is thus known as the "Western Province ...
or 'Asir, for example) and less religious zeal, although the Saudi leaders continued to go by the title of ''imam
Imam (; , '; : , ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a prayer leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Salah, Islamic prayers, serve as community leaders, ...
'' and still employed Salafi
The Salafi movement or Salafism () is a fundamentalist revival movement within Sunni Islam, originating in the late 19th century and influential in the Islamic world to this day. The name "''Salafiyya''" is a self-designation, claiming a retu ...
religious scholars. The second state was also marked by severe internal conflicts within the Saudi family, eventually leading to the dynasty's downfall. In all but one instance, succession occurred by assassination or civil war, the exception being the passage of authority from Faisal ibn Turki to his son Abdullah ibn Faisal ibn Turki.
Present form
After his defeat at Mulayda, Abdul Rahman bin Faisal went with his family into exile in the deserts of easternArabia
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
among the Al Murra bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu ( ; , singular ) are pastorally nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia (Iraq). The Bedouin originated in the Sy ...
. Soon afterward, however, he found refuge in Kuwait
Kuwait, officially the State of Kuwait, is a country in West Asia and the geopolitical region known as the Middle East. It is situated in the northern edge of the Arabian Peninsula at the head of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Kuwait ...
as a guest of the Kuwaiti emir
Emir (; ' (), also Romanization of Arabic, transliterated as amir, is a word of Arabic language, Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocratic, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person po ...
, Mubarak Al Sabah. In 1902, Abdul Rahman's son, Abdulaziz, took on the task of restoring Saudi rule in Riyadh. Supported by a few dozen followers and accompanied by some of his brothers and relatives, Abdulaziz was able to capture Riyadh's Masmak fort and kill the governor appointed there by Muhammad bin Abdullah Al Rashid. Abdulaziz, reported to have been barely 20 at the time, was immediately proclaimed ruler in Riyadh. As the new leader of the House of Saud, Abdulaziz became commonly known from that time onward as "Ibn Saud" in Western sources, though he is still called "Abdulaziz" in the Arab world.
Ibn Saud spent the next three decades trying to re-establish his family's rule over central Arabia, starting with his native Najd. His chief rivals were the Al Rashid clan in Ha'il, the Sharifs of Mecca in the Hijaz
Hejaz is a historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes the majority of the western region of Saudi Arabia, covering the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif and Al-Bahah. It is thus known as the "Western Province ...
, and the Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks () were a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group in Anatolia. Originally from Central Asia, they migrated to Anatolia in the 13th century and founded the Ottoman Empire, in which they remained socio-politically dominant for the e ...
in al Hasa. Abdulaziz also had to contend with the descendants of his late uncle Saud ibn Faisal (later known as the "Saud Al Kabir" branch of the family), pretender
A pretender is someone who claims to be the rightful ruler of a country although not recognized as such by the current government. The term may often be used to either refer to a descendant of a deposed monarchy or a claim that is not legitimat ...
s to the throne. Though for a time acknowledging the sovereignty of the Ottoman Sultans
The sultans of the Ottoman Empire (), who were all members of the Ottoman dynasty (House of Osman), ruled over the Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental empire from its perceived inception in 1299 to Dissolution of the Ottoman Em ...
and even taking the title of ''pasha
Pasha (; ; ) was a high rank in the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman political and military system, typically granted to governors, generals, dignitary, dignitaries, and others. ''Pasha'' was also one of the highest titles in the 20th-century Kingdom of ...
'', Ibn Saud allied himself to the British, in opposition to the Ottoman-backed Al Rashidis. From 1915 to 1927, Abdulaziz's dominions were a protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a State (polity), state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over ...
of the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
, pursuant to the 1915 Treaty of Darin
The Treaty of Darin, or the Darin Pact, of 1915 was made between the United Kingdom and Abdulaziz Al Saud (sometimes called ''Ibn Saud''), ruler of the Emirate of Nejd and Hasa, who founded the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in 1932.
Signing
The tre ...
.
Ibn Saud won final victory over the Al Rashidis in 1921, making him the ruler of most of central Arabia. He consolidated his dominions as the Sultanate of Nejd
The Sultanate of Nejd (, ') was the third iteration of the Third Saudi State, from 1921 to 1926. It was a monarchy led by the House of Saud, and a legal predecessor of modern-day Saudi Arabia. This version of the Third Saudi State was created ...
