Saturn I SA-2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Saturn-Apollo 2 (SA-2) was the second flight of the
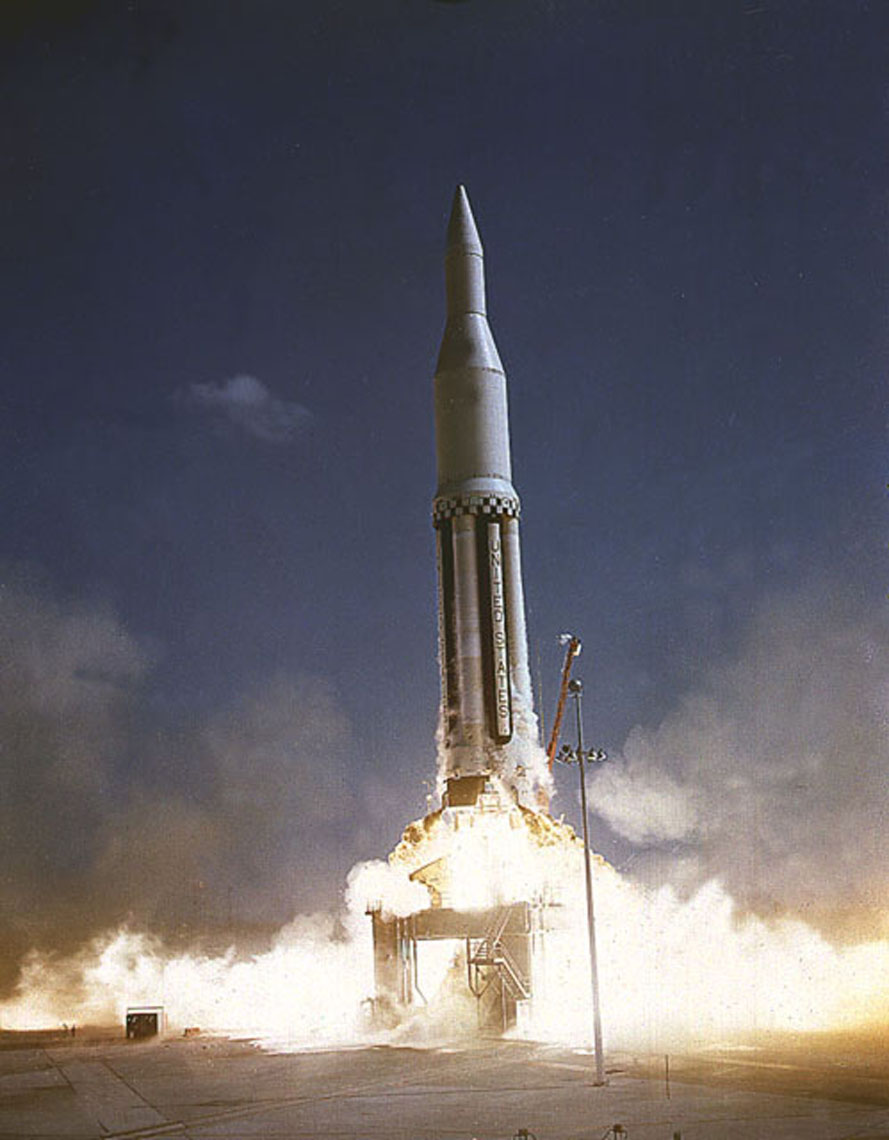 Saturn-Apollo 2 was launched at 14:00:34 UTC on April 25, 1962, from Launch Complex 34. The only hold in the countdown sequence was for 30 minutes due to a vessel which entered the flight safety zone down range. The rocket carried of propellant, about 83% of its maximum capacity.
The H-1 engines shut down at an altitude of after firing for 1 minute 55 seconds and reaching a maximum velocity of . The vehicle continued to coast to an altitude of , at which point, 2 minutes 40 seconds after launch, officials sent a terminate command to the rocket, setting off several charges which caused the vehicle to destruct.
Saturn-Apollo 2 was launched at 14:00:34 UTC on April 25, 1962, from Launch Complex 34. The only hold in the countdown sequence was for 30 minutes due to a vessel which entered the flight safety zone down range. The rocket carried of propellant, about 83% of its maximum capacity.
The H-1 engines shut down at an altitude of after firing for 1 minute 55 seconds and reaching a maximum velocity of . The vehicle continued to coast to an altitude of , at which point, 2 minutes 40 seconds after launch, officials sent a terminate command to the rocket, setting off several charges which caused the vehicle to destruct.
Saturn I
The Saturn I was a rocket designed as the United States' first medium lift launch vehicle for up to low Earth orbit Payload (air and space craft), payloads.Terminology has changed since the 1960s; back then, 20,000 pounds was considered "heavy l ...
launch vehicle, the first flight of Project Highwater
Project Highwater was an experiment carried out as part of two of the test flights of NASA's Saturn I launch vehicle (using battleship upper stages), successfully launched into a sub-orbital trajectory from Cape Canaveral, Florida. The Highwat ...