. He then turned his attention to the Hijaz, finally conquering it in 1926, just months before the British protectorate ended. For the next five and a half years, he administered the two parts of his dual realm, the Kingdom of Hejaz and Nejd
The Kingdom of Hejaz and Nejd (, '), initially the Kingdom of Hejaz and Sultanate of Nejd (Arabic: , '), was a dual monarchy ruled by Abdulaziz (Ibn Saud) following the Saudi conquest of Hejaz by the Sultanate of Nejd in 1925. It was the four ...
, as separate units.
By 1932, Ibn Saud had disposed of all his main rivals and consolidated his rule over much of the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
. He united his dominions into the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia that year. His father, Abdul Rahman, retained the honorary title of "imam". In 1937, near Dammam
Dammam (Arabic: الدمام ad-Dammām) is a city and governorate, and the capital of the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. Located on the coast of the Persian Gulf, it had a population of 1,386,166 as of 2022, making it the country's fifth- ...
, American surveyors discovered what later proved to be Saudi Arabia's vast oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) and lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturate ...
reserves. Before the discovery of oil, many family members were destitute.
Ibn Saud sired dozens of children by his many wives. He had at most four wives at a time, divorcing many times. He made sure to marry into many of the noble clans and tribes within his territory, including the chiefs of the Bani Khalid
Bani Khalid () is an Arab tribal confederation mainly inhabiting the Arabian Peninsula. The tribe ruled southern Iraq, Kuwait, and Eastern Arabia ( al-Hasa and al-Qatif) from the 15th century to the 18th century, and again under the protectio ...
, Ajman
Ajman ( '; Gulf Arabic: عيمان ''ʿYmān'') is the capital of the emirate of Ajman in the United Arab Emirates. It is the List of cities in the United Arab Emirates, fifth-largest city in UAE after Dubai, Abu Dhabi, Sharjah and Al Ain. Loca ...
, and Shammar
The tribe of Shammar () is a tribal Arab Qahtanite confederation, descended from the Tayy, which migrated into the northern Arabian Peninsula from Yemen in the second century. It is the largest branch of the Tayy, and one of the largest and mos ...
tribes, as well as the Al ash-Sheikh (descendants of Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab
Muḥammad ibn ʿAbd al-Wahhāb ibn Sulaymān al-Tamīmī (1703–1792) was a Sunni Muslim scholar, theologian, preacher, activist, religious leader, jurist, and reformer, who was from Najd in Arabian Peninsula and is considered as the eponymo ...
). He also arranged for his sons and relatives to enter into similar marriages. He appointed his eldest surviving son, Saud as heir apparent
An heir apparent is a person who is first in the order of succession and cannot be displaced from inheriting by the birth of another person. A person who is first in the current order of succession but could be displaced by the birth of a more e ...
, to be succeeded by the next eldest son, Faisal. The Al Saudi family became known as the "royal family", and each member, male and female, was accorded the title ''amir'' ("prince") or ''amira'' ("princess"), respectively.
Ibn Saud died in 1953, after having cemented an alliance with the United States in 1945. He is still celebrated officially as the "Founder", and only his direct descendants may take on the title of "his or her Royal Highness". The date of his recapture of Riyadh in 1902 was chosen to mark Saudi Arabia's centennial in 1999 (according to the Islamic lunar calendar
A lunar calendar is a calendar based on the monthly cycles of the Moon's phases ( synodic months, lunations), in contrast to solar calendars, whose annual cycles are based on the solar year, and lunisolar calendars, whose lunar months are br ...
).
Upon Ibn Saud's death, his son Saud assumed the throne without incident, but his lavish spending led to a power struggle with his brother, Crown Prince Faisal. In 1964, the royal family forced Saud to abdicate in favor of Faisal, aided by an edict from the country's grand mufti
A Grand Mufti (also called Chief Mufti, State Mufti and Supreme Mufti) is a title for the leading Faqīh, Islamic jurist of a country, typically Sunni, who may oversee other muftis. Not all countries with large Sunni Muslim populations have Gra ...
. During this period, some of Ibn Saud's younger sons, led by Talal ibn Abdul Aziz, defected to Egypt, calling themselves the "Free Princes
The Free Princes Movement () was a Saudi liberal political movement that existed from 1958 to 1964. Its members were known as the Young Najd (Najd al-Fattah in Arabic), Free Princes, and Liberal Princes.
Establishment
The movement was founded b ...
" and calling for liberalization and reform, but were later induced to return by Faisal. They were fully pardoned but were also barred from any future positions in government.
Faisal was assassinated in 1975 by a nephew, Faisal bin Musaid, who was promptly executed. Another brother, Khalid, assumed the throne. The next prince in line had actually been Prince Muhammad, but he had relinquished his claim to the throne in favor of Khalid, his only full brother.
Khalid died of a heart attack in 1982, and was succeeded by Fahd, the eldest of the powerful "Sudairi Seven
The Sudairi Seven (, ''As Sudayriyyūn as Sabʿah''), also spelled ''Sudairy'' or ''Sudayri'', is the commonly used name for a powerful alliance of seven full brothers within the Saudi royal family. They are also sometimes referred to as the Suda ...
", so-called because they were all sons of Ibn Saud by his wife Hassa Al Sudairi. Fahd did away with the previous royal title of "his Majesty" and replaced it with the honorific "Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques", in reference to the two Islamic holy sites in Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
and Medina
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
, in 1986.
A stroke in 1995 left Fahd largely incapacitated. His half-brother, Crown Prince Abdullah, gradually took over most of the king's responsibilities until Fahd's death in August 2005. Abdullah was proclaimed king on the day of Fahd's death and promptly appointed his younger brother, Sultan bin Abdulaziz
Sultan bin Abdulaziz Al Saud (c. 5 January 1931 – 22 October 2011) (, ''Sulṭān ibn ʿAbdulʿazīz Āl Suʿūd''), called ''The generous Sultan'' (, ''Sulṭan al Khair'') in Saudi Arabia, was the Saudi defense minister from 1963 to 201 ...
, the minister of defense and Fahd's "Second Deputy Prime Minister", as the new heir apparent. On 27 March 2009, Abdullah appointed Prince Nayef Interior Minister as his "second deputy prime minister" and Crown Prince on 27 October. Sultan died in October 2011 while Nayef died in Geneva, Switzerland
Geneva ( , ; ) ; ; . is the second-most populous city in Switzerland and the most populous in French-speaking Romandy. Situated in the southwest of the country, where the Rhône exits Lake Geneva, it is the capital of the Republic and Ca ...
on 15 June 2012. On 23 January 2015, Abdullah died after a prolonged illness, and his half-brother, Crown Prince Salman, was declared the new king.
Many princes and government officials were arrested in 2017 in an alleged anti corruption campaign by the king and crown prince. Then-United States President Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who is the 47th president of the United States. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he served as the 45 ...
expressed support for the arrests.
Political power
The head of the House of Saud is the King of Saudi Arabia who serves asHead of State
A head of state is the public persona of a sovereign state.#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 "
and he head of state
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (letter), the fifth letter of the Semitic abjads
* He (pronoun), a pronoun in Modern English
* He (kana), one of the Japanese kana (へ in hiragana and ヘ in katakana)
* Ge (Cyrillic), a Cyrillic letter cal ...
being an embodiment of the State itself or representative of its international persona." The name given to the office of head of sta ...monarch
A monarch () is a head of stateWebster's II New College Dictionary. "Monarch". Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest ...
of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The king holds almost absolute political power. The king appoints ministers to his cabinet who supervise their respective ministries in his name. The key ministries of Defence, the Interior and Foreign Affairs are usually held by members of the Saud family, as are all of the thirteen regional governorships. Most portfolios, however, such as Finance, Labour, Information, Planning, Petroleum Affairs and Industry, have traditionally been given to commoners, often with junior Al Saud members serving as their deputies. House of Saud family members also hold many of the kingdom's critical military and governmental departmental posts. Ultimate power in the kingdom has always rested upon the Al Saudis, though support from the Ulema
In Islam, the ''ulama'' ( ; also spelled ''ulema''; ; singular ; feminine singular , plural ) are scholars of Islamic doctrine and law. They are considered the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious knowledge in Islam.
"Ulama ...
, the merchant community, and the population at large has been key to the maintenance of the royal family's political ''status quo''.
Long-term political and government appointments have resulted in the creation of "power fiefdoms" for senior princes, such as those of King Faisal, who was foreign minister almost continuously from 1932 to 1975; King Abdullah, who had been commander of the National Guard
National guard is the name used by a wide variety of current and historical uniformed organizations in different countries. The original National Guard was formed during the French Revolution around a cadre of defectors from the French Guards.