, and was part of the American Apollo program
The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the United States human spaceflight program led by NASA, which Moon landing, landed the first humans on the Moon in 1969. Apollo followed Project Mercury that put the first Americans in sp ...
. The rocket was launched on April 25, 1962, from Cape Canaveral
Cape Canaveral () is a cape (geography), cape in Brevard County, Florida, in the United States, near the center of the state's Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast. Officially Cape Kennedy from 1963 to 1973, it lies east of Merritt Island, separated ...
, Florida.
History
Launch preparation for the mission began at Cape Canaveral on February 27, 1962, with the arrival of the second Saturn I launch vehicle. The only significant change made to the vehicle from the previous SA-1 flight was the addition of extra baffles in the propellant tanks to mitigate fuel sloshing. While no serious delays were encountered, there were several minor problems reported. A leak was detected between the liquid oxygen dome and injector for the #4 H-1 rocket engine; while attempts were made to fix the problem, it was eventually decided to launch without replacing the engine. Minor problems were found in the guidance subsystem and service structure operations, damagedstrain gauge
A strain gauge (also spelled strain gage) is a device used to measure Deformation (mechanics)#Strain, strain on an object. Invented by Edward E. Simmons and Arthur C. Ruge in 1938, the most common type of strain gauge consists of an Electrical in ...
s were found in a liquid oxygen stud and truss member, and a manhole cover on the dummy Centaur
A centaur ( ; ; ), occasionally hippocentaur, also called Ixionidae (), is a creature from Greek mythology with the upper body of a human and the lower body and legs of a horse that was said to live in the mountains of Thessaly. In one version o ...
(S-V-D) third stage had to be replaced. Problems arose with two of the fueling computers, but each was repaired. Three hydraulic systems were also listed as potential problems.
Despite the issues encountered during flight preparation, none required the target launch date of April 25 to be pushed back.
Flight
 Saturn-Apollo 2 was launched at 14:00:34 UTC on April 25, 1962, from Launch Complex 34. The only hold in the countdown sequence was for 30 minutes due to a vessel which entered the flight safety zone down range. The rocket carried of propellant, about 83% of its maximum capacity.
The H-1 engines shut down at an altitude of after firing for 1 minute 55 seconds and reaching a maximum velocity of . The vehicle continued to coast to an altitude of , at which point, 2 minutes 40 seconds after launch, officials sent a terminate command to the rocket, setting off several charges which caused the vehicle to destruct.
Saturn-Apollo 2 was launched at 14:00:34 UTC on April 25, 1962, from Launch Complex 34. The only hold in the countdown sequence was for 30 minutes due to a vessel which entered the flight safety zone down range. The rocket carried of propellant, about 83% of its maximum capacity.
The H-1 engines shut down at an altitude of after firing for 1 minute 55 seconds and reaching a maximum velocity of . The vehicle continued to coast to an altitude of , at which point, 2 minutes 40 seconds after launch, officials sent a terminate command to the rocket, setting off several charges which caused the vehicle to destruct.
Objectives
The objectives of SA-2 were much the same as those of SA-1 in that it was primarily a test of the Saturn I rocket and the new H-1 engines. Specifically, its goals were to prove propulsion performance and mission adequacy, vehicle structural design and aerodynamic characteristics, guidance and control systems, and launch facility and ground support equipment. NASA declared all objectives as successful. Additionally, the fuel sloshing issue from SA-1 was minimized. A second objective of both this mission and SA-3 wasProject Highwater
Project Highwater was an experiment carried out as part of two of the test flights of NASA's Saturn I launch vehicle (using battleship upper stages), successfully launched into a sub-orbital trajectory from Cape Canaveral, Florida. The Highwat ...
, the intentional release of ballast
Ballast is dense material used as a weight to provide stability to a vehicle or structure. Ballast, other than cargo, may be placed in a vehicle, often a ship or the gondola of a balloon or airship, to provide stability. A compartment within ...
water from the second and third stages which allowed scientists to investigate the nature of Earth's ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays ...
, as well as noctilucent clouds and the behavior of ice in space.
SA-2's dummy upper stages contained approximately of water, or , used to simulate the mass of future payloads. Stage two contained of water, and stage three contained . When the terminate command was sent to the rocket, dynamite charges split the second stage longitudinally, instantly releasing its water load. Primacord charges created several holes in the third stage, releasing its water over a period of several seconds.
Cameras on the ground immediately recorded the water cloud, and personnel at a ground station began to observe it about four to five seconds after release. Those personnel reported that the cloud dispersed from vision within an average of five seconds, while more sensitive instruments tracked the cloud to a maximum altitude of . The cloud produced lightning-like effects, which Dr. Wernher von Braun
Wernher Magnus Maximilian Freiherr von Braun ( ; ; 23 March 191216 June 1977) was a German–American aerospace engineer and space architect. He was a member of the Nazi Party and '' Allgemeine SS'', the leading figure in the development of ...
described as "probably the first synthetic thunderstorm ever generated in space." Project Highwater on this flight was also declared a success.
References
External links
{{Use American English, date=January 2014 Apollo program 1962 in spaceflight Test spaceflights Spacecraft launched by Saturn rockets Saturn I