...
since 1963 (until 2010, when he appointed his son to replace him); former Crown Prince Sultan, minister of defence and aviation from 1962 until his death in 2011; former Crown Prince Nayef who was the minister of interior from 1975 to his death in 2012; Prince Saud who had been minister of foreign affairs since 1975; and King Salman
Salman bin Abdulaziz Al Saud (; born 31 December 1935) has been King of Saudi Arabia since 2015, and was Prime Minister of Saudi Arabia from 2015 to 2022. He is the 25th son of King Abdulaziz, the founder of Saudi Arabia. He assumed the thro ...
, who was minister of defense and aviation before he was crown prince and governor of the Riyadh Province
The Riyadh Province ( '), is a province of Saudi Arabia, located in the geographic center of the country and the center of the Arabian Peninsula. It has an area of and with a 2022 population of 8,591,748, it is the second-largest region by ar ...
from 1962 to 2011. The current minister of defense is Prince Mohammad bin Salman, the son of King Salman and crown prince.
Such terms of service have enabled senior princes to mingle their personal wealth with that of their respective domains. They have often appointed their own sons to senior positions within their own portfolios. Examples of these include Prince Mutaib bin Abdullah as assistant commander in the National Guard until 2010; Prince Khalid bin Sultan
Khalid bin Sultan Al Saud (; born 24 September 1949) is the former deputy minister of defense, a member of the House of Saud, and a grandson of King Abdulaziz.
Early life and education
Prince Khalid was born on 24 September 1949. He is the olde ...
as assistant minister of defence until 2013; and Prince Mansour bin Mutaib as assistant minister for municipal and rural affairs until he replaced his father in 2009. In cases where portfolios have notably substantial budgets, appointments of younger, often full, brothers have been necessary, as deputies or vice ministers, ostensibly to share the wealth and the burdens of responsibility, of each fiefdom. Examples of these include Prince Abdul Rahman who was vice minister of defence and aviation under Prince Sultan; Prince Badr, deputy to King Abdullah in the National Guard; Prince Sattam, who was deputy governor of Riyadh during King Salman's term; and Prince Ahmed, who held the deputy minister's portfolio under Prince Nayef's interior ministry.
Unlike Western royal families
A royal family is the immediate family of monarchs and sometimes their extended family.
The term imperial family appropriately describes the family of an emperor or empress, and the term papal family describes the family of a pope, while the ...
, the Saudi monarchy has not had a clearly defined order of succession
An order, line or right of succession is the line of individuals necessitated to hold a high office when it becomes vacated, such as head of state or an honour such as a title of nobility.heir apparent
An heir apparent is a person who is first in the order of succession and cannot be displaced from inheriting by the birth of another person. A person who is first in the current order of succession but could be displaced by the birth of a more e ...
to the throne who serves as crown prince of the kingdom. Upon the king's death, the crown prince becomes king, and during the king's incapacitation the crown prince, likewise, assumes power as regent
In a monarchy, a regent () is a person appointed to govern a state because the actual monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge their powers and duties, or the throne is vacant and a new monarch has not yet been dete ...
. Although other members of the Al Saudis hold political positions in the Saudi government, it is only the king and crown prince who legally constitute the political institutions.
The royal family is politically divided by factions based on clan loyalties, personal ambitions and ideological differences. The most powerful clan faction is known as the 'Sudairi Seven', comprising the late King Fahd and his full brothers and their descendants. Ideological divisions include issues over the speed and direction of reform, and whether the role of the ulema should be increased or reduced. There were divisions within the family over who should succeed to the throne after the accession or earlier death of Prince Sultan. When Prince Sultan died before ascending to the throne on 21 October 2011, King Abdullah appointed Prince Nayef as crown prince. The following year, Prince Nayef also died before ascending to the throne.
Succession
Succession has been from brother to brother since the death of the founder of modern Saudi Arabia. Abdulaziz was succeeded by his son Saud who was succeeded by his half-brother Faisal. Faisal was succeeded by his brother Khalid who, in turn, was succeeded by his half-brother Fahd. Fahd was succeeded by his half-brother Abdullah, and Abdullah by his half-brother Salman, the current King. Salman appointed his half-brother Muqrin as Crown Prince in January 2015 and removed him in April 2015. Even Abdulaziz's youngest son was to turn 70 in 2015. Abdulaziz, in 1920, had said that the further succession would be from brother to brother, not from father to son. King Salman ended the brother-to-brother succession and appointed his 56-year-old nephew Muhammad bin Nayef as crown prince in April 2015, thus making the next succession from uncle to nephew. At the same time, King Salman appointed his son, Mohammad bin Salman, as deputy crown prince, thus making the next succession from cousin to cousin, as Muhammad bin Salman is the cousin of Crown Prince Muhammad bin Nayef. However, in June 2017, Salman elevated Mohammad bin Salman to crown prince, following his decision to strip Muhammad bin Nayef of all positions, making his son heir apparent to the throne, and making the next succession from father to son, for the first time since 1953, when Saud bin Abdulaziz Al Saud succeeded his father, the founder of Saudi Arabia,Ibn Saud
Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman Al Saud (; 15 January 1875Ibn Saud's birth year has been a source of debate. It is generally accepted as 1876, although a few sources give it as 1880. According to British author Robert Lacey's book ''The Kingdom'', ...
.
Amid international outcry over the killing of Jamal Khashoggi
On 2 October 2018, Jamal Khashoggi, a Saudi dissident journalist, was killed by agents of the Saudi government at the Saudi consulate in Istanbul, Turkey. Khashoggi was ambushed and strangled by a 15-member squad of Saudi operatives. His body w ...
, members of the Saudi royal family were allegedly distressed over the prospect of the crown prince becoming the next king. It was reported that dozens of princes and members of the Al Saud family were interested in seeing Prince Ahmed become the next king instead. During his London tour, Prince Ahmed criticized the Saudi leadership. He was also one of the three members of the ruling family to oppose Mohammad bin Salman becoming the crown prince in 2017.
Wealth
 In June 2015, ''
In June 2015, ''Forbes
''Forbes'' () is an American business magazine founded by B. C. Forbes in 1917. It has been owned by the Hong Kong–based investment group Integrated Whale Media Investments since 2014. Its chairman and editor-in-chief is Steve Forbes. The co ...
'' listed businessman Prince Al-Waleed bin Talal
Al Waleed bin Talal Al Saud (; born 7 March 1955) is a Saudi Arabian billionaire businessman, investor, and a House of Saud royal. In 2008, he was listed on ''Time'' magazine's ''Time 100'', an annual list of the hundred most influential people ...
, a grandson of Abdulaziz, the first king of Saudi Arabia, as the 34th-richest man in the world, with an estimated net worth of US$22.6 billion.
As of 2020, the combined net worth
Net worth is the value of all the non-financial and financial assets owned by an individual or institution minus the value of all its outstanding liabilities. Financial assets minus outstanding liabilities equal net financial assets, so net w ...
of the entire royal family has been estimated at around US$100 billion, which makes them the richest royal family among all monarchs, as well as one of the wealthiest families in the world. Some estimates of the Royal Family's wealth put the figure as high as $1.4 trillion, which includes holdings in Saudi Aramco
Saudi Aramco ( ') or Aramco (formerly Arabian-American Oil Company), officially the Saudi Arabian Oil Company, is a majority state-owned petroleum and natural gas company that is the national oil company of Saudi Arabia. , it is the fourth- l ...
.
Opposition and controversy
 Due to its
Due to its authoritarian
Authoritarianism is a political system characterized by the rejection of political plurality, the use of strong central power to preserve the political ''status quo'', and reductions in democracy, separation of powers, civil liberties, and ...
and quasi-theocratic
Theocracy is a form of autocracy or oligarchy in which one or more deities are recognized as supreme ruling authorities, giving divine guidance to human intermediaries, with executive and legislative power, who manage the government's daily a ...
rule, the House of Saud has attracted much criticism during its rule of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
. There have been numerous incidents, including the Wahhabi Ikhwan
The Ikhwān (, ), commonly known as Ikhwān man Aṭāʿa Allah (, 'Brethren of those who obey God'), was a Wahhabism, Wahhabi religious militia made up of traditionally nomadic tribesmen which formed a significant military force of the ruler Ibn ...
militia uprising during the reign of Ibn Saud. Osama Bin Laden
Osama bin Laden (10 March 19572 May 2011) was a militant leader who was the founder and first general emir of al-Qaeda. Ideologically a pan-Islamist, Bin Laden participated in the Afghan ''mujahideen'' against the Soviet Union, and support ...
, a critic of the US, was also a critic of Saudi Arabia and was denaturalized in the mid 1990s.
On 20 November 1979, the Grand Mosque seizure saw the al-Masjid al-Haram
Masjid al-Haram (), also known as the Sacred Mosque or the Great Mosque of Mecca, is considered to be the most significant mosque in Islam. It encloses the vicinity of the Kaaba in Mecca, in the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia. It is among the ...
in Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
violently seized by a group of 500 heavily armed and provisioned Saudi dissidents led by Juhayman al-Otaybi and Abdullah al-Qahtani, consisting mostly of members of the former Ikhwan militia of Otaibah
The Otaibah (, also spelled Otaiba, Utaybah) is one of the biggest Arabian tribes originating in the Arabian Peninsula. Their distribution spans throughout Saudi Arabia, especially in Najd and Hejaz. and the Middle East. The Otaibah are descended ...
but also of other peninsular Arabs and a few Egyptians enrolled in Islamic studies at the Islamic University of Madinah
The Islamic University of Madinah () is a public Islamic university in Medina, Saudi Arabia. Established by King Saud bin Abdulaziz in 1961, Sayy’id Abul Ala Maududi had played a significant role of establishing and running of Islamic Univers ...
. The Saudi royal family turned to the Ulema, who duly issued a ''fatwa
A fatwa (; ; ; ) is a legal ruling on a point of Islamic law (sharia) given by a qualified Islamic jurist ('' faqih'') in response to a question posed by a private individual, judge or government. A jurist issuing fatwas is called a ''mufti'', ...
'' permitting the storming of the holy sanctuary by Saudi forces, aided by French special ops units. According to Lawrence Wright
Lawrence Wright (born August 2, 1947) is an American writer and journalist, who is a staff writer for ''The New Yorker'' magazine, and fellow at the Center for Law and Security at the New York University School of Law. Wright is best known as ...
, the GIGN
The GIGN ( ; ) is the elite police tactical unit of the French National Gendarmerie. Among its missions are counterterrorism, hostage rescue, surveillance of national threats, protection of government officials, critical site protection (such ...
commandos did first convert to Islam prior to the raid. Most of those responsible, including Al-Otaybi himself, were soon beheaded
Decapitation is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and all vertebrate animals, since it deprives the brain of oxygenated blood by way of severing through the jugular vein and common c ...
publicly in four cities of Saudi Arabia.
In January 2016, Saudi Arabia executed
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence (law), sentence ordering that an offender b ...
the prominent Shiite cleric Sheikh Nimr, who had called for pro-democracy demonstrations, along with forty-seven other Saudi Shia citizens sentenced by the Specialized Criminal Court on terrorism charges.
Since May 2017, in response to protests against the government, the predominantly Shia town of Al-Awamiyah has been put under full siege by the Saudi military. Residents are not allowed to enter or leave, and the Saudi military indiscriminately shells the neighborhoods with airstrike
An airstrike, air strike, or air raid is an offensive operation carried out by aircraft. Air strikes are delivered from aircraft such as blimps, balloons, fighter aircraft, attack aircraft, bombers, attack helicopters, and drones. The official d ...
s, mortar fire along with sniper
A sniper is a military or paramilitary marksman who engages targets from positions of concealment or at distances exceeding the target's detection capabilities. Snipers generally have specialized training and are equipped with telescopic si ...
s shooting residents. Dozens of Shia civilians were killed, including a three-year-old. The Saudi government claims it is fighting terrorists in al-Awamiyah.
Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman kept his own mother away from his father for more than two years, fearing that she would stop the king from giving eventual power to him. Princess Fahda bint Falah Al Hithlain, third wife of King Salman, was said to be in America for medical treatment. However, according to American intelligence, this was refuted, stating that she was not in the country.
Some Royals have been criticised for various human rights violations, including the assassination of Jamal Khashoggi
On 2 October 2018, Jamal Khashoggi, a Saudi dissident journalist, was killed by agents of the Saudi government at the Saudi consulate in Istanbul, Turkey. Khashoggi was ambushed and strangled by a 15-member squad of Saudi operatives. His body w ...
, treatment of workers, the Saudi-led intervention in Bahrain and the Yemen war.
The Reuters
Reuters ( ) is a news agency owned by Thomson Reuters. It employs around 2,500 journalists and 600 photojournalists in about 200 locations worldwide writing in 16 languages. Reuters is one of the largest news agencies in the world.
The agency ...
news agency reported on 23 June 2020 that Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman had allegedly threatened and intimidated a former intelligence officer, Saad al-Jabri, along with his family of adult children, from returning to Saudi Arabia from exile in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
. Al-Jabri was a long-time aide to the former crown prince, Prince Mohammed bin Nayef, who was ousted in 2017. Al-Jabri allegedly has access to documents containing information sensitive and pivotal for the crown prince's leadership.
A group of intellectuals from Saudi Arabia, exiled in the US, the UK, and elsewhere, launched a political party in opposition to the royal family ruling the kingdom. The launch of the party was announced in September 2020 and was launched on the 2nd death anniversary of Jamal Khashoggi
Jamal Ahmad Hamza Khashoggi (13 October 1958 – 2 October 2018) was a Saudi journalist, Saudi dissidents, dissident, author, columnist for ''Middle East Eye'' and ''The Washington Post'', and a general manager and editor-in-chief of Al-Arab New ...
. The National Assembly Party (NAAS – people in Arabic) was launched with the aim of gathering the support of people, both inside and outside Saudi Arabia, against the ruling royals King Salman and Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman. Madawi al-Rasheed, a scholar, is also the co-founder of NAAS. Other members of the party include scholar Abdullah al-Aoudh, comedian and vlogger Omar Abdulaziz, and activist Yahya Assiri. The party's launch took place online from London as the Basic Law of Saudi Arabia
The Basic Law of Saudi Arabia (alternative name: Basic System of Governance; , ) is a constitution-like charter divided into nine chapters, consisting of 83 articles.
The Basic Law (in Article One) states that the constitution of Saudi ...
prohibits the formation of political parties. Forming a political party is considered sedition
Sedition is overt conduct, such as speech or organization, that tends toward rebellion against the established order. Sedition often includes subversion of a constitution and incitement of discontent toward, or insurrection against, establ ...
, punishable with lengthy jail terms.
Some members of the royal family have ill-treated their employees, even while visiting other countries. For example, Princess Buni Al Saud, a niece of King Fahd, pushed the staff down the stairs. Another princess attacked her worker with the help of a bodyguard. A Saudi prince and his children abused their maids when they were in France.
Heads
Emirate of Diriyah
First Saudi state
Second Saudi state
Third Saudi state
The Third Saudi state is the heir to the two earlier Saudi states: the first and the second, founded by Abdul Aziz bin Abdul Rahman (also known as "Ibn Saud"), who managed to capture the city of Riyadh on January 13, 1902. A long series of con ...
Most notable current members
Sons of King Abdulaziz
The list of King Abdulaziz's surviving sons, except for current Saudi monarch Salman, are as follows: # Abdul llah bin Abdulaziz (born 1939) Former governor of Al Jawf Province. He was special advisor to King Abdullah from 2008 to 2015. # Ahmed bin Abdulaziz (born 1942) Deputy minister of interior from 1975 to 2012; minister of interior from June 2012 to 5 November 2012. # Mashhur bin Abdulaziz (born 1942) # Muqrin bin Abdulaziz Al Saud (born 1945) Director general of the General Intelligence Directorate from 2005 to 2012; former governor of Ha'il andMadinah
Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ...
provinces. He was appointed second deputy prime minister on 1 February 2013 and he was made crown prince on 23 January 2015 when his half-brother Salman became king. On 28 April 2015 Muqrin was granted resignation based on his request to start the next generation of the royals.
Genealogy
Timeline
Faisal I
Faisal I bin Hussein bin Ali Al-Hashemi (, ''Fayṣal al-Awwal bin Ḥusayn bin ʻAlī al-Hāshimī''; 20 May 1885 – 8 September 1933) was King of Iraq from 23 August 1921 until his death in 1933. A member of the Hashemites, Hashemite family, ...
" fontsize:10
from: 1838 till: 1841 color:Imam text:" Khalid I" fontsize:10
from: 1841 till: 1843 color:Imam text:"Abdullah II
Abdullah II (Abdullah bin Hussein; born 30 January 1962) is King of Jordan, having ascended the throne on 7 February 1999. He is a member of the Hashemites, who have been the reigning royal family of Jordan since 1921, and is traditionally reg ...
" fontsize:10
from: 1843 till: 1865 color:Imam text:"Faisal I
Faisal I bin Hussein bin Ali Al-Hashemi (, ''Fayṣal al-Awwal bin Ḥusayn bin ʻAlī al-Hāshimī''; 20 May 1885 – 8 September 1933) was King of Iraq from 23 August 1921 until his death in 1933. A member of the Hashemites, Hashemite family, ...
" fontsize:10
from: 1865 till: 1871 color:Imam text:" Abdullah III" fontsize:10
from: 1871 till: 1871 color:Imam text:" Saud III" fontsize:10
from: 1871 till: 1873 color:Imam text:" Abdullah III" fontsize:10
from: 1873 till: 1875 color:Imam text:" Saud III" fontsize:10
from: 1875 till: 1876 color:Imam text:" AbdulRahman" fontsize:10
from: 1876 till: 1889 color:Imam text:"Abdullah II
Abdullah II (Abdullah bin Hussein; born 30 January 1962) is King of Jordan, having ascended the throne on 7 February 1999. He is a member of the Hashemites, who have been the reigning royal family of Jordan since 1921, and is traditionally reg ...
" fontsize:10
from: 1889 till: 1891 color:Imam text:" AbdulRahman" fontsize:10
from: 1902 till: 1953 color:Imam text:" Abdulaziz II" fontsize:10
from: 1953 till: 1964 color:Imam text:" Saud IV" fontsize:10
from: 1964 till: 1975 color:Imam text:" Faisal II" fontsize:10
from: 1975 till: 1982 color:Imam text:" Khalid II" fontsize:10
from: 1982 till: 2005 color:Imam text:" Fahd" fontsize:10
from: 2005 till: 2015 color:Imam text:" Abdullah IV" fontsize:10
from: 2015 till: end color:Imam text:"Salman
Salman may refer to:
People
* Salman (name), people with the name
Places in Iran
* Salman, Khuzestan, a village in Khuzestan Province
* Salman, alternate name of Deh-e Salman, Lorestan, a village in Lorestan Province
* Salman, Razavi Khorasa ...
" fontsize:10
Royal Standard
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
inscription and a sword featured in white, and with the national emblem
A national emblem is an emblem or seal that is reserved for use by a nation state or multi-national state as a symbol of that nation. Many nations have a seal or emblem in addition to a national flag.
Other national symbols, such as national ...
embroidered in gold in the lower right canton.
The script on the flag is written in the Thuluth script. It is the ''shahada
The ''Shahada'' ( ; , 'the testimony'), also transliterated as ''Shahadah'', is an Islamic oath and creed, and one of the Five Pillars of Islam and part of the Adhan. It reads: "I bear witness that there is no Ilah, god but God in Islam, God ...
'' or Islamic declaration of faith:
:
: '
:''There is no other god but Allah
Allah ( ; , ) is an Arabic term for God, specifically the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham. Outside of the Middle East, it is principally associated with God in Islam, Islam (in which it is also considered the proper name), althoug ...
, Muhammad is the messenger of God.''
* The Royal Standard consists of a green flag, in the center of the national emblem embroidered with gold.
See also
* Al ash-Sheikh * Bani Hareth *Bani Yas
The Bani Yas () is a tribe, tribal confederation of Najdi origin in the United Arab Emirates. The tribal coalition, consisting of tribes from Dubai to Khor Al Adaid in southeast Qatar, was called the Bani Yas Coalition (). The House of Nahyan, Al ...
* Banu Thaqif
The Banu Thaqif () is an Arab tribe which inhabited, and still inhabits, the city of Ta'if and its environs, in modern Saudi Arabia, and played a prominent role in early Islamic history.
During the pre-Islamic period, the Thaqif rivaled and co ...
* Banu Yam
Banu Yam (, ') is an Arabian tribe that belongs to the Qahtanite branch of Arabian tribes, specifically the group known as Banu Hamdan, and are, therefore, native to southwestern Arabia.
Their traditional way of life was well suited to life in ...
* Bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu ( ; , singular ) are pastorally nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia (Iraq). The Bedouin originated in the Sy ...
* '' Death of a Princess''
* King of Saudi Arabia
The king of Saudi Arabia, officially the king of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (; ''Malik al-Mamlakat al-ʿArabiyat as-Suʿūdiyya''), is head of state and of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, who holds absolute power. He is the head of the Saudi ...
* Saudi Royal Guard Regiment
The Saudi Arabian Royal Guard () is a unit in the Saudi military forces. Originally an independent military force, the Royal Guards were incorporated into the Armed Forces since its inception until 1953. It is not to be confused with the SANG. ...
References
Further reading
* Madawi Al-Rasheed, ''A History of Saudi Arabia'', Cambridge University Press, 2002, * David Fromkin, ''A Peace to End All Peace'', Holt, 1989, . * David Holden and Richard Johns, ''The House of Saud'', Pan, 1982, (reprint of the Sidgwick and Jackson edition, 1981, ) * Robert Lacey, ''Inside the Kingdom'', Hutchinson, 2009, * Robert Lacey, ''The Kingdom'', Hutchinson, 1981, * Craig Unger, ''House of Bush, House of Saud: The Secret Relationship Between the World's Two Most Powerful Dynasties'', Scribner, 2004,External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Saud Arab dynasties Wahhabi dynasties Kings of Saudi Arabia Rabi`ah